Normal heart rate for an adult: table by age
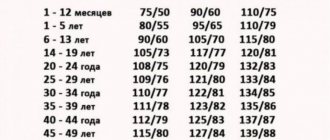
The normal heart rate of an adult by year (age) is given in the table:
| Age | Maximum and minimum limit | Average value |
| 15-50 years | 60-80 | 70 |
| 50-70 years | 66-87 | 76 |
| From 70 years old | 72-92 | 81 |
In an adult, the heart rate norms by age and the permissible heart rate limits in a child under 15 years of age differ significantly, which can be seen in the following table:
| Age | Maximum and minimum limit | Average value |
| Up to 3-4 weeks | 115-165 | 135 |
| From 1 to 12 months | 105-160 | 130 |
| 1-3 years | 90-150 | 122 |
| 3-5 years | 85-135 | 110 |
| 5-7 years | 80-120 | 100 |
| 7-9 years | 72-112 | 92 |
| 9-11 years | 65-105 | 85 |
| 11-15 years | 58-97 | 77 |
Knowing what the normal heart rate is for women and men by age, you can avoid many diseases. Measurements should be taken at rest. Under the influence of other factors (sports, pregnancy), slight deviations are possible.
Heart rate while walking
While walking, there is a slight increase in heart rate. How many heartbeats there will be per minute depends on the person’s fitness. For people leading a sedentary lifestyle, the heart rate can jump to 120, but for people who like to walk, it will remain within 90-100. To calculate the maximum permissible limit, subtract the person's age from 180.
When walking, the permissible heart rate is as follows:
- 15 years - 165;
- 35 years old - 145;
- 55 years old - 125;
- 75 years old - 105.
Heart rate at rest
The resting pulse is determined in the morning.
A person needs to sit on a chair and count his pulse. Changing body positions or taking measurements in the evening is not recommended, as the final result will be distorted. Generally accepted norms at rest:
- adults – 60-80;
- elderly – 70-90;
- teenagers - 70-80;
- children under 2 years old - 90-100;
- newborns - 130-140.
Heart rate while running
While jogging, a lot of stress is placed on the heart. People trying to lose weight should keep their heart rate close to the upper limit. If the goal is to strengthen the cardiovascular system, then you need to stop at a figure not exceeding 60-70%. To calculate the norm, you need to subtract your age from 200:
| Age | Maximum allowable heart rate | Pulse for weight loss | Pulse to strengthen the heart and increase endurance |
| 30 | 170 | 155-160 | 110-120 |
| 50 | 150 | 135-140 | 90-110 |
| 70 | 130 | 115-120 | 70-90 |
If, against the background of an increase in the pulse (within acceptable limits), the pressure readings remain normal, then the development of pathologies will not follow. Elderly people need to be especially careful. Their body is unable to withstand heavy loads.
Permissible heart rate during pregnancy
A woman who is expecting a baby experiences increased heart rate around the 5th month. This phenomenon is associated with an increase in circulating blood volume during fetal development. Usually the increase is insignificant and gradually the indicators return to the acceptable limit:
- Heart rate norms in children: table of heart rate correspondences from newborn age to adulthood
- at 14-26 weeks there is an increase of 10-15 contractions from the norm;
- the maximum increase occurs between 27 and 32 weeks;
- gradual normalization occurs closer to the birth of the child.
Causes of arrhythmia and methods of prevention
Disturbances in normal heart rhythm in adults occur for the following reasons:
- age-related changes;
- bad habits;
- stressful situations, psycho-emotional stress;
- lack of physical activity or its excess.
To maintain cardiovascular health, it is important to lead an overall healthy lifestyle. Experts say walking at an average speed is the most beneficial for the heart. Unlike running and other intense exercises, you can do walking for a long time without feeling very tired. While walking, there is no significant increase in heart rate, so this exercise is suitable even for people with heart disease.
Measurement
Pulse measurement is usually performed at the wrist. It is enough for a person to count the number of pulse waves in 1 minute. To obtain more accurate data, it is recommended to take measurements on both limbs. As a comprehensive examination in a hospital setting, the doctor will first find out the heart rate, then he will count the number of respiratory movements (RR) in 1 minute and determine the type of breathing. The resulting indicator is especially important for assessing the child’s development.
