Definition
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) occurs in repeated episodes, often lasting less than one minute. Attacks are triggered by changes in head position: turning, throwing back, as well as changes in body position, including lying down, even in sleep. Between attacks, autonomic disturbances (nausea, rarely vomiting, fluctuations in blood pressure, sweating) and imbalance may persist, so patients may describe constant dizziness.
Over time, the severity of attacks usually decreases. The word “benign” means that the disease goes away on its own, without treatment, without causing lasting harm to the patient.
BPPV is the most common type of dizziness. Attacks most often develop in older women. However, the disease can occur at any age.
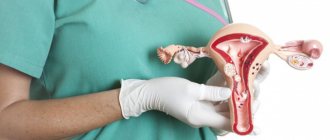
Attacks of BPPV, in most cases, are associated with separation, destruction or increase in size of the otoliths.
Otoliths (otoconia) are layered pebbles consisting primarily of calcium carbonate crystals, like mother of pearl or nacre. They are immersed in a jelly-like layer that envelops the hairs of sensitive cells on the surface of the macula (macula) of the spherical and eleptic sacs of the vestibular analyzer. The otoliths, the jelly-like layer and the hairs of sensory cells form the otolithic membrane.
The elliptic sac (uterus) connects to three semicircular tubules (SCC), located in three perpendicular planes: lateral, anterior and posterior. In their extensions at the junction with the uterus, there is also a sensitive area - the ampullar ridge, covered with a structure similar to the otolithic membrane - the cupula. Normally, the cupula separates the RCC and the utricle. It does not contain otoliths. The cupula provides the perception of angular accelerations of the head, responding to changes in pressure in the ampulla arising due to the inertia of the endolymph (the fluid that fills the RCC and the sacs of the vestibular analyzer).
Detached otoliths or fragments thereof may enter the ampullae of the RCC and irritate the cupular areas. This more common variant of BPPV is called canalithiasis.
Thanks to the balance between the formation and resorption of the layers that make up the otoliths, their renewal is ensured, as well as the resorption of detached otoliths. When the balance is disturbed, one of the otoliths becomes large (2-4 times larger than neighboring cells); the large mass leads to greater displacement compared to neighboring fixed otoliths, which is a source of irritation of the vestibular system. This variant of BPPV is called dome lithiasis; it is characterized by a longer course (several months) and lack of effect from vestibular maneuvers.
Asymmetrical signal input to the brain during unilateral stimulation of the vestibular apparatus disrupts the illusion of balance created by the interaction of the vestibular, visual and proprioceptive systems (receiving signals from muscles and ligaments, assessing the position of limb segments). There is a feeling of dizziness.
Sensitive cells of the vestibular analyzer send a signal of maximum intensity to the brain during the first second of stimulation, then the signal strength decreases exponentially, which underlies the short duration of BPPV symptoms.
The most common lesion is the posterior SCC (90%), less often the lateral one (8%), the remaining cases are caused by damage to the anterior SCC and combined damage to several tubules. Classic cases of BPPV due to posterior RCC involvement are idiopathic in 35% of cases, with previous traumatic brain injury (sometimes minor) and whiplash in the neck occurring in 15% of patients.
In other cases, BPPV is caused by other disorders: most often Meniere's disease (30%), vestibular neuronitis, surgical interventions on the organ of hearing, paranasal sinuses, herpetic lesions of the ear ganglion and circulatory disorders of the structures of the inner ear. Population studies have revealed a direct relationship between the likelihood of developing BPPV and age, female gender, migraine, giant cell arteritis, risk factors for cardiovascular complications - arterial hypertension and dyslipidemia, as well as a history of stroke, which confirms the importance of vascular causes in some cases.
Lindsay-Hemenway syndrome has been identified - acute dizziness, followed by the development of BPPV attacks and a decrease or complete disappearance of nystagmus in the caloric test due to circulatory disorders in the anterior vestibular artery system.
The diagnosis of BPPV is made based on the assessment of nystagmus during special maneuvers - techniques that cause angular accelerations of the patient's head.
Essence and basic principles
Brandt-Daroff vestibular gymnastics is one of the most effective techniques that helps speed up the compensation process and get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of dizziness. This set of exercises is often recommended for patients with BPPV (benign paroxysmal positional vertigo).
