One of the diseases of the musculoskeletal system is osteochondrosis, which is damage to the cartilage of the spinal column. There is a disturbance in the structure and functionality of the intervertebral discs, and if the disease is not treated, then over time irreversible changes begin to occur directly in the vertebrae themselves. Various exercises for osteochondrosis are very important in the treatment process: they help slow down the development of the disease.
Features of physical therapy for thoracic osteochondrosis
In order to do exercises at home, you do not need to purchase special expensive equipment. Improvement in well-being is already noted when a person begins to regularly perform exercises for half an hour a day. There are a lot of original programs and methods compiled by doctors, athletes and other people knowledgeable in this field.
Beneficial features
For osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, exercise therapy is prescribed to combat the main manifestations of the disease. A person usually experiences severe pain and cannot fully move. Therapeutic exercise is aimed at:
- Returning ease of movement to a person and eliminating stiffness in the spinal column.
- Relaxation of muscles that are constantly under tension and elimination of pain associated with this phenomenon.
- Strengthening the back muscles, due to which part of the load from the bone structures will be transferred to the muscles.
- Improving blood supply to tissues.
- Elimination of the lack of ventilation of the lungs, which accompanies osteochondrosis.
In addition, exercises are needed to prevent dystrophic and degenerative processes in the structures of the musculoskeletal system.
Rules for therapeutic exercises
To ensure that gymnastics for thoracic osteochondrosis at home does not cause a deterioration in well-being and brings the desired result, you need to pay attention to how correctly you perform the exercises. General recommendations are:
- you cannot move sharply, every movement must be slow and smooth;
- training should begin with a warm-up and end with stretching the muscles of the sternum, which will eliminate pain for a long time;
- do not do excessive exercises, intensity and loads should increase slowly and as far as possible;
- breathe slowly and deeply, taking care of proper ventilation of the lungs;
- do not do anything through pain - it will only make you feel worse;
- Be attentive to your feelings - nausea, headaches, dizziness and other unpleasant phenomena indicate that you have overexerted yourself and need to slow down.
If it is difficult for you to do the exercises that the doctor has selected, try doing them gradually, with less amplitude and tension, and rest more. Gradually you will be able to make your workout more intense.
Kyphosis
This is the name given to the physiological curvature of the thoracic spine with a backward convexity. The normal range of curvature varies from 20 to 50 degrees. This curvature corresponds to reverse curvatures called lordosis, which are found in the cervical and lumbar spine. This combination of curves allows people to sit, stand and move without damaging the spine.
The term kyphosis is commonly used to describe an excessive curvature of the upper back greater than 50 degrees, resulting in a forward lean. Kyphosis can develop at any age. As a rule, this is a disease of the thoracic spine, but kyphosis may develop in the cervical or lumbar spine5.
The most common causes of kyphosis:
- Kyphosis associated with osteoporosis. Because osteoporosis weakens bones, the vertebrae become deformed: the front part of the vertebra “sags”, while the back part maintains height. This results in an excessive kyphotic curve.
- Congenital kyphosis usually occurs in infants and young children due to abnormal development of the spine in the womb. This form most often requires surgery in childhood to realign the spine and prevent progressive deformity.
- Degenerative kyphosis develops due to wear and tear on the spine over time. The main cause is arthritis of the spine, accompanied by disc degeneration.
- Neuromuscular kyphosis may occur in children with certain neuromuscular disorders, such as cerebral palsy, spina bifida, or muscular dystrophy.
- Nutritional kyphosis. This condition is caused by vitamin deficiencies in childhood, such as vitamin D deficiency.
- Postural kyphosis is associated with poor posture. It occurs in people of all ages and is more pronounced in women than in men. To correct postural kyphosis, exercises to strengthen the abdominal and back muscles can help.
- Scheuermann-Mao disease occurs in adolescents due to the rapid growth of the spine and discs. Clinically, it can manifest itself in adolescents and adults along with a mild form of scoliosis. This condition is corrected with bracing, exercises and physical therapy. Surgery is used in cases of painful curvatures that exceed 70 degrees or progress.
- Traumatic kyphosis can develop due to improper healing of a spinal fracture or injury to the ligaments that support the spine6.
