Ishchenko Tatyana Vladimirovna, Candidate of Medical Sciences
With the advent of antibiotics, childhood rheumatism has ceased to be one of the most common diseases among children. Before the advent of antibacterial treatment, the disease was detected in five children out of a thousand. The use of a therapeutic course of antibiotics reduced the incidence of rheumatism in children by 1000 times.
However, the problem of early diagnosis and prevention of this difficult disease remains to this day. Often doctors simply do not detect it in the non-acute phase. But acute rheumatic fever (ARF) cannot be confused with anything else. In such cases, the diagnosis is unambiguous.
Symptoms and causes of rheumatism in children
The body's autoimmune reaction is the cause of the development of rheumatic syndrome. The immune system mistakenly attacks connective and cartilage tissues, heart muscle and other organs with antibodies. The reason for this failure of the immune system is the destruction of blood cells by streptolysin, produced by streptococcal infection.
It is important to know the first symptoms of rheumatism in children and contact a rheumatologist in time, and not a gastroenterologist and other specialists, since the symptoms can be similar to poisoning, acute respiratory infections and other common childhood diseases.
- The disease usually develops from an acute sore throat (pharyngitis) or otitis media. In some rare cases, the cause may even be caries or a boil.
- Children aged 6-15 years are most vulnerable to childhood rheumatism. Acute rheumatic fever is extremely rare in preschool children.
- A few weeks (from 1 to 5) after recovery from a sore throat, the child may have a sharp rise in temperature to 40°C, as well as pain in the head and joints.
- Under the skin, compacted nodules that are painful when pressed often appear.
Diagnostics
When diagnosing rheumatism in children, both clinical symptoms and examination results are assessed. But not only the signs of rheumatism in children give reason to assert the presence of this disease. In fact, both basic and additional criteria for diagnostic studies are important in this matter:
- myocarditis;
- polyarthritis;
- chorea;
- subcutaneous nodules;
- erythema, prolonged PQ;
- fever;
- fatigue;
- nosebleeds, etc.
In order to follow not only the signs of rheumatism in children, but also the results of research, the doctor prescribes:
- general, immunological and biochemical blood test;
- electrocardiography;
- echocardiography;
- chest x-ray.
Only when rheumatism in children has been diagnosed is treatment prescribed.
A full examination can be carried out at JSC “Medicine” (clinic of Academician Roitberg). The clinic is located in the center of Moscow.
Types of childhood rheumatism
- Acute rheumatic fever. ARF affects the joints and provokes the development of reactive arthritis in children. Swelling, redness and constant pain in the knees and ankles are the main symptoms. The pain syndrome is relieved by acetylsalicylic acid, but there is a high probability of its return after 2-6 days.
The danger of ARF lies in the high probability of an erroneous diagnosis. The temperature subsided, the pain went away, and doctors consider these to be common childhood diseases associated with acute respiratory infections and the development of the child’s body. But untreated rheumatism leads to serious heart problems.
- ARF and cardiac symptoms. Shortness of breath, cough and rapid pulse, and sometimes in combination with abdominal pain and vomiting, are signs of acute rheumatic fever with heart damage. They may appear several weeks after a sore throat.
Many parents and even doctors attribute such symptoms of ARF to poisoning, but delay can lead to serious problems in the heart muscle. You should immediately contact a rheumatologist and cardiologist.
- Rheumatic chorea. Several months (from 2 to 5) after suffering from pharyngitis and complete recovery, muscle twitching may appear on the face, legs and arms.
Since the sore throat was relatively long ago, parents are not inclined to associate these symptoms with the disease and do not mention it when visiting a doctor. Over time, the teak becomes more and more noticeable. This type of childhood rheumatism is more common among girls.
How to recognize the disease
The external signs of rheumatism are varied, and the course of the disease can be acute, subacute, protracted or recurrent. Symptoms depend on the nature of the process and which organs are affected by inflammation. A typical clinical picture appears in the second or third week after a streptococcal infection. The patient's temperature rises, weakness, increased sweating, and headaches develop. At an early stage, arthralgia is possible - painful sensations in large or medium-sized joints. They are present in almost all patients.
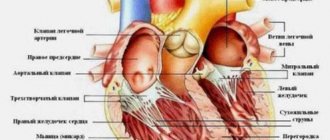
After two to three weeks, to the listed symptoms of rheumatism, signs indicating damage to the heart tissue are added. Various manifestations in the form of pain localized in the heart area, rapid heartbeat, and shortness of breath are recorded in 70-80% of patients. The disease affects all the membranes of the heart or some of them. Most often, the inflammatory process involves the tissues of the myocardium and endocardium, less often with the involvement of the pericardium.
Almost all patients experience asthenic syndrome, including fatigue, lethargy, and a feeling of malaise.
In approximately 10% of patients in the most acute phase of the disease, an annular rash appears on the skin - ring-shaped pink rashes that do not protrude above the surface. Very rarely, the inflammatory process affects other organs - lungs, kidneys, liver, etc. This mainly happens in the most severe form of the disease.