BPPV occurs when small crystals of calcium carbonate that form in the ear canals are released and move into the semicircular canals of the ears. This reaction sends mixed signals to the brain about the position of the body, and as a result, dizziness occurs.
But special exercises help break and knock out crystals, alleviating the symptoms of dizziness.
Brandt-Daroff exercises have a lot of positive aspects:
- with regular exercises, it is possible to gradually remove otolith particles from the semicircular canal in the vestibule of the labyrinth;
- during exercise, otolith particles can gradually dissolve in the endolymph;
- the maximum effect can be achieved thanks to the phenomenon of habituation: repeated provocation of dizziness leads to a significantly reduced likelihood of the central nervous system responding to an irritating factor.
Gymnastics helps restore the damaged organ of balance and helps to gradually adapt to the conditions of the outside world. This technique is quite effective, but gymnastics should be performed exactly as recommended by the doctor. It is in this case that you can achieve a positive result for a long time.
If you follow all the recommendations, vestibular exercises will help:
- reduce the likelihood of injury from a fall if you suddenly feel dizzy;
- remove symptoms of nausea and dizziness;
- improve and increase blood flow to the organs of the spinal cord and brain;
- improve quality of life;
- normalize coordination of movements;
- improve vision.
For older people, gymnastics helps them better navigate in space and maintain balance.
Such exercises not only have a positive effect on all organs of the human body, but also prepare the body for possible falls. As a result of this, the person will receive a minimal amount of injury if a situation suddenly arises.
Vestibular exercises for dizziness
The best workout is the swing. Vestibular gymnastics for dizziness must necessarily include swing riding. In this case, you need to start gradually, with rocking with a small amplitude. Each time it is necessary to increase the training time and the amplitude of the swings. Each person benefits from riding about 15 minutes a day.
Another possible way to simply train the vestibular system is to walk along a curb. We've all done this as children, trying to maintain balance for as long as possible. In adulthood, this exercise will help rid the body of seasickness. It is worth saying that vestibular gymnastics should be regular and progressive. After you have reached the limit, you need to rest for a week or two so that your body gets used to training, and then start exercising again.
The third simple exercise of vestibular gymnastics for dizziness is turning around yourself. It is necessary to turn around its axis in both directions about 10 times. After this you need to walk along a straight line. With each workout, you should increase the number of turns and the length of the straight line. Training the vestibular apparatus will quickly affect the general condition of the body, and dizziness will go away.
Vestibular gymnastics goes well with yoga. In order to get rid of nausea, it is enough to learn to breathe correctly
You need to study with trusted masters and in good centers, so that attention is paid not only to exercises, but also to breathing techniques and adjusting your way of thinking
In yoga there is one very good vestibular gymnastics breathing exercise that will quickly bring you back to normal. This technique does not require any special skills other than concentration. The exercise is performed with a completely straight back. It is necessary to exhale deeply with great effort, as if expelling the air from yourself. As you inhale, you should lower the diaphragm, inflate your stomach and fill the lower sections of your lungs with air to the limit. After this, you need to forcefully expand the chest, letting air into the middle sections of the lungs. Finally, due to the movement of the neck, the upper sections of the lungs are filled. Exhalation should be smooth, occurring in the same order: first the stomach, then the chest and neck. Remember to inhale through your nose and exhale through your mouth.
Vestibular gymnastics for the elderly has its own characteristics. They should avoid riding on swings, walking on curbs, and breathing too deeply. In various diseases, this can cause unpleasant or painful sensations in the body. Vestibular gymnastics after a stroke can be carried out only after examination by a doctor and his permission to practice. Therapeutic and preventive gymnastics under the supervision of an experienced specialist is the best solution for older people.
Vestibular gymnastics at home should be structured as follows:
The first week you need to practice turning your head in different directions, in circular movements. Do not be afraid of nausea, because this is quite normal. The main thing is to continue studying. The second week should be devoted to bending your torso back and forth and left to right.
At the same time, it is important to monitor your breathing and remember that you exhale when bending over. After 20 days, the training is supplemented with light boxing
You need to clench your fists and bend your elbows and box with an invisible opponent. Remember that your torso should also turn after your hand. The hand throw should be done with force. After this you should add walking. Step forward and then, without looking back. 10-15 repetitions will be enough.
