Services table
| Service name | Price |
| Promotion! Initial consultation with a fertility specialist and ultrasound | 0 rub. |
| Repeated consultation with a fertility specialist | 1,900 rub. |
| Initial consultation with a reproductologist, Ph.D. Osina E.A. | 10,000 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the mammary glands | 2,200 rub. |
| Program "Women's Health after 40" | RUB 31,770 |
The pituitary gland is a human endocrine gland that plays a very important role in his life. It is located under the cerebral cortex (in its temporal part) and is protected by the saddle-shaped cranial bones. The importance of this organ cannot be overestimated. Thus, it is indispensable for the normal functioning of the entire organism, being responsible for many processes occurring in it.
Location of the gland
The organ is localized in the lower part of the brain and belongs to its processes. The pituitary gland is located in the center of the skull, above it is the hypothalamus. The appendage is located in the recess of the sphenoid bone, in most cases it completely fills it, sometimes only half of the volume. With hypertrophic changes, the organ may extend beyond the bone pocket.
The size of the iron is small:
- in height – 3-8 mm;
- width – 10-16 mm;
- weight – does not exceed 1 g.
On the posterior, inferior and anterior sides, the pituitary gland is protected by bone structures and is covered on top by a diaphragm with an opening. A leg passes through it, connecting the gland to the hypothalamus.
How to prepare for an MRI of the pituitary gland
The magnetic resonance imaging procedure does not require special preparation. The patient needs to warn the doctor about the presence of metal prostheses, implants, implanted electrical devices and pacemakers. Before the examination, remove outer clothing and accessories.
To increase the information content of the method, MRI is performed with intravenous administration of a contrast agent. In this case, you need to make sure that the solution used is tolerable. Patients prone to allergic reactions should warn their doctor.
Before the procedure, the doctor conducts a conversation, explains how the examination is carried out, how long it takes. Reminds you to remain still during scanning. Following the specialist’s recommendations affects the quality of the image and the diagnosis.
Structural and physiological features
The organ has an oval shape; its structure has two uneven lobes: posterior and anterior. There is also a middle, intercalary part, in which beta-melanocyte-stimulating hormone is produced.
Experts distinguish two main lobes of the organ:
- Adenohypophysis
It is the anterior lobe of the inferior medullary appendage and includes three-quarters of the total volume of the pituitary gland. The structure of the organ contains glandular cells responsible for the production of tropic hormonal substances. Hormones are designed to control the activity of endocrine glands located in the periphery.
The anterior lobe is additionally equipped with zero cells that do not participate in the production of hormonal substances. Research has not been able to fully determine their function.
- Neurohypophysis
It is the posterior part of the pituitary gland and is not intended to produce hormones. Its functionality is based on the accumulation of neuropeptides synthesized by the hypothalamus. Vasopressin and oxytocin are activated in the organ; after completion of the process, the elements are redirected into the bloodstream.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of pituitary disease consists of the following steps:
- contacting a specialist in the field of endocrinology or neurosurgery,
- familiarization with the patient's medical history,
- conducting a skull examination - necessary to detect neoplasms,
- MRI, CT - thanks to these technologies, doctors are able to determine the exact dimensions and location of the tumor, which is extremely important before surgery,
- checking the blood for the presence of pituitary hormones.
It is worth noting that a medical specialist has the right to prescribe secondary research.
Characteristics of hormones
The main secretory function of the pituitary gland occurs in the anterior part of the gland - the adenohypophysis. The department is engaged in the production of hormonal substances used by the body to influence organs or tissues and regulate their functioning.
Features of the hormones of the anterior part of the gland are represented by the following characteristics:
- Growth hormone is responsible for enhancing protein synthesis, glucose formation and lipid breakdown. A somatotropic substance is used to regulate physical development, it affects body shape, stimulates muscle development, and reduces the percentage of fatty tissue.
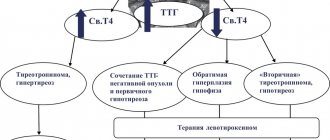
- Control of the growth of the thyroid gland is given to thyroid-stimulating hormone. The element is used for the secretion of thyroid elements: T4, T3.
- Gonadotropic hormone is responsible for the normal functionality of the ovaries in women and testicles in men. It is necessary for the normal course of ovulation, the production of male germ cells; with its help, estrogen, testosterone, and progesterone are synthesized.
- Normalization of adrenal functions, production of cortisol and other active components lies on adrenocorticotropic hormone.
- Prolactin or lactotropic hormone is responsible for the production of milk during lactation.
With the help of the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland, other elements appear in the body, represented by endorphins, enkephalins, and beta-melanocyte-stimulating substances. The latter are used to change the shade of the skin under the influence of ultraviolet rays.
The posterior lobe of the inferior appendage of the brain produces its own components, represented by:
- Oxytocin - is responsible for the contraction of the muscle tissue of the uterus during labor, the muscles in the area of the mammary gland ducts. In the latter case, milk is released and moves to the nipple area. The element is believed to instill trust, calm and a sense of affection in women and men.