When measuring your pulse, you need to pay attention to its rhythm. The shocks should be of equal strength and at equal intervals of time. If there are no deviations, it is enough to spend 30 seconds on the procedure, and then multiply the result by 2. If a clear disturbance in the heartbeat is detected, it is better to spend at least 1 minute on the measurement and consult a doctor. The specialist will prescribe instrumental examination methods. The main one among them is electrocardiography (ECG). It will allow you to evaluate the electrical activity of the heart and identify the causative factor of arrhythmia. As a supplement, the following tests are prescribed:
- Daily ECG monitoring will allow you to see changes in heart function throughout the day under the influence of various factors.
- A treadmill test is prescribed to assess heart rate under the influence of physical activity.
Due to problems with blood vessels or injuries, it is sometimes necessary to count pulse waves in other arteries. Instead of the wrist, you can palpate the neck. The vibrations will come from the carotid artery.
Characteristic deviations for women
There are 3 characteristic reasons for the deviation of the pulse from the norm in healthy women, which are not always taken seriously by them:
- Excess weight (obesity is an official disease in medicine, which is classified by stages).
- Uterine fibroids (a benign tumor that can sometimes cause certain symptoms when it appears).
- Menopause (during this age period, women experience a natural increase in heart rate).
Excess weight
Fat deposits in the area of the internal organs interfere with the normal movement of the diaphragm, a breathing muscle located between the chest and abdominal cavities. As a result, the depth of breathing decreases. If you are overweight, hypoventilation of the lungs and shortness of breath occur even with light exertion.
To compensate for the lack of oxygen, the heart is forced to work faster to provide blood supply to the body. The closer your body weight is to normal, the better your heart functions.
Uterine fibroids
Another condition characteristic only of women is uterine fibroids. This benign tumor often does not cause any symptoms, but is accompanied by heavy menstruation and becomes the cause of chronic posthemorrhagic anemia.
The disease develops gradually, and the woman does not feel any sudden changes in her well-being. However, a constantly rapid pulse becomes a sign of tension in the cardiovascular system, which works in an enhanced mode to compensate for the lack of oxygen in the blood.
Climax
During menopause, women often experience rapid heartbeats, significant changes in blood pressure, sweating, and pain in the heart. Many people do not pay attention to this and do not get treatment. However, modern gynecology offers many means to improve well-being during this period. You shouldn't refuse this opportunity.
A deviation of the pulse from normal values in women can be an early or even the only external sign of many diseases. Paying close attention to your health and regularly measuring this indicator will help you recognize dangerous diseases at an early stage, when their course is reversible.
Features of bradycardia
A slowing of the heart rate to 50 beats or below is called bradycardia. It is a sign of physiological and pathological factors. In the first case, the list of reasons for a decrease in heart rate is as follows:
- During sleep, a person's metabolism slows down, body temperature drops slightly and heart rate decreases by about 10% of normal. The reason for the change in indicators is the complete relaxation of the body.
- Stimulating reflex zones (eyeballs, carotid artery) can inadvertently cause a slight slowing of the pulse.
- In older people, bradycardia can be a consequence of age-related cardiosclerosis. Areas of connective tissue scattered throughout the myocardium impair cardiac contractility, which contributes to a decrease in heart rate
- When exposed to cold for a long time, the heart rate slows down as a protective reaction. The body begins to save resources in order to resist adverse effects longer.
- Constant physical activity forces the heart to work harder than it should. Tissue hypertrophy begins, against the background of which bradycardia develops. For professional athletes, a heart rate in the region of 40-45 beats per minute is considered normal.
The pathological form of bradycardia is a consequence of the following factors:
- inflammatory diseases of the heart muscle;
- myocardial infarction;
- taking antihypertensive medications;
- impulse conduction disturbance;
- hypothyroidism (thyroid hormone deficiency);
- hypotension (low blood pressure);
- stomach ulcer;
- high intracranial pressure.
If it is not possible to identify the causative factor, a diagnosis of “idiopathic bradycardia” is made. If it is not accompanied by other disorders and the symptoms are not particularly pronounced, then it is also equated to physiological forms.
How to measure pulse correctly?
