Tubal obstruction is a condition in gynecology that is characterized by the closure of the lumen of the tubes leading from the uterus to the ovaries. Most often it is not considered as a separate disease, because it is a consequence of other problems.
Obstruction of the fallopian tubes is very often the cause of female infertility. In some rare situations, this condition is considered as a separate nosology, which has its own characteristic manifestations and requires individual treatment.
The structure of the uterine auxiliary apparatus
Before moving on to consider tubal obstruction and its symptoms, you need to understand the anatomical structure of the internal genital organs and the functions they perform. The woman's pelvis contains the uterus and its appendages. The appendages are found around the uterus and include the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterine ligaments.
Fallopian tubes
- These are hollow tubes that connect the ovaries and the uterus. They are located on the sides of the base of the uterus and are directed to the side (distally). The main function of the fallopian tubes is the transport of an egg matured as a result of ovulation from the ovary to the uterine cavity. From this information it becomes clear that if an egg ready for fertilization cannot get from the abdominal cavity into the fallopian tubes and the uterus itself, then it will not be possible for sperm to fertilize it. Thus, tubal infertility occurs.
Each fallopian tube has 4 sections. Closest to the uterus is the intramural section, which is bounded on all sides by the walls of the uterus (its muscle fibers). This is followed by the isthmus of the fallopian tube - this is the place where the bend occurs and the greatest narrowing of the lumen of the entire tube is noted. The isthmus is followed by the convoluted section. It is the longest, wider than the previous one, and normally, in a healthy woman, fertilization most often occurs in this section. The fallopian tubes end in funnels - these are peculiar extensions that have fringed processes (fimbriae) at the ends. The latter formations are quite long and come into contact with the ovary. This pathology can occur in any of the above sections of the pipe.
After considering the sections of the fallopian tubes, you should pay attention to their membranes, which perform certain important functions. The mucous and muscular membranes are among the most important. It is the mucous membrane that has cilia that can move and guide the egg, or fertilized egg (zygote), from the abdominal cavity to the uterine cavity. The muscle membrane consists of smooth muscle cells and has the ability to contract under the influence of hormones and nerve impulses. These contractions complement the work of the cilia of the mucous membrane, promoting the advancement of the egg into the uterus.
Ovaries
these are paired organs that have an oval shape. They are located on the sides of the uterus. The ovaries perform a number of very important functions. They contain eggs that, during a woman’s reproductive years, will mature and be released into the abdominal cavity during ovulation. In addition to eggs, ovarian tissue has the ability to produce hormones.
Ligaments of the uterus
- This is an auxiliary device that does not itself perform any reproductive functions. They fix the uterus in the pelvic cavity. In some situations, when the uterine ligaments are stretched, various torsions and deformations are possible, which in themselves will become the reason why obstruction occurs.
The uterine appendages, interacting with each other, allow the egg, which left the ovary during ovulation and ended up in the abdominal cavity, to enter the fallopian tube, pass through all its sections and reach the uterine cavity. Normally, this entire journey takes about a day. Now it becomes clear that if pathology occurs in any of these sections, then the egg will not be able to travel the entire way, and, therefore, will not be able to meet sperm and be fertilized. Thus, any of the problems that arise can cause infertility. It needs to be determined individually and appropriate treatment selected. It will most often be surgical.
Causes
The fallopian tubes become deformed as a result of a number of diseases. The causes of tubal infertility can be:
- bacterial diseases,
- injuries of the internal genital organs,
- disruption of tissue innervation,
- congenital defects of the fallopian tubes,
- the presence of adhesions,
- pressure on the tubes of neoplasms - tumors, cysts, hematomas,
- changes in hormonal levels,
- spasms.
Tubal obstruction also occurs after sterilization surgery. When a woman is sure that she does not want pregnancy, or the birth of a child is contraindicated for her, the fallopian tubes are ligated. These are irreversible operations, after which pregnancy is impossible.
Main reasons
Conditions and diseases that cause this pathology are identified. These include:
- Diseases that are sexually transmitted.
- Congenital deformations of the fallopian tubes.
