Vaginal discharge in women
The opening of the urethra is located 1–2 centimeters above the vagina, so if hygiene is not observed, natural secretions can get into the urine, making it cloudy.
If a woman has vaginitis, or inflammation of the vagina, there will be more Vaginal discharge / Mayo Clinic discharge and an increased likelihood that it will end up in the urine.
What to do
This is usually noticed during a urine test. Therefore, the doctor who ordered the test may request that it be repeated, subject to the following Urinalysis/Mayo Clinic guidelines:
- Wash your genitals from front to back.
- Urinate a little in the toilet.
- Collect a medium portion of urine in a container.
- Finish peeing in the toilet.
- Deliver the sample to the laboratory within 60 minutes.
General rules for taking the test
Improper urine collection often leads to distorted results and is often the cause of cloudy urine. Because of this, a woman has to retake the test, wasting her time and energy. To prevent this from happening, you need to know the general rules for taking a urine test:
- before you start collecting urine, you need to wash yourself with clean warm water without using soap;
- the container for collecting material must be sterile;
- collect an average portion of urine. To do this, you need to flush the first stream into the toilet, then fill the jar and complete the urination process;
- before collecting urine, it is not recommended to consume foods that can change the color of urine, and you should also avoid diuretics;
- The jar must be taken for analysis within 2 hours after collecting the material.
Urine must be collected correctly. If it is not possible to take the jar right away, then it can be placed in the refrigerator, but for no more than a day. Based on the results of the study, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment.
Sperm in men
Sometimes after ejaculation, part of the sperm returns through the urethra to the bladder. This is called retrograde ejaculation / US National Library of Medicine ejaculation, and it results in cloudy urine. Pathology develops with diabetes, prostatitis, after prostate surgery or due to taking medications for high blood pressure.
What to do
You may need to change the drug or stop taking it Retrograde ejaculation / US National Library of Medicine if this causes retrograde ejaculation. And if you have diabetes or after surgery, you will need medications to normalize sperm excretion.
How to fix the problem
Before prescribing treatment, a thorough diagnosis is carried out. The first step is to submit urine for examination. There are several urine tests, the specific diagnostic method is prescribed by the doctor. In addition, a blood test is prescribed, and if necessary, the doctor refers to various instrumental diagnostic methods. Treatment for the problem will depend on the cause of the cloudy urine. If the cause is dehydration, dietary habits, or improper care of the genitals, then the drinking regime and diet are corrected, and personal hygiene must also be observed more carefully.
Treatment for the problem will depend on the cause of the cloudy urine.
If the cause lies in a pathological process, then drug therapy is prescribed. And in some cases, for example, with advanced urolithiasis, surgical intervention is necessary. If the problem is infectious, then antibiotics are prescribed. To eliminate cloudy urination, doctors can prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs, steroid drugs, uroseptics and diuretics, as well as other auxiliary medications. Since many gynecological diseases occur against the background of weakened immunity, vitamin-mineral complexes and immunostimulants are prescribed.
In addition to drug therapy, lifestyle is reviewed and, if necessary, a diet is selected. As soon as you notice cloudy urine or a change in its consistency, color, smell, and also begin to observe the presence of other symptoms, do not self-medicate, but consult a doctor. Timely diagnosis of the problem will allow you to avoid serious consequences.
Side effect of drugs
Cloudy urine may occur due to the use of drugs that are used to treat Solifenacin / US National Library of Medicine overactive bladder or Sunitinib / US National Library of Medicine kidney or digestive tract cancer. This is a side effect of medications.
What to do
If undesirable effects occur while using the drugs, you should immediately inform Sunitinib / US National Library of Medicine to the doctor who prescribed them. The medications may need to be changed.
Analysis of urine clarity: deviations
The following sediment indicators are analyzed:
- Urates - the biomaterial is heated, after which visual control of the color is performed. Clarification of urine and a decrease in turbidity are a sign of the presence of urates;
- Carbonates - acetic acid is mixed into the urine. In the presence of carbonates, the urine foams and becomes lighter in color;
- Phosphates - their presence is indicated by cloudiness of urine when heated;
- Oxalic acid salts, uric acid - acetic acid is added to the urine, after which the liquid normally clarifies. Lack of reaction is a sign of the presence of salts and uric acid;
- Epithelial cells - determined microscopically. The presence of cells indicates latent kidney inflammation;
- Red blood cells, leukocytes and cylinders are also determined using a microscope. Their presence in cloudy urine is a sign of urolithiasis, oncology, inflammatory or infectious processes of the genitourinary system;
- Purulent impurities - they can be detected by exclusion: urine with pus does not lighten when heated and the addition of various reagents.
