The most common reason for women to visit a gynecologist is complaints of itching, discomfort, pain and pathological discharge from the vagina. All these signs indicate vaginitis or, in other words, colpitis.
What is vaginitis, in what forms does it occur, what tests are needed to make a diagnosis and how the disease is treated, we will consider in the article.
Why does the disease develop?
When a woman is healthy, her body independently maintains the balance of flora in the vagina. Lactobacilli, which are located on its mucous membrane, produce lactic acid, which suppresses the excessive activity of opportunistic microflora. The situation changes when the body's defenses weaken.
Vaginitis can be caused by:
- infectious diseases;
- sexually transmitted infections;
- microtrauma of the vaginal mucosa. Including during childbirth;
- abortions, aggressive sexual intercourse, surgical procedures;
- endocrine pathologies. Among them are pregnancy, abortion, menopause, ovarian dysfunction;
- improper genital hygiene. Excessive cleanliness, abuse of aggressive detergents and rare irregular hygiene procedures are equally dangerous;
- uncontrolled use of antibiotics;
- unprotected sex, sexual intercourse with casual sexual partners;
- metabolic disease;
- allergic reactions to sanitary tampons, contraceptives, intimate gel lubricants;
- stress, tense psycho-emotional state;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- immunodeficiency.
How does the disease occur?
Anatomically, the vagina is a muscular tube protected from the inside by epithelium - several layers of cells tightly interconnected. The upper layer of the epithelium contains a supply of glycogen, a polymer of glucose that forms the body's energy reserve. Glycogen carbohydrates feed the beneficial microflora of the vagina - lactic acid bacteria.
By breaking down glycogen, bacteria release lactic acid, which creates an environment that is detrimental to pathogenic microflora. In addition, in a healthy woman, a layer of lactic acid bacteria lines the vaginal cavity so densely that other microorganisms simply have no place to create their own colony.
The vaginal mucosa constantly produces a little secretion, which flows down the walls and carries with it the old epithelium, dead bacteria and pathogenic microorganisms.
The glycogen content in the vagina depends on the amount and composition of sex hormones in the blood. An increased level of estrogen is a guarantee that there will be a lot of glucose polymer on the mucous membrane. Some steroid female sex hormones reduce the glycogen content in the epithelium.
The concentration of such hormones increases before menstruation, so many women feel itching in the vagina on the eve of menstruation. This is how chronic vaginitis worsens or the acute stage of the disease manifests itself.
Pathogenic bacteria can enter the vagina in two ways:
- Ascending - when the infection rises from the anus or perineal area, from the labia, urinary tract or vestibule of the vagina.
- Descending - the causative agents of vaginitis enter the vaginal mucosa with the flow of lymph or blood from foci of chronic infection. The “supplier” can be diseased kidneys, untreated dental caries and chronic sore throats.
As soon as pathogens enter the weakened vaginal tissue, inflammation develops as follows:
- The infection destroys epithelial cells; at the site of injury, the body releases biologically active substances.
- The blood vessels of the vagina dilate, this causes stagnation of blood in its cells. Immune cells - leukocytes and blood plasma - penetrate into the tissue through the walls of the vessels. The vaginal mucosa swells, and in more severe cases, the muscles, vulva and labia are involved in the process.
- The affected cells disintegrate, the decay products irritate the nerve endings in the mucous membrane and this causes itching. The situation is aggravated by edematous tissue, which puts more pressure on the vagina every day.
- To remove infection and dead cells from the surface, the epithelium actively produces mucus. Copious vaginal discharge appears. If many leukocytes are killed during inflammation, purulent inflammation develops and the mucus contains pus. When the small blood vessels of the mucous membrane are destroyed, the discharge is bloody. In cases of sexually transmitted diseases, vaginal discharge has a characteristic unpleasant odor.
Treatment
The treatment strategy depends on the type of vaginitis.
Photo: macniak / freepik.com Correct diagnosis is the key to successful treatment of vaginitis. Different forms of vaginitis are treated differently.
Systemic antifungal drugs are used to treat vulvovaginal candidiasis. Fluconazole, nystatin, itraconazole and natamycin are used for this purpose. Vaginal tablets and topical creams are often prescribed. These are drugs clotrimazole, miconazole, econazole, natamycin, butoconazole.