At the same time, it is worth knowing that people who move little often get motion sickness.
This is why it is so important to play sports and run more. Great for active ball games
Indications for use
Brandt-Daroff vestibular gymnastics helps to concentrate attention, but does not train muscles. This type of exercise is recommended for use by all people, including the elderly, who suffer from frequent attacks of dizziness.
This set of exercises is shown to people:
- those who have had a stroke;
- those suffering from BPPV;
- with general impaired coordination of movements;
- with osteochondrosis;
- with high numbers on the tonometer;
- with chronic migraine;
- with mental disorders;
- with lung pathologies
- with minor and serious spinal injuries;
- with dyscyclic encephalopathy;
- having pathologies affecting the ear areas.
Brandt-Daroff vestibular exercises are also recommended for people who have suffered a history of brain injury.
Symptoms
BPPV develops more often in women. The most likely cause of the disease is the deposition of calcium salts (otoliths) in the inner ear canal. Head movements (tilts, turns, tilts) provoke short-term attacks of dizziness. Between episodes, the patient may experience nausea, fluctuations in blood pressure, loss of balance, and impaired thermoregulation. Regular intense attacks can cause such great inconvenience that the question of what to do with dizziness is in the first place for the patient. With timely treatment, BPPV does not cause lasting harm to health; the benign nature of the disease implies a decrease in the severity of the episodes.
Contraindications for use
Vestibular gymnastics performed at home is very beneficial for the human body. But before you start doing exercises using the Brandt-Daroff method or using any other method, you should definitely consult a doctor. Such activities have a number of contraindications, and if they are not taken into account, then the patient’s already serious condition can be aggravated.
You cannot use gymnastics if:
- serious disturbances in breathing rhythm are observed;
- the patient’s medical history contains records of heart problems;
- The patient has a cold or infectious disease.
Diagnostics
In addition to a good medical history (occurrence of dizziness with typical movements) and a standardized neurological examination, the presence of characteristic nystagmus on the Dix–Hallpick test is a key factor in the diagnosis of BPPV.
Physical examination
The survey includes the following measures:
- internal (blood pressure measurement, heart rhythm disturbances, heart defects, anemia, orthostatic dysregulation: Schelling test);
- neurological (examination of cerebellar symptoms, sensory polyneuropathy with loss of position perception, damage to the trigeminal or facial nerve):
- gait study - falling on one side (on the affected side - vestibular causes, on the healthy side - cerebellar causes);
- Romberg test - positive (in the case of proprioceptive and sensory ataxia), negative (in the case of cerebral vertigo);
- Unterberger test – positive (for cerebral and vestibular damage);
- nystagmus (with the vestibular type - nystagmus in one direction, never vertical; with the central type - complex, changing direction);
- ear examination with an otoscope (herpes zoster, otitis media, perforation);
- hearing test (one-sided deafness is usually of vestibular etiology).
Instrumental studies
This method includes the following approaches:
- ECG – if there is a suspicion of heart rhythm disturbances;
- laboratory examination - blood test, glycemia, creatinine, liver tests, basal TSH (with a targeted examination, all studies are not necessary);
- if necessary, examination by an ENT specialist, neurologist, ophthalmologist, orthopedist.
Useful tips for patients
Vestibular gymnastics will be most effective if you follow a number of basic rules:
- The exercises should be performed in a well-lit room, so that there are no objects with sharp corners nearby, and a carpet without any folds that could lead to a fall and injury to the patient.
- The maneuver is performed using soft surfaces, such as a yoga mat, mat, blanket or thick mat.
- You need to choose comfortable clothing so that it does not constrain or limit movement. But it should not be too wide so that the patient does not get confused in it.
- Shoes must be flat-soled.
- While doing gymnastics, there must be a coach or a loved one nearby who can come to the rescue if necessary.
- You should not overload your body; as soon as even a slight feeling of fatigue appears, you need to stop.
- The load should be increased gradually to prepare the body and prevent relapses.
- Regularity is also important.
- If the patient is feeling unwell, it is better to postpone performing gymnastics until the condition improves.
- Gymnastics is not a separate type of treatment; it will only be beneficial in combination with drug treatment.
