Probiotics after antibiotics – rehabilitation of intestinal microflora
What is our intestinal microflora?
This is the foundation of immunity, the microflora that we received in the first minutes of life is our innate immunity. One of the most important parts of the immune system is beneficial bifidobacteria and lactobacilli, which activate it and suppress viruses that attack the body during diseases.
The human intestine alone contains 2 kg of beneficial bacteria, and the gastrointestinal system itself has about 80% of immune cells that actively fight various infections. Therefore, if the bacterial “population” in the body becomes smaller, all its work is disrupted.
As a result, when the composition of the intestinal microflora changes, pathogenic bacteria multiply: staphylococci, E. coli, candida fungi, Proteus, etc.
During and after taking antimicrobial drugs, the intestinal flora is especially vulnerable. Antibiotics kill all pathogenic bacteria in the body, but the beneficial ones also die along with them.
After completing a course of antimicrobial drugs, it is difficult for the body to begin to function normally again, and pathogenic microorganisms can still colonize the intestinal environment, especially if the drug was incorrectly selected. Under the onslaught of antibiotics, beneficial bacteria die, while harmful ones continue to fight, adapt to new conditions and survive.
In medicine, there is the term “antibiotic resistance,” which means the adaptation of painful bacteria to living conditions inside the intestine, and this is a global problem, because, despite the latest developments of antimicrobial drugs, the bacteria themselves are progressing. There is another problem - the unsystematic and uncontrolled use of “pills for all diseases”, which leads to the fact that they simply stop working.
At the slightest suspicion, for example, of an acute respiratory viral infection, most people familiar with antibiotics immediately buy them without seeking help from a doctor. But over time, our body gets used to the drugs and ceases to resist the disease on its own, and at the moment when antimicrobial drugs are really needed, they, unfortunately, may be ineffective or may not have the intended and proper effect at all.
Each antimicrobial drug kills those pathogenic bacteria that are sensitive to it, while the rest mutate, which leads to the emergence of new types of diseases. It is because of mutations that in the 21st century there is a new form of tuberculosis, pneumonia, a new form of typhoid fever and meningitis.
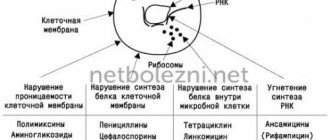
Any antimicrobial drug has an effect on the entire body, so if you used it to fight ARVI, the drug will still interact with all organs, and primarily with the intestines, and through it it will be absorbed into the blood and spread everywhere.
Antibiotic therapy can achieve results quickly, but possible side effects should be taken into account.
Side effects from unsystematic use of antibacterial drugs are toxic reactions, damage to the liver parenchyma, damage to the kidneys, peripheral nervous system and hematopoietic organs.
Some of the most common side effects during and after taking antibiotics are nausea, constipation, allergies, decreased immunity, and women may develop thrush. But most often, doctors are faced with the problem of diarrhea in patients; children suffer from it especially painfully.
The antimicrobial drug kills beneficial bacteria, against the background of which healthy microflora dies, and normal absorption and digestion become impossible.
It is obvious that it is completely impossible to refuse to take antimicrobial drugs, especially if we are talking about serious diseases that threaten life, for example, sepsis (complete damage to the body)
But let us emphasize once again that you should not take antibiotics uncontrollably, i.e. for any reason.
What can help overcome the disease and restore intestinal microflora? In order to reduce the negative impact of antimicrobial drugs, it is necessary to combine them with drugs aimed at preventing complications and restoring the microflora of the intestinal environment. Probiotics have such effects, which are completely opposite in their action to antimicrobial drugs.
These are live, beneficial bacteria, which we recommend drinking even after a course of antibiotics, thus populating the intestines with them.
- Normalize the functioning of intestinal microflora;
- Probiotics are acid-stable;
- Unaffected by antibiotics;
- Probiotics are safe and stable;
- They increase the components of normobiota, which displaces pathogens.
- What effects should be expected from the combined use of antimicrobials and probiotics?
