Pyelonephritis
Hepatitis
Cystitis
Diabetes
94898 03 August
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. We remind you that independent interpretation of the results is unacceptable; the information below is for reference only.
General urine analysis (with sediment microscopy): indications for use, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of the results and normal indicators.
Indications for prescribing the study
A general urine test is a routine laboratory test aimed primarily at screening for diseases of the urinary system, since pathological processes in the kidneys and urinary tract affect the properties of urine.
With this simple diagnostic test, infectious and inflammatory diseases such as glomerulonephritis
(inflammation of the renal glomeruli),
pyelonephritis
(inflammation of the renal pelvis),
cystitis
(inflammation of the bladder).
Microscopy of urine sediment allows one to suspect injury or infarction of the kidney, urolithiasis, some neoplasms, renal amyloidosis (a systemic disease in which a specific insoluble protein is deposited in the kidneys, which impairs the functioning of the organ).
In addition to diagnosing kidney and urinary tract diseases, the results of a general urine test with sediment microscopy can provide information about your general health.
Urine is formed as a result of ultrafiltration of blood plasma through the glomeruli of the kidneys. With the development of various diseases, pathological metabolic products enter the blood and are excreted from the body, including through the kidneys.
No. 116Clinical urine analysis
General urine analysis (Urine analysis with sediment microscopy) Method of determination Determination of physicochemical parameters is performed on an automatic analyzer using the “dry chemistry” method. Hardware microscopy is carried out by planar cytometry using axial hydrodynamic focusing and automatic recognition…
Up to 1 business day
RUB 370 Add to cart
Urine production and volume
The human body produces two main bioactive fluids: blood, which carries nutrients and oxygen to all organs and systems and takes waste products from them, and urine, which is responsible for removing “waste material” outside the body. Urine (urine) formation occurs in the kidneys. It is here that nephrons are located, special formations that filter the blood and synthesize urine, which is collected in the pelvis, then enters the bladder, and from there it is excreted outside the body.
This complex multi-step process is called diuresis. During the day, the body produces and excretes about 1.5-1.8 liters of urine. The rate of formation, composition, and amount of liquid depend both on the state of the body itself and the processes occurring in it, and on external conditions: ambient temperature, time of day, quantity and type of food and liquid consumed.
Deviations in the volume of urine produced from the norm are divided into several types:
- polyuria – characterized by an increase in the amount of urine excreted by the body; various kidney diseases, as well as types of diabetes, lead to this type of pathology;
- oliguria – decreased volume of daily urine;
- Anuria is a complete absence of urination, a sign of blockage of the urinary tract, kidney failure.
Urinalysis is an easy-to-perform procedure, while the information content of the results obtained is quite high and makes it possible to make an assumption about the development of a particular disease in the body, to choose the right direction and methodology for further examination. Taking this into account, doctors actively use the capabilities of this diagnostic method and prescribe a urine test:
- during preventive and mandatory medical examinations;
- to check the performance of the urinary system in order to identify existing diseases;
- for diagnosis and localization of the location of inflammatory processes occurring in the body;
- to assess the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment and monitor the resulting changes in the body.
For a more accurate diagnosis, the doctor writes out directions for laboratory tests in a comprehensive manner. Along with donating urine for laboratory testing, in most cases, patients also donate blood and feces. This makes it possible to identify abnormalities in the body’s functioning at an early stage. After all, as you know, coping with a disease at the initial stage is much easier than with advanced pathology.
Preparation for the procedure
Preparation for a general urine test begins the day before the collection of biomaterial.
Certain foods, the amount of fluid you drink, taking medications and dietary supplements, and intense physical activity can distort the results of the study. The day before collecting urine, you should avoid foods that can affect the color of your urine: for example, beets and blueberries give your urine a reddish tint; consuming large amounts of carrots or carotene supplements may change the color of your urine to orange.
On the eve of urine collection, it is not recommended to drink alcohol, coffee, dietary supplements or strong tea. If possible, you should limit your intake of diuretics (diuretics). It is necessary to exclude serious physical activity, as well as visiting a bathhouse or sauna.
