Causes
There are a significant number of factors that can cause noisy whistling breathing. Let's look at the most basic ones:
- Whistling noises occur when there is obstruction (narrowing of the lumen) of the respiratory tract - the nasal passages, larynx, trachea and bronchi. Obstruction can be caused by blockage of the airways by a foreign body or phlegm, swelling, spasm, or a neoplasm in these organs.
- Difficulty breathing and whistling are typical for attacks of bronchial asthma. They may be accompanied by a dry cough, which then gives way to a wet cough with thick discharge. During an attack of bronchial asthma, exhalation is difficult, it becomes long and noisy.
- The cause may also be an acute allergic reaction - Quincke's edema or anaphylactic shock. In these conditions, swelling of the larynx and spasm of the larynx and trachea develop, leading to a sharp complication of breathing and pronounced noise.
- Wheezing sounds when breathing accompanied by shortness of breath can also be a symptom of heart failure. In diseases of the cardiovascular system, capillary exchange disorders occur, which can lead to the accumulation of extravascular fluid in the lung tissue and impaired respiratory function.
Warning signs
There are a number of situations with lung diseases when you cannot delay seeking help. Thus, among the dangerous symptoms appearing that require immediate medical attention are:
- sudden shortness of breath;
- a drop in oxygen levels in the blood - today you can measure it at home yourself using pulse oximeters;
- the appearance of blood in the sputum when coughing,
- a sharp deterioration in general health,
- severe weakness
- loss of consciousness and some others, as well as wheezing and whistling in the lungs, which appeared out of nowhere, also require consultation with a doctor.
Symptoms
A sign of airway obstruction is, first of all, breathing noises, most often manifested during exhalation. The patient complains of shortness of breath, his breathing becomes noisy and heavy. There are wheezing sounds resembling a whistle or a high-pitched scream. A sharp dry barking cough, characteristic of croup, is possible. Against the background of respiratory dysfunction, the patient feels weak and dizzy, the skin becomes pale. A specific syndrome is a decrease in chest volume and neck girth.
Come on, open your mouth
Most often, false croup occurs in children at 2-3 years of age, can recur for several years, and then goes away. If false croup occurs in a child for the first time, it is better for parents to call an ambulance. Doctors will give the child clear instructions on what to do if the situation repeats. Thus, they can stop a new attack themselves.
But inexperienced mothers and fathers are better off seeking medical help. After all, false croup can be confused with Quincke's edema, which occurs as a result of allergies, a retropharyngeal abscess, or, for example, with a foreign object getting into the throat.
If a child (especially in the first years of life) coughs suddenly, against the background of complete health, the first thing you should worry about is whether this is due to aspiration of the respiratory tract. After all, children often put everything in their mouths while playing, which is why toys containing small parts have age markings and should not be given to children under 3 years of age. With such a cough, urgent help is required. By the way, a foreign body in the respiratory tract not only interferes with breathing, but can also cause recurring pneumonia.
Diagnostics
The presence of whistling noises and difficulty breathing is established as a result of a physical examination. In order to establish the cause, additional research is carried out.
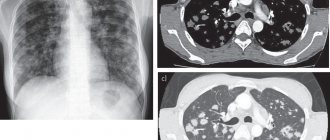
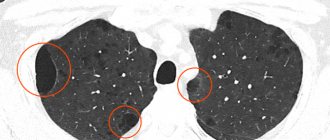
The presence of a foreign body is determined using fluoroscopy or bronchoscopy - examination of the respiratory tract using an endoscope. MRI and fluoroscopy can also diagnose tumors of the respiratory tract. Timely fluorography is mandatory to exclude pulmonary tuberculosis.
A clinical blood test and microbiological analysis of sputum secretion make it possible to determine the presence of inflammatory diseases of the respiratory system. An immunological blood test is also carried out, which can show changes characteristic of bronchial asthma - a decrease in the activity of T-suppressors and an increase in the level of immunoglobulins.
To assess the level of functional disorders of the respiratory system, spirometry is performed - measuring the volumetric parameters of breathing.
Preventive actions
Of course, many are interested in issues of prevention. After all, it is known that it is easier to prevent a disease than to deal with its consequences later. “For various diseases, there is prevention, which means preventing repeated cases of the disease and complications, especially if the disease is chronic, for example bronchial asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Prevention can be aimed at reducing contact with the allergen, treating concomitant diseases, chronic foci of infections such as sinusitis, inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, caries. It is recommended to maintain a healthy lifestyle, quitting smoking and other bad habits, vaccine prevention, spa treatment and many other measures to preventing exacerbations of diseases of the bronchopulmonary system,” says Evgeniy Popov.
Question answer
Pulmonologist and phthisiatrician - what is the difference?
Treatment
In case of sudden respiratory failure, accompanied by whistling sounds, shortness of breath, pale skin, swelling and loss of consciousness, emergency medical care is required. This condition can be a sign of a severe allergic reaction and can be fatal. Treatment is carried out only in a hospital setting.
The presence of a foreign body in the lumen of the respiratory tract also requires immediate medical intervention. Foreign inclusions are removed manually or using an endoscope.
