Trichomoniasis is one of the most common infections affecting the human genitourinary system. The source of the disease is Trichomonas, which live in the urethra, seminal vesicles and prostate gland (in men) and in the vagina (in women). After trichomonas enter the body, symptoms do not appear immediately - the incubation period lasts up to 4 weeks.
CONSULTATION ON THE RESULTS OF ANALYSIS AND ULTRASOUND — 500 rubles. (at the patient's request)
CLICK TO SIGN UP
The disease is dangerous due to complications: if the infection is not treated, sick men will face prostatitis, and women will suffer from inflammation of the genitourinary organs, problems with pregnancy, etc.
Causes of trichomoniasis: features of trichomonas
The content of the article
Trichomoniasis is caused by the bacterium Trichomonas vaginalis. Once in the body, Trichomonas provokes inflammation of the mucous membranes of the genitourinary system. This is one of the most common groups of bacteria that cause sexually transmitted diseases (STIs).
There are no exact statistics, but scientists believe that at the moment there are from 600 million to 1 billion people in the world infected or carrying the bacteria. Every year, more than 50 million cases of Trichomonas infection are registered worldwide.
This is an unusual bacterium. Trichomonas vaginalis is the simplest single-celled organism that forms colonies. By uniting, Trichomonas act as a whole organism. They attack mucous membranes and destroy lactic acid bacteria, which create the normal flora of mucous tissues. In total, three varieties of Trichomonas can be found in the human body, but only Trichomonas vaginalis is a dangerous variety capable of aggressive actions. Therefore, in tests for trichomoniasis, this particular subspecies is isolated.
Colonies of bacteria are localized in the lower genitourinary tract:
- Urethra;
- Vagina;
- Simple.
In the absence of proper treatment, bacteria spread throughout all organs of the genitourinary system, requiring comprehensive and targeted treatment.
Where does Trichomonas come from?
At the end of the fifties of the last century, several international conferences were held to discuss where Trichomonas comes from in the reproductive tract. They decided that this single-celled organism can be obtained not only through sexual contact, but also from a bath bench or basin, and even from swimming pool water and just tap water, not to mention wells. Bath accessories were blamed because trichomoniasis was practically not detected in men due to the absence of clinical symptoms. If a woman complains of inflammation, and a man is fine, then apparently the woman “caught the infection” somewhere else.
Where can a decent and faithful woman become infected with a sexually transmitted infection? Of course, in a public bath, where she is completely defenseless. And at that time, personal bathrooms were very rare; citizens went to the baths to wash themselves. Another five-year-old mankind was convinced that Trichomonas brought into a family was not at all a consequence of the infidelity of one of the spouses, but evidence of a woman’s failure to observe personal hygiene. One good thing is that this misconception helped save the family, because the infection happened through “non-sexual” means.
But in the mid-60s, scientific proof of the extremely poor survival of Trichomonas outside the human body came from Soviet Estonia, therefore infection by any other method other than sexual intercourse is simply unrealistic. Trichomonas does not like sunlight and hot water, and is immediately killed by any antiseptic. Indeed, Trichomonas is so delicate, so demanding of the external environment that even in the secretion of the genital tract collected for the purpose of research, it often dies before it is brought to the microscope. Since that time, the disease caused by Trichomonas vaginalis has been recognized as a venereal disease.
The main route of transmission of Trichomonas in adults, of course, is sexual, but oral sex does not contribute to infection, in any case, they could not prove this possibility of transmission. A woman in labor with trichomoniasis can infect her child, more often this happens to girls. This route of transmission of infection is called vertical. And today, 2–17% of newborns have trichomonas vaginitis or, in the old way, colpitis inherited from their mother. It is quite possible, because tests are taken from pregnant women several weeks before giving birth.
At risk for trichomoniasis are citizens who have multiple sexual partners, workers in the illegal sex industry, drug addicts and HIV-infected people, socially disadvantaged people, in general, comrades. True, citizens are still actively using the idea of contracting trichomoniasis in the pool, the main thing is to get treatment, and let them decide for themselves how to explain the appearance of Trichomonas vaginalis to their partner.
