1.General information
Laryngospasm (spasm of the larynx) is an involuntary and uncontrolled contraction of the muscles of the larynx, during which the glottis closes, the flow of air into the airways is blocked and a state of inspiratory asphyxia occurs (inability to inhale).
Prolonged asphyxia can lead to general oxygen starvation of tissues and death.
Due to the age-related characteristics of the structure and functioning of the ENT organs, laryngospasm is most often observed in children in the first months and years of life, but it also occurs in adults.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Cramps due to eating
Eating certain foods causes a sharp contraction of the muscles of the pharynx and esophagus. The cause of spasms in the throat can be a large lump of hard, dry food.
Accidental ingestion of sharp bones also leads to esophageal obstruction.
Errors in nutrition play an indirect role in reflux disease: eating spicy, fatty foods is a factor in increasing the acidity of gastric juice.
In a patient suffering from this disease, hydrochloric acid is partially released into the esophagus. The contents of the stomach irritate the walls of the organ and cause them to contract sharply, which feels similar to the feeling of a lump when swallowing.
A gastroenterologist decides how to relieve unpleasant spasms in the throat with reflux esophagitis.
2. Reasons
Laryngospasm is a neuromuscular reflex that can be caused by many factors.
The main groups of such reasons include:
- inflammation in the respiratory system (pneumonia, bronchitis, tracheitis, laryngitis, etc.);
- neurodegenerative diseases (especially those affecting the spinal cord);
- infections and tumors of the central nervous system;
- severe generalized infections (eg, tetanus);
- irritation of the larynx with chemicals, allergens, medications, very cold or hot air;
- deficiency of vitamins and/or microelements;
- vascular pathology (severe hypertension, aortic aneurysm, etc.);
- neuropsychic factors (psychotrauma, hysterical attack, nervous overstrain, severe crying in children, fear or laughter);
- foreign bodies or tumors in the upper respiratory tract.
Visit our Otolaryngology (ENT) page
Causes of spasm in throat
Spasms are distinguished:
- Situational. A sharp muscle contraction is provoked by external causes.
- Endogenous. Caused by internal factors. For example, we are talking about the presence of a concomitant disease in a person.
Situational spasms in the throat are caused by the following reasons:
- Inhalation of air containing irritating substances.
- Use of medications with spasmogenic side effects.
- Stressful situations, excessive emotional and physical stress, even severe sharp pain.
- Sloppy eating.
- Interaction with any source of allergens.
The main groups of pathologies that can cause muscle spasms in the throat area:
- Diseases of the endocrine system (damage to the thyroid and parathyroid glands).
- Psychoneurological disorders (hysteria).
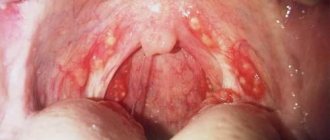
- Upper respiratory tract infections (common causes are laryngitis, acute tonsillitis, pharyngitis).
- Vascular pathology (condition after a stroke).
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (reverse reflux of hydrochloric acid with reflux esophagitis).
- Oncopathology (irritation of the nerve endings of the muscles by large tumors).
- Diseases of the musculoskeletal system (muscle spasm of the pharynx and esophagus due to hernia of the cervical spine).
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
Against the background of the above conditions, diseases and influences, laryngospasm often develops suddenly. However, in some cases it is preceded by such warning signs as shortness of breath, hoarseness or decreased voice volume (up to complete aphonia), and a “barking” cough with laryngitis. The classic clinical picture of laryngospasm includes changes in complexion, noisy shallow breathing, and panic (which in this condition can rapidly develop not only in a child, but also in an adult). The head is usually thrown back, and with severe hypoxia, cyanosis is observed. Choking, the patient may lose consciousness; in severe cases, cardiac arrest occurs. Sometimes laryngospasm is accompanied by an epileptiform seizure, including involuntary relaxation of the sphincters.
The duration of laryngospasm ranges from a few seconds to several tens of seconds. With hysteria, the attack passes spontaneously and does not require outside help (most often it is enough to eliminate the psychogenic situation or simply deprive the patient of the audience, i.e. leave the room).