Women during menstruation are not recommended to donate urine for testing, since even a small amount of blood will significantly distort the test result.
You should warn your doctor about the medications you are taking, as well as about invasive examinations (for example, cystoscopy) on the eve of the test.
Method of collecting urine for general analysis
- It is necessary to prepare in advance a disposable sterile container for collecting urine (can be purchased at a pharmacy or taken from the INVITRO medical office).
- Before collecting urine, hygienic treatment of the external genitalia should be carried out, without using antibacterial and disinfectants.
For children, you need to adhere to the following rules: girls are washed from front to back (from the pubis to the tailbone) so that bacteria that populate the intestines do not enter the urinary tract. Only wash the skin with soap, since contact with mucous membranes causes irritation, dryness and itching. In boys, the glans penis is fused with the foreskin (physiological phimosis), so it is not recommended to forcefully open the glans penis, as this leads to trauma to the delicate tissue. You just need to slightly pull the skin and rinse with water, but it is unacceptable to direct a stream of water into the opening of the urethra. - For general analysis, as a rule, the first morning urine sample is collected. First, release a small amount of urine into the toilet, then, without interrupting urination, place a container and collect approximately 50 ml of urine. In this case, it is necessary to ensure that the container does not touch the skin and mucous membranes.
- After collecting urine, close the container tightly with a screw cap.
- Special urinals have been developed for newborns and infants. You should not use urine squeezed out of a diaper or diaper - the results will be unreliable, since the diaper is a kind of filter for microscopic elements of urine, which are counted during the study.
- When taking the test during the day, it is not recommended to drink large amounts of water, tea, coffee or diuretics to stimulate urination.
The turnaround time for a general urine test is usually 1 business day.
OAM in pregnant women and children
Most often, pregnant women and children donate urine for analysis. This is explained by the fact that by deviations of parameter values from normal values, it is easy to identify the disease at a very early stage. Decoding the results in pregnant women does not differ from a similar procedure for an ordinary adult. Early diagnosis of diseases allows you to deal with them faster and protect the health of the unborn baby. Most often, pregnant women are diagnosed with inflammatory diseases of the bladder, kidney pathologies, and asymptomatic bacteriuria using OAM.
In children, normal values have a wider range of fluctuations. The results obtained after a general urine test may contain salts, glucose, bilirubin, protein, ketones, urobilinogen, which is not a sign of the disease, but is associated with the peculiarities of the children’s diet. But, in any case, it is necessary to show the results of OAM and consult with a pediatrician.
A general urine test is an important laboratory test. Doctors recommend taking urine to a laboratory for diagnosis at least once a year. At the same time, it is very difficult to judge the presence of any diseases in the body based on a single result. In order for the doctor to make a correct diagnosis, additional examination will be required. The doctor will tell you what procedures will be required.
What may affect the results
Factors that may distort the results of the study:
- Violation of hygiene procedures and urine collection techniques.
- Drinking large or small amounts of water.
- Consuming foods, medications, or dietary supplements that change the color of urine.
- Menstruation.
- High blood pressure.
- Intense physical and psycho-emotional stress on the eve of urine collection.
- Visiting a bathhouse, sauna, hypothermia.
- Carrying out invasive procedures on the urinary tract a week before the test.
You can take a general urine test at the nearest INVITRO medical office.
A list of offices where biomaterial is accepted for laboratory research is presented in the “Addresses” section. Urine examination includes the study of physical and chemical properties, as well as microscopy of sediment.
Physical properties: quantity, color, odor, transparency, relative density (specific gravity), urine reaction (pH).
Chemical properties: determination of protein, glucose, ketone bodies, urobilinogen, bilirubin, hemoglobin, nitrites, leukocyte esterase.
Microscopy: identification of erythrocytes, leukocytes, cells of flat, transitional and renal epithelium, cylinders, crystals, mucus, bacteria, fungi.
Urobilinogen UBG
Urobilinogen is contained in freshly released urine, and when it stands for a long time, it turns into urobilin, which is present in the body of a healthy person in small doses.
