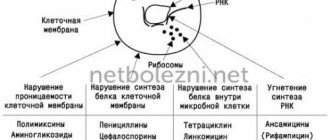
Despite their high effectiveness in the treatment of many diseases previously considered incurable, the scope of use of antibiotics is limited by strict indications, and their use may be accompanied by a number of adverse reactions that may appear during the treatment process. And this must be remembered by everyone who begins therapy with antibacterial drugs.
Most often, antibacterial drugs lead to nausea and disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. But in fact, there can be much more side effects from these drugs. And periodically, scientists add to the list of adverse reactions that may occur when taking antibiotics.
Fever
It happens that we independently decide to start taking antibiotics to fight diseases that have led to an increase in body temperature. At the same time, we hope that the temperature will drop. But it may turn out the other way around. It turned out that antibacterial drugs, in a certain percentage of cases, can cause fever or intensify it. 1 This is one of their side effects, which is observed in a number of antibiotics, including those used to treat complications of acute respiratory viral infections.
If your body temperature rises after taking antibiotics or if a previously started fever intensifies, you should stop taking the drug and seek help from a doctor. Don't wait until the heat becomes too intense. The lack of positive dynamics may indicate the ineffectiveness of this drug, which requires a medical decision and adjustment of therapy. High body temperature negatively affects metabolism, which can lead to disruption of water-salt balance when the nervous, cardiovascular and urinary systems are affected. 2
Such conditions are life-threatening, so before treatment it is necessary to make an informed decision and begin treatment with antibiotics only if there are compelling reasons and after consulting a doctor.
The harm of antibiotics to the intestines
The term intestinal dysbiosis refers to all diseases in the small intestine that occur due to microflora disturbances. They are accompanied by loss of intestinal cells and an increase in their permeability. The influence of antibiotics on this process is undeniable. Even one dose of an antibiotic can significantly affect the microflora.
In medicine, relatively recently, they began to realize the negative consequences that antibiotics cause, the side effects of which must be minimized immediately. Any antibiotics can change the intestinal flora, but some of them - penicillins, cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones, clindamycin - are a direct cause of antibiotic-associated and pseudomembranous colitis. The first develops under the influence of antibiotics, the second is caused by clostridia bacteria, which rapidly multiply against the background of damaged microflora.
Think about your immune system in time. If antibiotics are essential for you, talk to your doctor about which medications you should take at the same time as antibiotics to restore your levels of beneficial bacteria. This will help minimize the effects of taking antibiotics, and intestinal treatment will not be so long and expensive.
If you are prescribed antibiotic treatment, you need to take preventive measures and undergo a course of probiotic therapy to restore beneficial bacteria that were destroyed during therapy. The most optimal preparations after antibiotics are liquid concentrates of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli Bifidum Bagh and Trilact. In addition to the fact that beneficial bacteria cover the intestines with a continuous protective biofilm, leaving no chance for fungi, they also normalize metabolism and digestion, which reduces bloating, the body quickly cleanses itself of toxins, and improves immunity. To achieve this effect, the number of probiotic bacteria must reach a certain titer. It is generally accepted that a probiotic should contain 10 million colony forming units per gram. For comparison: the liquid probiotic Bifidum Bag contains 10 to 12 power (1000 billion) bacteria, that is, this figure is higher than other probiotic preparations that are prescribed after antibiotics.
At the same time, intestinal dysbiosis is corrected with a diet high in soluble and insoluble fiber and low in saturated fat and animal protein. These reduce the concentration of bacteroids and increase the concentration of bacteria that produce lactic acid: bifidobacteria, lactobacilli and lactic acid streptococci.
Adding fiber to the diet can have different effects on the treatment of dysbiosis. Insoluble fibers reduce the concentration of bacteria and their activity. Soluble fiber, on the other hand, increases bacterial concentrations and enzymatic activity while increasing levels of beneficial short-chain fatty acids. In most cases, you can successfully eliminate mild symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome by learning to manage stress and making diet and lifestyle changes.
Fungal diseases
Antibiotics can lead to dysbiosis and contribute to the development of fungal infections. 3 It turns out that you can treat one disease, and in the “load” get another.