Once a diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis is made, treatment is usually prescribed in two stages. The anaerobic flora is affected by drugs such as metronidazole, tinidazole, ornidazole and clindamycin, as well as chlorhexidine or lactic acid in the form of vaginal suppositories. At the second stage, probiotics are prescribed - means to restore vaginal flora. These are preparations of lactobacilli in the form of vaginal suppositories. When combining therapy with metronidazole and tinidazole with alcohol-containing drugs, severe reactions of the body are possible. Therefore, it is important to avoid any medications that contain alcohol or alcohol while taking the medications and for three days after the end of treatment.
For the treatment of aerobic vaginitis, local agents are used that contain clindamycin (in the form of vaginal cream and vaginal tablets). European clinical guidelines suggest the use of kanamycin and moxifloxacin, systemic antibiotics that have little effect on the normal flora of the vagina. The drugs of choice in the treatment of aerobic vaginitis may be antibiotics, to which the flora of a particular patient is sensitive according to the results of bacterial culture.
Trichomonas vaginitis is a reason to get tested for all STIs and a full examination of a woman’s sexual partners.
In men, trichomonas infection in 70–80% of cases occurs latently, in the form of carriage.²
Partners of women with trichomoniasis should not only have a urethral smear analyzed by microscopy, but also be offered a study of prostate juice with cultural and molecular diagnostic methods. If there is only one trichomonas infection, then the drugs metronidazole, tinidazole, ornidazole can be used. With mixed infections, all factors must be taken into account.
Forms of vaginitis
The disease is distinguished by a complex of symptoms.
According to its duration, vaginitis can be:
- Spicy. Lasts 1.5–2 months.
- Subacute. This is a transition phase from acute to chronic form. It is characterized by swelling of the vaginal walls and copious discharge from the genital tract. The cycle and nature of menstruation changes (they may become more painful). After sexual intercourse, bloody discharge is noticeable on the underwear. The duration of the phase is from 2 to 6 months.
- Chronic. Inflammation resumes after a short remission, then clinical signs disappear again. The only symptom can be considered itching, which intensifies before menstruation, after sexual intercourse, playing sports or physical exertion. Vaginitis is considered chronic if it cannot be cured for more than six months.
Depending on the cause of the inflammation, vaginitis can be:
- Bacterial (non-specific). Its causative agents are opportunistic streptococci, staphylococci, and bacilli.
- Trichomonas. Occurs when infected with the causative agent of trichomoniasis.
- Mycoplasma. Develops during an attack by the intracellular parasite mycoplasma. This infection is transmitted sexually.
- Yeast. The reason for its occurrence is the proliferation of candida fungus, the causative agent of thrush.
- Atrophic. Appears during a period of decreased estrogen levels in a woman’s blood. For example, with the onset of menopause, if ovarian function is impaired or if they are removed.
- Vaginitis in pregnant women. During gestation, a woman’s immunity is weakened, because her body is subjected to serious stress. The occurrence of vaginitis is also facilitated by changes in hormonal levels in the body of the expectant mother. Therefore, lactobacilli in the vagina weaken, and opportunistic bacteria develop successfully.
- Allergic. It is provoked by allergens that get on the vaginal mucosa. Irritants may include: lubricant of condoms, fragrances in intimate hygiene products, local contraceptives, vaginal rings, tampons and sanitary pads with fragrance, vaginal suppositories. In this case, vaginitis is a reaction to allergens of immune cells.
According to the nature of inflammation, vaginitis occurs:
- Serous - its development is accompanied by clear, liquid discharge;
- Mucous - thick and viscous discharge appears from the vagina. They are opaque and have a dull gray tint;
- Purulent - The vagina secretes cloudy mucus-like contents, which have a yellow, yellow-green color. The discharge has an unpleasant odor.
Vaginitis can develop not only in adults, but also in children and adolescents. This is dangerous, because the child cannot understand what is happening to him, and sometimes he is simply embarrassed to complain about pain and burning in an intimate place. If left untreated, the disease enters the chronic stage. In girls, the vaginal mucosa is very thin, so when it becomes inflamed, it forms scars, polyps, and even synechiae (fusion of the labia). If you have the slightest suspicion of colpitis in a girl, immediately consult a gynecologist.