To relieve attacks of suffocation, adrenergic agonists are used, prescribed strictly according to a doctor’s prescription. For persistent airway obstruction, treatment is aimed at relieving swelling, increasing the lumen of the bronchi and reducing the amount of sputum. For this purpose, antihistamines, antispastic and sedatives are used.
For concomitant dry cough, antitussive drugs (codeine, glaucine) are prescribed; for wet cough, mucolytic drugs (ambroxol, acetylcysteine) are prescribed. For severe forms of obstruction, corticosteroid drugs (prednisolone, hydrocortisone) are prescribed. In the presence of infectious diseases of the respiratory system, antimicrobial therapy is mandatory.
The reception is conducted by specialists
Raevsky Joseph Valerievich
Otorhinolaryngologist
Leis Kristina Vladimirovna
Otorhinolaryngologist
Cost of services
Initial consultation with an ENT doctor of the highest category
1300₽
Repeated consultation with an ENT doctor of the highest category
1000₽
Physiology of the respiratory system
“The lungs consist of a bronchial tree and alveoli, large bronchi conduct air, and as the lumen of the bronchi decreases, the air encounters more resistance and begins to squeeze through the narrow walls of small bronchi and bronchioles, this process is called diffusion. The penetration of air from the alveoli through the capillary wall into the blood also occurs as a result of diffusion,” says pulmonologist at the National Medical Research Center for Phthisiopulmonology and Infectious Diseases of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation Evgeniy Popov .
If this process proceeds normally, and nothing interferes with the breathing process, then extraneous noise in the lungs will not be heard and is unlikely to appear. And if an obstacle appears in the path of air, says Evgeny Popov, the force of friction begins to act. Such an obstacle may be:
- sputum;
- narrowing of the bronchi due to swelling in the presence of some kind of inflammation;
- allergic spasm;
- foreign body
- tumor.
All these phenomena lead to the formation of so-called adverse respiratory sounds or wheezing. The person himself can hear them, but he can hardly give them the correct interpretation.
Guide to lung diseases. How to distinguish the symptoms of diseases? More details
When?
With a retropharyngeal abscess (this is an inflammatory process of a purulent nature that affects the soft tissues of the pharyngeal wall), with the development of diphtheria (a true narrowing of the larynx occurs due to the accumulation of mucous discharge in it), with acute laryngotracheobronchitis, then the inflammatory process of the mucous membrane of the trachea, larynx and bronchi begins . Often laryngotracheobronchitis occurs due to exposure to the influenza virus. Wheezing may occur when a foreign object enters the throat.
Bromhexine for easier breathing
In the presence of difficulty breathing and coughing, doctors determine that the main goal is to eliminate the cause of the pathology. With the infectious-inflammatory nature of the respiratory disease, increased discharge of sputum and mucus from the respiratory tract is required. For this, expectorants and mucolotics may be prescribed depending on the productivity of the cough, as well as antihistamines.
Bromhexine allows you to treat an unproductive or wet cough and make breathing easier by freeing the bronchi from excess phlegm. It is widely used for acute and chronic bronchitis, pneumonia, asthma, COPD, pulmonary tuberculosis. Various release forms have been developed for the drug, which ensures ease of administration and allows you to individually calculate the amount of the active component for a child or an adult.
The use of bromhexine and its analogues is recommended only as prescribed by a doctor. For asphyxia, heart disease and some other causes of breathing problems, these drugs do not help.
Cough and shortness of breath
Shortness of breath when inhaling is called inspiratory shortness of breath. It usually occurs with pathologies of the upper respiratory tract: asphyxia, edema, foreign body, neoplasm in the trachea, and also in some cases with heart disease.
Dyspnea during exhalation (expiratory) indicates impaired patency in the bronchial tree, bronchospasm. When coughing, difficulty in exhaling can be caused by allergies, exacerbation of bronchial asthma, bronchitis, or emphysema.
Tinnitus
This sound can be produced in one or both organs. It is caused by damage to the hair cells in the inner ear due to loud noise, infections, and also occurs in older people. In this case, sound waves are transformed into electrical signals.
A girl found an egg in the park and took it with her to see who would hatch. Coronavirus sharply reduces the level of vitamin A in the body, doctors say. Scientists have developed an implant for depression that can be controlled from a smartphone.
You should be concerned when the described symptoms last more than two days and are accompanied by headache or dizziness. In this case, incessant sounds mean the presence of neurological problems or a dangerous infection. You should consult a doctor immediately.
Wheezing when breathing
In the absence of any health problems, breathing does not require effort and does not have additional sound: noises, wheezing or whistles. Normally, only newborn children in the first weeks of development may experience whistling when breathing due to insufficient development of the respiratory tract. Whereas in adults:
- Wheezing and dry wheezing when exhaling can be caused by a narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi: for example, with allergies, asthma, chronic bronchitis or tuberculosis.
- The cause of dry, buzzing wheezing during inspiration is often pathologies of the vocal cords, larynx, trachea, and inhalation of foreign bodies.
- Moist rales , which are easier to hear when inhaling, can appear with pneumonia and pulmonary edema.
- In asthma and COPD, wheezing and coughing are accompanied by shortness of breath and difficulty in air circulation.