If there is a predisposition to laryngospasms, they may occur repeatedly during the day. There is a tendency towards seasonality: laryngeal spasms are more often observed in the cold season.
The diagnosis is established clinically and anamnestiically. During laryngoscopy, a tight closure of the vocal cords and arytenoid cartilages is observed.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Main and accompanying symptoms
Spasms in the throat can manifest themselves in the form of the following main symptoms:
- Breathing problems. The degree can range from mild difficulty in breathing (inspiratory dyspnea) to a feeling of suffocation. Inhalation of air is accompanied by noise, sometimes a slight whistle and a barking cough (in a child).
- Feeling of a lump or foreign body in the throat. The patient is unable to quickly get rid of it; drinking water does not always help. Throat spasms may become worse when swallowing.
- Pain syndrome. Caused by pathological tension of the cervical muscles. Light pressure on the throat may increase spasm and pain.
4.Treatment
First aid includes providing a supply of fresh, preferably moist, air. It is extremely important to calm the patient and stop panic, but if laryngospasm occurs in a child, this is extremely difficult to do in practice. In some cases, locally distracting pinching, patting, artificially inducing vomiting, or sprinkling the face with drops of water help. It should be remembered that prolonged asphyxia can be fatal; Thus, laryngospasm is an emergency condition and requires an immediate call to the ambulance. In the most severe cases, the patient is intubated or an emergency tracheostomy is performed, but it is obvious that these operations can only be performed by a doctor.
Treatment strategy and tactics are determined by the results of a mandatory diagnostic examination. In particular, the primary measure may be to eliminate hypovitaminosis and micronutrient deficiency. In other cases, neurological or psychotherapeutic treatment is necessary. Physiotherapeutic procedures, restorative measures, and sanatorium-resort treatment play an important role.
It is noted that the tendency to laryngospasm in children usually decreases spontaneously during puberty and adulthood.
Endocrine pathologies
The feeling of squeezing of the throat and lack of air is sometimes caused by pathology of the thyroid gland. This is due to the pathological growth of organ tissue - goiter. The throat is subject to compression in moderate to severe cases of the disease. Then the pain may join.
Severe muscle spasms in the throat are also caused by damage to the parathyroid gland. A decrease in the level of parathyroid hormone leads to a pronounced lack of calcium and an excess of phosphates in the blood. Such an imbalance in the body is the cause of painful cramps.
The pain affects almost all muscle groups, including the esophagus.
Diagnostics
Finding the pathology that provoked the syndrome is difficult. This is explained by the polyetiology (multiple causes) of throat spasm. What to do if this complaint occurs will be determined correctly by your attending physician.
The first doctor you should contact with a problem is a therapist. Given the location of the complaint, the patient should be examined by an otolaryngologist. If necessary, consultations with an oncologist, gastroenterologist, and other specialists are held.
If there are no signs of persistent physical pathology, the diagnostic search begins with the exclusion of external causes that can provoke a throat spasm and its accompanying symptoms.
For example, the doctor may ask whether the patient is allergic to any substances or whether stress preceded the throat spasm.
Basic research methods:
- Pharyngoscopy. The search for the cause begins with a direct examination of the pharynx using a spatula.
- Laboratory blood tests. Helps identify common signs of inflammation. If a tumor is suspected, tumor markers are checked. In some cases, hormonal levels are examined.
- Laryngoscopy. An instrumental diagnostic method that allows you to assess the general condition of the mucous membrane of the larynx and glottis.
- FGDS (fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy). A method aimed at finding the cause of pathology along the digestive tube.
- Ultrasonography. Used to exclude thyroid diseases.
The list of studies is supplemented during the diagnostic search to determine the reason why the patient suffers from muscle spasms in the throat.
Throat spasm prevention
To avoid symptoms such as throat spasms, pain and choking, it is recommended:
- Compliance with the work and rest regime.
- Avoiding stressful situations.
- Proper nutrition, eating sufficiently crushed foods, chewing thoroughly.
- No contact with already known allergens.
- Timely treatment of concomitant diseases.