An increased content of urobilin is typical when the liver is damaged, when it loses the ability to excrete it with bile, as well as when the bile duct is blocked (for example, by a stone).
Diagnosis of urobilinuria in medical practice is important for identifying the causes of jaundice and determining liver damage.
Normal indicators
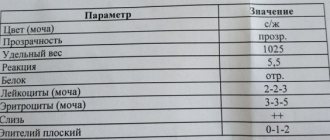
| Index | Result |
| Quantity | 50 ml |
| Color | Colorless, light yellow, straw yellow, yellow, amber yellow |
| Smell | Odorless or non-specific |
| Transparency | Transparent |
| Relative density of urine (specific gravity) | 1003-1035 |
| Urine reaction (pH) | 5.0-8.0 (in children under 1 month – 5.0-7.0) |
| Protein | > 0.140 g/l |
| Glucose | > 2.8 mmol/l |
| Ketone bodies | > 1 mmol/l |
| Urobilinogen | > 34 mmol/l |
| Bilirubin | Not detected |
| Hemoglobin | Not detected |
| Leukocyte esterase | Not detected |
| Nitrites | Not detected |
| Red blood cells | Up to 2 cells per field of view |
| Leukocytes | Up to 5 cells in field of view |
| Epithelium | Up to 5 squamous epithelial cells per field of view |
| Cylinders | Not detected |
| Crystals | Little or no detectable amounts of urates, calcium oxalates, amorphous phosphates |
| Slime | In small quantities |
| Bacteria | Not detected |
| Fungi | Not detected |
Interpretation of a general urine test
In addition to knowledge of normal indicators, to decipher the results of OAM, knowledge about the physiology and pathophysiology of its formation is needed. Urine acts as an indicator of the condition of not only the urinary system, but also the entire body as a whole. Therefore, after taking a urine test, a doctor should decipher the indicators.
Deviations in the composition of urine and what they are associated with
Urine color . Normally, this indicator depends on the concentration of the pigment - urochrome, which is released during the breakdown of hemoglobin. With pathology, urine is completely painted in a different color or a change in the color of its sediment may be observed. Thus, a rich yellow color is observed with an excess of urates, whitish - with phosphates, brown - with oxalates.
Different shades of urine indicate the presence of the following pathologies:
- intense yellow – with dehydration of any etiology, edema due to cardiovascular failure;
- pale yellow, “diluted” - diabetes insipidus, taking diuretics;
- orange-yellow – due to taking B vitamins;
- red-pink – consumption of coloring foods and medicines;
- red – for renal infarction, renal colic;
- red-brown - as a result of poisoning with phenols, taking metronidazole, sulfonamides;
- “meat slop” – acute glomerulonephritis;
- brown and dark - with hemolytic anemia;
- black – with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria;
- “beer jaundice” – parenchymal jaundice;
- greenish – obstructive jaundice;
- “milk” – for urinary tract infections, kidney lymphostasis.
Transparency of urine . Turbidity is caused by the ingress of blood cells, bacteria, epithelial cells, fat particles, and salts into urine.
Urine density . This indicator depends on the concentration of organic substances (uric acid, urea), electrolytes (sodium, potassium, chlorine) and the amount of water.
An increase in density is observed with the accumulation of protein (glomerulonephritis, nephrotic syndrome), glucose (diabetes mellitus), loss of water (diarrhea, vomiting), gestosis in pregnant women, intravenous administration of mannitol, dextran and radiopaque agents.
A decrease in SG in urine is also not normal, but is associated with insufficient concentration function of the kidneys. It is observed in diabetes insipidus, polyuria, and renal failure.
Acidity. A slightly acidic urine reaction is considered normal. Fluctuations in pH are possible during the following processes:
- to the alkaline side (˃ 7) – with preference for nutrition of food of plant and dairy origin, with respiratory and metabolic alkalosis, prolonged vomiting, infections and tumors of the urinary organs, hyperfunction of the parathyroid gland, chronic renal failure;
- to the sour side (˂ 5) – during fasting or eating large amounts of meat, prolonged diarrhea, fever, dehydration, diabetes.
on the pH of urine . If the pH is less than 5, uric acid stones are formed, if the pH is greater than 7, phosphate stones are formed, and 5-7 are oxalate stones.