- Damage to the fallopian tubes, as well as their mucous membrane due to mechanical stress.
- Inflammatory diseases, including neighboring organs that are located next to the fallopian tubes.
- Compression of the fallopian tubes from the outside by other organs.
- Disorders that are functional in nature.
- Previous surgical tubal ligation procedure, etc.
It's a matter of adhesions
The inflammatory process in the body and pelvic organs is the main reason for the development of obstruction of the fallopian tubes. It can be caused by infectious diseases, sexually transmitted diseases, the consequences of artificial termination of pregnancy and surgical interventions in the woman’s reproductive system.
Why does obstruction form? The inflammatory process leads to the formation of adhesions, because a scar forms at the site of any wound. Adhesions can be located on different parts of the fallopian tubes, deform them, disrupt the structure of the fimbriae, and partially or completely close the lumen of the tube. All these pathological changes certainly affect the possibility of fertilization and implantation of the embryo in the uterus.
But it happens that a woman has not encountered any sexually transmitted infections, or operations, or termination of pregnancy, and the fallopian tubes have still lost their patency. What's the matter then? The causes of obstruction of the fallopian tubes may lie in undiagnosed diseases that are asymptomatic. Paradoxically, one of them is chlamydia. The danger lies in chronic stress and decreased immunity. The female body is vulnerable to negative external influences, and the fallopian tubes are no exception. But how can we find out about the disease, how can we check whether we have it? What are the symptoms and signs of tubal obstruction, and what is the medical diagnosis of the disease?
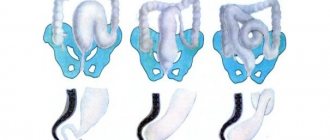
Fallopian tube obstruction: types
There are different classifications of tubal obstruction. The main characteristics that determine the pathology are the cause of obstruction, the degree of obstruction, its level, and the side of the lesion.
Depending on the side of the lesion, unilateral obstruction or a bilateral process is distinguished.
Depending on the level of closure of the lumen of the pipe, obstruction of its funnel, tortuous part, isthmus or intramural area is distinguished.
According to the degree of obstruction of the fallopian tubes, complete or partial obstruction is distinguished.
It is clear that the obstruction (symptoms) will be more severe with complete obstruction.
Depending on the causes, obstruction is also divided into functional and anatomical.
Doctors
- Terekhova
Lyudmila Alexandrovna - Gynecologist-endocrinologist
- Highest category
- 37 years of experience
More details
- Krupenkina
Lilia Alexandrovna - Ultrasound diagnostics doctor (ultrasound)
- Highest qualification category, candidate's degree
- 29 years of experience
More details
Symptoms
In the vast majority of cases, there are no specific symptoms indicating obstruction of the fallopian tubes. The reasons for seeking help are the presence of infertility or other problems of the reproductive system. Most often, obstruction is detected during the examination.
If the obstruction occurs as a result of an acute inflammatory process, symptoms of this particular process will occur: pain, increased body temperature, mucous, purulent or foamy vaginal discharge, etc.
If the pathology arose as a result of an adhesive process, then there will be no general intoxication symptoms, but there may be pain that increases with pressure and movement.
In some cases, when there is obstruction of the fallopian tubes, an ectopic pregnancy occurs, which will manifest itself with its own symptoms. This is the absence of menstruation (amenorrhea), pain in the lower abdomen, which has a pulling nature due to the growth of the embryo and stretching of the walls of the fallopian tube.
Based on the above material, it is clear that the symptoms that are observed with obstruction of the fallopian tubes will directly depend on the reasons that caused it.
Diagnosis of tubal obstruction
To make a final diagnosis, it is necessary to carry out diagnostic laparoscopy, which allows not only to clarify the diagnosis, but also in some cases to restore the patency of the fallopian tubes (for example, when compressed from the outside in the absence of changes in the fimbriae and the inner layer of the tube). If the patency of the fallopian tube has been restored, the woman is given recommendations on planning a pregnancy within 3-4 months. If pregnancy does not occur during this period, there is a high probability of functional disorders in the tubes, and the woman is offered IVF.