Damage to the lateral semicircular tubule
A lesion of the lateral RCC is detected with the patient lying down by turning the head in the plane of the canal from right to left and vice versa (roll test). Horizontal nystagmus occurs, with a clonic component directed downward, mainly when the affected ear is turned downward; if the healthy ear is located below, nystagmus also occurs, the clonic component of which is directed downward, but less pronounced.
In a quarter of patients, canalolithiasis in the lateral RCC is combined with canaloliasis in the posterior RCC. In contrast to downward-directed nystagmus, the clonic component of evoked nystagmus is directed toward the overlying ear. This form is combined with the location of otoliths in the anterior part of the lateral ACC or the otolith fixed to the cupula, while with freely moving otoliths, nystagmus occurs directed towards the underlying ear.
Test results may be influenced by cervical spinal canal stenosis, radiculopathy of the cervical segments of the spinal cord, severe kyphosis, restrictions of movement in the cervical spine: rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, Paget's disease, spinal cord injury, morbid obesity, Down syndrome. In this case, it is possible to use a Barany swivel chair.
If the test results are negative, a preliminary diagnosis of BPPV is made based on complaints of positional vertigo and is confirmed by successful performance of vestibular maneuvers.
If examination reveals a nystagmus that differs from that described above, as well as other neurological symptoms, it is necessary to exclude other lesions of the nervous system.
A number of types of dizziness and nystagmus appear only when the position of the head in space changes - they are positional.
Nystagmus and rotational vertigo can cause both central (for example, associated with damage to the brain stem or cerebellum) and peripheral (canalolithiasis, vestibular neuronitis, damage to the ear ganglion, perilymphatic fistula) lesions of the vestibular analyzer, as well as combined damage to central and peripheral structures - meningitis, intoxication.
Dizziness can be caused by circulatory disorders: thrombosis of the vestibular arteries, migraine, orthostatic hypotension, paroxysmal heart rhythm disturbances.
The relevance of the differential diagnosis of these causes is due to the fact that the central forms require special intervention.
The most commonly ordered test is an MRI of the brain. In some cases, diagnosis may require an orthostatic test, blood pressure and ECG monitoring, duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries/transcranial Doppler sonography, radiography of the cervical spine, and an ophthalmological examination.
Positional maneuvers are also used to treat the patient. Treatment is carried out with the participation of a doctor and takes into account the location of the otolith according to the diagnostic maneuver.
Main complex
This type of vestibular gymnastics can also be performed at home, since it does not provoke any negative reactions in the body of a person suffering from frequent attacks of dizziness.
Outside help in performing the exercise is not required, but it is better if someone is nearby, because it is unknown how the human body will react, this is especially important when performing the maneuver for the first time.
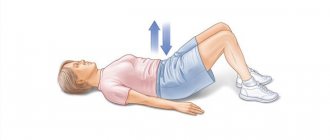
The patient should take a sitting position, you can use a regular table or ottoman, and your feet should be on the floor or simply dangling. You can just sit on the bed.
Brandt-Daroff vestibular gymnastics
And after the movement it should be like this:
- When a person calms down and feels comfortable in a sitting position, he will need to lie on his right or left side.
- You need to turn your head up, maintaining an angle of 45 degrees.
- Fix in this position for 30 seconds.
- Next, the person must again take a sitting position and stay in it for half a minute.
- Afterwards you need to repeat the procedure, but lie on the opposite side.
This is how you need to do 5 repetitions on each side. You need to rest for 15 seconds between repetitions.
If a person does not experience dizziness during the exercise, then the maneuver should be repeated, but only after a day. If dizziness occurs even for a short time in any of the positions, then the maneuver should be repeated at least 2 more times, in the evening, and then in the morning.
Vestibular exercises work in several directions at once. Their main essence is an increased supply of stimuli to the nerve endings of the central part of the vestibular apparatus, which are localized in the area of the brain stem.
gymnastics every morning for 1-2 months
- In a lying position, you need to move your eyes first horizontally, and then vertically, bring your eyes closer together, and direct your gaze to the tip of the finger approaching your nose.
- Next, you need to add gradually accelerating head movements, initially doing everything with your eyes open, and then with your eyes closed.
