Factors that contribute to the entry of pathogens into the genitourinary system and their reproduction include unprotected sexual contact (vaginal, anal, oral), poor personal hygiene, traumatic injury to the genital organs, immobility of the foreskin (phimosis), sexually transmitted diseases (trichomoniasis, chlamydia, gonorrhea and etc.). In addition, the cause of balanoposthitis can be allergies, obesity, diabetes mellitus and systemic dermatological diseases.
Balanoposthitis in boys can develop as a result of complications of infectious diseases. However, the most common causes of inflammation of the glans and prepuce of the penis in children are considered to be lack of proper hygiene and rubbing of the penis with tight clothing.
Causes of the disease
Balanoposthitis on the penis most often occurs when infected with sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and manifests itself as a disease concomitant with the main infection. For example, this disease occurs when infected:
- fungi of the genus Candida albicans (most often);
- trichomonas;
- streptococci;
- anaerobes (fusobacteria, actinomycetes, clostridia - often in mixed form);
- gram-variable bacteria Gardnerella vaginalis;
- Staphylococcus aureus;
- treponema pallidum;
- herpes viruses.
Many of these infectious agents are normally present in the prepuce in men, but due to a number of predisposing factors they can multiply greatly and cause an inflammatory process.
Balanoposthitis of the penis can also be of a non-infectious nature, for example, associated with skin problems (lichen sclerosus, lichen planus, contact allergic dermatitis, psoriasis), poor hygiene, injuries and irritations.
Development of balanoposthitis
In most cases, balanoposthitis is an infectious disease; there are also allergic and toxic types of balanoposthitis, but these types are much less common.
For the development of this condition, two conditions are necessary - an infectious agent and favorable conditions for its development. Infectious agents are considered to include any opportunistic flora, for example, Escherichia coli, streptococci, staphylococci and enterococci.
Infectious agents can penetrate the skin of the head of the genital organ in the following cases:
- Unprotected sexual intercourse by women who have dysbacteriosis of the vaginal microflora. Oral sex with a partner who has infectious and inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
- Anal intercourse without a condom.
Infectious factors. Quite often, balanoposthitis is an infectious disease. Among the infectious agents, one can distinguish a variety of viruses, for example, HPV, fungi (Candida), viruses, bacteria - staphylococcus, streptococcus, mycoplasma, and others.
Balanitis can manifest itself as a complication of sexually transmitted diseases, such as gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia, primary or secondary syphilis. A viral etiology of balanitis and balanoposthitis is also possible. Thus, the human papillomavirus is often found in the tissues of the foreskin in patients undergoing circumcision.
Skin diseases. Non-infectious causes of the development of balanitis and balanoposthitis include: fixed medicinal erythema, contact dermatitis, psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, lichen planus, lichen sclerosus and Queyra's erythroplasia; many other skin diseases with clinical signs on the glans penis can occur.
Autoimmune factors . Some studies have established a connection between the development of balanitis and autoimmune diseases, for example, vitiligo, alopecia, endocrine gland diseases, diabetes mellitus, pernicious anemia, cicatricial pemphigoid, psoriasis, polymyalgia rheumatica, systemic lupus erythematosus and primary biliary cirrhosis.
Hormonal factor. In some cases, disturbances in the absorption of male sex hormones by tissues can lead to the development of xeratic balanitis.
Genetic factors. There are a number of reasons that suggest the possibility of genetic factors for xeratic balanitis.
All the situations described above can lead to a one-time and severe exacerbation of balanoposthitis. In the absence of repeated infections, exacerbations do not occur, and the primary inflammation goes away on its own within a couple of days.
Risk factors
Risk factors contributing to the occurrence of balanoposthitis in men include:
- general diseases that reduce immunity, HIV;
- promiscuous sexual intercourse;
- diabetes;
- atherosclerosis;
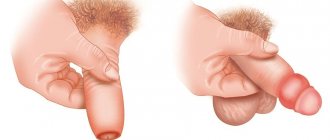
- narrowing of the foreskin (phimosis);
- pathologies associated with urinary retention;
- working conditions in an aggressive environment.
Symptoms also occur when a person is predisposed to allergies, as a result of the use of certain detergents, lubricants, etc.
Symptoms of balanoposthitis
Simple balanoposthitis is manifested by acute inflammation, redness of the skin, discomfort when exposing the head of the penis, swelling and the subsequent appearance of reddish erosions with discharged purulent contents and foul-smelling discharge from the urethra. Subjectively, the patient feels a burning and itching in the area of the head, sometimes pain when trying to move the foreskin.