A long scientific path from nonspecific vaginitis to bacterial vaginosis
Since the late nineties of the last century, when Döderlein described lactobacilli, later called Döderlein's bacilli, attempts have been made to discover the causative agent of vaginitis, in the secretions of which there were no signs of vaginal trichomoniasis and yeast fungi. The lack of a definitive cause for the clinical symptoms described has led to the disease being referred to as nonspecific vaginitis (NSV).
It was not until 1955 that Gardner and Dukes described a bacterium similar to the genus Haemophilus, which they found in 81 of 91 symptomatic women. Recognizing that they had discovered the causative agent NSV, they named the bacterium Haemophilus vaginalis and gave the disease Haemophilus vaginalis a name: vaginitis.
Vaginitis
In 1963, Zinneman and Turner assigned Haemophilus vaginalis to the family of corynobacterium bacteria, so the nomenclature of Corynobacterium vaginalis vaginitis can be found in the literature of the seventies. Scientists Greenwood and Pickett in 1980 classified the bacterium described by Gardner and Dukes into a new genus in which only one species occurs. In recognition of the discoverer's achievements, the genus was named Gardnerella, and the species Gardnerella vaginalis.
Further studies of vaginal secretions from NSV showed that the cause of the infection is not a single microorganism, but the proliferation of colonies of many bacteria, especially anaerobic ones, not accompanied by an increase in the number of polynuclear leukocytes. In addition, teacher Spiegel and Roberts described the new anaerobic bacterium Mobiluncus, identifying two species: Mobiluncus mulieris and Mobiluncus curtisii. These are microorganisms that are never found in the normal vaginal microflora.
The taxonomy of the vaginal flora of patients with NSV was finally established at the Stockholm Symposium in 1984, replacing the name nonspecific vaginitis with bacterial vaginosis. The new nomenclature has received international recognition.
Bacterial vaginosis
How does vaginitis manifest?
With vaginitis, a woman most often does not experience fever, she does not develop a high temperature and general weakness. However, the feeling of general discomfort in the perineum and itching does not stop throughout the course of the disease.
If the temperature nevertheless rises, symptoms of general intoxication and severe pain in the vagina appear, then the inflammatory process has gone far. And we are talking about an acute inflammatory process along the entire height of the vagina and fatty tissue surrounding the uterus.
Bacterial
Bacterial vaginitis is a purulent inflammation, it is accompanied by copious yellow-green discharge.
Bacterial vaginitis can be caused by:
- unbalanced diet;
- alcohol abuse;
- hormonal disorders;
- frequent colds;
- genital injuries;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- chronic urinary tract infection.
This type of vaginitis is called aerobic, because inflammation is provoked by opportunistic microflora, where there are many aerobic bacteria. To develop, they need oxygen, so colonies are usually located on the surface of the skin of the perineum. When the body's defenses weaken, representatives of aerobes penetrate the vagina and multiply on the mucous membrane. Thus, bacterial vaginitis is not a bacterial lesion of the vaginal mucosa, but the death of its natural microflora.
When examining the vagina, the doctor will note areas of redness on the vaginal mucosa. The organ itself is swollen and covered with pus. When analyzing vaginal smears, an acidic reaction will be detected; the epithelial cells are attacked by a layer of aerobic bacteria. There are few lactic acid bacteria, and sometimes they cannot be detected at all.
This type of inflammation becomes chronic more often than others. In this case, vaginal discharge becomes moderate, but retains its distinctive feature - yellow-green color and unpleasant odor.
This form of vaginitis is not easily cured as a result of systemic treatment. In addition to local medications, it will be necessary to take general strengthening medications.
Trichomonas
The disease is severe. Inflammation develops 3 to 12 (and sometimes up to 30) days after infection - unprotected sex with a carrier of the infection. This is the stage of infectious accumulation, and nothing worries the woman when acute vaginitis suddenly occurs.
Foamy discharge is discharged from the vagina, which is accompanied by a strong unpleasant odor. Most often they are cloudy white or have a yellow tint. A woman suffers from itching of the perineum, the discomfort is localized in the abdomen.