How can you become infected with trichomoniasis: routes of transmission
The main cause of trichomoniasis is classical sexual contact; the disease is not transmitted by kissing. As for the domestic route of infection, such cases in the practice of doctors are very rare and are usually questioned.
The risk of infection through unprotected contact is up to 70%. When using a condom, the risks are minimal, but still remain - 10%. A condom is not an absolute protection, so if Trichomonas is detected, it is imperative to check your sexual partner, even if he does not have any symptoms of the disease.
Household transmission through shared towels, sheets or toilet seats is 98% excluded. Trichomonas are poorly adapted to existence in the open air and can live no more than 15 minutes outside the human body. According to statistics, the percentage of people infected through household contact does not exceed 2% of all infections.
Why is trichomoniasis dangerous for women?
Consequences of the chronic course of the disease:
- Sexual disorders (lack of orgasm, sexual desire);
- Oncological process in the tissues of the cervix;
- Pregnancy pathologies: fetal death during gestation or childbirth, premature pregnancy, chorioamnionitis;
- Infertility caused by obstruction of the tubes and inflammation of the appendages.
According to medical research, trichomoniasis in chronic form provokes diabetes mellitus, mastopathy, allergies, and oncological processes in the pelvic organs.
How carrier status turns into disease
After entering the body, Trichomonas can remain in an incubation state for a long period of time, existing in small quantities on mucous tissues and without causing harm to the host. The development and active reproduction of bacteria occurs only in the event of a violation of the flora of mucous tissues.
In the normal state, the flora of the mucous membranes of the genital organs includes a large number of lactobacilli. Lactobacilli maintain the acid-base level of the environment of mucous tissues, which does not allow pathogenic (hazardous to health) microorganisms to multiply. When the acidity or composition of the flora changes (dysbacteriosis), Trichomonas receive an excellent opportunity for development and reproduction.
Changes in the level of acidity and composition of the flora occur for the following reasons:
- Violation of the rules of personal intimate hygiene;
- Using caustic cleaning agents - only special neutral products can be used;
- Promiscuous sexual intercourse with various partners;
- Lack of hygiene during menstruation - rarely changing tampons and pads;
- Frequent wearing of panty liners;
- Using synthetic, tight-fitting underwear;
- Hormonal imbalances during pregnancy.
Causes of the disease
- Promiscuous sexual life in the form of frequent changes of sexual partners;
- Unprotected coitus;
- Unsanitary living conditions;
- Using someone else's personal hygiene products (towel, razors, washcloth, bed linen).
Also, the risk of the disease increases with a decrease in the acidity of the vaginal environment. This is facilitated by:
- Pregnancy period;
- Menstruation;
- Decreased immunity due to infectious diseases (ARVI, acute respiratory infections, chicken pox, measles, rubella).
Symptoms of trichomoniasis
When trichomonas enter the mucous membrane in an environment that is acceptable for their life, the bacteria secrete mucous substances to attach to the membrane. Also, during the life of bacteria, a specific enzyme is released, which leads to the breakdown of cells of the mucous membrane.
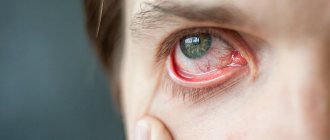
Violation of the mucous membrane provokes inflammation, which gives the following symptoms:
- Swelling of the mucous membranes;
- Redness of the mucous membrane;
- Detachment of the surface layer of cells;
- Subfebrile (from 37.1 to 38 degrees) temperature;
- Unpleasant sensations, itching, burning.
Inflammation is caused by the body's natural defense reaction. The bacterium is attacked by biologically active substances of immune cells, which contribute to irritation of nerve endings. Trichomoniasis manifests itself differently in women and men.
Why is it important to prevent infection?
Although medical treatment and medications are constantly improving, treating trichomoniasis is difficult. Flagellated parasites have a high degree of adaptation. They are able to change shape and pretend to be platelets and lymphocytes. Therefore, diagnosing the disease can be difficult.