- Reducing the frequency and severity of adverse drug reactions;
- Reducing the frequency and severity of negative effects on the microbiocenosis of the body;
- Increasing the effectiveness of therapy.
The simultaneous use of antibiotics and probiotics helps reduce the threat of adverse drug reactions, protect the intestinal microflora and increase the effect of complex therapy, complementing the antibiotic and improving it.
Probiotics, when taking antibiotics and after, stimulate the immune system and increase the body's resistance to infections; the drugs have a beneficial effect on the gastrointestinal tract, help it absorb vitamins and microelements, and have a preventive effect, preventing re-infection.
In addition, when taking antibiotics, pathogenic bacteria will die, leaving behind waste, which probiotics will help remove.
To quickly remove toxins and waste, we also advise you to drink more fluids and not overload your body with heavy foods. But you can’t kill probiotics with hot water. In addition, the temperature of the dishes should not be higher than 45 degrees, otherwise beneficial microorganisms will die without completing their work.
Follow a diet: give up fatty, fried, spicy, smoked foods and various canned foods, sour fruits. While taking antibiotics, it is strictly forbidden to drink alcoholic beverages. Also, temporarily reduce your consumption of coffee drinks and tea. All these products negatively affect the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, therefore, your diet should not overload it.
Add fermented milk products to your diet: natural yogurt, kefir, acidophilus. These foods are rich in bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. Doctors also recommend drinking more water, eating white bread, and eating more vegetables and fruits.
What are probiotics for?
- Probiotics such as Lactobacillus spp., Bifidobacterium spp. and Saccharomyces boulardii, are strains of living microorganisms that are components of the normal intestinal microflora and are largely responsible for our health. They are obtained from food or in the form of medications.
- Probiotics improve antibacterial therapy because they combat microbial adhesion and the growth of pathogenic flora, have immunomodulatory properties, and improve the integrity of the intestinal barrier. In patients treated with antibiotics, probiotics help restore the microbial flora and increase treatment tolerance.
- Probiotics should be used cautiously, in consultation with a doctor, especially in premature infants and patients with severe immunodeficiency
What is the best probiotic to take while taking antibiotics?
Probiotics are divided into 4 groups. Each of them affects the body differently.
The first group includes first-generation drugs; they contain only one strain of beneficial bacteria. The second group includes second-generation drugs; they represent bacteria that are not typical for the gastrointestinal tract and therefore are quickly eliminated from the human body. Third generation probiotics are combination drugs. They include several strains of beneficial bacteria and dietary supplements that enhance the activity of “living” microorganisms. Probiotic preparations "Vector-Bialgam" - 4th generation, they represent those beneficial bacteria that are in the intestines, and they will be the best helpers in restoring the intestinal microflora.
The fourth generation is probiotics, which include bifdobacteria and lactobacilli; they are the main representatives of the intestinal environment.
Taking a probiotic and an antibiotic at the same time will help relieve the latter's side effects on the gastrointestinal system. Probiotic cultures also help prevent side effects. Earlier we talked about the consequences of the death of friendly organisms; we emphasize that this reduces the protective properties of epithelial tissues and develops pathogenic and opportunistic bacteria.
The intestinal microflora, suppressed by taking antimicrobial drugs, takes a long time to recover. Even with an individually developed antibiotic treatment plan, taking into account the sensitivity of harmful bacteria to them, the correct dosage and short duration of the course, the restoration of the qualitative and quantitative composition of the microflora occurs no earlier than after 1 month.
Therefore, the most optimal option for taking probiotics is throughout the entire course and after it for 30-40 days (after the course, dosages should be age-appropriate). If taking antibiotics is planned, you should start taking probiotics a week before the start of the course.
With a well-designed treatment plan and an integrated approach, you can achieve the maximum beneficial effect from antibiotics, while maintaining the beneficial properties of friendly bacteria when taking probiotics.