Under what conditions and/or diseases is cloudiness of urine observed?
- Violation of water-salt balance as a result of dehydration;
- Pyelonephritis;
- Glomerulonephritis;
- Urolithiasis disease;
- Cystitis;
- Venereal diseases;
- Toxicosis in pregnant women (cloudy urine - the result of dehydration due to vomiting);
- Increased load on the kidneys in late pregnant women;
- Dehydration in infants.
Urinary tract infections
The bacteria can cause Urinary tract infection (UTI) / Mayo Clinic inflammation of the kidneys, bladder, or urethra, leading to cloudy urine. Other symptoms will also appear:
- strong desire to urinate;
- frequent urination in small portions;
- burning and pain in the urethra;
- strong-smelling urine
- blood or pus in the urine.
Depending on the type of disease, fever, pain in the abdomen, above the pubis, or in the lower back may also occur.
What to do
You need to see a urologist. Your doctor will prescribe a Urinary tract infection (UTI) / Mayo Clinic appropriate antibiotic to fight the infection. And to reduce pain, he will recommend over-the-counter analgesics.
Cloudy urine due to sexually transmitted diseases
Diseases are often transmitted through sex.
This is a specific group of infections.
These include more than a dozen pathogens of various natures:
- viral;
- mycotic;
- parasitic;
- bacteriological
According to statistics, STIs can be detected in every tenth person.
This indicates a high prevalence.
The number of cases includes people from adolescence to retirement age.
Infections provoke the occurrence of inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs.
They can lead to serious problems such as infertility.
STIs have the following pathogens:
- mycoplasma;
- ureaplasma;
- Trichomonas;
- candida;
- gardnerella;
- chlamydia;
- herpes virus;
- human papillomavirus;
- molluscum contagiosum.
Characterized by high sensitivity to external environmental conditions.
Successful infection requires contact between a clinically healthy person and an infected person.
It's not just about intimacy.
For infection, everyday contact is enough, for example, with viral infections.
Violation of the integrity of the skin and mucous membranes serves as a gateway for the penetration of microflora.
In this case, the risk of infection increases during oral and anal sex.
This also happens when using general products for personal intimate hygiene.
Most infectious agents can penetrate the placental barrier.
In utero they infect the fetus.
This can cause significant harm to its physiological growth and development.
The sad consequences of intrauterine infection sometimes appear even years after the birth of the child.
This can be manifested by disturbances in the functioning of the heart muscle, liver and kidneys.
Important!
It is necessary to undergo regular preventative testing to detect infection.
STI transmission factors:
- unprotected sexual intercourse;
- close contacts in everyday life;
- neglect of the rules for sterilization of medical instruments;
- transfusion of blood and its components;
- organ and tissue transplantation.
Each infection has certain symptoms.
But the general picture of clinical manifestations is very similar for all infections.
These symptoms include:
- cloudy urine;
- various types of discharge from the urethra;
- itching and burning sensation;
- pain during urination or sexual intercourse;
- discomfort and nagging pain in the lower abdomen.
Many sexually transmitted diseases are characterized by an asymptomatic course.
When the first signs are detected, you should urgently consult a specialist.
This will prevent the disease from progressing.
Remember!
If you find any suspicious signs, be sure to notify your sexual partner!
For diagnosis, the specialist collects a complete medical history from the patient.
Women undergo a full gynecological examination, and men visit a urologist.
Experts evaluate the severity of manifestations characteristic of the presence of an STI.
Laboratory diagnostic methods:
- a smear from the cervix or urethra;
- bacteriological culture and determination of sensitivity to antimicrobial drugs;
- identification of fragments of DNA chains of pathogens using the polymerase chain reaction method.
Non-infectious cystitis
Sometimes inflammation of the bladder is not associated with an infection, but the urine also becomes cloudy and other symptoms appear:
- burning and itching when urinating;
- frequent urge to go to the toilet, including at night;
- reducing Interstitial cystitis / Mayo Clinic urine output;
- incontinence;
- change in the smell and color of urine.
