Traumatic brain injuries are the most common injuries in various accidents. And often doctors diagnose a “concussion.” What the problem is, how exactly to recognize it, and whether a diagnosis can be made based on external signs, the doctor told AiF.ru.
“A concussion can be caused by trauma - a fall, a blow, a high-energy injury to the head or skull. With such an injury, there is a disruption of the system that is responsible for consciousness, awakening, sleep, and information processing,” says Mark Ivanov, an orthopedic traumatologist at the Khimki Regional Hospital .
General information
A concussion is a condition that occurs as a result of a mild traumatic brain injury. As a result of the concussion, interneuronal connections are temporarily disrupted. It occurs very often and ranks 1st among conditions associated with traumatic brain injuries. Despite the fact that the injury is considered relatively minor, it is extremely important after any traumatic brain injury to consult a doctor, conduct examinations and follow his instructions. After all, this condition requires obligatory observance of rest and following other doctor’s recommendations. The ICD-10 code for concussion is S06.0.
Pathogenesis
Normally, the human brain is located in the cerebrospinal fluid. When you shake your head sharply, a hydraulic shock occurs, triggered by a pressure difference in the cerebrospinal fluid. Sometimes the brain can hit the inside of the skull.
With injuries and contusions, a concussion of the entire brain tissue occurs. At the very beginning, there is a diffuse dysfunction of the brain ( fainting ). After a couple of minutes or hours, the severity of general phenomena decreases, and only signs of focal disorders remain in a certain area of the brain.
Symptoms of trauma develop due to the development of functional disconnection of the brain stem and hemispheres. When a shock occurs, some of the physical and chemical properties of neurons change, which can lead to changes in the spatial organization of protein molecules. It is also likely that there is a temporary disconnection of signals between the synapses of neuron cells and parts of the brain. A synapse transmits nerve impulses between cells. This is the site of contact between neurons or between a neuron and the effector cell that receives the signal. And if the relationship is temporarily disconnected, functional disorders develop. During a concussion, the entire substance of the brain is affected pathologically.
Classification
Depending on the severity of the damage to health and what the clinical symptoms are, there are 3 degrees of this condition:
- Easy. If a mild concussion occurs, the victim’s consciousness is not impaired, but he may experience dizziness , disorientation, headache, and nausea for 20 minutes. after suffering a trauma. A mild concussion can lead to a slight increase in temperature - up to 38 degrees. Further, general health improves, unpleasant symptoms disappear.
- Average. The person remains conscious, but he exhibits characteristic signs of this condition - nausea, disorientation, headache, dizziness. These signs do not disappear for more than 20 minutes. Brief memory loss may also occur. In most cases, this is retrograde amnesia , where the victim does not remember the several minutes before the injury occurred.
- Heavy. There is a loss of consciousness for a short time. This state can last for minutes or hours. The person does not remember what happened - he develops retrograde amnesia. After an injury, unpleasant symptoms may remain with the victim for one or several weeks. During this period, dizziness, headaches, nausea, disorientation, fatigue, poor sleep and appetite .
It takes time to recover
A person who has suffered a head injury needs time to recover. Do not return to exercise until your doctor allows it.
Those who begin vigorous physical activity too early have a high chance of suffering a second concussion due to poor coordination and balance. New head injury may cause permanent damage
brain
Try to stop reading (especially on mobile devices!), watching TV, and working on the computer for at least a week.
Symptoms of a concussion
It is important to understand that a concussion can occur even when the severity of the injury is relatively minor. Therefore, it is very important to be attentive to the condition of the victim and not to miss the first signs of a concussion.
So, the first signs of a concussion are as follows:
- Confusion that disappears after a short time.
- Dizziness – the patient’s head is dizzy even at rest, but when the body moves or the head tilts, it intensifies. Such symptoms of a concussion are associated with impaired blood circulation in the vestibular apparatus.
- Throbbing headache.
- Feeling of tinnitus.
- Feeling weak.
- Nausea, vomiting, occurring once.
- Noise in ears.
- Confusion, lethargy, incoherent speech.
- Double vision. Even a mild concussion can cause a person's eyes to hurt when trying to read.
- Photophobia . Even the usual level of light can cause discomfort. Increased sensitivity to sounds is similarly manifested.
- Impaired coordination of movements.
In many situations, after an injury, it is very important to find out whether a person has a concussion. There is a very simple method for determining a concussion at home. To do this, the victim must close his eyes, stand, raise his arms to the sides, and then try to touch the tip of his nose with his index finger. Even if signs of a mild condition appear, this will be difficult to do.
