In the first year of a child’s life, the nervous system is extremely changeable; it rapidly matures and improves, while the baby’s behavior and his reactions to the outside world change. There are quite a lot of factors that influence development, so often even in completely healthy children at least some of the parameters may be outside the normal range.
Today there is no such diagnosis in medical practice; there is the concept of perinatal damage to the central nervous system. It is determined by neonatologists or resuscitators in the first day of a child’s life, and often even immediately after birth in the delivery room.
Thus, perinatal encephalopathy (or PEP) is a term that combines lesions of the central nervous system, and in particular the brain, of different origins and development mechanisms that arise in the perinatal period.
Perinatal is the period from 22 weeks of pregnancy to seven days of the baby’s life (168 hours) from the moment of birth. It, in turn, consists of three periods: antenatal (from 22 weeks until birth), intranatal (during the birth itself) and postnatal (from the moment of birth to seven days of life).
Frequency of occurrence
According to statistics, approximately three to five percent of newborns are born with signs of perinatal brain damage. Thus, this pathology is quite common. It is possible and necessary to work with it; it is not a death sentence at all.
What causes perinatal encephalopathy?
The most common and main cause of perinatal damage to the central nervous system in newborns is the negative impact of various harmful factors on the body of the expectant mother. These include:
- chronic diseases in the mother;
- acute bacterial or viral diseases during pregnancy;
- inadequate nutrition of a pregnant woman - all tissues and organs of the baby are formed from substances that the mother receives, and due to the lack of necessary building material, the entire process of development of a new organism suffers, which subsequently results in deviations in physical development, underdevelopment of internal organs, low quality of immunity and damage to the nervous system systems;
- metabolic disorders (metabolism) and hereditary diseases;
- mother's age is too young;
- pathological course of pregnancy (threats of miscarriage or premature birth, early or late toxicosis, etc.);
- pathological course of labor (quick or prolonged labor, weak pushing), as well as birth injuries;
- unfavorable environmental conditions, harmful environmental influences (for example, ionizing radiation, pollution with industrial waste or heavy metal salts, use of medicines, etc.);
- prematurity;
- stress during pregnancy - excess hormones quite easily penetrate the placenta and are transmitted to the fetal nervous system. Thus, excess cortisol and adrenaline destroys neurons even in adults, and a child’s brain that has not yet formed can be quite seriously damaged, since during the period of its intensive development every cell counts.
Treatment of AEDs in children with movement
But the most important thing for forms of PEP of any complexity are gentle and drug-free methods of restorative treatment: reflexology, special therapeutic massage techniques, elements of therapeutic exercises, hydrotherapy with massage and therapeutic exercises in water of various temperatures and compositions, etc.
They require persistence and a lot of effort from the child’s parents—giving medicine is probably easier than doing a set of exercises every day—but they are very effective. This is explained by the fact that the injured brain, receiving the correct “information” through massage, swimming and gymnastics, recovers more quickly.
Reflexomassage (impact on active points) is first done by the hands of an experienced massage therapist, who then passes the baton of competent handling of the baby to the parents. Don’t forget: babies get tired quickly, all procedures should be carried out briefly, but often, at the height of positive emotions.
Early swimming of a child with mandatory diving is also a huge help in solving the neurological problems of the baby. What is painful and unpleasant to do on land can be done with a bang in water. When diving into the water column, the body experiences a baroeffect - gentle, soft and, most importantly, uniform pressure on all organs and tissues. Hands clenched into fists, spasmed muscles and ligaments of the body straighten. The thickness of the water restores intracranial pressure in all directions, provides baromassage to the chest, equalizing intrathoracic pressure.
After emerging, the child receives a full, competent breath, which is especially important for babies born by cesarean section, who had hypoxia, etc. Water also helps with problems with intestinal colic - stool improves, spastic painful phenomena go away.
Types of perinatal brain damage
Perinatal lesions of the central nervous system are classified depending on the causes that cause them. Accordingly, four main groups are distinguished.
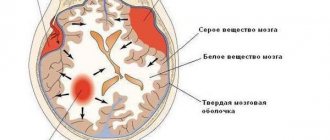
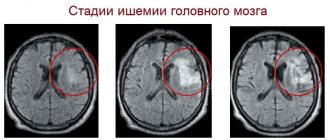
- Hypoxic. It, in turn, is divided into hypoxic-ischemic (HIE or post-hypoxic encephalopathy), which occurs as a result of acute or chronic lack of oxygen, and hypoxic-hemorrhagic, in which intracranial hemorrhages are noted. Depending on the severity, there are three degrees of cerebral ischemia: mild, moderate and severe.