If during the operation gross morphological defects are revealed that disrupt the main function of the tube, it is removed (tubectomy) to prevent complications of a purulent-inflammatory nature in the abdominal cavity, as well as to prepare for IVF.
The gold standard for testing patency is laparoscopy
, since the possibility of spasm of the fallopian tubes and obtaining a false positive or false negative result is excluded.
List of factors that play a role when choosing a treatment method
- In the event that the patient has severe symptoms of the disease (menstrual irregularities), there is a long course that cannot be treated conservatively, surgical treatment is resorted to.
- If during the examination a chronic disease of various organs and systems (bronchopulmonary, cardiovascular, digestive system, diabetes mellitus) is diagnosed, or there are other contraindications to surgical treatment, it is recommended to treat the obstruction of the fallopian tubes using a conservative method.
- When there is a threat to a woman’s life (neoplasms, acute inflammatory processes in the abdominal cavity), preference is given to surgical treatment on an urgent basis.
- And the last point is the patient’s desire. Since obstruction of the fallopian tubes in itself rarely causes any discomfort or complaints from the patient other than infertility, the patient’s desire will play a decisive role in choosing a treatment method.
Diagnosis and treatment
The main diagnostic tool has long been an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity or, more familiar to the ear, ultrasound. In most cases, ultrasound is sufficient to diagnose the problem, especially with the intravaginal method of inserting a diagnostic device. Using ultrasound, you can determine swelling of the fallopian tube, the presence of adhesions or neoplasms1.
Another effective method is endoscopy. A special fiber optic tube with a camera at the end is inserted into the uterine cavity and moves towards the fallopian tubes. Any pathological changes are recorded on a separate monitor4.
A less common method, but especially popular if obstruction is suspected, is hysterosalpingography (HSG). A special contrast agent is injected into the uterine cavity, after which an x-ray of the abdominal cavity is taken. In the image, the uterus is immediately completely visible, and areas of complete obstruction of the tubes are easily identified1.
In addition to the basic methods, doctors take blood, urine and vaginal smears for a general analysis. Typically, the diagnostic process takes place in a gynecologist’s office, but if necessary, a neurologist, oncologist, infectious disease specialist and endocrinologist can be involved in the process.
The choice of treatment method depends entirely on the cause of tubal obstruction and the extent of the lesion2:
- Drug treatment is prescribed for the progression of infectious processes or other failures. The doctor prescribes a specific drug - antibiotics, antiviral drugs, immunostimulants, hormonal drugs and much more.
- Physiotherapy is used after defeating the infection and as a preventive measure. As part of physiotherapy, special baths, massage, electrophoresis and myostimulation are used.
- Surgical treatment is the most effective method and the only one in the presence of adhesions or tumors. Typically, a gentle and modern method of surgery is used - laparoscopy.
If no treatment method produces results, then a diagnosis of infertility is made and the woman should pay attention to artificial methods of insemination. In most cases, the uterus is still functioning, and obstruction of the fallopian tubes is not a contraindication to pregnancy.
Womenfirst
- Abashidze, A. Methods of rehabilitation of reproductive function in women with tubo-peritoneal infertility / A.A. Abashidze // Medical and social examination and rehabilitation – 2014 – No. 2 – pp. 42-46.
- Yakovleva, E. Ways to restore the functional activity of the reproductive organs of women after inflammatory diseases / E.A. Yakovleva // Scientific Gazette - 2013 - No. 25 (168) - Issue 24 - P. 66-72.
- Ayushinova, N. Assessment of the severity of adhesions in the abdominal cavity / N.I. Ayushinova, I.A. Shurygina, M.G. Shurygin, E.V. Glinskaya // Siberian Medical Journal – 2014 – No. 7 – P. 10-14.
- Yakovleva, N. The importance of endoscopic technologies in the diagnosis and selection of treatment methods for patients with tubo-peritoneal infertility / N.V. Yakovleva // Mother and child in Kuzbass - 2013 - No. 2 (53) - pp. 31-37.