Protein. Its presence in urine is called proteinuria. When a urine test is completed, PRO is key for diagnosing kidney diseases. Detection of protein may indicate glomerulonephritis, diabetic kidney damage, tumors of the urinary organs, myeloma, heavy metal poisoning, Fanconi syndrome, sarcoidosis, nephrosclerosis, nephrotic syndrome, cystitis, urethritis, circulatory disorders in the kidney with heart failure.
Sometimes proteinuria is observed normally - during hypothermia or stress. During puberty, protein may appear in the urine when standing.
Glucose (glucosuria) . Normally, glucose does not enter the urine. But if you overuse sweet foods, the body will get rid of excess sugar through urine, then occasional moderate glucosuria (up to 1 mmol/l) is observed. When deciphering the urine analysis of people with suspected diabetes, the glucose indicator is extremely important. Together with a blood test, it provides information about the presence and progression of this disease.
Also, the presence of glucose in the urine is observed in the following conditions:
- pancreatitis;
- Cushing's syndrome;
- pregnancy.
Bilirubin . This indicator must be negative. Bilirubinuria indicates liver damage and obstruction of bile flow. As a result of obstructive jaundice, liver cirrhosis, viral hepatitis, and the presence of intrahepatic metastases, the appearance of bilirubin in the urine is noted.
Urobilinogen . This pigment is formed in the intestines from bilirubin under the influence of intestinal bacteria. Urobilinogen is mainly excreted in feces, but traces of it are also found in urine. This indicator has a wide diagnostic range. When deciphering a urine test, URO may indicate various diseases:
- blood – hemolytic and pernicious anemia, hemolysis, polycythemia, resolution phase with massive hematomas;
- Gastrointestinal tract – inflammatory and obstructive diseases;
- liver – viral hepatitis, chronic form of hepatitis, cirrhosis;
- intoxication – alcoholic, infectious, organic compounds.
The increased content of urobilinogen in the blood is compensated by its excretion in the urine.
Ketone bodies . Normally they are not detected. Their penetration into the urine indicates decompensation of diabetes mellitus and a high risk of developing hyperglycemic coma. Ketonuria is also characteristic of alcohol intoxication, hyperinsulinism, prolonged hunger, refusal of carbohydrates in the diet, severe fever, eclampsia, precoma and cerebral coma.
Epithelium. A permanent component of urine. Microscopy reveals elements of squamous, transitional, and renal epithelium. They adhere to the following quantitative guidelines:
- flat – up to 3-5 cells per p/z;
- transitional - no more than 1 cell in the subsection;
- renal – should be absent.
Reasons for the increase or appearance of epithelial cells in the sediment:
- flat – for urinary tract infections;
- transitional – with cystitis, pyelonephritis, urolithiasis;
- renal - glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, toxicosis caused by salts of heavy metals, bismuth, impaired renal circulation.
Red blood cells (erythrocyturia). BLD decoding should take into account anamnestic data, because the detection of red blood cells is often associated with physiological reasons. For example, standing for a long time, walking for a long time, excessive physical activity, or taking certain medications, there is a natural release of these blood cells into the urine.
A pathological increase in red blood cells (˃2 in p/z) is associated with arterial hypertension, hemorrhagic diathesis, glomerulonephritis, urolithiasis, pyelonephritis, kidney injury, and tumor process.
Leukocytes. Leukocyturia (˃ 5 in p/z) is observed with the development of inflammation in the genitourinary organs (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, cystitis, urethritis, prostatitis), urolithiasis, and kidney transplant rejection.
Excessive accumulation of white blood cells causes cloudy urine, called pyuria.
Hemoglobin (hemoglobinuria). Normally, urine is clear of hemoglobin and myoglobin. Their appearance in analyzes is associated with various pathologies of the body:
- myoglobin – muscle damage, myocardial infarction;
- hemoglobin - hemolytic anemia, poisoning with phenol, aniline, mushrooms, sepsis, burns.