- Afterwards, in a sitting position, you need to turn your head, bend over, and do everything first with your eyes open, and then with your eyes closed.
- Later, you can add throwing a small ball from one hand to the other, and then complicate the task by throwing the ball under the knee.
- Next, you can add squats, also closing and then opening your eyes. As soon as all the exercises go well, without any unpleasant symptoms, you can move on to twisting your torso.
- Afterwards you need to walk on a flat surface with your eyes open and closed. You can add head turns while walking.
This whole complex helps to better navigate in space and protect against dizziness.
Symptoms
BPPV develops more often in women. The most likely cause of the disease is the deposition of calcium salts (otoliths) in the inner ear canal. Head movements (tilts, turns, tilts) provoke short-term attacks of dizziness. Between episodes, the patient may experience nausea, fluctuations in blood pressure, loss of balance, and impaired thermoregulation. Regular intense attacks can cause such great inconvenience that the question of what to do with dizziness is in the first place for the patient. With timely treatment, BPPV does not cause lasting harm to health; the benign nature of the disease implies a decrease in the severity of the episodes.
Consolidate the result
Today, in the world of modern technology, dizziness is mainly treated without the use of medications. Oral medications may be prescribed if the patient is experiencing an acute period when the person’s standard of living has reached critical levels and dizziness is also accompanied by nausea and a gag reflex.
Drug treatment helps alleviate the condition and improve the condition of life.
The patient may be prescribed the following medications:
- Dramamine. This is an antihistamine that inhibits the vestibular apparatus of the inner ear, affecting primarily the otoliths. The medicine has an antiemetic, sedative, anorexigenic effect, and eliminates dizziness. Take 1 tablet. up to 3 times a day. The duration is set individually. A package of 10 tablets will cost an average of 300 rubles.
- Cinnarizine. This medicine belongs to the group of vasodilators and effectively helps with migraines and dizziness. For each disease, and the drug can be prescribed for pain relief and treatment of vascular pathologies, the dosage and course are selected individually. The standard dosage for the treatment of dizziness is 1 tablet up to 3 times a day. It should be taken only after meals, as the drug can irritate the gastric mucosa. The average price for 1 unit of goods is 100 rubles.
Cinnarizine tablets - Vestibo. This is a drug from the group of vestibulolytics, prescribed to people suffering from attacks of dizziness. The medicine has similar properties to histamine, improves the flow of blood into the basilar arteries, slowing down the work of some prescriptions and relieving the symptoms of dizziness, and has a positive effect on the brain stem. Packaging the drug will cost an average of 200 rubles.
- Tanakan. This is a drug from the group of herbal nootropics. Helps improve all metabolic processes in the body, improves blood flow, increases blood flow to the brain, normalizes vascular tone, and stops the active development of thrombosis. Take the drug 1 pill three times a day. The average cost of the drug is from 500 rubles.
- Cerucal. This is an antiemetic. Acute dizziness often causes bouts of vomiting, and Cerucal helps eliminate them. The dose and course are selected individually, taking into account contraindications and features of the course of the disease. The average cost of the drug is from 200 rubles.
But doctors use positional maneuvers as the primary treatment for dizziness. Their action is to change the position of the patient’s body and head in space. It is thanks to such exercises that it is possible to move the otoliths, located in the ear canals, to the part of the vestibular apparatus, where they should be. BPPV attacks may occur during such maneuvers.
There are several such maneuvers that you can perform independently without the help of a specialist at home, including the Brandt-Daroff maneuver, and there are also those that must be supervised by a doctor or trainer.
The table below shows several maneuvers that can help relieve dizziness. They are recommended if Brandt-Daroff vestibular gymnastics did not produce the desired results or there are contraindications to its use.