- Dubinskaya, E. Pelvic peritoneal adhesions (endoscopic characteristics) / E.D. Dubinskaya, A.S. Gasparov, S.K. Nazarov, M.F. Dorfman // Bulletin of RUDN University, Medicine. Obstetrics and Gynecology, – 2010 – No. 6 – P. 166-173.
RUDFS183119 dated 10/03/2018
How to treat tubal obstruction with medication
There is a wide range of medications that are used to treat tubal obstruction. These are anti-inflammatory drugs, antibacterial drugs, and hormones. Auxiliary drugs are homeopathic, vitamin, and immunostimulating drugs that support the woman’s body as a whole.
In addition to medications, a conservative treatment method involves the prescription of physiotherapeutic procedures: electrophoresis, ultrasound therapy, balneotherapy, gynecological massage and electrical stimulation of the uterus and appendages.
Why is it desirable to remove the fallopian tube before IVF?
Tubectomy is always performed only with the woman's consent. It is important to understand that with a long history of infertility, and even more so with unsuccessful IVF attempts, we can confidently talk about dysfunction of the fallopian tubes. A functionally defective fallopian tube is a source of infection, which can enter the uterine cavity and lead to its inflammation. In addition, there is a risk of ectopic pregnancy.
During the IVF procedure, the cultivation of embryos occurs under sterile conditions, since theoretically any pathogenic or opportunistic microorganism can lead to the death of the embryo. For the same purpose, all foci of infection in a woman’s body are identified and treated - through blood vessels, infection, even from distant foci, can enter the uterine cavity and cause the death of the embryo. In addition, if pregnancy occurs, there will be a high risk of non-developmental pregnancy or miscarriage.
Before carrying out the IVF procedure, it is very important to determine in advance how complete the fallopian tubes are and whether there is a risk of an unfavorable outcome in assisted reproductive technology programs.
If you have any questions related to IVF with fallopian tube obstruction, you can ask them to the doctors at Nova Clinic. You can make an appointment with a doctor by calling the number listed on the website or using the booking button.
The path to pregnancy
At the initial stages of the development of adhesions in the tubes, conservative treatment may be recommended - anti-inflammatory and physical therapy. If the adhesions have already become full-fledged masters of the situation, experts recommend surgical treatment, namely, an operation called “laparoscopy.” This is a minimally invasive operation during which the surgeon cuts through the adhesions and restores the patency of the fallopian tubes. Laparoscopy may be effective if the adhesions are around the tubes. In the case where the adhesive process has spread inside the pipes and significantly deformed them, the treatment is unlikely to lead to the expected results. It is advisable to remove the affected pipes to avoid irreversible consequences for the woman’s health. It would seem that it sounds disappointing, and you can forget about pregnancy. This is wrong! If treatment does not help, and especially if the fallopian tubes are removed, pregnancy is possible with the help of IVF. The absence of fallopian tubes is an absolute indication for IVF and the success of the program is very great.
Take the first step - make an appointment!
or call 8 800 550-05-33
free phone in Russia
Methods to combat tubal infertility
If the causes of tubal infertility are functional disorders, then to eliminate them they resort to conservative treatment, during which nervous tension is relieved and hormonal levels are restored.
Partial obstruction can be treated by laparoscopy. If there is complete obstruction, all these measures do not work. The only effective way to experience the joy of motherhood in this case is in vitro fertilization (IVF), which can be carried out professionally at the Baltic Institute of Human Reproductology. During IVF, the fallopian tubes are not used at all, so their condition does not play any role. The egg is fertilized by a sperm in a test tube, and then the embryo is implanted directly into the woman's uterus. print version
Clinical prognosis
In addition to oncological diseases that pose a direct threat to a woman’s life, the most severe pathologies of the fallopian tubes include hydrosalpinx, pyosalpinx and salpingitis. These diseases carry a high risk of developing difficult-to-treat forms of female infertility, and therefore the main efforts should be aimed at their prevention.
Other diseases of the fallopian tubes are successfully treated and have favorable clinical prognoses both in terms of recovery and in the matter of preserving the possibility of subsequent childbearing - of course, subject to timely seeking medical help.
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category. Kosolapova Ekaterina Vitalievna