This procedure can be carried out either by a doctor or independently at home, using an automatic tonometer with a pulse sensor or your own fingers. This method is called palpation. To avoid distorted results, measurements should be taken at rest, in a sitting or lying position. It is optimal to measure your heart rate after a night's sleep without getting out of bed. You should not measure your pulse immediately after eating, taking medications, walking, or being in the cold or heat.
The traditional way is to measure the pulse through the arteries in the wrist. You need to place your index and middle fingers on the artery and note the time. You should know that measuring your pulse by placing your thumb on your wrist is incorrect.
To ensure accurate results, time is recorded on a stopwatch. You can count the pulsations per minute or use the 20 second method. During this time, the pulse is measured, after which the result is multiplied by three. In what areas of the body can the pulse be measured?
The palpation method for determining heart rate is applicable not only to the wrist, but also to other parts of the body:
- artery in the elbow area
- carotid artery
- armpits
- temporal artery
- groin area
- radial artery.
Pathological causes
The heart rate can vary in one direction or the other due to pathological changes in the body. We are talking about six main diseases.
- Algorithms for measuring respiratory rate, pulse and blood pressure in children
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a deficiency of thyroid hormones and the reverse process is hyperthyroidism with an excess of substances in the bloodstream. Hemodynamic disturbances affect the third reflex zone of the heart.
In the first situation, tachycardia occurs, in the second - a decrease in heart rate per minute. Prolonged course of both conditions is associated with an increased risk of fatal or disabling complications.
Diabetes
Generally destroys organs and systems, right down to the visual analyzer. With endocrine pathology, the heart wears out faster; without proper treatment, natural death occurs 10-15 years ahead of schedule.
Diabetes of the first type is especially dangerous, since it is not treated, but only corrected with medication, and not always to a sufficient extent.
Hypercortisolism or Addison's disease (reverse phenomenon)
Impaired synthesis of cortisol and other corticosteroids (to a lesser extent). Maintenance hormonal therapy and surgery to eliminate the root cause are required (in the vast majority of cases, the main factor is a tumor in the adrenal glands or pituitary gland).
Congestive heart failure
Causes cardiac ischemia and accelerates the rhythm, sometimes to significant levels. The course without therapy entails a heart attack, sooner or later (usually within 3-5 years from the onset of the first symptoms, by which time the disease is far from at the initial stage of development).
The first signs of heart failure are described in this article.
- Why calculate your heart rate if you decide to play sports?
Acute myocardial ischemia
Leads to death in 35-50% of cases. An extensive type of heart attack is fatal in 95% of clinical situations. Arrhythmia is the hallmark of the process, along with accompanying manifestations.
Rhythm
Normally, the intervals between heartbeats should be the same. This pulse is called rhythmic. Normally, a person should not feel the heartbeat at rest. If you can feel your heart beating, the person may have an arrhythmia.
It is manifested by the loss or appearance of extra beats, an increase or decrease in the intervals between them. With arrhythmia, the heart seems to freeze or, conversely, begins to beat too quickly. Arrhythmia can be determined using an ECG.
The most commonly diagnosed are extrasystolic arrhythmia (extrasystole) and atrial fibrillation.
Extrasystolic arrhythmia is the appearance of extra heart contractions. Patients complain of a feeling of cardiac arrest, weakness, and dizziness. This phenomenon is typical for a number of diseases. These include cardiac malformations, VSD, and ischemia. Extrasystoles may indicate the presence of pathologies of internal organs and occur due to abuse of tobacco products. Isolated occurrences of extra heartbeats occur in healthy people, but regular extrasystoles are a reason to consult a doctor. Atrial fibrillation or atrial fibrillation is characterized by a pulse deficit. With this pathology, the heart rate does not coincide with the pulse. Atrial fibrillation is caused by chaotic twitching of the atria. Because of this, the ventricles of the heart cannot contract synchronously and at the same rhythm.
Atrial fibrillation can be episodic, long-term or chronic. If the pathology occurs sporadically, it may go away on its own. People with long-term (more than a week) and chronic atrial fibrillation require drug therapy - taking beta1-blockers. Also, a special procedure is used to restore the heart rhythm - ablation or ablative destruction. It involves applying electric current to the pathological area.