Hemoglobinuria and myoglobinuria are very similar to each other, so diagnostic errors are often found in them.
Slime. Its presence indicates chronic inflammation in the urinary tract.
Casts (cylindruria). By origin, these are proteins that stick together in the lumens of the renal tubules with different cells - hemoglobin, bilirubin, blood cells, pigments, sulfonamides. According to physiology, urine should not contain cylinders. Their formation occurs with kidney damage. When deciphering a general urine test, you can find the following types of cylinders:
- hyaline - present in fever, overheating, congestive heart failure, arterial hypertension, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, tuberculosis and kidney tumors, physical overload;
- granular - caused by viral infections, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, hyperthermia, lead poisoning;
- waxy - with amyloidosis, nephrotic syndrome, chronic renal failure.
Leukocyte, erythrocyte and epithelial forms of casts are also found. They indicate primary or secondary renal pathology.
Salt. Healthy urine contains virtually no salts. When their number increases, there is an increased risk of stone formation, since when urine sits, salts precipitate to form crystals. High doses of ampicillin and sulfonamides lead to the formation of crystals.
An increase in uric acid (urate) is observed with gout, nephritis, chronic renal failure, a meat diet, and dehydration. Phosphates are concentrated in the urine during vomiting, Fanconi syndrome, cystitis, and hyperparathyroidism. The appearance of oxalates is associated with the frequent presence in the diet of foods enriched with oxalic acid (spinach, sorrel, tomato, etc.), as well as developing pyelonephritis and diabetes mellitus.
Bacteria, fungi and parasites are normally absent from urine; their detection is associated with a corresponding disease of the urinary tract.
Cost of seeing a doctor
| Name of service | Price, rub.) |
| Primary appointment with a general practitioner | 2000 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with a general practitioner | 1500 rub. |
Urinalysis
| Code | Name of the study | Biological material | Result | ****Execution period | Price | ***CIT | Note |
| 110101 | General urine analysis | urine (morning portion) | count | 1 k.d. | 345 rub. | 690 rub. | 0 |
| 110102 | 2 glass sample | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 575 rub. | 1150 rub. | 0 |
| 110103 | 3 glass sample | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 690 rub. | 1380 rub. | 0 |
| 110104 | Rehberg's test | urine + blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 403 rub. | 805 rub. | 0 |
| 110105 | Urine analysis according to Zimnitsky | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 920 rub. | 1840.00 | 0 |
| 110106 | Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 345 rub. | 690 rub. | 0 |
Advanced urine analysis study
| Code | Name of the study | Biological material | Result | ****Execution period | Price | ***CIT | Note |
| 090101 | Creatinine | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090102 | Urea | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090103 | Uric acid | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090104 | Phosphorus | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090105 | Magnesium | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090106 | Glucose | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090107 | Calcium | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090108 | Alpha amylase | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 345.00 rub. | 690.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090109 | Total protein | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090110 | Na+/K+/Cl- | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 460.00 rub. | 920.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090112 | Microalbumin | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 575.00 rub. | 1150.00rub | 0 |
| 090121 | Deoxypyridinoline (DPID) | urine | count | 3-5 k.d. | 2300.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
All our services and prices
Protein PRO
The urine of a healthy person contains less than 0.002 g/l of protein . The content of this element in an amount exceeding the norm is called proteinuria, which is classified into renal and urinary tract proteinuria.
To differentiate proteinuria, additional examination of urine sediment is necessary (according to Nechiporenko, Addis-Kakhovsky). Only with a cumulative analysis of all indicators (erythrocytes, casts, leukocytes) can the cause of the protein content be identified, these are: pathological conditions of the kidneys (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, tuberculosis, amyloidosis and pathological conditions of other organs: anemia, hypertension, heart failure.
Protein can be detected in small quantities if the patient consumed protein foods or performed heavy physical exercise the day before the test. If traces of protein are detected in the urine, the patient is prescribed a repeat test.