Are you experiencing symptoms of rheumatism?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Early diagnosis
To make a diagnosis of ARF, the disease criteria must match in one of the following ratios:
- two main ones;
- one main and two minor;
- three minor ones.
Main criteria:
- twitching;
- inflammation of the heart membranes;
- joint inflammation;
- dense nodules under the skin;
- red blisters.
Minor:
- body temperature more than 38.5°C;
- joint pain;
- increased ESR and ASLO, increased reactive protein.
Why is it dangerous?
In case of severe, protracted or recurrent course of the disease, the patient may develop complications of rheumatism. As a rule, they manifest themselves in the form of impaired cardiovascular function. These are atrial fibrillation, circulatory failure, myocardiosclerosis, heart defects, etc. The result can be thromboembolism of various organs, cavity adhesions of the pleura or pericardium. With thromboembolism of the main vessel or decompensated heart muscle defect, death is possible.
Treatment methods for rheumatism
Treatment of this disease is always complex and consists of successive stages: the first of them is hospitalization and treatment in a hospital, then follow-up treatment occurs in a cardio-rheumatology sanatorium, after which the child is observed by a cardio-rheumatologist at the place of residence.
Drug treatment consists of prescribing an antibacterial drug that acts directly on streptococcus, the use of non-steroidal and steroidal (hormonal) anti-inflammatory drugs, antihistamines and vitamin therapy.
How to treat?
Since the disease is systemic in nature, treatment of rheumatism is carried out under the strict supervision of medical specialists. As a rule, complex therapy is used, the main goals of which are to suppress infection, stop the inflammatory process and prevent or treat cardiovascular pathologies. The therapy consists of three stages.
- Hospital treatment. It includes drug therapy - taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotic therapy, and other prescriptions depending on the symptoms. If necessary, to eliminate the source of chronic infection, tonsils can be removed, but not earlier than 2-3 months after the onset of the disease. In addition, the patient is prescribed nutritional therapy and exercise therapy. Special diets for rheumatism involve split meals (at least 5-6 meals a day), a high protein content and a minimum of carbohydrates, fresh and processed vegetables. Protein foods are mainly fish, eggs and dairy products.
- Cardio-rheumatic sanatorium. The therapy started in the hospital continues, dosed physical activity, walks, hardening and restorative physical procedures, and dietary nutrition are added to it.
- Dispensary observation. At this stage, the goal of treatment efforts is preventive measures to prevent relapses and stop the process.
Timely detection and adequate therapy, as a rule, lead to complete recovery of patients.
Forecast
The prognosis for this disease is made taking into account the nature of the disease and the degree of myocardial damage.
The frequency of observation by a cardiologist depends on:
- phases of the disease
- attack frequency
- severity of attacks
- associated septic condition
- circulatory failure.
An unfavorable prognosis is observed in young patients with associated septic process, when death is possible. Deaths are observed in patients due to acute coronary circulatory disorders.
Don't risk your health! Timely contact with a qualified doctor and the adoption of emergency measures, as well as competent organization of the regime in the active phase of the disease, can prevent the development of irreversible heart damage and improve the prognosis.
Medical diagnostic methods
To diagnose rheumatism, the patient is usually prescribed:
- ECG to detect disturbances in the contractile rhythm of the heart;
- an x-ray of the heart, which reveals changes in the configuration of heart tissue and signs of a decrease in its contractile function;
- Heart ultrasound or echocardiography to identify defects;
- laboratory tests, the results of which show the presence of streptococcal infection, inflammatory process and immune pathology.
According to the generally accepted diagnostic rule, the presence of the disease is confirmed by identifying two major criteria or two minor and one major criterion for rheumatism.
Symptoms
The manifestation is very diverse and is largely determined by the localization of the process. There may also be a hidden latent current.
In 100% of cases with rheumatism, the heart is affected, so-called rheumatic carditis develops, which manifests itself:
- severe shortness of breath
- rapid heartbeat, irregular heartbeat
- pain in the heart
- swelling
- Expansion of the borders of the heart is detected during examination, and a heart murmur is detected during listening.
Rheumatism also affects the joints - typically an acute onset, damage to predominantly symmetrical large joints, rapid spread from one joint to another (“volatility”), pain of varying severity, up to sharp pain in the joints with limited mobility, swelling of the periarticular tissues, redness. A rapid response to adequate therapy with a decrease in symptoms is also typical.
When the central nervous system is damaged, the following manifestations of the disease may appear: movements of various involuntary muscles (facial muscles, upper and lower extremities, neck and torso). This is manifested by grimaces, antics, theatrical movements, sudden changes in handwriting, and slurred speech.
Also possible:
- increase in body temperature (in some cases up to 40 degrees)
- bouts of severe chills
- pronounced sweating
- general loss of strength
The first rheumatic attack may go unnoticed. After months or even years, a long remission may suddenly end. Repeated attacks occur with similar manifestations, which often lead to severe joint deformities and heart defects.
Types of rheumatism
There are four forms of the disease:
- cardiovascular
- polyarthritic
- nodose
- cerebral
Each form of the disease has its own distinctive signs, according to which only a cardiologist is able to assess the situation and prescribe competent treatment.