Warm-up and preparation
Gymnastics for thoracic osteochondrosis at home must begin with a warm-up. It is very important, even if at first glance it seems that it is not so. The quality of your workout, as well as your well-being after it, depends on how responsibly you approach it. Without warming up, it is easy to get injured because the muscles are not ready for the load. So, to warm up, do the following exercises, standing and ten times:
- Press your body against the wall, checking that your heels and the back of your head are in the desired position. Take two steps forward, keeping your torso in the same position.
- Squeeze your shoulder blades together for five seconds and return them back.
- Pull your shoulders forward, similar to what you did with your shoulder blades, for five seconds. Return to the starting position.
- Raise and lower your shoulders up and down together.
- Raise your shoulders one at a time.
- With your palms on your shoulders, rotate your elbow joint in one direction and the other.
After this, you can move on to the training itself.
How to treat idiopathic scoliosis?
Most people have moderate scoliosis that does not require treatment. However, regular checkups are necessary for children to ensure that scoliosis does not worsen as they get older. When bone growth stops after puberty, scoliosis usually does not get worse. Special gymnastics, some sports and yoga help support the body. But it is better to consult a doctor who will determine which sports or exercises are best avoided for a particular type of scoliosis.
Exercises for the thoracic spine with osteochondrosis
Exercises for osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine can be different. There are several options for performing it - standing, lying down or sitting on a chair. Each complex is useful in its own way, and often they are used all together. First, a person exercises while standing, then in a lying position, and then in a sitting position.
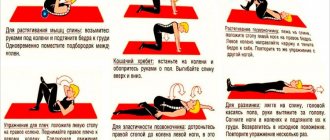
Complex from a standing position
To begin the exercises, stand straight and place your feet shoulder-width apart. After that:
- with your hands on your waist, bend down, simultaneously stretching your left elbow to your right leg, and your right to your left;
- extend your arms, close them and turn first to the left and then to the right;
- wrap a long towel around your chest, take the ends of it in your hands, inhale deeply and, exhaling slowly, begin to tighten the towel on your chest, but do not overdo it;
- with your hands behind your head, lean left and right;
- lean down forward, but do not try to immediately reach the floor, it may hurt;
- after bending, straighten up and stand on your toes, raising your arms up.
This completes the set of standing exercises, and you can move on to the next stage.
Complex from a lying position
Exercise therapy for a diagnosis of thoracic osteochondrosis from a lying position is best done on a special mat. It does not allow the body to slip and at the same time is soft and elastic enough to make training comfortable. You will need:
- place a small cushion on your back, then slowly lift the body and then smoothly lower it;
- lying down, bring your shoulder blades together without rising - only the chest can rise a little;
- lying on your stomach, stretch your arms forward and hold them in this position while slightly lifting your body;
- lying on your back, do the same with your legs - lift and hold them, while simultaneously trying to lift your lower back.
After this, you can begin the exercises while sitting.
Complex from a sitting position
Very useful for thoracic osteochondrosis is gymnastics, which is done while sitting. It is the final stage and is performed like this:
- press yourself against the back of the chair, your arms should be down, then, inhaling, put your hands behind your back and bend forward, and as you exhale, bend forward;
- turning right and left, trying to reach the back of the chair with your hands.
From the very beginning, it is not recommended to do all the exercises at once, in full force and with a wide amplitude. You need to do exercises as much as possible so as not to harm yourself. The most important thing in this matter is regularity and a responsible approach.
Stages of disease development
Experts distinguish three main stages of development of thoracic osteochondrosis:
Stage 1 – the beginning of the development of the disease. Characterized by the absence of clinical manifestations.
Signs of stage 1 thoracic osteochondrosis:
- barely perceptible, slight painful lumbago, accompanied by a nagging pain in the chest. Unpleasant sensations intensify after strenuous work or heavy lifting;
- muscle spasms, constant tone of the muscle frame for no apparent reason;
- discomfort in the heart area.
Seeing a doctor at the initial stage of the disease guarantees a complete cure of the disease.
Stage 2 – the progression of the disease leads to the formation of microcracks in the intervertebral discs, which causes limited mobility and the appearance of severe pain.