Antibiotic-associated diarrhea
AAD is a disease characterized by three or more episodes of loose stools over 2 consecutive days or more, developing during the period of antibiotic therapy and up to 4-8 weeks after its discontinuation [2].
Antibiotic therapy provokes the development of AAD in 5-50% of patients. It is believed that the occurrence of diarrhea is associated with a disturbance in the composition of the intestinal microbiocenosis and its consequences, such as changes in the spectrum of production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), disruption of microbial metabolism of carbohydrates and bile acids [11].
A systematic review of data from 59 RCTs assessing the effect of probiotics in preventing AAD identified several probiotic products that have been shown to be effective for AAD in at least 2 RCTs. This is S. boulardii
I-745, a probiotic from a mixture of 3 strains of lactobacilli (
L.acidophilus
CL1285 +
L. casei
Lbc80r
+ L. rhamnosus
CLR2) and a probiotic based on the
L. casei
DN114001 (see table). These probiotic products at a dose of 107-1010 CFU/day had a preventive effect when taken from the 1st-2nd day of antibiotic therapy and then for 1-4 weeks after the end of antibiotic therapy.
According to the WGO recommendations of 2021, the use of probiotics prevents the development of AAD in children and adults; the level of evidence is high [13]. Among the bacteria that have shown their effectiveness, VGO identifies several strains of Lactobacillus acidophilus
(CL1285, NCFM), yogurt containing
Lactobacillus casei
DN114,
L. Bulgaricus
and
Streptococcus thermophilus
,
Saccharomyces boulardii
CNCM I-745
, Lactobacillus rhamnosus
GG
, Lactobacillus reuteri
DSM 17938, etc. [13].
In approximately 1/3 of cases, the cause of AAD is Clostridium difficile
, in severe cases the development of pseudomembranous colitis and toxic megacolon is possible.
It is known that C. difficile
can also be found in the intestines of healthy individuals, however, against the background of taking antibiotics and reducing the microbial diversity of the colon, this bacterium acquires the ability to synthesize extremely aggressive toxins (A and B) that cause inflammation of the intestinal wall (due to disruption of the epithelial barrier, induction proinflammatory cytokines, apoptosis and necrosis of epithelial cells).
The problem of the appropriateness of using probiotics in the prevention of Clostridium difficile
-associated disease was studied in 23 RCTs [2], the results of some of them concluded that
S. boulardii
CNCM I-745,
L. casei
DN114001,
L. rhamnosus
GG and a probiotic consisting of a mixture of 3 strains
of Lactobacillus acidophilus
CL1285
, L casei
LBC80R and
L. rhamnosus
CLR2 [26–31] (see table). At the same time, more than 50% of studies did not find any benefit from taking probiotics containing the above strains [2].
Probiotics are often used not only for prevention, but also in treatment regimens for Clostridium difficile
, as an addition to antibiotic therapy (vancomycin and metronidazole) to prevent relapse of the disease [32].
To date, data from two RCTs are available (see table) showing that the use of S. boulardii
I-745 reduces the likelihood of recurrent infection.
L. rhamnosus
strain as a probiotic did not provide evidence of the effect of this strain on reducing the frequency of relapses of
Clostridium difficile
[33–36].
According to the WGO recommendations, the advisability of using probiotics to prevent Clostridium difficile
and its relapses need further study, since the level of evidence of most of them does not inspire confidence [13].
It is known that eradication therapy carried out by a combination of 2-3 antibiotics together with proton pump inhibitors is often accompanied by the development of a wide range of side effects and adverse events (diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain), including those associated with the effect on the microbial composition of the gastrointestinal tract. - intestinal tract. As shown by RCT data (see table), S. boulardii
I-745,
L. rhamnosus
GG, as well as a combination of 2 strains of lactobacilli
L. helveticus
R52 +
L. rhamnosus
R11, used during eradication, can improve the tolerability of therapy, reducing the severity of side effects [2].