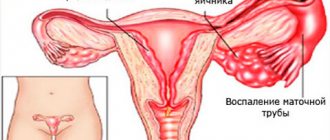
Trichomonas moves easily and penetrates from the vagina into the uterus, fallopian tubes, peritoneum and surrounding tissues. At this stage of the disease, the woman’s temperature rises to 39 degrees. Pain in the abdominal area becomes stronger, menstruation occurs irregularly.
Examining the vagina, the doctor notes uniform redness of the vaginal walls, swelling of the mucous membrane, and the presence of foamy discharge.
However, there are cases when trichomoniasis colpitis is practically asymptomatic, except for some redness of the vagina.
In men, most often the disease does not manifest itself, but both partners must be treated, otherwise the entire genitourinary system will be involved in the painful process.
Gonorrheal
This infection is transmitted exclusively through sexual contact. Its signs appear 3-4 days after infection, when the woman begins to experience discomfort, burning, pain and itching in the vagina. The discharge is mucous, purulent, sometimes you can see white spots in it - areas of dead cells of the mucous membrane.
The walls of the vagina are swollen and overfilled with stagnant blood, especially swollen red papillae. In the advanced stage, erosions form in the vagina. At first they are covered with a whitish layer of dead bacteria, then ulcers appear and begin to bleed. Blood appears in vaginal discharge.
Yeast
Many women have suffered from thrush or candidal vaginitis. In this case, the infectious agent does not necessarily have to be brought by a sexual partner. Candida fungus inhabits the vagina of 25% of women. It is a representative of opportunistic microflora; in its normal state it does not cause concern to a woman.
However, if the immunity of the carrier of a yeast-like fungus decreases, under stress or metabolic disorders, candida begins to actively multiply.
The fact that the process has begun to develop is indicated by itching in the genitals. Then the woman feels dryness in the vagina. If swelling and severe pain appear on the labia majora, then the course of the disease is complicated by vulvovaginitis.
1–2 days after the onset of itching, a white, curd-like discharge with a sour odor appears from the vagina. In rare cases, thrush may occur without discharge.
Often, signs of a fungal infection appear before the onset of menstruation, during pregnancy, or when using intrauterine contraceptives. It provokes the appearance of thrush and unbalanced use of antibiotics.
This disease produces a record number of relapses.
However, treatment of yeast vaginitis is simple, using special creams. And although, due to the structure of the genital organs, candidiasis colpitis does not occur in men, the woman’s sexual partner should also undergo treatment.
Atrophic
Most often it occurs during postmenopause (menopause), when estrogen production decreases. As a result, the vaginal epithelium becomes thinner, and there are fewer lactobacilli in the epidermal layer. This leads to a change in the acidity of the vagina, which triggers the inflammatory process.
With atrophic vaginitis, vaginal itching is especially painful; women have a hard time with vaginal dryness and impaired elasticity. Another symptom of atrophic vaginitis is frequent urination.
With such inflammation there is almost no discharge, it is not colored and has no odor. Sometimes bloody discharge appears.
When examining the vagina, the doctor will find that the mucous membrane is pale yellow with hemorrhagic spots (bruises). With atrophic vaginitis, the vagina narrows and adhesions form on the posterior fornix.
This disease requires complex treatment, the use of hormonal drugs and local therapy.
Chronic
Acute vaginitis can become chronic if a woman does not seek help from a doctor or receives insufficiently effective treatment. Gradually, the symptoms of acute inflammation subside, vaginal discharge appears from time to time, but not as abundant as in the acute stage. Women can live with confidence that they have recovered and learn about their diagnosis by chance.
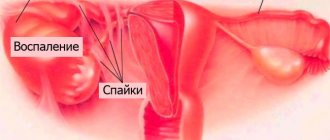
Chronic inflammation reduces the elasticity of the vaginal walls, they thicken and become rough. During sexual intercourse, unpleasant sensations may occur; the inflammatory process invades the uterus and ovaries, forming adhesions there. As a result, it is more difficult for a woman to become pregnant.
Next, the inflammation spreads to the urinary system and pelvic organs.