In addition, Trichomonas are resistant to the effects of immune cells, and the non-protein shell of pathogens is resistant to antibacterial drugs. Therefore, it is so important to know how the infection enters the body and how you can avoid it.
Symptoms of Trichomonas infection in women
After Trichomonas enters the female body, the development of the disease begins with damage to the vaginal flora, then the bacteria spread to the urinary ducts, bladder and other mucous tissues of the genitourinary system.
Symptoms of the disease with varying intensity appear 5-7 days after infection; the incubation period of bacteria ends 30 days after entering the body. After this period, pronounced symptoms can be observed.
Trichomoniasis manifests itself in the form of trichomonas colpitis or vaginitis - vaginal dysbiosis, leading to inflammation of the surface layers of the vaginal mucosa.
An infected woman will experience:
- unpleasant-smelling vaginal discharge, discharge has a yellowish tint;
- burning sensation or severe itching on the outer surface of the genitals;
- characteristic pain during urination or sexual intercourse;
- increased sensitivity of the outer walls of the vagina to injury and other factors,
- which is manifested by bleeding and purulent discharge.
With vaginitis caused by Trichomonas, the following symptoms of the disease appear:
- Unpleasant-smelling discharge with a foamy structure. May be yellow or gray, depending on the stage of the disease. Foam occurs due to bacteria that produce gas during their life processes.
- A feeling of severe itching and burning localized in the vaginal area is a sign of inflammation of the mucous membrane.
- Redness of the skin of the labia and around.
Women who are sexually active are susceptible to the disease. Age from 18 to 45 years. Vivid symptoms and vaginitis appear in cases of weakened immunity, leading to rapid dysbiosis of the vaginal flora. With good immunity, the disease can manifest itself with minimal symptoms, or occur in a latent, chronic form. In this case, moments of exacerbation may occur in the period before menstruation.
If symptoms of trichomoniasis are detected, regardless of their intensity, you should immediately contact a gynecologist.
Possible complications
The peculiarity of the biological properties of the pathogen and the predominance of a latent or asymptomatic course of infection in men lead to damage to the prostate gland, the occurrence of vesiculitis, and epididymitis. Therefore, a possible outcome of undiagnosed and untreated trichomoniasis in men is infertility. In addition, there is a disturbance in the microbiocenosis of the genitourinary tract with the addition of other pathogenic microorganisms that support chronic inflammation in the prostate gland. Long-term prostatitis can subsequently lead to the development of cancer.
Symptoms of trichomoniasis in men
During unprotected sexual intercourse, Trichomonas enter the urethra. If the bacteria take root, they may spread deep into the canal to the prostate. When it comes into contact with the prostate, inflammation begins, leading to acute or chronic prostatitis.
In the male body, in most cases the disease is practically asymptomatic. In rare cases, there may be discharge from the urethra and pain when urinating. In cases where the disease affects the prostate gland, the symptoms of Trichomonas can be completely similar to prostatitis.
At the stage of chronic trichomoniasis, urethritis appears, accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Burning in the urethra after urination;
- Mucus or foamy discharge;
- Difficulty passing urine accompanied by pain or tension in the abdomen;
- Feeling of bladder fullness after urination.
Trichomonas is transmitted to men in 65-70% of unprotected sexual contacts with a carrier of the infection. Microorganisms often leave the body naturally. A week after infection, Trichomonas disease is detected in only 30% of men. This is due to the fact that the flora inside the urethra does not meet the conditions necessary for the reproduction of Trichomonas.
In men infected with Trichomonas, trichomoniasis can occur in a latent, chronic form, asymptomatic or with minimal symptoms until exacerbation caused by decreased immunity. In this case, the man will act as a carrier of infection.
Clinical picture
The incubation period of trichomoniasis ranges from several days to 2 months. This depends on the immunity of the infected person, the presence of concomitant diseases and the form of development of trichomoniasis. If it occurs in an erased (latent) form, then the first signs of the disease appear several weeks after infection.