Additionally, according to a meta-analysis by L. McFarland et al.[37], supplementation with a probiotic containing S. boulardii
CNCM I-745, in eradication therapy regimens, increases the effectiveness of eradication (RR=1.11, 95% CI 1.07-1.16;
p
<0.05).
According to the same work, strains Clostridum butyricum
588,
L. rhamnosus
GG,
L. acidophilus nr
,
L. reuteri
17938 and
L. casei
114001 do not have a significant effect on the success of eradication.
Another meta-analysis including 19 RCTs found that probiotics containing a combination of L. acidophilus
La5 +
B. animalis lactis
Bb12;
L. helveticus
R52 +
L. rhamnosus
R11;
L. acidophilus nr
+
B. longum nr
+
E. faecalis nr
also increase the rate of successful eradication [38].
Thus, from the standpoint of evidence-based medicine, the prescription of probiotics for the period of eradication therapy seems appropriate both from the point of view of achieving successful eradication and to prevent side effects and better tolerability of therapy.
In the Russian Federation, the above-mentioned combination of 2 strains of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli ( L. acidophilus
La5 +
Bifido.
lactis Bb12), which has proven the ability to increase the level of successful eradication in at least 3 RCTs, is presented in the preparations Probiologist and Probiologist forte (Majoli Spindler, France), containing at least 1·109 and 2.5·109 CFU in 1 capsule respectively.
LA-5 ( Lactobacillus acidophilus
) and BB-12® (
Bifidobacterium
) are one of the most studied strains of lacto- and bifidobacteria in the world, used in the food and medical industries since 1979 and 1985, respectively, which allows us to have no doubt about their safety, confirmed by GRAS statuses (FDA, USA) and QPS (European Food Safety Authority).
The probiologist is distinguished by his original production technology, which allows maximum preservation of the viability and functional activity of the strains.
Strains of live bacteria LA-5 and BB-12 are enclosed in an acid-resistant polysaccharide shell, which, when released into a liquid, turns into an insoluble gel that is resistant to acid. Due to this, the survival rate of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli (according to an in vitro
) is 73%. Probiologist recommends adults and children over 7 years old to take 1-2 capsules per day with meals, with water. Duration of treatment is 10-30 days.
S. boulardii were effective in the prevention of traveler's diarrhea, which, according to rough estimates, affects 24-40 million people per year
I-745. You should start taking probiotics a few days before your trip, continuing during your trip and for 5 days after returning. The recommended dose is 2-5·109 CFU/day.
To date, a large number of research results have been published studying the effect of probiotics on the course of inflammatory bowel diseases. Bifido. longum) was effective in combination with basic therapy
BL03,
Bifido.
infantis subsp. lactis BI04,
Bifido.
breve BB02,
L. acidophilus
BA05,
L. plantarum
BP06,
L. paracasei
BP07,
L. helveticus
BD08,
Streptococcus thermophiles
BT01).
Application of the probiotic S. boulardii
I-745 in patients with ulcerative colitis with low and moderate levels of activity also contributed to longer maintenance of remission.
The effect of probiotics containing L. rhamnosus
GG and
E. coli Nissle
on inflammatory bowel diseases has not been proven [2]. The effectiveness of probiotics in Crohn's disease has not been confirmed [39].
Data published in a systematic review by J. Sniffen et al. [2], obtained from an analysis of more than 20 RCTs, indicate a decrease in the severity of symptoms and an improvement in the quality of life of patients with IBS when using probiotics containing L. plantarum
299v and
B. infantis
35624 (high level of evidence).
Strains of L. rhamnosus
GG,
S. boulardii
CNCM I-745,
B. lactis
173010 and the probiotic VSL#3 have not shown unambiguous effectiveness in alleviating the symptoms of IBS, and therefore the advisability of their use in IBS is questionable [2, 39].
VGO also emphasizes the possibility of using probiotics in patients with IBS to reduce the severity of abdominal pain, bloating, distension, and improve quality of life [13]. Lactobacillus plantarum as strains that have proven effective in IBS.