Further, depending on the nature of the infection and the degree of neglect of the process, there may be options:
- Erosive type - characterized by the appearance of white swollen zones of dead epithelium and the formation of extensive erosions. These symptoms often accompany inguinal lymphadenitis and lymphangitis. Possible consequences include phimosis or paraphimosis (strangulation of the glans penis due to the inability to move the foreskin), in which urgent surgical intervention is indicated.
- Gangrenous type - characterized by the formation of necrotic ulcers with purulent discharge, severe redness and swelling of the penis. The patient, as a rule, has a fever and symptoms of general intoxication appear. With a lightning-fast course (in the case of Fournier's gangrene), death is possible.
Certain types of balanoposthitis, such as gonorrhea and trichomonas, are usually combined with urethritis - inflammation of the urethra.
The herpetic type is characterized by a chronic form - small watery blisters periodically appear on the skin of the head and foreskin, which, after opening, form erosions that subsequently turn into age spots.
What else are associated with spots on the head in men?
Hyperemia, red pimples, itching on the head of the penis are caused by diabetes mellitus, kidney and liver diseases. For people over 30 years of age who have a family history of diabetes, we check their blood for glucose. If necessary, we determine glycated hemoglobin, perform an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, determination of bile acids and blood nitrogen, and a general examination of blood, urine and feces.
Redness and discomfort on the penis occur with increased sensitivity or dry skin. Tight underwear, stay in a hot climate, and prolonged unsanitary conditions lead to the accumulation of sweat and smegma in the fold of the foreskin. Under these conditions, the usual skin flora - staphylococci and streptococci - are activated. Their increased reproduction will cause inflammation. The same thing happens when intestinal bacteria from the anus get on the foreskin.
Diagnosis of balanoposthitis
Balanoposthitis of the penis is usually accurately diagnosed by external signs; it is difficult to confuse it with any other disease. However, to identify the causes of the disease, an examination is carried out:
- clinical and biochemical blood tests (determination of cholesterol and sugar);
- determination of sugar in urine;
- PCR analysis for STIs;
- serological diagnosis of syphilis;
- microscopic examination of scrapings from inflamed areas;
In some cases, a skin biopsy is prescribed to exclude a malignant process.
Treatment of balanoposthitis with drugs
After consultation, examination and identification of causes, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment. The main drugs for balanoposthitis eliminate the infection and fight its manifestations.
If the disease is infectious, antibiotics that are specific to the identified pathogens of this disease are almost always prescribed. The exception is the candida form.
To relieve symptoms associated with inflammation, the doctor prescribes creams and ointments based on antihistamines and corticosteroids.
In case of bacterial infections, a simple and effective remedy is baths of a solution of potassium permanganate, hydrogen peroxide or furatsilin.
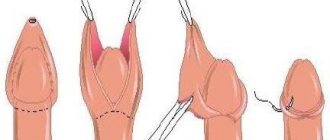
In chronic forms of the disease, circumcision (circumcision) is indicated.
Ointments and creams for balanoposthitis
Various gels, creams and ointments are classified as local therapy. If the inflammation is caused by a bacterial infection, medications containing an antibiotic are used. For fungal infections of the foreskin and head of the penis, ointments with antimycotics are used. Depending on the nature and course of the pathology, combination drugs may be prescribed.
Local treatment of balanoposthitis is aimed at restoring affected tissues, relieving inflammation, as well as eliminating itching, burning and other manifestations of the disease. At the recovery stage, creams with an epithelializing component are used.
The choice of an effective local drug is made by the doctor, taking into account the cause of the pathology and the severity of the symptoms. Self-prescription and use of ointments can aggravate the situation and lead to adverse complications.
Features of balanoposthitis in children
In childhood, the disease can be caused by:
- overzealous hygiene procedures;
- injuries caused by scratching;
- overheating from wearing diapers;
- use of medications.
Allergic reactions to washing powder or food products can also trigger the disease.
Typical childhood signs of the disease include:
- crying when urinating;
- refusal to sit on the potty;
- lack of urination when complaining that the child wants to go to the toilet.
The therapy is carried out by a pediatric urologist, who prescribes medications based on test results. Warm baths are recommended for home remedies, including with decoctions of medicinal herbs, rinsing with a solution of furatsilin and potassium permanganate.