In women, the disease is more severe than in men. Symptoms of female trichomoniasis manifest themselves faster and stronger, intensifying before and after menstruation. In most cases, male trichomoniasis exists in the form of carriage. Trichomoniasis is rarely diagnosed in childhood. Infection can occur from a sick mother when passing through the birth canal, using the same towel. Symptoms are similar to those of adults; in girls, it often occurs in the form of vulvovaginitis.
Classification of trichomoniasis
- Acute form - primary infection with early and severe manifestation of symptoms.
- The subacute form is a primary infection with vague, not obvious symptoms.
- Chronic form - occurs in the absence of treatment, can last for years with mild symptoms or alternate with periods of calm and recession.
- Trichomonas carriage - there are no manifestations of the disease, the pathogen is detected accidentally during laboratory tests.
The nature and volume of discharge directly depends on the stage of the disease. With chronic development, a small amount of mucus is secreted. Over time, the symptoms may subside, but recovery will not occur.
Trichomoniasis is often combined with other STIs: gonorrheal infection, chlamydia, mycoplasma bacteria. Increases the risk of contracting HIV infection. Complications include: infertility, premature birth, stillbirth. The chronic form can lead to prostatitis, prostate cancer and cervical cancer. It is important to monitor your health, hygiene, and avoid casual sexual contact without using contraception. You should undergo medical examinations in a timely manner and treat any identified diseases.
Consequences of trichomoniasis during pregnancy
Trichomoniasis during pregnancy has a number of serious consequences. Exposure to bacteria on the organs of the genitourinary system during pregnancy, as well as at the stage of conception, can lead to the following problems:
- Sperm phagocytosis is a reaction of the immune system during an inflammatory process. The concentration of macrophages and neutrophils – cells that ensure the destruction of the source of inflammation – increases. Along with pathogenic bacteria, the immune system also destroys sperm, which leads to male infertility.
- Reduced sperm motility - Trichomonas actively secrete toxic metabolic products that inhibit sperm.
- Miscarriage - due to the effects of Trichomonas, prostaglandins are released into the blood - substances that provoke contractions of the muscular system of the uterus, which can result in spontaneous abortion;
- Premature birth - due to the reason described above, due to the increased tone of the uterus, it is possible to provoke premature birth.
Thus, at the stage of pregnancy planning, it is imperative to be tested for Trichomonas and undergo a course of treatment.
Features of the disease during pregnancy
Since during pregnancy the acidity of the vagina is reduced, and the immune system is significantly weakened, trichomonas manifest themselves with clear signs, or an exacerbation of a chronic illness occurs. In this case, there may be several lesions at once. Affected:
- rectal mucosa;
- urethra and bladder;
- vagina.
When a woman becomes pregnant, the body begins to create conditions that will help protect the fetus from any negative external influence. Therefore, the immune system begins to work much more actively when any microorganism penetrates. Additional protective mechanisms are present from the moment of conception until the baby is born.
The possibility of infection depends on how far along the expectant mother is. From the first trimester, the body changes, the mucus in the cervical area becomes thicker and more viscous to prevent the penetration of bacteria and viruses.
Important! It is better to identify the disease at an early stage and then carry out full treatment than to face unpleasant symptoms and consequences of trichomoniasis. In acute cases, microorganisms can cause pathologies in the fetus, miscarriage or early birth.
Diagnosis of trichomoniasis: how to identify trichomonas
You should not lead the disease to complications; to detect trichomoniasis in a timely manner, it is enough to visit a doctor for preventive purposes and take a smear for infections. Well, if you start to experience the first symptoms, you should contact the clinic immediately.
If symptoms similar to trichomoniasis are detected, a specialist (gynecologist or urologist) prescribes tests to identify pathogenic organisms in the flora
Trichomoniasis can be diagnosed at any stage, for this purpose the following are carried out:
- Study of the drug (discharge from the urethra, vagina) at the microscopic level, using the Gram and Romanovsky-Giemsa method;
- Biological and molecular studies NASBA and PCR, etc.