299v,
Lactobacillus rhamnosus
NCIMB
30174,
L. plantarum
NCIMB
30173,
L. acidophilus
NCIMB 30175,
Enterococcus faecium
NCIMB 30176, as well as a combination of 3 strains:
Pediococcus acidilactici
CECT 7483,
Lactobacillus plantarum
CECT 7484,
L. plantarum
CECT 7485 and others [13].
On the Russian pharmaceutical market, a medicine containing the above-mentioned combination of strains ( Pediococcus acidilactici
CECT 7483,
Lactobacillus plantarum
CECT 7484,
L. plantarum
CECT 7485), represented by the drug Probiolog SRK (Majoli Spindler, France), containing at least 3·109 CFU of viable bacteria in each capsule.
The strains included in the drug Probiologist IBS are facultative aerobes/anaerobes, which, on the one hand, allows them to remain viable in capsules and not die in the stomach and small intestine, and on the other, to colonize the large intestine. In addition, these strains demonstrate high survival rate in an acidic environment. Thus, when comparing the viability of the L. rhamnosus
GG1 strain and the strains included in Probiologa IBS, it turned out that the latter are much more resistant to the action of an acidic environment with pH 2.3 [40].
When studying the mechanisms of action of the strains included in Probiologist IBS, their high activity in the production of SCFAs (mainly acetate), acetylcholine, polyphosphate granules and other important metabolites was shown. Taken together, the action of these metabolites leads to a decrease in the severity of microinflammation in the intestinal mucosa, reduces its permeability, increases mucin production, promotes the differentiation of immunocompetent cells, inhibits the activation of mast cells, blocks the synthesis of endotoxins and hydrogen sulfide by opportunistic bacteria Enterobacteria ceae
and
Pseudomonas
[41, 42].
The clinical effectiveness of the combination of strains included in Probiologist IBS was studied in a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled interventional clinical trial. In this study, 84 patients suffering from IBS with diarrhea were divided into three groups who took placebo, low (3-6 109 CFU/day) or high (1-3 1010 CFU/day) dose of probiotic for 6 weeks ( combination of Pediococcus acidilactici
CECT 7483,
Lactobacillus
plantarum CECT 7484,
L. plantarum
CECT 7485). The result was assessed after 3 and 6 weeks of therapy by filling out validated questionnaires to assess the quality of life in IBS (IBSQoL), visceral sensitivity index (VSI). On day 21 of the study, patients taking the probiotic at a therapeutic dose (3-6·109 CFU/day) showed a statistically significant improvement in quality of life compared to patients taking placebo. Moreover, according to the results of the questionnaire, the quality of life of patients taking probiotics improved by 2 times compared to those taking placebo. After 6 weeks of probiotic therapy, it was possible to show that gut-related anxiety, assessed by the visceral sensitivity index, was statistically significantly reduced compared to patients in the placebo group. It is important that in patients with IBS who took a high dose of probiotic (1-3 × 1010 CFU/day), no side effects or adverse events were recorded during therapy, which may indicate an impeccable safety profile of the drug [43].
Considering the high content of bacteria in 1 capsule of Probiologist IBS, as well as the survival of strains in the acidic environment of the stomach, it is enough to take the drug once a day. To achieve a lasting clinical effect in IBS, the course of treatment with Probiologist for IBS should be at least 3 weeks, optimally 6 weeks.
Acute diarrhea in children can be caused by both bacterial and viral infections. Studies examining the effectiveness of probiotics for the treatment of acute diarrhea in children have shown that supplementation with S. boulardii
helps reduce the duration of diarrhea compared with patients taking placebo (-1.1 days,
p
= 0.04).
The use of S. boulardii
together with
L. acidophilus
,
L. rhamnosus
and bifidobacteria showed slightly worse results (–1 day,
p
= 0.06) [44].