Clinical manifestations include:
- visually noticeable deformation of the spinal column;
- decrease in pressure;
- accompaniment of an attempt to place the hand behind the head with palpable pain in the sternum;
- chronic feeling of fatigue;
- discomfort in the area of the heart and spinal column of the thoracic region.
If the disease is detected at this stage, the process of restoring health may require a fairly long period of time.
Stage 3 is an advanced process that has a negative impact on the entire body as a whole.
Dangerous manifestations such as:
- limited mobility of the spine;
- sharp pain;
- the appearance of intervertebral hernias;
- pinching of blood vessels and nerve roots;
- diseases of the biliary tract.
Refusal to treat thoracic osteochondrosis at this stage can lead to disability.
Contraindications
Sometimes exercises in the treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region are contraindicated, since they can only harm the patient, but not make it better. The decision regarding the use of exercise therapy should remain with the doctor.
During an exacerbation of the disease
The acute phase of osteochondrosis is accompanied by severe pain, which in itself excludes the possibility of performing exercises. You can’t do them through force and pain, since you can injure tense and inflamed structures in the thoracic region.
In the early postoperative period
If the treatment of osteochondrosis included surgery, immediately after surgery and for some time thereafter, back loading is contraindicated. This will allow the tissues to heal properly and also ensure the integrity of the seams.
For high blood pressure
Exercise therapy in the treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region will not bring the desired result if a person has high blood pressure. High blood pressure causes increased stress on all organs, and exercise can cause a sharp deterioration in well-being. If pressure surges are caused by osteochondrosis, you need to use medications that will correct the situation, and only then start training.
General principles and rules of exercise therapy for osteochondrosis
Before starting classes, you must consult a specialist so that he can select the most suitable set of exercises.
When performing exercise therapy, you must adhere to the following rules:
- perform gymnastics for osteochondrosis in a ventilated room;
- It is advisable to study in the morning, but if this is not possible, you can do it in the evening;
- it is necessary to gradually increase the load on the muscles, starting with light, gentle exercises;
- monitor your breathing while performing exercise therapy. So, you need to breathe evenly, deeply and smoothly;
- avoid overstrain in the lumbar and cervical regions;
- exercise regularly;
- do not rush, but try to fully concentrate on the exercises;
- do exercises at least three times a week, but preferably every day;
- Gradually increase the number of repetitions of exercises.
For osteochondrosis and its prevention, exercises are first prescribed to help tone the muscles, then the exercises gradually become more complicated and new elements are added to strengthen the spine.
Training effectiveness
Daily exercises help increase the range of motion in the thoracic spine and eliminate muscle spasms. And after performing stretching exercises, the distance between adjacent discs and vertebrae increases. They stop squeezing the spinal roots, which allows you to avoid the risk of acute, piercing pain. What positive changes are still happening:
- surges in blood pressure, panic attacks, and dizziness, often caused by pinched vertebral arteries, disappear;
- the muscles of not only the thoracic region, but also the entire back, as well as the neck and shoulder girdle are strengthened;
- ventilation of the lungs improves, which allows patients not to worry about pain when taking a deep breath;
- blood circulation in the area of vertebral structures affected by osteochondrosis is accelerated, nutrient reserves are replenished;
- Correct posture is formed and the physiological curves of the spine are restored.
Physical therapy exercises are indicated not only for patients with osteochondrosis. They are recommended for people who are at risk of premature disc failure. As a rule, their work involves staying in one body position for a long time.
General rules of therapeutic exercises
Only compliance with all the rules of therapeutic exercises will help achieve the expected result. This is due to irreversible changes in the discs and vertebrae that have already occurred in the thoracic region. It is necessary to dose the loads so that strengthening the back muscles does not cause even greater destruction of the vertebral structures. The following medical recommendations should be followed:
- warm up before training and stretch after it;
- increase physical activity gradually as you build up your muscle corset;
- completely eliminate any sudden movements that provoke microtrauma of the discs;
- exercise every day, and skip workouts only because you feel unwell.
During classes, you need to listen to the sensations that arise. Pain, shortness of breath, and dizziness become signals to stop training. And if certain movements lead to a pleasant feeling of muscle stretching, then they need to be done more often - in 2, and sometimes in 3 approaches.