Another option is used to help you understand at home that you have a concussion. The victim should close his eyes, raise his arms and walk in a straight line, placing one foot after the other. But someone must monitor this, since the victim risks falling due to disorientation.
Symptoms of concussion in adults after injury can vary in severity. As a rule, pronounced signs of a concussion in adults persist for 1-3 days after a blow or other injury.
As for whether there can be a temperature in this condition, it must be taken into account that such a manifestation occurs often. After a concussion, there may be a temperature - it rises to low-grade levels.
Sometimes victims exhibit neurological symptoms. However, in some cases they are absent. As a rule, victims experience changes in pulse rate and blood pressure, lethargy, and memory deterioration.
It is important to understand that people with a concussion may not exhibit all of the symptoms described. But in any case, if you suspect a concussion, you should not hesitate to visit a doctor.
Symptoms of a concussion in a child
If you can check the condition of an adult using the methods described above, then recognizing the signs of such a condition in an infant or in a child 2-3 years old is more difficult. This condition manifests differently in children than in adults. Diagnosis is complicated by the fact that it is not always possible to trace the connection between symptoms and the disease. In addition, the signs are often nonspecific.
How to determine this condition in a baby? Typically, an infant who has suffered a concussion will exhibit the following symptoms:
- regurgitation during feeding;
- vomit;
- rapid heartbeat;
- decreased blood pressure;
- manifestation of anxiety, which is soon replaced by severe lethargy;
- crying for no reason.
The first signs of a concussion in children may include severe pale skin. Consciousness may not be impaired.
Signs of a concussion in a child 1 year of age and older manifest themselves with the same symptoms as in adults. Such babies, as well as children 2 years of age and older, may experience loss of consciousness. Sometimes the baby feels nauseous, is bothered by vomiting, has a headache, and the baby complains of tinnitus and dizziness. The child may not sleep well or sweat a lot. In some cases, children experience temporary post-traumatic blindness. Sometimes there is a so-called period of “imaginary well-being”, when immediately after the injury the baby feels normal. But later the condition worsens.
If a child has a brain or spinal cord injury, you should see a doctor immediately.
Treatment methods
A neurologist will tell you how to treat a mild concussion. Usually the patient is under medical supervision in the hospital for several days, then he is sent home. The patient is prescribed bed rest. In the acute period, symptomatic treatment is carried out. In most patients, regression of symptoms (head pain, dizziness) occurs without treatment within a few days. In some cases, the recovery period takes longer – several weeks.
The speed of recovery correlates with the severity of the injury, the age and general health of the patient. In young patients whose duration of loss of consciousness was no longer than a few seconds, complete recovery usually occurs within 1-2 weeks. In patients over 50 years of age, recovery processes are slow, and recovery may be incomplete. Factors influencing the recovery process:
- History of somatic diseases and mental disorders.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Rental attitudes (readiness to receive benefits associated with an unfavorable situation - insurance, disability benefits, medical care, increased attention from loved ones).
Medical observations show significant heterogeneity in clinical manifestations in patients who have suffered an episode of mild concussion. A head injury is a significant stress factor that can cause serious consequences in the future.
Drug therapy
Therapy for a minor concussion involves eliminating symptoms - headaches, sleep disturbances, irritability and anxiety. An important therapeutic direction is the restoration of brain functions. Treatment for mild concussion includes taking pharmaceutical medications:
- Analgesics (to relieve pain).
- Vestibulolytics (to eliminate vestibular disorders - dizziness, impaired motor coordination).
- Tranquilizers, antidepressants (to combat anxiety disorders and depression).
- Anticonvulsants (to eliminate seizures).
- Hypnotics (to combat sleep disorders).
The doctor will determine what medications the patient should take, due to the need for complex therapy taking into account clinical manifestations. Psychotherapy refers to auxiliary methods of treatment.
Tests and diagnosis of concussion
Often people do not understand exactly which doctor to contact if they have a concussion. It is important to note the following: you should contact your doctor immediately. That is, after an injury, it is important to call emergency care, whose specialists will assess the patient’s condition and determine who to take the child to in case of a concussion or where to hospitalize the adult. Such signs should be addressed to neurological specialists.
How to diagnose a concussion? The doctor conducts a survey and examination, paying attention to the characteristic signs of the condition:
- The victim experiences pain when he moves his eyes to the sides; he cannot move them to the most extreme position.
- Immediately after the injury - in the first hours - there is a slight narrowing or dilatation of the pupils. However, they react normally to light.