This is how non-infectious cystitis manifests itself, which sometimes occurs after severe bladder infections, radiation and chemotherapy, as well as due to the use of certain hygiene products and spermicidal contraceptives.
What to do
You need to see a urologist. The causes of cloudy urine cannot always be eliminated, but your doctor will prescribe Cystitis - noninfectious / US National Library of Medicine medications to relieve pain or medications to relax the bladder. You should also avoid spicy foods, alcohol, citrus fruits and caffeine - all of this can irritate the organs of the excretory system.
What does a change in urine color mean?
09.09.2021
Everyone knows that normal human urine is yellow, but very often we wonder what it means when the liquid is a completely different color.
Changes in color, cloudiness, and blood in the urine can cause panic and anxiety because it makes us think that something wrong is happening in the body.
If you're wondering what you can learn just by looking at your urine , read on.
What does normal urine look like??
Under normal conditions, urine can range from translucent yellow to amber and is caused by the pigment urochrome.
Urine is a liquid that is excreted from the body and is a product of cellular metabolism.
The color and amount of urine can be affected by certain foods and drinks, as well as many medical conditions.
If your urine becomes darker, it is usually a sign that you are not getting enough fluids . But this is no cause for alarm.
All you need to do is drink more fluids, preferably water.
The lighter and more transparent the urine , the healthier our body. Light yellow color indicates that our body is properly
hydrated, and this is typical for those who drink water regularly. However, be careful - urine may be a sign
waterlogging or water intoxication. And increased production of clean urine without sufficient water intake may be a sign of diabetes .
Some people often wonder why their urine becomes clear after drinking too much alcohol. There is a simple explanation for this -
Alcohol is a diuretic, meaning it increases the rate of urine . Because drinking alcohol makes you frequent
toilet, your body extracts water from other organs. The problem is that along with the fluid, you throw out important electrolytes from the body.
This is why excessive amounts of alcohol cause poor health or severe headaches.
Abnormalities in urine color
Sometimes the urine comes out a much lighter yellow to amber color. Here are the colors of urine and what they mean:
Green or blue
It has to do with what we ingested. Some foods, drinks, and medications can turn urine these colors, especially if they contain
blue dye. Asparagus also gives your urine a greenish color and also changes its odor.
Red or pink
Some foods that are red in color can cause this change in urine . Laxatives and some medications may also be
cause of red urine . In some cases, however, it is not coloring but blood in the urine . This may be a sign of a disease such as increased
prostate, bladder or even kidney cancer .
Cloudy urine
This may be a sign of urinary tract infection or kidney . In men, this may be due to sperm into the urine .
Orange
Blueberries, beets, rhubarb and some medications with dyes can cause an orange coloration. Sometimes jaundice and dehydration also stain
urine orange.
Foamy urine
Foaming does not affect the color of urine , but it does give it a foamy appearance. Too much foam in the urine is usually a sign of use
too much protein.
When to Seek Medical Help
Often, sharply colored urine is due to the fact that we have eaten or drunk something. Note any color changes and record when
and how often they occur. If we can rule out food or medications as possible factors for the change in urine , you should call your doctor .
Other symptoms that may require seeking medical attention: frequent urination , painful urination , difficulty urinating ,
passing small amounts of urine with normal hydration, waking up at night with an urge to urinate , passing larger amounts
urine than usual.
Published in Articles without category Premium Clinic
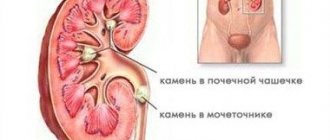
Stones in the kidneys
Often a person does not even know about them: there are no symptoms. But the larger the stone, the more signs appear. These could be Kidney Stones/National Kidney Foundation:
- severe bilateral lower back pain;
- prolonged abdominal pain without clear localization;
- bloody urine;
- nausea and vomiting;
- fever, chills;
- cloudy urine with an unpleasant odor.
What to do
It all depends on the symptoms, the size of the stones, their composition, density and shape. In some cases, doctors will prescribe Kidney Stones/National Kidney Foundation medications to change the acidity of the urine to dissolve the stones. If they are large and block the ureter, then surgery is performed. Sometimes you can do without it and crush the formations using shock wave lithotripsy. During this procedure, ultrasonic waves are sent to the kidneys, which crush the stones. Their fragments are then excreted in urine.