- Traumatic. Develops as a result of damage to the tissues and organs of the fetus during childbirth. These include birth injuries of the central (brain and spinal cord) and peripheral nervous system.
- Toxic-metabolic. Occurs, as a rule, during inflammatory processes during pregnancy in the mother or malformations of the fetal organs.
- Infectious. You should pay attention to the group of the most dangerous and common intrauterine infections, the so-called TORCH complex (toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus, herpes, rubella) and others (syphilis, hepatitis, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, HIV).
The Apgar scale allows you to objectively assess the degree of brain damage. The assessment is carried out in the first and fifth minutes of the baby’s life and takes into account the functioning of his heart, lungs, reflexes, motor activity and skin color. The data obtained are evaluated in points, based on the number of which one can judge the severity of hypoxia. Accordingly, the lower the indicator, the more significant the degree of damage.
First results
When treating encephalopathy, how can you understand that the efforts of doctors and parents have been successful? The child became calmer, stopped crying for a long time, and his sleep improved. He began to hold his head in time, sat down, then stood up and took the first step. His digestion has improved, he is gaining weight well, and his skin is healthy. This is visible not only to doctors, but also to yourself. This means you have helped your baby overcome damage to the nervous system.
And finally, one example of what a mother's love can do.
In the mid-60s, in one of the maternity hospitals on distant Sakhalin, a daughter was born to a young midwife. As, unfortunately, often happens with doctors, the birth was extremely difficult, the child was born in deep asphyxia, did not breathe for a long time, and then was practically paralyzed for several weeks.
The girl was fed from a pipette and nursed as best she could. To be honest, the doctors thought that this child was not a survivor. And only the mother thought differently. She did not leave the baby, mastered massage perfectly and persistently massaged the barely reviving body.
Eighteen years later, the author of this article met his daughter and mother in Leningrad. They came to enter Leningrad University. It turned out that the girl graduated from school on Sakhalin with a gold medal. It was difficult to take your eyes off her - she was so slender and beautiful. Then she graduated from university, defended her PhD thesis in biology, became a scientist, got married, and gave birth to two beautiful children. None of this might have happened if the mother’s love had been less selfless and reasonable.
Clinical picture of perinatal encephalopathy
There are several main symptom complexes of perinatal encephalopathy.
- Syndrome of increased neuro-reflex excitability (hyperexcitability). It is characterized by restlessness, crying, short and shallow sleep, problems falling asleep, activation of innate reflexes and spontaneous movements, as well as fluctuations or increased muscle tone, tremor (shaking) of the chin, arms or legs. With this syndrome, premature babies are quite likely to experience seizures that occur when exposed to irritating factors, for example, elevated body temperature.
- Convulsive (or epileptic) syndrome. These are paroxysmal movements of the body, twitching, shuddering and spasms of the limbs.
- Central nervous system depression syndrome occurs with lethargy, weakened reflexes and motor activity. It is also characterized by focal neurological disorders: anisocoria (different pupil sizes), ptosis (drooping of the upper eyelid), convergent strabismus, nystagmus (involuntary eye twitching), asymmetry of the nasolabial folds, impaired sucking and swallowing.
- Movement disorder syndrome can be noticeable from the first weeks of life. It is manifested by high or decreased muscle tone, movements are activated or slowed down. There is a lag in speech and psychomotor development and, accordingly, intellect, since the child cannot fully master motor skills and carry out purposeful movements. Also characteristic is a delayed reaction to sound and visual stimuli, weak facial expressions, delayed crawling, sitting and walking.
- Vegetative-visceral dysfunction syndrome is characterized by increased nervous excitability. Frequent regurgitation, changes in temperature and skin color, delayed weight gain, disturbances in heart and breathing rhythm, and thermoregulation are noted. Damage to the gastrointestinal tract is often observed: enteritis or enterocolitis (inflammation of the small or large intestine), which is manifested by upset stool and poor weight gain.
- Hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome. It is manifested by an excess amount of cerebrospinal fluid, which causes increased intracranial pressure. The mechanism of development can be different: excessive formation of cerebrospinal fluid, impaired absorption into the bloodstream, or a combination of both. The main clinical signs are a high rate of increase in head circumference, the condition and size of a large fontanel, as well as frequent profuse regurgitation, restless sleep, monotonous crying with increased pulsation and bulging of the fontanel, throwing the head back.
- Comatose syndrome is manifested by severe lethargy, lack of motor activity, sucking and swallowing reflexes, as well as depression of vital functions.