- There is a slight asymmetry of reflexes - skin and tendon. On the right and on the left they are different. But since this sign is very variable, upon repeated examination the picture may change.
- In the extreme position, slight return movements of the pupil are observed.
- Unsteadiness is noted when a person takes the Romberg position (eyes closed, legs together, arms in front of you).
- Your doctor may notice mild neck tension that goes away within the first three days.
In the process of establishing a diagnosis, a specialist can use the following methods:
- examination, questioning of the patient;
- radiography of the skull bones;
- CT scan;
- MRI;
- electroencephalography;
- neurosonography (children under 2 years old).
Diagnostics
When diagnosing a concussion, it is especially important to take into account the circumstances of the injury and information from witnesses to the incident. Traces of trauma on the head and factors such as alcohol intoxication, the psychological state of the victim, etc. can play a dual role.
A concussion often has no objective diagnostic signs. In the first minutes and hours, the doctor and other witnesses may see a loss of consciousness (for several minutes), twitching of the eyeballs when looking away to the side, disturbances in balance and coordination of movements; victims complain of double vision.
There are no laboratory or instrumental signs for diagnosing a concussion:
- There are no fractures of the skull bones during the concussion.
- Pressure and composition of cerebrospinal fluid without deviations.
- Ultrasound examination (M-echoscopy) does not reveal displacement or expansion of the midline structures of the brain.
- Computed tomography in patients with concussion does not reveal traumatic abnormalities in the state of the brain substance.
- Magnetic resonance imaging data for concussion also do not reveal any damage.
A concussion often masks more severe traumatic brain injuries, so patients are subject to emergency hospitalization in a neurosurgical hospital (or another profile where neurotraumatological care is provided) mainly for examination and observation.
Thus, a concussion can be identified based on:
- data observed or reported by the patient about loss of consciousness at the time of injury.
- nausea, vomiting, complaints of dizziness and headache.
- absence of signs of more severe injury (loss of consciousness for more than 30 minutes, convulsive seizures, paralysis of limbs).
Treatment with folk remedies
To speed up the healing process, you can use some folk remedies.
- Infusion of mint, lemon balm and mistletoe. Take 1 tbsp. l. each of the herbs, pour into a thermos and pour 2 tbsp. boiling water Infuse overnight, drink half a glass 4 times a day.
- St. John's wort decoction. It is prepared from 2 tbsp. l. St. John's wort and 1 glass of water. The decoction should be brought to a boil, infused and drunk 100 g three times a day.
- Restoring infusion. Take 10 g of mint leaves, hop cones, buckthorn bark, lemon balm herb and 20 g of valerian root. Mix all ingredients, take 2 tbsp. l. means and fill it with 2 tbsp. boiling water Drink 100 g several times a day, be sure to take the infusion before bed.
- Soothing infusion. You need to take 2 tbsp. l. herbs mint, motherwort and lemon balm, pour 1 liter of boiling water and leave overnight. Drink half a glass three times a day.
- The infusion is soothing and restorative. It is necessary to take hop cones, buckthorn bark, lemon balm, valerian root, birch leaves, fireweed, and St. John's wort in equal proportions. Pour 3 tbsp. l. this collection with one liter of boiling water and leave for 2 hours. Drink half a glass 3 times a day.
- A remedy for insomnia. Mix 1 tbsp. l. mint herbs and 1 tsp. cinnamon. Pour boiling water (1 liter) and leave in a thermos for 2 hours. Drink 4 r. 100 g per day, also taken before bed.
- A mixture of honey and nuts. Chopped nuts should be mixed with honey in equal proportions and take 1 tbsp of this remedy. l. every day for six months.
- Bee pollen. It is recommended to take its granules - half a teaspoon per day for a month. Repeat after six months.
- It is recommended to sleep on a pillow with soothing herbs - mint, lemon balm, lovage, clover.
Treatment of concussions
In case of a concussion, treatment is prescribed by a neurologist.
Drug treatment for concussion is often not required and is symptomatic (the main treatment is rest and healthy sleep). Pharmacotherapy is mainly aimed at normalizing the functional state of the nervous system, eliminating headaches, dizziness, anxiety, insomnia and other complaints.
Typically, the range of medications prescribed upon admission includes painkillers, sedatives and sleeping pills, mainly in the form of tablets, and, if necessary, injections.
Among the painkillers, the most effective drug for a given patient is selected:
- analgin,
- pentalgin,
- dexalgin,
- sedalgin,
- maxigan, etc.