For severe arrhythmia that cannot be treated, the patient is advised to undergo surgery to install a pacemaker or portable defibrillator.
Characteristics
When studying the pulse, the following indicators are assessed:
- symmetry on the vessels of the same name on opposite sides of the body;
- rhythm of pulse waves;
- frequency per minute or equal periods of time;
- tension, resistance;
- fullness;
- average value;
- ripple waveform;
- the presence or absence of a deficit between heart rate and pulse.
What does each of these criteria mean? The following are the characteristics with explanations:
- Symmetry - assessment of pulse fluctuations in the vessels of the same name in different halves of the body (on the radial arteries of the arms or carotid arteries on both sides of the neck). With a normal pulse, there are no differences in time interval, size or strength. The exception is when the patient has an injury to the upper or lower extremity, a scar or scar in the palpable area, swelling of this area, or changes in the lymph nodes on the corresponding side.
- Rhythm is the time interval between the sensation of pulse waves. Normally it should be the same. If the difference is noticeable, they speak of an arrhythmic pulse and heart rate. In differential diagnosis, the state of respiratory arrhythmia is taken into account, during which the heartbeat evens out during inhalation and air retention. Another reason for rhythm disturbances: single or multiple extrasystoles, blockades with episodes of interruption in the pulse, incoming attacks of paroxysmal tachycardia, a dangerous form of fibrillation or flutter of the atria/ventricles of the heart, which requires mandatory treatment.
- Frequency per unit of time is the number of pulse beats per minute. With a regular, correct rhythm, they count in 15 seconds and multiply the data obtained by 4, for the total - in 60 seconds. When palpating an irregular pulse, take into account the number of waves per minute without interruption. Normally, in an adult, it ranges from 60 to 80 beats at rest and 90-120 under load. Compare the results obtained using the table, which shows the criteria for each age group. Pathology is indicated by a significant excess of the upper and lower limits of the norm. Pulse less than 40-30/min. in an adult - a sign of complete heart block, weakness of the sinus node, or poisoning with medications or narcotic drugs. Speed up more than 120/min. characteristic of endocrine pathology, serious heart rhythm disturbances or taking stimulant substances/medicines.
- Tension is an indicator of the resistance of the arterial wall under the blood flow at the moment the vessel is pressed with fingers for counting. There is a relationship between the level of systemic pressure and the severity of fluctuations - the higher it is, the stronger the tension is felt and the greater the force required to press the artery until the pulse wave disappears. Experts distinguish three degrees, when the pulse is soft, normal or hard, which often indicates hypertension.
- Fullness - this indicator reflects fluctuations of the arterial wall under the influence of blood flow from the cavities of the heart to the periphery. To measure, the doctor presses the vessel with three fingers and changes the position and pressure of the hand until the extreme degree of decrease and then the greatest resistance is felt. A normal human pulse is of satisfactory filling. With a weak alternation of oscillations, they speak of an empty or intermittent pulse as a consequence of blood loss, shock, injury, congenital or acquired heart disease.
- is determined by the filling and voltage of the pulse waves . The indicator depends on cardiac activity, the change in cycles of systole, when the arteries expand and fill, and diastole, during which the vessels collapse. This value is influenced by the degree of vibration of the walls and their ability to stretch. In elderly patients with atherosclerosis or pathology of the valve apparatus, vascular tone is reduced, which is manifested by less compliance of the arteries and a higher pulse. With slow cardiac activity against the background of progressive cardiac failure, reduced blood volume and slight fluctuations, the pulse decreases.
- The shape of the pulse wave depends on the speed of the heart rate, the time during which blood is expelled from the left ventricle, the degree of arterial resistance, and venous outflow. If the function of the heart valves is preserved, if there is no cardiac congestive pathology, it does not change. To determine, the doctor presses the artery with his fingers and tries to feel the rate of increase in the pulse wave. After which it makes a conclusion about whether a person’s pulse is high or low/small.
- Pulse deficiency is a condition when the frequency of pulse fluctuations differs from the number of heart beats. Or weak waves are not tactilely detected when an artery is pressed on the arm or neck, against the background of rhythmic contractility of the organ, heard during auscultation. The disorder occurs more often with extrasystole or atrial fibrillation, fibrillation.