If the patient has studied many information sources and theoretically knows how to get rid of a spasm in the throat, this does not eliminate the need for qualified medical care.
At best, illiterate self-medication will lead to a loss of time, at worst, it will cause death. Only a doctor will correctly determine how to treat a patient’s throat spasm. Treatment depends on the cause of the condition, of which there are many.
Throat neurosis, dysphagia (spasms, VSD)
Anastasia, Moscow
7842 views
May 26, 2020
Good afternoon, dear specialists! I will briefly describe my problem: over the course of 4 years, due to stress and family disasters, all the symptoms of VSD and laryngeal neurosis appeared in all their glory (I know that it is not a disease, but a number of neurological disorders). Now the slightest stress, tears or anxiety with worry: immediately there is nervous dysphagia! It has reached such a point: I can’t eat or drink for periods; I have a strong spasm in my throat and I CAN’T SWALLOW anything. I’m exhausted, I can endure anything! But here there is a complete shutdown of the swallowing function, a spasm of the throat (a choking sensation and the throat is all constrained with the nasopharynx) and after a while saliva is swallowed with difficulty, then saliva disappears, insomnia torments, cramps and numbness in the arms and legs, face, tremors. Coldness of the extremities and numbness (everything inside has been examined - there are no pathologies, only gastritis, esophagitis and reflux, a lump in the throat is bothering me. The thyroid gland is also normal, all hormones are normal (nodules now and no pathologies there) except androgens - dihydrotestosterone: increased, struggle with I've been around for a long time) I have to control the swallowing process, it gets to the point of fright and it becomes even worse. There is osteochondrosis of the cervical spine (and this is asthenic weakness, almost constant headaches and severe pain in the back of the head, difficulty breathing and low blood pressure: 90/60, rarely rises higher than that). Plus, 7 years of sinus tachycardia (when walking and after eating, the pulse can be 120-150 at once, and out of the blue, ultrasound of the heart was done more than once and recently a Holter was installed, a small number of systoles: mitral valve prolapse of 1-2 degrees, periods of extrasystole). How can you combat such disorders, in particular swallowing problems. Thank you very much! (There were 2 thrombosis of the legs of the lower extremities after injuries). AND THE MOST IMPORTANT THING: WHAT TO REMOVE STRONG LARRYNAL SPASMS so that the water doesn’t get stuck (this week I was in an ambulance 3 times and couldn’t relieve the spasms). The next appointment at the neurosis clinic is in a week or two. I would be very glad for any tip or specialist (because this is already a complete nightmare). Abdominal ultrasound done, MRI 3 years ago: nothing to complain about, 3 years in a row: gastroscopy, superficial gastritis, and in 2021 they diagnosed cardiac insufficiency of the esophagus, they said it’s no big deal). In turn, I will list the main drugs that were prescribed by specialists: Cipralex was in 2016 for 7 months (nothing else from the blood pressure is suitable, the last one was prescribed 2 weeks ago amitriptyline: it was wildly bad and I tried to take it for a week, I just lay there and didn’t eat) , from tranquilizers: phenazepam and clonazepam are known to everyone (I took a clone for almost 1.5 years, 1/4 or 0.5, rarely of Polish origin), our Russia does not help, (now there was a break of 7 months in taking it), then we tried: phenibut, Atarax, Stresam, Grandaxin, Trittico, Velaxin, Fevarin, Taraligen, Prosulpin, Alprozalam (I took it for 3 weeks: there was a zombie effect, it did not help with dysphagia). I understand that the issue is complex and, unfortunately, I can’t overcome the problem. Thanks a lot!
The question is closed
tremor
Dysphagia
throat neurosis
the spasm is strong
Spasm in the throat treatment
If a throat spasm suddenly occurs, what should you do? First of all, you should not give in to panic.
Measures:
- Provide fresh air by opening a window.
- Give some water at room temperature. Hot or too cold liquid can make the condition worse.
- Loosen tight clothing, remove your tie, unbutton your shirt collar.
- If a spasm of smooth muscles in the throat is caused by inhalation of irritating substances, immediately stop their intake or take the patient to a safe place.
- Conveniently position the patient.