Meta-analysis by S. Feizizadeh et al. from
22 RCTs, also showed a shortening of the diarrheal period by an average of 19.7 hours when taking S. boulardii .
In another meta-analysis, H. Szajewska et al. [45] noted a decrease in the duration of diarrhea when taking L. acidophilus
LB (by 21.6 hours).
According to a systematic review by J. Sniffen et al. [2] and included data from 61 RCTs of probiotics based on S. boulardii
I-745,
L. rhamnosus
GG,
L. reuteri
17938,
L. acidophilus
LB,
L. casei
DN114001, mixture of 4
Bac strains.
clausii mix (O/C, N/R84, T84, Sin8), as well as VSL#3, significantly improved the results of treatment of acute diarrhea in children.
According to the WGO recommendations, the use of probiotics for acute diarrhea is safe and helps reduce its severity and duration by at least 1 day. However, this effect is strain-specific. It should be noted that the strains effective against diarrhea in children and adults are different [13].
Thus, from the standpoint of evidence-based medicine, today the use of probiotics is justified for the treatment and prevention of the following nosologies: antibiotic-associated diarrhea in adults and children, diarrhea associated with Clostridium difficile
, acute infectious diarrhea in children and adults, eradication therapy, ulcerative colitis, irritable bowel syndrome. The choice of a probiotic product should be based on nosology; therefore, it should include strains with proven effectiveness for a given disease. You should choose the optimal form of release of the drug (lyophilisate, enteric-coated capsules). In addition, it is necessary to take into account the correct design of the packaging, which must contain information about the genus, species, strain of bacteria included in the probiotic, and an adequate dosage (optimally 109-1010 CFU).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Information about authors
Kaibysheva V.O. — Ph.D., senior researcher, https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0114-3700, e-mail: [email protected] ;
Nikonov E.L. - Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5231-711X
Corresponding author
: Kaibysheva V.O. — e-mail: [email protected]
Kaibysheva V.O., Nikonov E.L. Probiotics from the perspective of evidence-based medicine. Evidence-based gastroenterology
. 2019;8(3):45-54. https://doi.org/10.17116/dokgastro20198031
Liquid probiotics when taking antibiotics - quick effect!
All probiotics are divided into 2 groups: dry and liquid. It is liquid probiotics that contain beneficial bacteria in their original form and begin active work in the body after just a few hours, unlike dry forms.
Dry probiotics have an effect only after 18 hours, and the content of bacterial synthesis products is too low. When entering the human body, most bacteria die immediately, since they cannot overcome the acidic environment of the stomach.
The original line of drugs from the world leader in biotechnology “Vector-Bailgam” Ecoflor, Bifidum Bag and Trilact are liquid probiotics that use only natural ingredients and the most human-friendly bacteria. Their action has no delay and has a positive effect on the entire gastrointestinal tract.
What is microflora?
Microbiota or microflora of the human body are all microorganisms that live with humans in symbiosis, mutually beneficial “cohabitation”. The microbiota of different organs and systems differs in composition: the microflora of the oral cavity is considered separately, the skin separately, the bile ducts, vagina, etc. separately.
The most numerous and diverse intestinal microflora
. It consists of bacteria, fungi, yeast and other microscopic “residents”, the balance between which is extremely important for the health of the entire organism. There will be no balance - the gastrointestinal tract will not be able to fully function, absorbing all the necessary substances from food.
The number of microorganisms in the human intestine reaches 50 trillion, and their total weight is 3 kilograms
.
In the intestines of a healthy person, the microbiota is distributed as follows:
- 1% – opportunistic microflora (clostridia, staphylococci, some fungi);
- 99% – beneficial microflora (lactobacteria, bifidobacteria, aerobes, enterococci, E. coli, etc.).
So, if this healthy balance (eubiosis) “sways” towards pathogenic microorganisms, and their number exceeds 1%, dysbiosis
.
How to properly take probiotics while taking antibiotics and after?
The drugs Bifidumag Bag and Trilact must be taken during the entire course of antimicrobial drugs, their dosage is doubled, and the time interval between their use and the use of antibiotics is at least 1 hour.