Cloudy urine due to nephrolithiasis
Urolithiasis is one of the most commonly diagnosed pathologies of the urinary tract.
According to statistics, the disease is most often registered in people aged 30 to 55 years.
Reasons for the development of nephrolithiasis:
- disturbance of phosphorus and calcium metabolism;
- increase in serum Ca concentration;
- disorders of metabolism and functions of the digestive system;
- vitamin deficiency A, B and D;
- malformations of the pelvic organs;
- pathological changes in the urodynamic process.
Concretions are found of organic and inorganic origin.
Large, inactive stones cause less damage to kidney health than small, mobile stones.
Kidney stones are very often complicated by pyelonephritis.
Stagnation of infected urine provokes exacerbation of pyelonephritis.
Complications such as carbuncle, kidney abscess and even sepsis may develop.
In the case of nephrolithiasis, cloudy urine indicates restoration of ureteral patency.
Typical manifestations of nephrolithiasis:
- presence of blood in the urine;
- pain in the lumbar region;
- discharge of stones and salts;
- urination disorder;
- renal colic.
The clinical picture is closely related to the size and location of the stones.
It depends on concomitant diseases, congenital anomalies and defects.
Diagnosis of urolithiasis:
- collecting and studying anamnesis;
- general urine analysis with sediment microscopy;
- Ultrasound of the urinary system;
- X-ray or CT scan of the urinary tract.
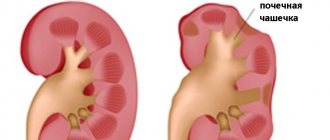
Glomerulonephritis
This is a disease in which Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis / US National Library of Medicine glomeruli, small plexuses of blood vessels that filter the blood, become inflamed. Usually the disease is asymptomatic, but in severe forms or in advanced cases, the urine becomes dark, cloudy, its volume is significantly reduced, and blood may appear. Swelling also occurs in different parts of the body, attentiveness decreases, and blood pressure increases.
What to do
The doctor will prescribe Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis / US National Library of Medicine a special diet, diuretics, immunosuppressants, and medications to lower blood pressure. Dialysis or a kidney transplant will be needed if the organ stops performing its function.
What to do and how to treat?
If cloudy urine is the result of an infectious bacterial disease, first of all a course of antibacterial therapy is prescribed, with the help of which it will be possible to destroy the pathogen and stop the inflammation. Antibiotics such as Monural or Nitrofurantoin are used. For urolithiasis, conservative treatment is prescribed, in which the medications “Canephron”, “Enatin” or “Olimethin” are prescribed. If such therapy does not produce results, the stones are crushed using a laser. When cloudy urine is caused by non-pathological factors, the doctor will advise you to improve your diet, normalize your drinking regime, get rid of bad habits, and lead a healthy lifestyle.
prourinu.ru
Papillary renal necrosis
With this disease, the papillae in the kidneys die, through which urine enters the calyces and then into the ureters. Necrosis can develop for various reasons. For example Renal papillary necrosis / US National Library of Medicine:
- excessive use of painkillers;
- diabetes;
- kidney infection (pyelonephritis);
- rejection of a transplanted kidney;
- sickle cell anemia;
- blockage of the urinary tract.
With necrosis, pain appears in the side or back, body temperature rises, urine becomes cloudy, bloody or dark, and pieces of tissue can be seen in it. Sometimes it hurts to go to the toilet, the urge becomes frequent, and urination becomes difficult. Sometimes incontinence occurs.
What to do
Renal papillary necrosis / US National Library of Medicine can cause kidney failure due to papillary necrosis, so you need to see a doctor as soon as possible. He will prescribe treatment depending on the cause of the disease. In severe cases, dialysis or a kidney transplant will be required.
Leukocytes are the main source of sediment in the urine
Leukocyturia indicates an increased number of leukocytes in a person’s urine. The reasons for the proliferation of these cells lie in common diseases:
- pyelonephritis, acute or chronic;
- glomerulonephritis;
- cystitis;
- stones in the ureter;
- urethritis or prostatitis;
- nephritis.
More than 70% of all types of leukocytes belong to neutrophils, which can change in the direction of increasing or decreasing their number. Most often, there is an increase in the total number of leukocytes due to neutrophils; such a deviation in urine analysis is called neutrophilia.