| Maneuver | Execution Features |
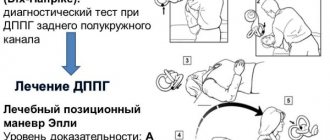
| Semonta | This technique is quite effective, but it is better to perform it in the presence of a doctor, because during it an attack of dizziness may occur that will need to be stopped. The maneuver is performed in a sitting position, with your feet on the floor. The patient turns his head 45 degrees to one side, all movements are slow, without jerking. The doctor fixes the head in this position, and the patient takes a position lying on his side and stays there for 2 minutes. Afterwards the patient returns to the original position. They repeat the maneuver, only turning their head and lying down on the other side. |
| Epley | This maneuver is also performed in the presence of a medical professional. The patient should assume a sitting position. Feet are on the floor, head is turned to the side 45 degrees. The medical worker fixes the head, and the patient lies on his back, throwing his head back as far as possible, hold for 1 minute. Next you need to turn your head in the other direction, and then the person turns his whole body on its side. Hold again for 30 seconds, and then return to the starting position. |
| Lempert | This type of gymnastics is very similar to the Epley maneuver. The main difference is that after the body turns on its side, its movement does not stop. The body must continue to rotate around its axis. |
All the maneuvers described above are often used to treat dizziness; there are a number of others, but as practice has shown, it is the 4 described that give the best effect. Treatment usually lasts no more than a week, but most often it goes away faster.
In the most difficult cases, surgery for dizziness can be used:
- labyrinthomia – used for the chronic stage of Meniere’s disease;
- ototoxic antibiotics - effective for Meniere's disease;
- neurovascular decompression – for vestibular paroxysm;
- surgery to remove neuroma;
- perilymphatic fistula surgery.
Dizziness - causes, symptoms, diagnosis, therapeutic methods
The illusion of rotation that occurs in a person with dizziness is accompanied by eye movement (nystagmus). During diagnosis, the doctor uses certain methods to induce an attack in order to determine the direction of the nystagmus. This can be done using a device (a more accurate and reliable method) or visually when a feeling of rotation occurs.
There are 2 main therapeutic methods used for dizziness:
- Exercises. A special system of exercises is used to adapt the vestibular system to an unhealthy state. But this method is long-term (months of treatment), and also does not address the problems that cause dizziness.
- Maneuvers. For dizziness, positional therapeutic movements (maneuvers) are used. They (in particular, Epley's maneuvers) involve the doctor changing the position of the patient's head. With the help of maneuvers, it is possible to move the otoliths from the semicircular canals to the healthy part of the system, eliminating irritation. There is no pain during the maneuver and it usually lasts up to 30 minutes. It is often possible to get rid of dizziness after the 1st session of the maneuver; sometimes it is necessary to repeat the procedure.
When to expect an effect
As experts and patients themselves say, a positive result after using gymnastics using the Brandt-Daroff method can be expected after completing the first set. You need to perform the maneuver 5 repetitions each morning, afternoon and evening.
Each set should take no more than 10 minutes. If an episode of dizziness has occurred, then it is better to perform the maneuver for 2 weeks. But doctors say that within a day after the gymnastics, the patient’s condition improves significantly.
Vestibular gymnastics, regardless of which of the Brandt-Daroff or Epley maneuvers was used, is a safe and most effective way to independently reduce, and in some cases completely get rid of, the symptoms of dizziness.
If maneuvers do not help, then it is better to seek qualified help. The doctor will help you choose a different set of exercises and, if necessary, prescribe medication.
Diagnostic methods
The study of equilibrium functions is carried out through a comprehensive examination.
Physical examination
Physical examination methods:
- Detailed anamnesis. The nature and type of equilibrium disorder is determined.
- Study of spontaneous vestibular phenomena: standing, when walking, deviation of the limbs (the patient should stand straight, walk in a straight line for several steps, etc. - this allows you to control which side he is leaning towards, what feelings of dizziness he has). The examination provides important information about the external manifestations of balance disorders.
Instrumental studies
Instrumental research methods:
- If an organic cause is suspected, X-rays, CT, MRI (damage to the brain stem and cerebellum) are performed.
- Orientation study of brain nerve function to compare the functions of the right and left equilibrium apparatus.
- Stimulation testing of equilibrium functions (electronystagmography) usually requires special devices.
- Audiometric examination.
How to understand that a person has BPPV
People aged 50 years or older are more likely to experience this type of dizziness. Moreover, this disease occurs 2-3 times less often in males than in females.
The list of diseases that are accompanied by dizziness is huge. But there are basic clinical features characteristic of this disease, according to which the doctor can make the correct diagnosis even during the initial examination.