Perinatal brain damage occurs in several periods, which differ in the uniqueness of symptoms, severity and outcomes:
- Acute – in the first month of life. During this period, brain depression syndromes are observed, even coma is possible, convulsions, increased neuro-reflex excitability, and increased intracranial pressure due to hydrocephalus are also characteristic.
- Restorative – up to one year in full-term babies and up to two years in premature babies. During this phase, the above-described syndromes persist, although under the influence of treatment their severity becomes lower. However, there is a noticeable delay in psychomotor development.
- The period of residual changes - it occurs with a lag in speech and psychomotor development, neurasthenia, hyperactivity; in severe cases, convulsive syndrome and hydrocephalus may persist.
Early signs of perinatal brain damage can be detected by a neonatologist immediately after birth. These include a weak cry of the newborn, long-lasting cyanosis (bluish coloration of the skin), decreased reflexes and motor activity, and absence of the sucking reflex.
As a rule, there is a combination of several syndromes of varying severity, and each of them has its own treatment regimen and prognosis.
Already at an older age, the following symptoms can be noted:
- disorders of attention, memory, sensation and perception;
- signs of depression: depressed state, lack of appetite, increased irritability, fatigue, absent-mindedness, tearfulness, poor sleep;
- lack of desire for cognitive activity (narrow range of interests);
- inability to express thoughts;
- signs of vegetative-vascular dystonia: headaches, dizziness, low blood pressure;
- speech disorders.
Encephalopathy due to injury
Traumatic brain injury can lead to the development of encephalopathy, and this does not depend on the age or gender of the person. It can develop either immediately or several months or even years after the incident. Encephalopathy occurs to one degree or another in 80% of people who have suffered concussions or other brain injuries.
If a person has suffered a mild concussion, then such an injury will not lead to the development of encephalopathy. As a rule, the development of this syndrome can be provoked by a concussion of the 2nd degree of severity, contusion, skull fracture and crushing of the brain. Most often, people receive such injuries in road accidents, during a fight, or after falling from a height.
Symptoms of post-traumatic encephalopathy
The following signs will indicate that a person develops encephalopathy after receiving an injury:
- Intense headache, nausea, constant desire to sleep. Taking analgesics can relieve pain only for a short period of time, but they can be completely relieved by changing body position.
- Possible loss of consciousness.
- A person begins to suffer from dizziness, he experiences frequent falls, and his gait changes.
- Memory, attention, reaction speed suffer, the ability to analyze and draw conclusions is lost.
- Patients develop depression, they become apathetic and lethargic.
- Convulsive seizures are characteristic.
Treatment of post-traumatic encephalopathy
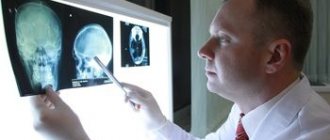
To identify developing encephalopathy, the patient should undergo an MRI. Auxiliary diagnostic techniques are: radiography, electrocardiogram, blood tests.
Immediately after the injury, the patient should be hospitalized. When he is discharged from the hospital, he needs to attend an appointment with a neurologist. If encephalopathy manifests itself acutely, the patient is again hospitalized.
To treat the consequences of injury, antioxidants, vascular drugs and nootropics are prescribed.
Diagnosis of perinatal brain damage
Unspecified encephalopathy in an infant can be diagnosed based on the characteristics of pregnancy and childbirth, as well as clinical manifestations.
Instrumental examination methods are of an auxiliary nature; they make it possible to clarify the degree and nature of brain damage and subsequently evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment.
Ultrasound examination of the brain (neurosonography, or NSG) is the safest examination method that allows you to assess the condition of tissues and liquor spaces (ventricles). It can be used to determine various intracranial lesions and their nature.
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method for studying the electrical activity of the brain. Based on the data obtained, they judge the existing interhemispheric asymmetries, the degree of delay in brain development, the presence of epileptic activity and its foci in different parts of the brain.
Doppler ultrasound helps assess the state of blood flow in the vessels of the brain.
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging (CT and MRI) are modern diagnostic methods that allow a more detailed study of structural changes. Their widespread use in early childhood is quite difficult due to the need to use anesthesia, since throughout the entire examination the child must lie still, and in the case of small children this is quite difficult.
Electroneuromyography is an indispensable method in the diagnosis of both congenital and acquired diseases of the neuromuscular system.
Video monitoring is a method that, using video recordings, allows you to assess a child’s spontaneous motor activity. The combined use of video and EEG monitoring helps to accurately determine the nature of seizures in young children.
The most common examination methods for perinatal brain damage today are neurosonography (NSG) and electroencephalography (EEG).
In case of pathology of the central nervous system, an examination by an ophthalmologist is also required. Based on changes in the fundus, he assesses the condition of the optic nerves and the level of intracranial pressure.