Neutrophilia can be observed in the following pathologies and diseases:
- infections and inflammatory processes;
- postoperative period;
- diabetes;
- physical and stressful activities;
- tumors of various organs;
- myocardial infarction;
- postpartum period.
Acute nephritic syndrome
This is the name for a group of symptoms that are the same for any kidney pathology: cloudy or bloody urine, swelling of the face and limbs, high blood pressure, decreased urine output and general malaise. These signs occur Acute nephritic syndrome / US National Library of Medicine due to various diseases that damage the kidneys. Among these ailments:
- Hemolytic uremic syndrome is a condition in which red blood cells are destroyed due to an infection of the digestive tract.
- Henoch-Schönlein purpura is a disease of the immune system in which purple spots appear on the skin and damage to the vessels of the intestines and kidneys.
- IgA nephropathy is a pathology in which immunoglobulin proteins accumulate.
- Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis is an inflammation of the kidneys that occurs after a sore throat or skin infection.
- Abdominal abscesses.
- Goodpasture syndrome is a disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the kidneys.
- Hepatitis B or C.
- Endocarditis is inflammation of the inner lining of the heart.
- Lupus nephritis. Occurs in the kidneys against the background of an autoimmune disease - systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Vasculitis, or inflammation of blood vessels.
- Viral infections: measles, mononucleosis, mumps. They can cause an abnormal immune response.
What to do
The main goal of therapy for acute nephritic syndrome is to support the body, reduce symptoms and prevent the person from dying. To improve kidney health, doctors prescribe Acute nephritic syndrome / US National Library of Medicine a diet low in salt, potassium, and fluid restriction. Medicines for blood pressure and to reduce inflammation are also prescribed. In some cases, dialysis will be needed.
Treatment approaches
To treat problems that cause cloudy urine, you need to use medications that act on the cause of this change in the tests. Let's consider the directions of therapy according to the main etiological factors:
1. Bacterial inflammation (cystitis, pyelonephritis) requires the prescription of antibiotics, most often from the group of fluoroquinolones, since they penetrate well into the kidney tissue and cover the main spectrum of pathogens. In a mild form, you can use herbal antiseptics, for example, the drug Monural, which is also suitable for pregnant women. After completing the course, other herbal preparations are prescribed: Canephron, Phytolysin, Urolesan and others. The course of treatment ranges from 1 to 3-6 months. Pharmacies produce special herbal mixtures for oral administration and prevention of kidney problems: the herbs have anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic effects. As part of treatment, diuretics may be prescribed.
2. Urolithiasis usually does not require medication if the stones are not bothering you, since most of them are almost impossible to dissolve, despite popular belief. They also take herbal teas to improve kidney condition. Sometimes removal of stones using extracorporeal lithotripsy is indicated, but this is a surgical intervention.
3. Glomerulonephritis after streptococcus usually requires the administration of cytostatics and steroids to suppress the inflammatory response in the kidneys. Diuretics (Furosemide, Torasemide) and detoxification drugs (Reamberin) are actively used. To improve blood supply to the kidneys, pentoxifylline is used in courses.
4. Kidney damage in autoimmune diseases is treated with basic therapy: hormones, cytostatics or bioengineered drugs. The latter are indicated if there is no effect or it is impossible to use the first two groups.
5. Gout with kidney damage is treated with allopurinol and anti-inflammatory drugs in severe attacks. But it is worth remembering that the drugs themselves can be toxic to the kidney.
6. To treat cancer, including the circulatory system, different approaches are used: chemotherapy, radiation, surgical removal. To support hematopoiesis, blood and its components are transfused.
7. In the terminal state of the renal system, patients are indicated for hemodialysis when glomerular filtration rates are less than 29 ml per minute, which corresponds to the fifth stage of renal failure.
The general principles of treatment for urinary and urinary disorders include:
- limitation of nephrotoxic drugs, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- use of diuretics;
- adequate drinking regime;
- monitoring blood electrolytes and replenishing them if necessary;
- use of detoxification medications (Reamberin and others);
- improvement of renal rheology (Pentoxifylline);
- keeping the body warm, avoiding hypothermia and drafts.
Risk factors
The risk of kidney complications after Covid is higher in patients with the following conditions:
- renal failure;
- glomerulonephritis;
- pyelonephritis;
- urolithiasis disease;
- strictures;
- cysts, tumors.
It is especially important for such patients to undergo timely diagnosis, even when there are no signs of abnormalities.