Let's look at the symptoms of this difficult disease:
- when a person changes body position, he may feel a sudden onset of dizziness. Moreover, most often it appears precisely when turning the head. Very often, an attack occurs when people suddenly sit up in bed after sleep. Benign positional vertigo can also be triggered by head movements made during sleep. The symptom cannot occur in a state of complete relaxation and rest;
- sudden unexpected attacks can be caused by performing simple and seemingly safe exercises, such as raising and lowering the head and squats;
- As a rule, the attack lasts about one minute. Although there are cases in which dizziness lasts much longer, up to several hours;
- often dizziness can be felt as a movement of the body in weightlessness, as a feeling of rising and falling, similar to the state while riding on a swing;
- nystagmus is unregulated eye movements. It is a symptom often present in BPPV. Nystagmus disappears immediately after the dizziness stops;
- often paroxysmal positional vertigo is accompanied by a feeling of heat, pallor, sweating, nausea and vomiting, changes in heart rate (in particular, its slowdown); as a rule, with benign positional paroxysmal vertigo, other neurological symptoms are not observed, the attacks are similar to one another;
- BPPV attacks most often occur in the morning and early afternoon; when benign dizziness occurs, symptoms such as deafness and tinnitus, pain in the head, generally do not appear;
- attacks can spontaneously disappear, which leads to a sudden improvement in the patient’s condition, after which he feels like a completely healthy person.
It will not be difficult for a doctor to identify paroxysmal positional vertigo and distinguish it from other types of vertigo.
How is the diagnosis made?
So, in order to timely and correctly diagnose the disease, the doctor collects in great detail information from him about his feelings during attacks of dizziness, the time and frequency of attacks, and the symptoms accompanying this painful condition. If there are no other complaints besides those described above, then, as a rule, the patient is asked to undergo the Dix-Hallpike test, since it is the easiest to identify BPPV.
To begin with, the patient is seated on the couch, asking him to look at the center of the doctor’s forehead. After this, his head begins to turn first to the right, then to the other side. The rotation angle should be about 45 degrees. After the turns are completed, the person lies on his back. At the same time, your head should be thrown back, slightly over the edge of the couch.
It is fixed in this position. The doctor then begins to carefully study the patient's eye movements. 25-35 seconds are enough if nystagmus is not observed, and a little more if it makes itself felt.
After this, the patient is seated again, turning his head to one side, and the same observation is carried out. Then the same actions are performed when turning the head in the other direction. The side on which the nystagmus appeared is the affected side. During this procedure, the doctor uses special glasses to detect nystagmus.
To exclude abnormalities in the functioning of the brain and the presence of tumors, the patient is prescribed MRI and CT. It should be noted that paroxysmal dizziness is accompanied by a complete absence of neurological signs.
Surgical intervention
In some cases, the use of maneuvers does not lead to recovery. Then the doctor may consider it necessary to use surgery. But, as a rule, it is used only as a last resort, as a “last resort”.
During the operation, to achieve the desired effect, nerve fibers can be cut, the semicircular canal can be sealed, or the vestibular apparatus can be removed completely.
If you notice symptoms of BPPV, you should immediately consult a doctor, namely a neurologist. Most often, the prognosis is favorable; in most cases, cure is achieved using the techniques described above. Sometimes self-healing is observed, apparently when the otoliths independently return “to their place.”
Etiological factors in the development of functional dizziness (causes)
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), a very complex condition in etiology, in some cases it is not possible to establish the true cause of the disease.
The most common causes of BPPV include:
- traumatic injuries of the skull and concussions;
- inflammatory processes in the labyrinth of the inner ear;
- undergone surgical interventions in the head area.
Features of symptomatic manifestations
Symptomatically, benign paroxysmal vertigo manifests itself in the form of a feeling that objects around are rotating, this feeling appears after a sudden change in body position.
Paroxysmal dizziness usually manifests itself in the morning after sleep; it is difficult for a person to navigate in space after getting out of bed.
The duration of the paroxysmal period is, as a rule, no more than three minutes, then it goes away on its own without the use of auxiliary techniques.
An important aspect in diagnosing the disease is that benign positional vertigo is not accompanied by syndromes of organic disorders of the nervous system.
With this pathology, no pathologies develop in the organs of hearing, vision or smell. Thus, the disease does not pose a particular threat to human life, but causes some discomfort.