The most accurate way to detect Trichomonas is to go through several stages of testing.
Popular tests for Trichomonas
- Microscopic examination method
- for diagnosis, biomaterials are taken for analysis. For women - a smear from the posterior vaginal vault, cervical canal, urethra. In men, a scraping is taken from the urethra, prostate secretions and seminal fluid. The study is performed under a microscope. A 0.9% sodium chloride solution is added to the taken materials, after which the microorganisms change color and can be seen during examination. The advantage of the method is its efficiency: research must be carried out within no more than 30 minutes from the moment the material is taken.
Photo by isis325
- The method of cultivating Trichomonas
is a smear containing biological material from the patient’s body and is placed in a special nutrient medium to accelerate the development of microorganisms. After some time, the flora is examined and if initially there were Trichomonas in the sample, their number increases significantly, allowing us to speak with confidence about the presence of bacteria in the body. The method allows you to diagnose the degree of infection, the stage of the disease, and also identify the most effective drug for killing bacteria. - PCR method - for research, any biological fluids are taken, from a vaginal smear to a blood test. The study searches for DNA and RNA of pathogenic microorganisms. The advantage of the technique is the ability to detect Trichomonas, even if the disease is asymptomatic or in a chronic stage. The method is the most expensive, but very accurate.
Each method has its own advantages and differs in effectiveness and time to obtain results. Diagnosis is prescribed by the attending physician, gynecologist or urologist after a visual examination.
Diagnostics
Source: Leif Hellmann/Pixy.org
Diagnostic measures consist of determining the clinical signs of the disease and identifying pathogenic microorganisms. Laboratory methods help in this.
Smear microscopy
If Trichomonas vaginalis is immediately detected using microscopy, no additional studies are required to prove infection; treatment is prescribed.
Bacterial culture of samples
Usually used for the chronic form. Using this method, you can not only detect Trichomonas, but also find out its sensitivity to various drugs.
Serological method
Identifies specific proteins that the immune system produces in response to an infection in the body.
PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
Detects Trichomonas DNA or RNA in patient biological material. One of the most accurate modern methods makes it possible to detect the infectious agent even in small quantities.
Important! If trichomoniasis is suspected, it is advisable to prescribe additional tests for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis B and C, as well as for the presence of TORCH infections (a group of infections dangerous to pregnancy and the fetus).
Treatment of trichomoniasis: comprehensive treatment
The simplicity of the structure of Trichomonas is deceptive - these are the oldest bacteria, coexisting with humans for millions of years. This is due to their resistance to drugs. Treatment of trichomoniasis is prescribed by the doctor individually for each patient, based on the results of his examination. The wellness course must be carried out comprehensively, in three stages, and until complete recovery, otherwise the disease, after some time, will be able to manifest itself again. Monitoring of cure is mandatory.
- Antimicrobial drugs taken orally or intravenously are used to treat the infection. In some cases, combined use of drugs in various forms is required to provide local and general effects.
- When using strong antibiotics, women may develop thrush; the gynecologist should take this into account and, if necessary, prescribe vaginal suppositories to combat the fungus and special preparations containing lactic acid bacteria. Drugs can be prescribed in the form of suppositories or douching solutions.
- Treatment must be supplemented with local treatment: tampons, baths, urethral and bladder installations, suppositories.
- In cases of acute form, the course of treatment requires additional procedures, such as prostate massage, physical and immunotherapy, and instillation of the urinary canal. In any case, you should not self-medicate.
The general course of treatment lasts from 2 weeks to 1 month, depending on the effectiveness of the selected drugs and the patient’s immune system. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate. An error in choosing a drug and insufficient dosage will lead to stimulation of the bacteria’s immunity to the drugs used, which in the future will only complicate treatment.
If the patient has a regular sexual partner, he should also be examined by a specialist and, if necessary, undergo a course of treatment.