Popular questions
The doctor diagnosed vaginitis and prescribed Miramistin for 7 days, Metromicon suppositories and Lactoginal for 14 days.
I didn’t remember the details of using all this at the same time or one by one. I'd be grateful for any advice. Irrigation with Miramistin solution and the first suppositories are carried out simultaneously. Laktozhinal serves to restore the balance of microflora and is used as the second stage of treatment.
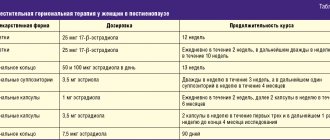
The doctor diagnosed atrophic vaginitis. Beginning of menopause. I started using the Klimara patch on the doctor’s recommendation. But I’m very afraid of hormonal drugs. Tell me, can Ginocomfort Klimafemin + Intimate Moisturizing Gel replace hormone-containing drugs? or Klimafemin also contains hormones, if so, which is less safe? Phytoestrogens and topical moisturizer are not a substitute or equivalent in action to hormonal menopausal therapy. Therefore, they are not interchangeable, but complement each other or are used for individual contraindications. Unfortunately, the effectiveness of the method and the possibility of combining drugs can only be determined by the attending physician after an examination and interpretation of the examination results and the patient’s medical history.
Hello! I have vaginitis, now the fungus is in question, is it possible to use a washing gel and a restoring gel for thrush?
Hello! These drugs can be used together with the main therapy for bacterial vaginosis, for example in combination with Elzhin suppositories. The main drug is used at night, therapeutic and prophylactic agents are used in the morning.
Flora, cocco-bacillary tests are normal, atrophic vaginitis, what to do?
Hello!
For the treatment of atrophic vaginitis, in the absence of contraindications to local hormone therapy, Ornion cream is used, 1 dose once a day for 10 days, then 2 times a week for a long time. Otherwise, a non-hormonal remedy is suitable - Ginocomfort gel with mallow extract in a similar mode of application. For an accurate diagnosis, contact a specialist
How to make a diagnosis
A gynecologist diagnoses the disease.
The examination will take place as follows:
- Collection of primary data. The doctor receives the necessary information during a conversation with the patient. You need to remember when and why the unpleasant sensations arose, and whether something similar happened before. It is important to be aware of any endocrine diseases you have, your general health, and any medications you were taking shortly before your symptoms began.
- Gynecological examination using special mirrors. This way he will reveal swelling, hyperemia (redness), and the condition of the vaginal walls.
- Taking a smear to determine the composition of the microflora. The sample is taken from the vagina, urethra and cervix. An antibiotic sensitivity test is also taken. To determine sexually transmitted infections, vaginal discharge is examined using the polymerase chain reaction method.
Before visiting a gynecologist, abstain from sex for a day. There is no need to use sanitary tampons or douche - this way you will preserve the composition of the microflora. Two days before the examination, stop using intimate lubricants, do not use vaginal suppositories, and do not take antibiotics - unless this contradicts your doctor's recommendations.
Diagnostics
The clinical picture and clarification of the disease history significantly simplify the laboratory diagnosis of the disease. The main diagnostic task is to find the causative agent in order to prescribe specific treatment later. There are three main methods for determining microorganisms:
- bacterioscopy – visualization of vaginal secretions under a multiple magnification microscope. The technique is widespread due to its practicality, ease of use and low cost. The disadvantage of the study is low specificity. In many cases, the method allows you to see microorganisms, but does not make it possible to accurately differentiate them;
- a bacteriological method known to many as “seeding”. Vaginal secretions are placed in special conditions on a nutrient medium where microorganisms grow. The procedure has a fairly high specificity, but it often takes up to 7 days to complete. In conditions of progressive disease, such a long wait-and-see approach is unacceptable;
- PCR is a highly informative diagnostic method that allows you to quickly identify the causative agent of the disease. Disadvantages - high cost. Conducting a blind study, simply identifying all the most common sexually transmitted infections, is not a cheap pleasure. The technique is justified by a competent approach, in which selective testing is carried out only for certain infections, justified by the clinical picture of the disease.
How to cure vaginitis
Provided that the woman consults a doctor on time and intends to follow all his recommendations, vaginitis can be successfully treated on an outpatient basis. Neither hospitalization nor sick leave is required.