Fungi can affect the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as the skin and genitourinary system. If the fungal disease is generalized, that is, has spread throughout the body, then there is a risk of damage to internal organs. 4
When a fungal disease develops, other infections are often associated, which can lead to a sharp decrease in immunity, ulcers, even baldness and other unpleasant and dangerous consequences. To avoid such complications, doctors sometimes prescribe antibiotics along with antifungal drugs, which increases the burden on the body.
Antibiotic overdose: symptoms and consequences?
In case of overdose, toxic, neurological and allergic reactions of the body are possible. Liver and kidney dysfunction, stomach and intestinal diseases may also occur.
Symptoms of overdose depend on the group of antibiotics. In case of an overdose of penicillins, nausea, vomiting, convulsions, and a sharp increase in potassium in the body are observed.
Excess chloramphenicol is characterized by impaired respiratory function, gastrointestinal disorders, and heart failure. The safest in this regard are aminoglycosides, but you can’t joke with them either.
In case of an overdose of antibiotics, the stomach is washed and the patient is sent to the hospital. There, a specialist prescribes a course of therapeutic measures aimed at cleansing the body, and drug therapy to normalize the functioning of internal systems and organs.
Allergy
Of course, one of the most common side effects of antibiotics is allergies. 5 In this case, an itchy rash and swelling may appear on the skin. In severe forms, the eyelids, lips and tongue become swollen, there is difficulty swallowing and speaking, severe weakness appears, heaviness is felt behind the sternum and shortness of breath even at rest. This is how anaphylactic shock manifests itself - an acute pathological condition that is life-threatening. In case of rapid development of allergy symptoms, emergency medical care and resuscitation measures are necessary.
It is also necessary to take into account the fact that antibiotics can enter our body along with some food products - for example, meat may contain penicillins. This means that almost every person has a risk of developing allergies when taking antibacterial drugs. 6 This once again indicates the need for medical supervision when taking antibiotics.
Antibiotic therapy support
Particularly important for patients with allergies.
During treatment, it is recommended to take probiotics as part of complex therapy orally and, if indicated, locally from the first day of treatment and during the recovery period after treatment. It is recommended to increase the daily dose of probiotics by 2 times relative to age. The minimum interval between taking the probiotic and the drug is 2-3 hours.
The order, duration and frequency of administration, the amount of daily and single doses of a probiotic for a particular patient are determined by the attending physician and may differ from the recommended regimen. For example, according to the decision of the attending physician, it is possible to take only one or two of the three drugs of the complex.
Probiotics when taking antibiotics
Probiotics Bifidum BAG and Trilact are indicated for use from the first to the last day of taking the antibiotic in double dosage with a spread of time for taking the probiotic and antibiotic at 2-3 hours. After a course of antibiotics to restore your own microflora, a probiotic course is 3-4 weeks in age-specific dosages.
Broad-spectrum antibiotics eliminate both the causative agent of infection (staphylococcus, streptococcus, Klebsiella, Proteus and many other bacteria) and beneficial microflora. Bifidobacteria and lactobacilli are among the main ones in the functioning of the body's immune system. Without them, the immune system does not work.
Short course of antibacterial therapy (5 - 10 days)
Taking increased doses of probiotics orally and locally as indicated from the 1st day of treatment.
The interval between taking an antimicrobial drug and a probiotic is 3 hours.
According to the decision of the attending physician, Ecoflor from 2 to 3 packs can be added to Bifidum BAG and/or Trilact. per day for the entire period of therapy to prevent toxic damage to the liver and other organs.
Recovery period after treatment (rehabilitation) - recommended after completion of any treatment that requires medication. Necessary for consolidating the results of treatment and obtaining a longer and more lasting result, achieving long-term remission, reducing the number of relapses of the disease and improving the patient’s quality of life
After completing the treatment course, it is recommended to conduct a restorative course of taking probiotics - 40 days (see)
Recommended regimen for use of Bifidum BAG/ Trilact/ Ecoflor for the correction of intestinal flora after antibiotic therapy, children over 12 years of age and adults.