They do the same for dizziness, choosing one of the available medications:
- belloid,
- cinnarizine,
- platiphylline with papaverine,
- tanakan,
- microzer, etc.
Used as a sedative
- valerian, motherwort, corvalol, valocordin,
- tranquilizers grandaxin, sibazon, phenazepam, nozepam, rudotel, etc.
To eliminate insomnia, it is prescribed at night
- donarmil,
- relaxon.
Conducting a course of vascular and metabolic therapy for concussions contributes to a more rapid and complete recovery of brain dysfunction. A combination of vascular (Cavinton, Stugeron, etc.) and nootropic (Nootropil, Pantogam, Noopept, Mexidol, etc.) drugs is preferable.
Possible combinations could be as follows:
- "Cavinton" 1 tablet (5 mg) and "Nootropil" 2 capsules (0.8 mg) three times a day for 1-2 months
or
- “Stugeron” 1 tablet (25 mg) and “Noopepta” 1 tablet (0.1 mg) three times a day for 1-2 months.
A positive effect is brought by the inclusion in the course of therapy of drugs containing magnesium (Magne-B6, Magnelis, Panangin) and antioxidants Cytoflavin 2 tablets 2 times a day, Mildronate 250 mg 1 tablet 3 times a day.
To overcome frequent asthenic phenomena after a concussion, one of these drugs is prescribed:
- "Phenotropil" 0.1 1 time in the morning,
- "Cogitum" 20 ml once a day,
- “Vazobral” 2 ml 2 times a day,
- multivitamins and polyminerals such as Unicap-T, Vitrum, etc. 1 tab. 1 per day.
Tonic preparations include ginseng root, eleutherococcus extract, lemongrass fruit, Saparal, and Pantocrine.
In elderly and senile people who have suffered a concussion, anti-sclerotic therapy is intensified - statins are prescribed (atorvastatin, rosuvastatin). They also pay attention to the treatment of various concomitant diseases.
After suffering a concussion, the patient is placed under dispensary observation by a neurologist at his place of residence. He visits the doctor several times throughout the year, undergoes an examination, and, if necessary, examinations. If no pathological abnormalities are detected during this time, then the person is removed from the dispensary register.
First aid
If a person is injured and is unconscious or shows signs of disorientation, an ambulance should be called immediately.
- The unconscious victim must be laid on his right side, with his legs and elbows bent and the surface hard. The head should be tilted back and turned towards the ground to ensure good air flow and to prevent choking when vomiting. You should not turn the patient over again and try to determine how badly he was injured. It's better to wait for the doctors.
- If a person is bleeding, it should be stopped with a bandage.
- The conscious victim should be placed in a horizontal position and his head should be raised slightly. It is necessary to monitor his condition, since a period of imaginary well-being may be replaced by a sharp manifestation of serious symptoms.
- It is important to see a specialist, even if the injury seems minor.
In children
A concussion in a child is a serious condition. If children experience the symptoms described above after being injured, they should immediately consult a doctor. In addition, as pediatrician Komarovsky and other experts note, parents should take into account that alarming symptoms can develop within 24 hours after the injury. Therefore, it is important to pay close attention to the baby’s condition.
You cannot use any treatment methods on your own. What to do and what treatment regimen to use is determined only by the doctor. Therapy is usually carried out in a hospital to monitor the child’s condition and prevent possible consequences. With the right approach to treatment, the child’s condition returns to normal in about 3 weeks.
Diet
Diet for the nervous system
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 2 months
- Timing: constantly
- Cost of food: 1700-1800 rubles per week
Nutrition during the period of treatment and recovery must be correct - you need to eat light food, do not overeat, so as not to additionally burden the body. The menu should consist of fresh vegetables and fruits, boiled food or steamed dishes.
During the recovery period, it is important to provide the body with the following substances:
- B vitamins – they normalize the function of the nervous system. The menu should include liver, nuts, asparagus, eggs, legumes, whole grain bread, and fish.
- Iron is necessary for the normal absorption of B vitamins. You should eat buckwheat, oatmeal, wheat groats, legumes, spinach, and chicken.
- Lecithin – improves brain function. This substance is found in poultry meat, eggs, and liver.
- Potassium – It is important to replenish potassium if a person is prescribed diuretics. It is found in dried apricots, dairy products, nuts, raisins, and legumes.
- Vitamin C – improves stress resistance. It is found in rose hips, currants, citrus fruits, viburnum, cabbage, etc.
- Magnesium – protects the body from stress. Contained in nuts, millet, buckwheat, seaweed, and legumes.