Diagnosis of PEP in neurology. Through the eyes of a specialist
What do neurologists pay attention to during examination? Firstly, on reflexes and muscle tone. Are the reflexes equal on the right and left? Are there any muscle spasms? And vice versa - aren't they contracting too weakly?
Then they check whether the child has signs of increased intracranial pressure. To do this, an ultrasound (neurosonogram) is performed through an open fontanel - they look to see if the ventricles of the brain are dilated. And in conclusion, the child’s behavior is examined, the correspondence of his so-called psychomotor and physical development to his age.
Treatment of perinatal encephalopathy
Treatment of a baby with perinatal brain damage in the acute period is carried out in the intensive care unit, and then in the pathology of newborns. He is shown a gentle regimen, oxygen support (oxygen therapy), and, if necessary, feeding through a tube.
Drug treatment is carried out taking into account the prevailing symptoms. In order to reduce intracranial pressure, dehydration therapy (with the help of diuretics), hormonal drugs, and a spinal puncture are used.
To normalize metabolic processes and increase the resistance of nervous tissue to a lack of oxygen, infusion therapy is carried out (glucose solutions, ascorbic acid, calcium, potassium, magnesium, etc.). Anticonvulsants are used to combat seizures. As part of the treatment of this pathology, drugs are also prescribed that improve blood circulation and metabolism in the brain.
Treatment of a child in the recovery period of the disease is usually carried out in a day hospital or on an outpatient basis. Repeated courses of drug therapy, physical therapy, massage, swimming, physiotherapy, herbal medicine and osteopathy are provided.
In case of delayed speech development or other speech disorders, correctional classes with a speech therapist are indicated.
The child was diagnosed with PEP. What's next?
If the matter is limited to a violation of muscle tone and excitement of the nervous system, the neurologist usually prescribes massage, mild sedatives and drugs that improve cerebral circulation.
If a neurologist discovers an increase in intracranial pressure , which usually depends on excess production of cerebrospinal fluid, he prescribes him a course of so-called dehydration therapy (dehydration - dehydration). For this purpose, various diuretics are given. To compensate for the loss of potassium due to increased urination, drugs containing potassium are prescribed.
One should not hope that these phenomena will go away on their own as the skull grows - this may not happen. By the way, monitoring of intracranial pressure indicators should be carried out later, for several years, which will relieve your child of headaches and attacks of the so-called vegetative-vascular dystonia in preschool and school age.
Consequences
Perinatal brain damage has a fairly positive prognosis for recovery. However, there is also the possibility of developing a number of negative consequences that are caused by the neglect of the disease, ineffective treatment or individual characteristics of the body.
Such complications include:
- delayed psychomotor development (in most cases, the child is not limited in his abilities and can lead full independent life activities);
- disorders of the vegetative and, as a consequence, the main vital systems caused by metabolic disorders and pressure changes;
- neurotic disorders, which manifest themselves in the form of mood swings, sleep disturbances, attacks of tearfulness or aggression;
- psychoemotional disorders (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), increased physical and emotional activity);
- epilepsy attacks;
- cerebral palsy (CP).
The consequences of perinatal brain damage are treatable. If they occur, you should immediately consult a pediatrician or neurologist in order to prescribe the correct step-by-step treatment and the necessary course of rehabilitation.
Rules for everyone
- Study and show an experienced pediatrician the extract from the maternity hospital. If it contains low scores on the Apgar scale (6 and below), or other marks (for example, he did not cry immediately after birth, there was cephalohematoma, hypoxia, asphyxia, convulsive syndrome, etc.), do not delay a consultation with a pediatric neurologist.
- If there are no objective indications for consulting a neurologist, but it seems to you that the baby is overly excited, whiny, and capricious beyond all reasonable limits, trust your parental intuition and show the child to the doctor. The baby is unlikely to be healthy if in the first weeks of life he is pathologically passive, lies like a rag, or vice versa, cries 24 hours a day, if he is indifferent to food or vomits “fountain” after each feeding.
- Breastfeeding is necessary for your baby! Even the highest quality and most expensive adapted milk formulas place additional metabolic stress on the baby’s body. It has been scientifically proven that breastfed children “overcome” infantile problems (neurological, intestinal, etc.) faster and have a higher rate of emotional and physical development.
- If you are planning your next child, find out all the causes of perinatal encephalopathy in your firstborn. And if possible, try to correct the situation if it is associated with inattention to your health during pregnancy and childbirth. Attend courses to prepare couples for childbirth. Carefully choose doctors and medical institutions where you plan to give birth to your baby.