If the cause of vaginitis is a sexually transmitted infection, the sexual partner should also undergo treatment.
You will have to abstain from sexual intercourse for the time prescribed by your doctor. During sex, the mucous membrane can receive additional microtraumas, this will aggravate the course of the disease, and the causative agent of the disease will take an even more reliable position.
Treatment for each type of vaginitis is specific and depends on the type of pathogen. As a rule, antibiotics, antifungal and antimicrobial agents are used in therapy. After completing the course, the use of vaginal suppositories with lactobacilli is indicated.
To relieve itching, you should use special vaginal suppositories.
Additionally, douching with medications is prescribed.
As a maintenance therapy, sitz baths with a decoction of medicinal herbs can be recommended.
There are drugs that do not disrupt the work of vaginal lactobacilli and are not absorbed into the blood. It is them that doctors prescribe to pregnant women with vaginitis, for use in the second and third trimester of pregnancy.
During treatment it is necessary:
- change your underwear every day, wash yourself after each visit to the toilet;
- follow a special diet, including fermented milk products with live bifidobacteria and lactobacilli, products with polyunsaturated acids, vitamins and minerals;
- Use unscented sanitary pads.
Chronic vaginitis is more difficult to cure. In addition to drug therapy, the doctor will include physical therapy - magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, UHF. You need to strengthen your immune system, get more rest, take immunomodulators and vitamin complexes.
It is important that the woman's sexual partner also see a doctor. A man may be prescribed medications that differ from those used by a woman. And self-prescribed treatment can only do harm and delay the recovery time for both partners.
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category Oksana Anatolyevna Gartleb
In cases of vaginitis in pregnant women, alternative treatment is used due to the contraindication of metronidazole. Use clotrimazole at a dose of 100 milligrams for one week. This drug has a cure effect in only 25% of cases, but it does a good job of reducing the symptoms of vaginitis. Metronidazole is used only in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters, in a single dose of no more than 2 mg.
In cases of postpartum vaginitis when using metronidazole, breastfeeding should be stopped for at least one day.
For pregnant women, local treatment with an antifungal drug is used for candidiasis.
The use of imidazoles should be a short course. Nystatin is also used with injection into the vagina for two weeks. Sources:
- BACTERIAL VAGINOSIS AND BACTERIAL VAGINITIS: CLINICAL AND MICROBIOLOGICAL VARIANTS OF COURSE. Zakharova T.V. // Bulletin of new medical technologies. – 2008. – No. 2. – P.192-194.
- TREATMENT OF CANDIDIA VAGINITIS IN PREGNANT WOMEN. Kupert A.F., Kravchuk L.A., Kupert M.A. // Siberian Medical Journal (Irkutsk). – 2010. – No. 8. – P.160-162.
- Microecology of the vagina and prevention of obstetric pathology. Ankirskaya A.S. // Infections and antimicrobial therapy. - 1999. - No. 3. - P. 80–82.
- Species identification of vaginal lactobacilli isolated from women of reproductive age. Isaeva A.S., Letarov A.V., Ilyina E.N., et al. // Obstetrics and gynecology. // 2012. - No. 3. - P. 60–64.
- Bacterial vaginosis. Kira E.F. // M.: Medical Information Agency. - 2012. - P. 472.
- https://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/vaginitis/conditioninfo/treatments
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/175101.php
- https://www.medicinenet.com/vaginitis_overview/article.htm
- https://www.aafp.org/afp/2018/0301/p321.html
Disease prevention
The main condition for successful prevention of vaginitis is sex using barrier contraceptives or with a regular, reliable partner.
In addition, the following will help protect you from an unpleasant disease:
- regular observation by a gynecologist and examination of smears for flora;
- healthy eating;
- giving up bad habits and physical activity;
- regular intimate hygiene, especially during menstrual periods - but using special intimate hygiene products that have a suitable pH level;
- habit of wearing underwear made from natural materials;
- timely replacement of sanitary pads (including daily pads);
- taking antibiotics only as prescribed by a doctor;
- absence of aggressive sexual intercourse and alternation of anal and vaginal sex.