Drug therapy
Once the cause of the symptoms is determined, the doctor may prescribe treatment for the patient, which includes drugs that destroy these microorganisms. Metronidazole is one of the most popular and powerful drugs; it is prescribed to patients. To treat the infection, the doctor prescribes taking 1 tablet twice a day, it is important to take the medicine with plenty of water. The course of treatment is 10 days, after which tests are taken again.
Metronidazole penetrates the body and then begins to actively affect Trichomonas, destroying the DNA of single-celled organisms. Since all biological processes are stopped, the microbe quickly dies. But it is worth noting that the medicine has a number of side effects and contraindications. For example, it is not recommended to use the drug when carrying a child or if the body is hypersensitive to the components.
There are also other pharmaceutical medications that can be prescribed to treat trichomoniasis.
- Klion D. This is a combination drug, it contains Metronidazole and Miconazole. Klion D is often prescribed to patients who are faced with diseases of the genitourinary system. The product can be prescribed to a woman in the form of vaginal suppositories. The medication is used for 10 days, suppositories are inserted into the vagina in the evening before bedtime.
- Tinidazole. This drug belongs to the same group as Metronidazole; the effect of the main components of the drugs is very similar. This remedy can be used not only to eliminate Trichomonas, but also to get rid of gonococci. The medication should not be used in case of hypersensitivity to the components, as well as in diseases associated with the hematopoietic organs. Tinidazole is prohibited during breastfeeding and pregnancy.
During the treatment process, the doctor must constantly monitor the patient's condition in order to see the result of the therapy. The treatment process is tracked in the following ways:
- women should take a vaginal smear after the end of menstruation, 1-3 days later, based on the result of the smear examination, the effectiveness of treatment will be obvious;
- after therapy is completed, within three months the patient is prescribed a vaginal and urethral smear to detect the presence of Trichomonas.
Diet and restrictions
Also, while taking medications, the specialist will recommend a diet and introduce some restrictions. In particular, recommendations may be of the following nature:
- Eliminate fried, fatty, spicy foods from the diet;
- Add fermented milk products that help restore lactobacilli;
- Strictly refrain from intimacy, since during treatment the flora is most vulnerable and there is a risk of getting an additional infection or fungus.
Following these recommendations will speed up treatment and achieve the best result with minimal discomfort to the body.
Advantages of JSC "SZDCM"
You can get tested for trichomoniasis and other infections in the laboratory of the Northwestern Center for Evidence-Based Medicine. Qualified specialists have the latest diagnostic equipment at their disposal, so we can guarantee:
- accuracy of the result;
- quick readiness of analyzes;
- performing all types of tests for a complete examination.
The results can be obtained in any way convenient for you: in person, via the email specified during registration.
Trichomoniasis can be prevented: preventive measures
To prevent the disease, you must adhere to simple rules in intimacy and lead a healthy lifestyle:
- Be careful during sexual intercourse, do not be promiscuous, it is better to choose a single partner - mutual trust and honesty are the best cure for sexually transmitted diseases;
- Use a condom during sexual intercourse, use contraception correctly;
- Follow the rules of intimate hygiene - taking a shower and changing linen every day, using soap made from natural ingredients;
- Timely treatment of any urological diseases that provoke vaginal dysbiosis.
- Be examined annually by a gynecologist or urologist, and consult a specialist when the first alarming symptoms appear.
By adhering to these simple rules, you can avoid most sexually transmitted diseases and reduce the risk of dysbacteriosis and related infections.
Prevention measures
The main cause of infection is considered to be sexual intercourse that took place without using a condom, for this reason it is so important not to abandon traditional methods of protection. Gynecologists and venereologists give useful advice on how to avoid infection, and it’s worth listening to them:
- you should refrain from promiscuity;
- it is better to refuse contact with an unfamiliar partner in whom there is no confidence;
- It is recommended to use a condom during sexual intercourse;
- after the act, bactericidal solutions are used to disinfect the genitals in case of accidental contact;
- Conduct rapid diagnostics at least once every six months.
If you follow these simple rules, you can significantly reduce the risk of contracting this infection. Venereologists strongly recommend not to refuse examinations twice a year. Pregnant women are required to undergo tests to detect hidden infections in order to cure the disease in time.