Antibiotics for balanoposthitis
If inflammation is caused by bacteria, antibacterial drugs are prescribed without fail. Various microorganisms, including pathogenic ones, live on the epithelium of the genital organ and in the vagina. When local immunity is weakened, viruses and bacteria begin to multiply and spread. According to statistics, it is opportunistic agents (anaerobic microorganisms, protozoa, bacteria, etc.) that more often lead to the formation of balanoposthitis.
The use of antibiotics is not necessary in cases where inflammation is caused by viruses, allergens, fungi, tumors and autoimmune processes. If balanoposthitis is accompanied by the formation of cracks, ulcers or erosions, the doctor may prescribe an antibacterial agent. This will avoid secondary infection and the development of inflammation when pathogenic microorganisms enter through microdamages on the mucosa.
From the glans and prepuce of the penis, bacteria can penetrate the kidneys, bladder and urethra. If pyelonephritis, urethritis or cystitis is diagnosed against the background of balanoposthitis, antibiotics are also prescribed. To select the most effective drug, an antibiogram is performed before starting therapy.
List of used literature
- Yakobzon, L. Ya. Balanitis and balanoposthitis // Encyclopedic Dictionary of Brockhaus and Efron: in 86 volumes (82 volumes and 4 additional). - St. Petersburg, 1890-1907.
- Edwards S. Balanitis and balanoposthitis: a review // Genitour. Med. - 1996; 72 (3): 155-159.
- Zabirov K.I., Derevyanko I.I., Marchuk N.V. Modern aspects of the problem of balanoposthitis // Consilium medicum. - 2004; 6 (3): 215-218.
- Chaine B., Janier M. Balanitis: diagnosis and treatment // Ann. Urol. - 2006; 40 (2): 126-138.
- Derevyanko I.I., Zabirov K.I., Marchuk N.V. Modern aspects of the problem of balanoposthitis // Handbook of a polyclinic doctor. - 2006; 5:57-59.
Frequently asked questions about balanoposthitis
How to treat candidal balanoposthitis in men?
Candidiasis balanoposthitis in men occurs during unprotected sexual intercourse. It manifests itself as burning and pain in the area of the glans penis and the formation of an easily removable white coating that forms clots like cottage cheese. For treatment, Fluconazole (or its analogues: Diflucan, Flucostat) is used, 200–400 mg once a day. The duration of taking the tablets is determined by the doctor depending on the severity and course of the disease. Conventional antibiotics cannot be used for balanoposthitis caused by fungi, as they can provoke even greater infection.
How long to treat balanoposthitis?
Balanoposthitis should be treated until symptoms disappear completely in accordance with your doctor's recommendations. The primary disease usually goes away within a week, relapses are more difficult to cure and often become chronic. If you have been prescribed antibiotics, take them to the end - this is the only way to defeat the course of the infection and prevent it from becoming chronic.
What is chronic balanoposthitis?
Chronic balanoposthitis is associated with neglect of specialist recommendations and incomplete treatment. Relapses that occur are becoming increasingly difficult to treat. Some patients note that symptoms go away only when taking medications, and then immediately appear again. The way out of this situation is circumcision of the foreskin, but first you need to conduct a thorough analysis of the causes of the disease. Modern methods of laser exposure in combination with the use of Lamisil spray can save patients from possible relapses in more than 90% of cases.
Treatment results for balanoposthitis
If you contact a specialist in a timely manner and prescribe etiological treatment, recovery occurs fairly quickly. The recovery time will depend on the form of inflammation. Treatment of allergic balanoposthitis takes several days. In this case, the inflammation may go away on its own after eliminating the allergen. The recovery stage will be longer if the allergic reaction provokes the appearance of small defects on the mucosa and epithelium. The correct choice of antibiotic for bacterial balanoposthitis will allow you to get rid of the disease in 8-14 days. It takes several weeks to treat inflammation caused by a sexually transmitted infection. The viral form of the pathology takes longer to treat than others (several months). Deep injuries (ulcers, erosions, gangrene) require inpatient treatment. As a rule, surgery is performed, followed by a long recovery (2-3 months).
In order for the treatment to be as safe and effective as possible, you should undergo regular examinations with a doctor and contact a specialist when you detect the first signs of balanoposthitis. After a series of examinations, the doctor will determine the cause of the inflammation, determine the nature of the pathogen and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Attention!
This article is posted for informational purposes only and under no circumstances constitutes scientific material or medical advice and should not serve as a substitute for an in-person consultation with a professional physician.
For diagnostics, diagnosis and treatment, contact qualified doctors! Number of reads: 1461 Date of publication: 08/23/2018
Urologists - search service and appointment with urologists in Moscow