Consequences and complications
It is important to understand that the effects of a concussion sometimes occur even years after the injury has occurred. Most often, complications appear after a concussion suffered on the legs. If it is not treated correctly, the risk of such complications also increases significantly.
What consequences can occur after a concussion? The following manifestations are possible as short-term consequences:
- Severe headaches. As a rule, such symptoms disappear after 2-4 weeks, depending on the severity of the disease. Particularly intense pain occurs in those who suffer from hypertension. What to do if you have a headache after this period, the doctor will determine after additional examinations.
- Memory impairment, concentration, absent-mindedness . In a child, these manifestations can lead to deterioration in school performance.
- Dizziness.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Drowsiness, severe fatigue, weakness.
- Difficulties with writing and reading.
The danger of such manifestations depends on their duration. It is important that they gradually disappear over 3-4 weeks. Otherwise, additional examinations and treatment will be required.
Concussions in adults and children can lead to long-term consequences occurring after a couple of months or years:
- Post-concussion syndrome usually develops in adults and children who have not received adequate treatment for the disease. This condition manifests itself as headaches, dizziness, sleep disorders, severe anxiety, impaired concentration, cognitive impairment, VSD, epileptic seizures, and severe fatigue during normal activities.
- Post-traumatic epilepsy - trauma is a provoking factor for epilepsy if a person is predisposed to it. Doctors often encounter difficulties in detecting cause-and-effect relationships if a patient comes to them in this condition.
- Personality changes - a person may exhibit aggression , touchiness, irritability, etc. He is in a predominant bad mood, and frequent outbursts of anger or euphoria are possible.
- Cognitive disorders - memory deteriorates, high fatigue is noted. A person’s vocabulary and knowledge may decrease.
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia – autonomic disorders develop. Worries about shortness of breath , headache, tachycardia , severe sweating, blood pressure surges.
- Other consequences can be neuroses , psychoses, inadequate perception of alcohol by the body, increased production of cerebrospinal fluid, decreased production of cerebrospinal fluid.
When such complications occur, doctors prescribe the necessary medications and other treatment methods.
Manifestations of concussions
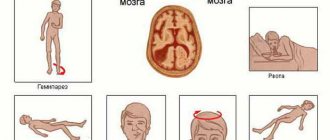
The main symptom of a concussion is loss of consciousness at the time of injury. The only exceptions may be children and the elderly. Immediately after a concussion, you may also experience:
- one-time vomiting;
- increased breathing rate;
- increased or slow heart rate;
- impaired memory for current or previous events.
These deviations bother you for a short time, the condition soon returns to normal. Blood pressure quickly returns to normal limits, but in some cases it can persistently increase - this is due not only to the injury itself, but also to the stress factors accompanying it. Body temperature during a concussion remains normal.
Upon restoration of consciousness, typical complaints are
- headache;
- nausea;
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- noise in ears;
- flushes of blood to the face;
- sweating;
- sleep disturbance.
According to a study conducted in 2021 on the basis of the Research Center for Emergency Pediatric Surgery and Traumatology of the Moscow Department of Health, in adolescents in the acute period of a mild concussion, indicators for such parameters as
- performance
- fatigue
- restoration of performance
- pace of activity
- concentration of attention
There were also difficulties in solving intellectual problems in the form of difficulties in generalizing and diversity of judgments; a significant number of impulsive errors were noted when completing tasks.
With a concussion, the general condition of the victims usually improves quickly during the first, and less often, the second week. However, it should be taken into account that headaches and other subjective symptoms can last much longer for various reasons.
Summary table of common concussion symptoms
| Early symptoms (should go away within a few hours at most) | Late symptoms (last from several days to several weeks) |
|
|
Features of manifestations in children and the elderly
The pattern of concussion is largely determined by age factors.
In infants and young children, concussion often occurs without impairment of consciousness. At the time of injury - sharp pallor of the skin (primarily the face), rapid heartbeat, then lethargy, drowsiness. Regurgitation occurs during feeding, vomiting, anxiety, and sleep disorders are noted. All manifestations disappear within 2-3 days.
In children of younger (preschool) age, concussion can also occur without loss of consciousness. The general condition improves within 2-3 days.
In older people, primary loss of consciousness due to a concussion is observed much less frequently than in young and middle age. At the same time, pronounced disorientation in place and time often manifests itself. Headaches are often pulsating in nature, localized in the occipital region; they last from 3 to 7 days, differing in significant intensity in people suffering from hypertension. Attacks of dizziness are common.