gastritis
bloating
diarrhea
sour taste in mouth
Helicobacter pylori
What are the consequences of changes in stomach acidity?
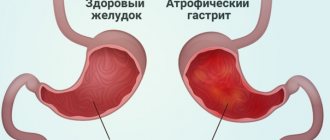
The main danger of increasing the secretory function of the stomach is the development of an inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of the organ, followed by its damage and the development of structural defects. A change in the pH of the gastric environment is always accompanied by clinical symptoms, the severity of which depends on the severity of the inflammatory process and the nature of the structural and functional disorders.
general information
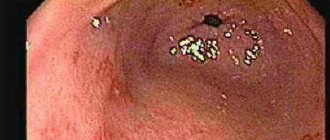
In 80% of cases, the cause of the development of the inflammatory process with high acidity of the stomach is the microorganism Helicobacter pylori, which disrupts the natural protective properties of the stomach and leads to damage to the epithelium of the organ. Gastritis with high acidity can develop in people regardless of age, including children.
Other factors predisposing to the development of this condition include:
- Regular exposure to stress on the body.
- Poor nutrition, predominance of fried and fatty foods in the diet, as well as deep-fried dishes.
- Abuse of so-called snacks.
- Long-term or uncontrolled use of drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Frequently eating food that is too hot or too cold. In addition, people with thyroid diseases, diabetes mellitus and gout have a high predisposition to the development of hyperacid gastritis.
Why is high acidity dangerous?
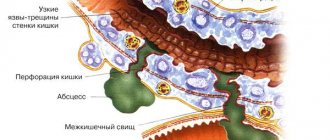
Gastric juice contains hydrochloric acid, which is necessary to break down food components. To prevent the acidic environment from damaging the walls of the stomach, protective mucus is produced. With increased acidity of the stomach, destruction of the mucous protective layer is observed, followed by the formation of an inflammatory process, the formation of erosions and ulcers.
Clinical symptoms
Inflammatory damage to the organ with increased secretion of gastric juice often worsens during the off-season, in the autumn or spring months. Symptoms of high stomach acidity include:
- Drawing or cramping pain in the epigastric region, which often intensifies after eating. In the acute course of the inflammatory process, the pain may be accompanied by vomiting, which brings temporary relief.
- Heartburn, which is caused by acidic stomach contents refluxing into the esophagus.
- Belching sour.
- Bad breath.
- Stool disorders such as constipation or diarrhea.
Other symptoms of increased stomach acidity during gastritis include weakness, dizziness, increased sweating, excessive gas formation in the intestines (flatulence), increased salivation, increased or decreased appetite, and the appearance of a white or gray coating on the surface of the tongue. Reduced stomach acidity is accompanied by symptoms such as decreased appetite, a feeling of heaviness in the epigastrium, and rotten belching.
2. Reasons
There are so many possible reasons for a persistent increase in acidity that they are usually divided into two large groups: endogenous and exogenous (internal and external, respectively).
The most common endogenous factors include:
- hereditary predisposition;
- chronic infections and/or presence of parasites;
- persistent hypoxia (lack of oxygen supply to tissues and organs);
- metabolic (metabolic) disorders;
- hypovitaminosis, deficiency of microelements, amino acids, etc.
Main exogenous factors:
- smoking and drinking alcohol, especially strong drinks;
- distortions in the daily diet (infatuation with spicy, fatty, spicy, over-salted, too hot and other dishes that irritate the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract);
- long-term or amateur use of medications without prior consultation and supervision of a gastroenterologist;
- work in some hazardous industries, which involve, in particular, constant contact with nitrates;
- physical inactivity, sedentary lifestyle, haphazard eating with long breaks and a predominance of sandwiches, fast food, sour juices, coffee, carbonated drinks and similar “stomach killers.”
Visit our Gastroenterology page
Diagnostics
One of the key methods for determining the acidity of the stomach is to conduct a urease breath test to identify the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. Also, PCR and ELISA studies are performed to identify antibodies to this microorganism. Other mandatory research methods for suspected gastritis with high acidity include:
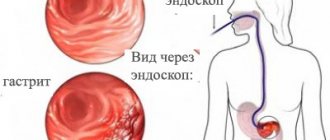
- Endoscopic examination of the stomach (gastroscopy). Using this method, the condition of the stomach, esophagus and duodenum is assessed. If necessary, during the examination, fragments of the mucous membrane are taken (biopsy).
- Intragastric pH-metry. To conduct the study, a pH-metric transnasal probe is used, which is connected to an autonomous recording unit. If the pH of the gastric contents is less than 1.5 units, then the diagnosis of hyperacid gastritis is confirmed.
An ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs may be prescribed as an auxiliary examination method.
Acidity - what's the point?
As the specialist notes, gastric acidity is a characteristic of the concentration of hydrochloric acid in gastric juice, which is measured in pH units. Hydrochloric acid is produced by the cells of the fundic glands, they are called parietal glands.
There are several types of pH environments in gastroenterology:
- increased (maximum pH 0.86);
- reduced (minimum pH 8.3);
- neutral or normal (1.5-2.0 pH.).
“Only the last type is considered healthy. With a normal pH environment, the gastrointestinal tract quickly and well digests incoming food and neutralizes toxins and infections that come with it. If the acid level deviates in any direction, the person begins to experience unpleasant symptoms,” notes the therapist.
