How does pain occur? What is coccydynia?
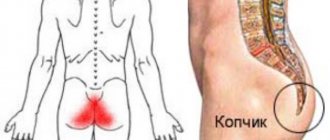
Pain in the tailbone when sitting
Spasm of the pelvic floor muscles occurs reflexively, as a reaction to injury, diseases of the pelvic organs, degenerative changes in the spine and intervertebral discs.
A long-term spasm leads to a secondary change in the structure of muscles and ligaments, in the form of their thickening and shortening (fibrosis and contracture are formed). Both spasm and fibrosis cause tissue tension in the tailbone area. This tension ultimately leads to compression (pinching) of the nerve fibers, resulting in pain in the tailbone.
Painful sensations in the coccyx area have a medical term - “coccydynia”. Pain in the coccyx is also what is meant when talking about pelvic floor muscle syndrome or sacrococcygeal joint syndrome.
Pain after injury
Most often, a serious injury to the tailbone is caused by a sharp fall - in winter or during training - or by strong blows, accidents, when other injuries are superimposed on the bruise. Riding on a hard seat over potholes and rocks can also damage the integral structure of the coccyx, but this happens gradually.
As a rule, victims are in no hurry to go to medical institutions, hoping for self-healing.
Women damage their tailbone during difficult childbirth, especially if the child is large. Pregnancy itself is a factor that thins bones, so the risk of fracture or crack increases.
A deformed coccyx also occurs in infants. Coccyx injuries are classified depending on the type of violation:
- bruise of himself and nearby soft tissues, internal and external;
- dislocation and subluxation, there are anterior and posterior;
- displacement with a bend - forward, to the side, with displacement of the vertebrae in different directions;
- fractures, like any other bone structure, are divided into closed, open, displaced, fragmentation;
- damage, sprains, ruptures of the ligaments of the sacrococcygeal structure.
If there is a bruise in the lower back, hematomas, vascular hemorrhages, excision of the muscles and fat layer, and deformation of the vertebrae are possible in this area. And the symptoms of even a simple bruise are very painful. If the coccygeal region is injured, the general condition may deteriorate, headaches, and nausea may appear as a sign of a concussion.
Pain in the tailbone has its own characteristics
Pain in the tailbone or coccydynia can be aching, cerebral, convulsive, with a burning sensation. According to patient descriptions, the pain is “boring”, deep, and gets on the nerves. Pain and burning often radiate to the anus, buttocks, sacrum, genitals, lower back, and posterior thighs.
The pain often decreases or disappears when standing. Pain appears or intensifies when lying on your back, when bending the torso forward, or while sitting, especially on a hard chair. The longer the patient is in a sitting position, the more pronounced the pain is, and when standing up it may intensify.
Unpleasant sensations in the tailbone area often worsen during menstruation and sexual intercourse. During the act of defecation, pain in the tailbone can also intensify, especially in people who have suffered a severe injury to the tailbone.
With coccydynia, constipation, urinary retention, and sexual dysfunction are common. As a rule, the above complaints are accompanied by a decrease in mood, up to the development of a depressive type of personality.
Pain after childbirth
Nagging pain in the tailbone after childbirth can occur for some time, up to six months. This is explained primarily by hormonal changes and the load on the tailbone directly during the birth of a child. Sometimes injuries occur that require treatment or require wait-and-see tactics, massages, or a visit to the pool.
Also, women who have recently given birth to a child need to sit less
. The brand has been shrinking for some time and sometimes there is excess weight. It is this that can also provoke curvature of the spine, since a woman leans forward when sitting. When walking, the tailbone and hip joints also suffer due to excess weight.
What will help with pain after childbirth
take medications while breastfeeding
, including painkillers, so in this case, an effective and optimal method of quick recovery would be to prescribe a massage and visit the pool, water aerobics is especially helpful. This procedure is usually carried out both with women individually and in groups of several mothers with children.
Hydrotherapy helps
, electric shock, other physiotherapeutic procedures.
Pain during pregnancy
The tailbone often hurts during pregnancy. This is also explained by the heavy load, since as the child grows, the abdomen enlarges, the spine bends, blood circulation worsens, and there is a greater load on the pelvis and legs. At the same time, the pelvis naturally expands, preparing for the birth of a child. This process is quite normal, but it can lead to severe pain, which you often just have to endure. You can alleviate the syndrome by visiting a fitness center for pregnant women.
, in which, with the help of special exercises on a fitball, you can relieve the load from the pelvis and spine.
What causes severe pain in the sacrum?