The time interval between taking Ecoflor and antibiotics is 3 hours.
By taking an antimicrobial drug prescribed by your attending physician in combination with a probiotic from the first day of treatment, your own intestinal microflora will be preserved, delegating most of its functions to the beneficial bacteria contained in the drugs.
They will provide suppression of candida, staphylococcus, proteus, streptococcus and many other bacteria, including those that are resistant to antibiotics.
Probiotics influence the gastrointestinal ecosystem by stimulating immune and non-immune mechanisms through competition and suppression of pathogenic microorganisms.
Bifidobacteria that are part of the probiotics Bifidumag Bug, Ecoflor and lactobacilli in the probiotic Trilact are resistant not only to the action of antimicrobial drugs. They cope well with acids and alkalis, but most importantly, they are absolutely safe even with long-term use and increased dosages.
Probiotics contain the highest possible titer of active bacteria (the number of colony-forming units in one milliliter of the drug) 10 to 12 degrees. For restoration, a bacterial density of at least 500,000 per 1 cm2 of the gastrointestinal tract is required, which corresponds to the titer of the Vector-Bailgam probiotics.
Thanks to this, the film of the body’s own normal flora bacteria is quickly restored and a protective mechanism is launched.
Clinical and experimental studies confirm: probiotics have a beneficial effect on metabolic processes in the intestines (anti-carcinogenic effect), intermediate metabolism (for example, on liver detoxification), and on stimulating one’s own defenses.
The author’s line of probiotics does not contain harmful additives, is tasty and has a pleasant aroma, so our main patients – children – will especially like it.
Probiotic preparations "Vector-Bialgam" have patents for bacterial strains, medium composition and manufacturing technologies, their production is carried out in accordance with the requirements of the international standard for the production of medicinal products.
Bifidum Bag, Trilac and Ecoflor can be purchased on the website, the price range for each drug is from 700 rubles, the set includes 10 bottles of Bifidum Bag and Trilact, Ecoflor - 10 packages.
When is a probiotic prescribed?
Taking antibiotics is necessary for treatment (if prescribed by a doctor). But antimicrobial drugs kill all bacteria. Thus, along with pathogens, the drugs kill the good bacteria in the gut, leaving the body defenseless against pathogens such as the fast-growing Candida albicans. After a course of antibiotics, this yeast can quickly become dominant in the small intestine.
Taking probiotics before, during, and after a course of antimicrobials can help maintain the balance of microorganisms in the digestive system. Many Candida sufferers doubt this, thinking that antibiotics will quickly kill off the good bacteria in probiotics. However, research has shown that probiotics are extremely effective during antibiotics.
How to choose the right probiotics?
The choice of probiotics, like any other biologically active drugs, should be entrusted to a doctor who can analyze all possible contraindications. Particular attention should be paid to the selection of probiotics if the patient has allergies or any serious health problems (oncological diseases, immunodeficiency, etc.).
But general factors that may guide a physician's choice of probiotics include:
- Patient's age
. A young and practically healthy person leading an active lifestyle can take the simplest probiotic preparations containing 1-2 strains of beneficial bacteria. But for an elderly patient, more “serious” probiotics containing a larger number of strains are suitable. - Number of colonies (CFU, colony-forming units)
. Many colonies of beneficial bacteria contained in probiotics die in the upper digestive tract without reaching their “ultimate goal.” Therefore, it makes sense to take probiotics with a high CFU count - from 15 to 100 billion. - Release form and storage conditions
. Probiotic preparations are available not only in the form of capsules, but also in the form of powder for preparing a suspension. For people with an active lifestyle, preparing a suspension will be an unnecessary headache, which may prevent them from completing a full course of microflora restoration - therefore, it is better for such people to give preference to the capsule form. As for storage, some probiotics must be stored in the refrigerator, otherwise the live bacteria they contain will quickly die. That is, such drugs cannot be taken with you on a trip or to work - this also needs to be taken into account when planning a course.