- Vasopressin - an ingredient used to control thirst, it helps the body track the amount of urine excreted through the kidneys. The element stabilizes water balance at the cellular level.
Both of these hormones are produced by the hypothalamus. When they enter the neurohypophysis, they change, and after release they are redirected to a specific target organ.
The most common diseases of the pituitary gland
pituitary gland disease
Neoplasms
As a rule, dysfunction of the pituitary gland is associated with adenomas. Such tumors may be hormonally active and produce appropriate hormones. The symptoms are completely different. This depends on the hormones that produce the tumor.
Gigantism
This pathology of the pituitary gland spreads when children and young people secrete a lot of somatotropin. Within this age category, bone growth gradually continues, so they continue to increase. Bone growth is accompanied by muscle growth. However, for normal functioning it is necessary to improve blood circulation, which is not possible. The result is a violation of the cardiovascular system and heart rhythm.
Acromegaly
Pathology usually appears in people aged 30–50 years. At this age, we are not talking about bone growth. For this reason, the bone increases in width, which leads to damage and increased body weight. Facial features become rougher. The skin becomes callous and darkened, not to mention other factors. Heart problems may develop as a result of an increase in the size of the heart.
Stunting
Appears with growth hormone deficiency in early childhood. In female representatives with this diagnosis, the height is no more than 120 cm, and in men - no more than 130 cm.
Itsenko-Cushing's disease
A complete set of symptoms that were provoked by the synthesis of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) by the pituitary gland. The main indicators of this pathology are swelling of the upper body, swollen face, thin skin, muscle loss, bruising and stretch marks.
Sheehan syndrome
An unexpected decrease in the function of adenohypophysis hormones in girls after the birth of a child. Tissue death occurs due to difficult labor with hemorrhages, which leads to a decrease in blood volume. After giving birth, girls do not have milk to feed the baby; hair loss in the armpits, a rapid drop in blood pressure, nausea and a gag reflex can be observed. In this case, you definitely need to contact specialists.
Diabetes insipidus
The cause of pituitary gland disease can be, among other things, neoplasms of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus, impaired blood circulation, and damage to the skull.
This disease is reflected in dry mouth, frequent urination, etc. If the neoplasm is large in size, but is not active, then the following symptoms may appear on the first lines: pain, dry mouth.
signs of pituitary gland
Decoding brain MRI data
Pituitary gland dysfunction is associated with pathological processes, which result in structural changes in gland tissue. Magnetic resonance imaging will help differentiate the disease, determine the nature of the lesion and its location. The method allows you to visualize the slightest deviations from the norm; thanks to MRI, it is possible to diagnose pituitary gland diseases in the early stages.
Empty sella syndrome is characterized by a thinning gland that does not fill the pituitary fossa. On a sagittal section, the organ has a crescent shape and occupies the lower part of the bone pocket.
Empty sella turcica on MRI
MRI of the pituitary gland also reveals tumors and cystic formations, allowing timely treatment of the pathology. An adenoma on MRI images is defined as an area with a changed structure, most often located in the anterior lobe. The following factors indirectly indicate the presence of a tumor:
- asymmetry of the gland, change in shape and size;
- violation of boundaries, deformation of the bone pocket;
- displacement of the pituitary stalk from the central axis.
Depending on the size, neoplasms are divided into:
- picoadenomas (up to 3 mm);
- microadenomas (3-10 mm);
- macroadenomas (10-30 mm);
- giant adenomas (over 30 mm).
MRI can detect small tumors that develop asymptomatically. Timely diagnosis of microadenoma is possible during a native study, but if the tumor is small, as well as if malignancy is suspected, the administration of contrast is necessary.
The nature of the blood supply to a malignant formation has significant differences from a similar benign process. A solution of gadolinium salts illuminates the vasculature, revealing the adenocarcinoma's own system. In the photographs, the tumor has a heterogeneous glandular structure, its boundaries are blurred.
Depending on the location, endosellar and endoextrasellar tumors are distinguished. The former do not extend beyond the sella turcica, the latter grow beyond the boundaries of the bone pocket.
Pituitary cysts on MRI appear as dark spots (on T1-weighted images) with clear boundaries. They need to be differentiated from macroadenomas, which are round formations with a compacted membrane.
Insufficient production of somatotropin is characterized by hypoplasia of the adenohypophysis and infundibulum, and an atypical location of the neurohypophysis. These signs help to identify the cause of hormonal disorders and correct the functioning of the gland with the help of medications, preventing possible disturbances in the growth and development of the body.
The MRI method helps to differentiate the pituitary gland lesions from pathological processes occurring in the surrounding tissues and having a similar clinical picture.
Causes of dysfunction
Pituitary adenoma is a benign tumor, the main reason why the gland begins to produce large amounts of the hormone.
A decrease in secretion can be caused by a greater number of factors:
- irradiation;
- cerebral hemorrhages;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- surgical intervention;
- congenital pathologies of the pituitary gland;
- brain tumors compressing the gland;
- any form of cerebrovascular accident;
- inflammatory diseases (encephalitis, meningitis).