Also due to stress, incorrect position when sitting or lying. An unpleasant feeling in pregnant women and women who have already given birth may be associated with constipation, which, as a rule, goes away almost immediately after the birth of the baby.
Thus, painful sensations bring a fair amount of discomfort, they are usually dealt with with the help of painkillers, but it is not recommended to delay diagnosis and treatment
if, while sitting or standing up, you feel an aching feeling that radiates to other parts of the body - to the lower back, spine, stomach. This is especially dangerous if the cause of all the pain is a tumor, inflammatory or infectious processes, or hemorrhoids. Depending on how quickly treatment was started, it will be possible to effectively overcome the pain and alleviate the condition.
Initially, it is better to consult a therapist
, he will also refer you to a proctologist, rheumatologist, possibly an orthopedist, surgeon or other specialist. It depends on what symptoms, signs and suspicions doctors have for certain diseases in a particular patient.
Treatment of coccydynia
In order to properly treat patients with complaints of coccydynia, it is necessary to determine the true cause of this suffering, that is, to make the correct diagnosis.
Most often, these are functional and structural changes in the muscles and ligaments of the pelvic floor, which appeared as long-term consequences of injuries or osteochondrosis of the spine with hernias and protrusions of intervertebral discs. But pain in the coccyx can be caused by diseases of the rectum and organs of the genitourinary system, as well as injuries, tumors and infectious inflammatory processes in the coccyx or sacrum itself.
Sign up for a consultation by phone
Diagnosis of the problem
For diagnostic purposes and to exclude a wide range of diseases, the patient is examined to identify the source of coccydynia - an examination is carried out during which the anal canal, rectum, organs of the reproductive system, lumbar and sacral spine are examined.
The use of hardware examination methods is justified:
- X-ray of the spinal column showing degenerative changes in the lumbar and sacral regions;
- CT and MRI;
- Ultrasound of the reproductive system and pelvic organs.
What research is needed?
If you are concerned about pain in the tailbone, then the following diagnostic measures are necessary:
- A thorough survey. Attention is drawn to previous injuries, operations, manipulations of the pelvic cavity and abdomen, and patterns of pain in the perineum.
- Neuroorthopedic examination of the condition of the pelvic joints, ligaments, muscles of the perineum, buttocks, and pelvic floor. Palpation of the pelvic floor muscles is carried out through the rectum.
- X-ray of the coccyx in two projections after preliminary bowel preparation (cleansing with an enema or laxative).
- Laboratory tests of blood and urine.
- According to indications - consultations with a proctologist, urologist, gynecologist.
Final indicators
Pain level assessment
- 4-dimensional pain intensity index (P4).
- Brief pain questionnaire.
- Numerical pain rating scale.
- Brief McGill Pain Questionnaire.
- Visual analog scale.
Level of function in daily life
- Pain Disability Index (Oswestry).
Specific questionnaires
- Pelvic floor questionnaire.
- Questionnaire for assessing the pelvic girdle.
What treatment for tailbone pain is effective?
In order for the treatment of coccydynia to be successful, it is necessary to relax the pelvic floor muscles, restore the elasticity of the ligamentous apparatus, and normalize the function of the sacrococcygeal joint and sacroiliac joints using manual therapy techniques.
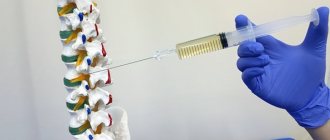
The chiropractor performs relaxation of the pelvic floor muscles through the rectum. This process is painful, but quite tolerable. According to indications, therapeutic blockades of trigger zones are included in the treatment regimen for pain in the coccyx.
Therapeutic blockades are also performed by a chiropractor. If there is simultaneously pain in the coccyx and a disease of the genitourinary system or rectum, then, in addition to a chiropractor, treatment by a gynecologist, urologist or proctologist is necessary.
Sign up for a consultation by phone
Relief at home
NSAID tablets help relieve pain. But they cannot be used for more than a week, as they provoke ulceration of the gastric mucosa. It is better to use products for local application - anesthetic ointments, gels, creams. You can reduce the severity of pain using orthopedic pillows and bandages.
How is the tailbone structured?
How many vertebrae are there in the coccyx
In humans, the coccyx consists of 3-5 coccygeal vertebrae. The coccygeal vertebrae are connected to each other by cartilaginous plates. In older people, the coccygeal vertebrae often fuse into one bone.
Muscles and ligaments of the coccyx
Partially the piriformis and partly the gluteus maximus muscles, as well as the coccygeal muscles lying on the sacrospinous ligament, are attached to the outer parts of the lower sacral and upper coccygeal vertebrae.