Course duration 40 days
| Stages of treatment | Duration | Time and dosage of medications |
| Preliminary stage | 1-15 day | In the morning – Ecoflor 1 pack During the day – Ecoflor 1 pack In the evening – Bifidum BAG 6 ml |
| 1st stage | 16-40 day | In the morning – Trilact 6 ml In the evening – Bifidum BAG 6 ml |
View all articles in the “Microbiocenosis” section
Pregnancy
An unexpected side effect of antibiotics, isn't it? In fact, we are talking about an increased risk of becoming pregnant in those women who simultaneously take oral contraceptives and certain antibiotic medications. The reason is that certain antibacterial drugs increase the production of enzymes in the liver, which increase the breakdown of estrogen from the pill, thereby reducing the effectiveness of birth control medications. 8
Currently, scientists continue to study the mechanism of the effect of various antibiotics on contraceptives. If you are not planning a pregnancy, use additional barrier methods of contraception during treatment and for another week after completion of the course.
Is it possible to take antibiotics during pregnancy and breastfeeding?
Taking antibiotics during pregnancy and breastfeeding is undesirable - many drugs are not properly tested. Antibiotics from the group of tetracyclines and aminoglycosides are strictly prohibited - they have a toxic effect on the fetal liver and accumulate in the bones, increasing the risk of developing congenital anomalies.
What do you need to remember?
It is necessary to be very careful when choosing medications and, if possible, choose those that have the greatest therapeutic and least toxic effects. Therefore, you should not take antibiotics if there is no indication for this and these drugs are not recommended to you by your doctor.
For ARVI and sore throat, in most cases it is advisable to choose symptomatic therapy, which helps to get rid of unpleasant symptoms, regardless of the cause of their occurrence. The drug Strepsils® Intensive, lozenges [honey-lemon] has a local analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect on the mucous membrane of the mouth and throat: reduces swelling, difficulty swallowing, pain and irritation in the throat.9
The drug helps eliminate sore throat, regardless of the cause of its occurrence (be it viruses, bacteria or fungi).
Treatment of antibiotic-associated diarrhea
Diarrhea that develops while taking antibiotics requires adjustment of the treatment regimen. You should not stop taking medications on your own; you should consult your doctor. Typically, the course of antibacterial therapy is interrupted or the drug is replaced with an antibiotic of a different group.
Normalization of digestive processes, intestinal motility and stool consistency are tasks that require an integrated approach. There are three general principles that are important for all people suffering from diarrhea after taking antibiotics:
- Nutrition correction: it is important to follow a diet. The diet should include crackers and rice water. It is important to reduce the amount of carbohydrates consumed as much as possible, and also give up milk, dairy products, baked goods, fresh vegetables, berries and fruits; legumes, pasta.
- Compliance with the drinking regime: it is necessary to drink at least 2 liters of water per day to replenish fluid loss during watery stools.
- Symptomatic therapy: the pathological process can be stopped with the help of medications.
Due to the fact that many sources of natural probiotics and prebiotics are prohibited for diarrhea, one of the key principles of treatment is the prescription of medications containing these components. Strict dietary restrictions require the use of probiotics and prebiotics for antibiotic-associated diarrhea: it is important to restore normal intestinal microflora to prevent the proliferation of opportunistic microorganisms.
In most cases, medication correction is indispensable. Remember that only a doctor can prescribe medications.
There are several groups of drugs that can be recommended for antibiotic-associated diarrhea.
Sorbents
Infectious and inflammatory diseases are accompanied by intoxication of the body, and in the process of antibacterial therapy, decay products of pathogenic microflora accumulate. Therefore, the doctor may prescribe enterosorbents - products that literally absorb toxins and harmful substances and remove them from the body.
Probiotics and prebiotics
It is important to address the root cause of diarrhea and restore normal intestinal microflora after taking antibiotics. For this, probiotics are used - bifidobacteria, lactobacilli, as well as prebiotics - a nutrient substrate to stimulate the growth of one's own beneficial microflora. Synbiotics include both probiotics and prebiotics and are widely used in gastroenterological practice.
If there is a pronounced shift in the microbial balance, the doctor may recommend intestinal antiseptics or bacteriophages - they are designed to prevent the growth of opportunistic microflora and help restore the number of beneficial microorganisms.
Enzymes
Enzyme replacement therapy is not the mainstay of treatment for antibiotic poisoning. However, preparations based on digestive (pancreatic, gastric, intestinal) enzymes stimulate the digestion of food, normalize intestinal motility and peristalsis and participate in the restoration of normal microflora of the large intestine.