It is easier to prevent an infection than to treat it. As experts say, at the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor and undergo an examination. This will help to detect infection in time and begin treatment. If therapy is not started on time, trichomoniasis will become chronic, and as a result, the disease will constantly worsen. To prevent infection, barrier methods of contraception should be used, as well as strict hygiene rules.
Features of the pathogen
Trichomonas vaginalis is a unicellular organism 8-24 microns long, has flagella, due to which it moves well and can penetrate the upper floors of the woman’s genital tract. Optimal conditions for life: pH 5.9 – 6.5, temperature 35 – 37°C.
In acute trichomoniasis, small individuals with a length of 8-11 microns are found, in chronic cases, large individuals with a length of 30-45 microns are more common.
Epidemiology
How can you become infected with trichomoniasis and how is trichomonas transmitted? The source of infection is a sick person or carrier. Infection in the vast majority of cases occurs through sexual contact. Other routes of infection with trichomoniasis are extremely rare:
- Transmission of trichomoniasis through household contact as a result of indirect contact through toilet items, gloves, bedpans, oilcloths and toilet seats, chamber pots, infected linen, etc.
- It is even less common for newborn girls to become infected when passing through the mother’s infected birth canal.
The greatest significance in the epidemic process is played by sluggish, low-symptomatic forms of the disease and trichomonas carriage, in which there are no signs of inflammation, and trichomonas are not detected in the smear and are detected in the analysis only when the disease relapses in sexual partners. It should be noted that Trichomonas carriage is not an ordinary transient carriage of protozoa, but is a systemic active infectious process with a reaction of T. vaginalis to a pathogenic factor with suppression of the immune response to infection, due to the antigenic affinity of T. vaginalis with certain human tissues. It is Trichomonas carriage that contributes to the active epidemiological spread of the pathogen among sexual partners. According to the survey data, the carriage frequency among the examined women ranges from 10-35% and 5-41% among men.
According to various authors, trichomoniasis occurs as a monoinfection in 3-15% of cases; it is more often observed in combination with other STIs (on average in 86.5% of patients): gonorrhea , chlamydia , candidiasis , mycoplasmosis , etc. Moreover, it has been established that that Trichomonas can be carriers of viruses: herpes simplex, human papillomavirus. After attachment to the vaginal epithelium, T. vaginalis enhances the processes of desquamation and loosening of the epithelium, which contributes to the rapid invasion of bacterial flora with the development of mixed infectious lesions.
The causes of Trichomonas in women/men are the practice of unprotected sex, indiscriminate choice of sexual partners, and alcohol/psychoactive substance abuse.
It is important to consider that Trichomonas vaginalis produce highly immunogenic antigens that can neutralize cytotoxic T lymphocytes and antibodies. Also, trichomonas are characterized by antigenic mimicry (the ability to sorb plasma proteins on their surface), which does not allow the immune system to identify them as foreign organisms. That is, trichomonas infection does not lead to the development of a pronounced immune response, and the detection of serum/secretory antibodies in recovered individuals only indicates a past/existing infection, but is not capable of providing lasting immunity.
The resistance of Trichomonas vaginalis to unfavorable environmental conditions is insignificant. They die quickly (within 10 minutes) at a temperature of 45-50°C and instantly at 60°C. T. vaginalis are more resistant to low temperatures: at temperatures down to –10°C they remain viable for up to 45 minutes. Trichomonas can survive for a long time and do not tolerate drying well, but are viable in a humid environment (sponges/cotton fabrics). They die instantly when surfaces are treated with antiseptic agents. On rubber gloves/gynecological speculum, Trichomonas can remain viable for 5-30 minutes.
Predisposing factors for the development of the disease in women include a shift in pH to the alkaline side, hormonal deficiency, vitamin disorders, and concomitant diseases of the genitourinary tract. The incubation period of urogenital trichomoniasis can vary from two to three days to a month, averaging 10 days.