Below is the muscle that lifts the anus. All these muscles are a structural element of the pelvic floor.
The sacrospinous and sacrotuberous ligaments are partially attached to the anterior walls of the coccyx.
The anal sphincter and anal-coccygeal tendon are attached to the tip of the coccyx.
The coccyx connects to the sacrum through a full intervertebral disc.
In addition to the intervertebral disc, the sacrococcygeal joint includes anterior, posterior longitudinal and lateral ligaments.
Coccygeal nerve plexus
In front of the coccyx is the coccygeal nerve plexus, formed by the anterior branches of the fifth sacral and coccygeal nerves. This plexus is located on the coccygeal muscle and the sacrospinous ligament, is anatomically connected to the lower parts of the sympathetic nerve trunk and provides innervation to the organs and tissues of the pelvis. The anal-coccygeal nerves extending from the coccygeal plexus innervate the skin in the area of the coccyx and anus.
Diagnostic and treatment methods
If your tailbone hurts when you sit and stand up, a comprehensive examination is necessary. The following are used today as effective diagnostic methods:
- X-ray
: allows you to identify pathologies and injuries of the coccygeal bone; - ultrasound examination: necessary to identify pathologies of organs and soft tissues of the pelvis;
- examination of the intestines using endoscopic and non-endoscopic techniques: this is an effective way to confirm the diagnosis with a proctologist;
- tomography: necessary for a detailed examination of already identified pathologies.
A patient with this symptom requires consultation with a number of specialists: proctologist, surgeon, neurologist, gynecologist
or
urologist
. How to treat the tailbone, which hurts when you stand up and sit, the doctor decides based on the diagnosis. The patient may be prescribed the following treatment methods:
- Medication: in this case, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to relieve swelling and spasms.
- Physiotherapy: gentle pressure on the muscles improves blood supply to the coccygeal area and speeds up recovery.
- Massage: aimed at improving blood circulation, suitable for chronic pain.
- Exercise therapy: helps not only to improve the patient’s condition, but also to prevent relapse of the disease.
- Surgery: performed only in extreme cases, when other treatment methods have not brought the expected result over a long period of time.
It is worth knowing that if the tailbone hurts when you sit and stand up, especially severely, and the disease is in the acute phase, some treatment methods are contraindicated. Therefore, using them without the knowledge and consent of a doctor is strictly not recommended.
What happens to the tailbone when pain occurs in it
When the muscles of the lower pelvic floor contract on both sides, the tailbone bends forward; if the muscles contract on one side, the tailbone simultaneously bends and moves to the side.
Normally, movements in the sacrococcygeal segment in the anteroposterior direction are possible within 30 degrees, and lateral deviations are up to 1 cm. Such displacements of the coccyx on an x-ray should not be regarded as a fracture or dislocation. With spastic tension of the pelvic floor muscles, the tailbone in relation to the sacrum takes a position of excessive flexion, and pain most often appears.
Pain in the tailbone may intensify when getting up from a chair. This is explained by the tension of the gluteus maximus muscles, some of the bundles of which are attached to the lateral sections of the sacrum and coccyx.
Sign up for a consultation by phone
Evidence base
- Stretching the piriformis and iliopsoas muscles, as well as Maitland rhythmic oscillatory chest mobilization for 3 weeks (5 sessions per week) showed a significant improvement in pain threshold.
- Extracorporeal shock wave therapy was more effective and acceptable in reducing the discomfort and disability caused by coccydynia than the use of other physical methods. Thus, it has been recommended as an alternative treatment option for patients with coccydynia.
- A combination of manipulation and corticosteroid injections was more effective in treating coccydynia compared with manipulation or corticosteroid injections alone. Patients who underwent treatment were completely free of pain at the end of the year.
- 16% of patients (Wray) had a positive effect from short-wave diathermy.
Prevention
Having figured out why a woman’s tailbone hurts, it is within our power to do everything to eliminate the possibility of a pathological condition occurring. To begin with, you should lead an active lifestyle. This does not mean that you need to immediately sign up for a gym or start running marathons: physical activity must be proportionate to your age and current condition. At a minimum, try to walk every day - half an hour will be enough. Try not to lift weights, this can not only injure your back muscles, but also cause prolapse of your internal organs. In your diet, pay special attention to a balanced diet; avoid frequent consumption of fast food and other generally harmful foods. This is especially true for those who are already experiencing problems with excess weight, endocrine system, and gastrointestinal tract.