Total Density SG
The SG in healthy people can range from 1.010 to 1.025 . Deviations from the norm in a single study cannot have a decisive clinical significance. Detailed tests are required aimed at daily determination of density and its fluctuations: Reiselman, Zimnitsky, dry eating, water tests.
An increased RPL of urine is observed in cases of dehydration, diabetes mellitus, and edema that occurs due to pathologies of the heart and kidneys.
Low OPl - with excessive drinking, decreased swelling, long-term fasting, kidney failure, diabetes insipidus.
Chemical composition of urine
| Index | Units | SI units |
| Reaction | Neutral or slightly acidic 1 | |
| Protein | Absent, traces (25-70 mg/day) 2 | 0.025—0.070 g/day |
| Sugar | Absent, traces (no more than 0.02%) 3 | |
| Acetone | Absent | |
| Ketone bodies | None | |
| Urobilin bodies | None | |
| Bilirubin | Missing 4 | |
| Ammonia | 0.6—1.3 g/day | 36-78 mmol/day |
| Uric acid | 270-600 mg/day | 1.62-3.6 mmol/day |
| Purine bases: | ||
| hypoxanthine | 9.7 mg/day | |
| xanthine | 6.1 mg/day | |
| Urea | 20—35 g/day | 333.0—582.8 mmol/day |
| Creatinine: | 0.5—2 g/s | 4.4—17.6 mmol/day |
| men | 1—2 g/s | 8.8—17.6 mmol/day |
| women | 0.5—1.6 g/s | 4.4—14.08 mmol/day |
| Creatine | Absent | |
| a-amylase | 20—160 mg starch/(h—ml) | 20—160 g/(h—l) |
| Uropepsin | 38—96 mg/day | |
| Potassium | 1.5—3 g/s | 38.4—76.7 mmol/day |
| Sodium | 3—6 g/s | 130.5—261.0 mmol/day |
| Chlorine | 120–170 mEq/L (600–740 mg%) | 120—170 mmol/l |
| Inorganic phosphorus | 0.6—1.2 g/s | 0.019—0.038 mmol/day |
1 An alkaline reaction appears on a vegetable diet, alkaline drinking, and at the height of digestion. 2 Transient proteinuria occurs as a result of muscle work and physical stress. 3 Functional glycosuria occurs with emotional stress, excess sugar in food and the administration of adrenaline. 4 Taking antipyrine gives a false positive reaction
When are Zimnitsky tests prescribed?
The Zimnitsky analysis is prescribed to study kidney functionality.
The diagnostic factors of this method are: the density of urine and changes in its numerical indicators in different portions, and diuresis - the ratio between the amount of fluid consumed and excreted in 24 hours.
Normal indicators:
- The difference in urine density between the highest and lowest values is not less than 0.012;
- Daytime diuresis is twice as prevalent as nighttime diuresis;
- The daily amount of urine is not less than 65% and not more than 85% of the fluid consumed;
- The allowed minimum density of urine is 1.005, the maximum is 1.030.
Deviations indicate kidney disease: pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis .
How to prepare for the analysis?
For the study to be informative, the material must be collected correctly. General recommendations are as follows:
- you need to buy sterile plastic containers at the pharmacy;
- There is no need to collect the first few drops of urine;
- Before collection, the genitals should be thoroughly washed;
- For women, it is advisable to insert a tampon and spread the labia;
- For women, the test is not recommended during and a few days after menstruation to avoid vaginal discharge;
- morning urine is collected in a container;
- It is enough to collect 100 ml of urine;
- Delivery of the material to the laboratory should take no more than 1 hour.
Usually the result form can be collected the same evening, the material is delivered to the laboratory between 8 and 10:00.
How to collect urine from infants?
With boys, the situation is relatively simple - you just need to wait and place the can in time.
For girls, you can place a circle made from a diaper under the buttocks by placing the dish in the recess. After some time, the child will definitely go to the toilet and the urine will collect in a container.
This way, the child’s parents can easily collect urine for analysis. And its results will not be distorted, which inevitably happens when using other methods, for example, when turning diapers.