Look into the stomach. Why do gastroscopy through the nose Read more
Treatment
Information on how to reduce stomach acidity should be obtained from a gastroenterologist. Any options for self-medication at home using improvised means are not only ineffective, but can also lead to the development of complications. For symptoms of gastritis with high acidity, diet and treatment include exclusion from the diet of fried and fatty foods, smoked meats, fast food, alcohol, canned meat, fish and vegetables, spices, seasonings, and sauces. You should eat in small portions, 4-5 times a day. Dishes must be prepared mainly by steaming or boiling. In case of increased acidity of the stomach, diet No. 1 according to Pevzner is prescribed.
For symptoms of gastritis with low acidity, treatment and diet include recipes for dishes that stimulate the acid-forming function of the stomach.
To treat high stomach acidity, traditional medicine uses the following groups of pharmaceuticals:
- Antibacterial drugs that are effective for hyperacid gastritis caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
- Enveloping agents.
- Proton pump inhibitors.
- Antacids.
- H2 histamine blockers.
- Bismuth preparations.
To maintain normal gastric acidity, it is important to maintain a balance of normal gastric microflora. For this purpose, it is recommended to use metaprebiotics, which contain a natural nutrient substrate for gastric and intestinal bacteria. Metaprebiotic Stimbifid Plus helps not only restore the balance of normal gastric and intestinal microbiota, but also promotes the eradication (destruction) of Helicobacter pylori. Also, metaprebiotic components accelerate the process of restoration of the gastric epithelium.
Diet
During the period of exacerbation (when pain is tormented), you need to endure at least a week on dietary soups without frying, porridges, stewed or boiled potatoes, small portions of boiled meat. During this period, you can drink teas, jelly, compotes (not sour), juices - only pumpkin, and then only a little. Alcohol, smoked, spicy, salty foods, carbonated drinks, sour fresh vegetables and fruits are completely excluded. The bread is stale, optimally dried. All food is neither hot nor cold (the best option is warm).
During the period of remission, the diet expands. The patient can eat low-fat varieties of fish (hake, cod, pink salmon), meat (rabbit, chicken, beef); The side dish is porridge, potatoes, maybe pasta, but not much and not often. Eggs, fresh non-acidic fruits and dairy products are also included in the diet. It is useful to drink fresh cabbage juice. Restrictions on the intake of fatty foods, smoked peppers, alcohol and strong teas and coffee remain.
Menu for the week
The diet used for stomach acidity is based on food that is gentle on the functions of the gastrointestinal tract. During such a diet, fatty and spicy foods, sausages, pickles, marinades, carbonated drinks, and fast foods are excluded from consumption. The basis of the diet consists of foods that reduce acidity levels.
Day 1−2:
- Breakfast: ground buckwheat porridge (with milk), cottage cheese soufflé, herbal tea.
- Lunch: soft-boiled egg, vegetables.
- Lunch: light vegetable soup, meatballs, carrot puree, jelly.
- Dinner: fish cutlets, pasta.
- Before bed: milk or kefir.
Day 3−4:
- Breakfast: oatmeal, carrot puree, tea.
- Lunch: pancakes.
- Lunch: zucchini soup, steamed cutlets, pasta, compote.
- Dinner: lazy dumplings, plum soufflé.
- Before bed: milk or kefir.
Day 5−6:
- Breakfast: baked omelette, avocado toast, tea.
- Lunch: carrot-apple soufflé.
- Lunch: rice soup (milk-based), boiled meat, jelly.
- Dinner: mashed potatoes, a little spinach, low-fat cottage cheese.
- Before bed: milk or kefir.
Day 7:
- Breakfast: semolina porridge, dry cookies, tea with milk.
- Lunch: egg soufflé.
- Lunch: chicken soup with croutons, baked apples with honey, fresh vegetable salad, dried fruit compote.
- Dinner: baked chicken with rice, boiled potatoes, stewed vegetables.
- Before bed: milk or kefir.
Don't go to bed on a full stomach. Lying down immediately after eating can cause stomach acid to move back up the tract instead of down. As a result, this only contributes to the stimulation of an increase in acidity levels.
Prevention
To prevent increased acidity, you need to follow a number of rules. They are not heavy and do not require serious effort, but will help keep your stomach acidity in order. Of course, proper nutrition comes first in importance. The amount of proteins, carbohydrates, fats, fiber, vitamins must be balanced. It is important to follow a meal schedule. The last meal is 3 hours before bedtime. If we are talking about light meals, for example, low-fat dairy products, you can eat them even 30 minutes before bedtime.
Try to avoid hunger and mono-diets, do not overeat, but eat dry. It is better to avoid fried, fatty foods and dishes. Eat warm food, not hot or cold. It is better to give up bad habits (alcohol, smoking) if you decide to get your acid-base balance in order. Observe the storage conditions and terms of food products.
It is necessary to maintain individual hygiene and sanitize the mouth in a timely manner. Treat any illnesses on time, since all organs and systems in the body are connected. And the most unexpected disease can affect the balance of the stomach. Any medications should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor. Try to think positively and avoid stress; it is with psycho-emotional stress that most gastrointestinal diseases begin.