The laboratory diagnostic of genitourinary trichomoniasis (literature review)
N. S. Makhlay.
Abstract. The laboratory diagnostics of trichomoniasis is strongly recommended for the diagnosis confirmation. Current review summarizes diagnostic methods directed to identification by morphology of protozoa, by antigenic properties of T.vaginalis, by specific antibodies and by the pathogen DNA detection. Overview reflects the existing problems in the interpretation of results and information about the efficacy of each method in the patient's examination algorithm.
Key words: laboratory diagnostics, urogenital trichomoniasis.
Drugs of choice
- trichopolum,
- metronidazole,
- ornidazole (tiberal).
Generally active drugs are used simultaneously with local drugs. They use metronidazole (Flagyl), ornidazole (Tiberal), neo-penotran and others.
Pregnant women are treated with metronidazole, excluding the first trimester of pregnancy.
Children are treated with metronidazole.
To treat recurrent trichomoniasis, a vaccine was invented - solcotrichovac.
Treatment with the vaccine must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor! Possible side effects. The use of the drug does not always lead to the desired result.
After taking the drugs, cure criteria are established 7 to 10 days after completion of treatment. To do this, they take smears and, if necessary, do a culture.
General information
Urogenital trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted infectious disease (STI) and is characterized by damage to the human urogenital tract (Wikipedia).
According to WHO, about 250 million people of childbearing age are infected annually with the single-celled parasite Trichomonas vaginalis (trichomoniasis vaginalis). Trichomoniasis occupies a leading place in the structure of all STIs among people who turn to specialists for urological and obstetric-gynecological care. According to epidemiological data in the Russian Federation, despite a slight decrease in the incidence rates of urogenital trichomoniasis among males and females, they continue to remain at a fairly high level - 63.2 cases per 100 thousand population. The disease is registered with equal frequency in people of both sexes and is found everywhere.
The causes of trichomoniasis in women and men are due to intestinal Trichomonas entering the human body. About 50 varieties of Trichomonas are known, of which only 3 species are parasitic in the human population: urogenital, intestinal and oral. Urogenital trichomonas are an independent species that has cultural and morphological differences from oral/intestinal trichomonas. Oral Trichomonas, as is clear from its name, is an inhabitant of the oral cavity (between the gum and neck of the tooth/in gum pockets) and supports the inflammatory process in the oral cavity ( caries , gingivitis , periodontal disease ), and intestinal Trichomonas - in the large intestine. Intestinal Trichomonas, being opportunistic organisms, in the presence of unfavorable factors can transform into pathogenic ones and cause intestinal trichomoniasis, which occurs mainly in the form of enterocolitis and colitis .
Is trichomoniasis dangerous and if so, why is trichomoniasis dangerous? The problems of trichomoniasis lie mainly in the frequently recorded complications that develop after the disease. Urogenital trichomoniasis is dangerous due to the potential danger of sterile marriages, the development of infertility, pregnancy pathologies, difficult childbirth of a newborn, as well as the risk of infant mortality. Considering the lack of real progress in recent years towards reducing the number of patients with trichomoniasis, the fight against this disease is an urgent problem in venereology, gynecology and urology.
Classification
According to the severity of inflammation and the clinical course of trichomoniasis, they are distinguished:
- Fresh trichomoniasis (acute, subacute torpid) - the duration of the disease does not exceed 2 months.
- Chronic trichomoniasis - with an unknown onset of the disease or a duration exceeding 2 months.
- Trichomonas carriage.
Based on the presence of complications, the following types are distinguished:
- Uncomplicated trichomoniasis is the development of an inflammatory process localized in the lower parts of the urogenital system. In women - cystitis , vulvitis , urethritis , vaginitis , cervicitis ; in men - urethritis , cystitis , balanoposthitis and balanitis .
- Complicated trichomoniasis is the development of an inflammatory process localized in the upper parts of the urogenital tract/other genitourinary organs. In women - vestibulitis , salpingitis , paraurethritis ; in men - epididymitis , prostatitis , vesiculitis .