Symptomatic therapy
Diarrhea is often accompanied by painful symptoms: flatulence, nausea, cramping and abdominal pain. You can quickly alleviate the condition with the help of medications. They are unable to cope with the main problem, but will bring temporary relief. Report your symptoms to your doctor, and he will select one or more remedies to improve your well-being:
- for increased gas formation - defoamers (drugs based on simethicone) or herbal carminatives;
- analgesics or antispasmodics for pain;
- Oral rehydration solutions are products designed to replenish normal fluid volume and prevent dehydration.
If diarrhea is accompanied by elevated body temperature, the doctor will select an antipyretic drug.
General strengthening agents
Weakened by an infectious or inflammatory disease, as well as subsequent use of antibiotics, the body may require complex recovery. A specialist can prescribe immunomodulators, vitamin-mineral complexes and restorative drugs.
Restrictions in food during diarrhea can also cause hypovitaminosis and lack of minerals. During long-term antibiotic therapy, it is necessary to discuss preventive measures with your doctor in advance.
Antidiarrheal drugs
If you cannot cope with diarrhea, your doctor may prescribe drugs from the following groups:
- eubiotics - live bacteria that are designed to restore the balance of intestinal microflora and restore normal digestive function;
- synthetic drugs based on loperamide: bind to opioid receptors of the intestinal wall and inhibit the release of mediators that stimulate intestinal motility;
- herbal preparations based on tannins.
Sorbents also have an antidiarrheal effect. They are natural and synthetic. Enterosorbents, entering the intestines, absorb toxins and harmful substances, contribute to the formation of stools and their reduction. It is important to remember that at least two hours should pass between taking sorbents and other drugs.
For severe antibiotic-associated diarrhea, antibacterial agents targeting Clostridium difficile or another infectious agent may be appropriate.
The drug “Fitomucil Sorbent Forte” can be used as an adjunct to relieve diarrhea syndrome. It contains inulin, a prebiotic that promotes the growth of normal microflora, as well as 5 types of probiotic bacteria. In addition, the drug contains psyllium, a natural component that helps reduce diarrhea and relieve intoxication, since it turns into a gel and absorbs toxins. The triple effect (enterosorbing, detoxifying and restorative) distinguishes Fitomucil Sorbent Forte from other sorbents prescribed for AAD. Live bacteria populate the intestines and not only help relieve diarrhea, but also improve the condition of the microflora that has been damaged by taking antibiotics.
However, to restore microflora it is not enough to take one drug.
Only a doctor prescribes specific therapy. It is necessary to stop taking uncontrolled medications and agree with a specialist on medications for symptomatic therapy.
Which groups of antibiotics are more suitable for children, or is there no difference between them?
Children of different ages have their own physiological characteristics, and when choosing antibiotics you need to be extremely careful. The use of some drugs in pediatrics is prohibited or limited due to the risk of severe adverse reactions.
For example, tetracyclines are contraindicated in children under 8 years of age, as they affect the formation of teeth and bone tissue.
As a doctor, I have a positive attitude towards antibiotics - they save hundreds of thousands of lives.
The whole issue is their often unjustified use. The World Health Organization is sounding the alarm, calling for attention to this problem. If the world does not unite in the fight against resistance, soon (perhaps within the next 30-50 years) infections will appear for which there is simply no cure. Interview and text: Natalia Kapitsa
What happens if you refuse antibiotic therapy?
Antibiotics are used to treat diseases of a bacterial nature: pneumonia, bronchitis, sinusitis, purulent-inflammatory processes, sore throat, tuberculosis. There is not a single branch of medicine where it would be possible to do without them.
If you refuse antibiotic therapy, at best, the disease will become chronic and the person will become a carrier of the infection; at worst, death is possible.
Tatyana Dzyaduk
Allergist-immunologist
What effect do antibiotics have on the immune system?
Antibiotics have an indirect effect on the body's ability to cope with infection. This occurs with improper use (short course) or excessive use of antibiotics (longer than necessary, or not at all according to indications, for example, for the treatment of acute respiratory viral infections).
Antibiotics kill or block the proliferation of bacteria that are susceptible to them. The rest remain alive and continue to reproduce. They are easily transmitted from person to person, and all infections caused by resistant bacteria can no longer be treated with previously used antibiotics. It becomes very, very difficult to choose therapy.
There is no direct effect on immunity!