Why might an arrhythmia attack occur?
Rhythm disturbances appear due to changes in cardiomyocytes (the working mass of the heart muscle), the conduction system (cells that establish the order of contractions), or due to pathology of other systems and organs. The following reasons are identified:
- Physical overload . An untrained heart tries to provide blood to the suddenly working muscles of the limbs, which leads to natural tachycardia. In this case, it is very important to know your submaximal heart rate - a limit beyond which you should not go. At higher heart rates, the organ wastes energy irrationally, since the period of myocardial relaxation is critically reduced.
- Psychological stress . Under the influence of strong emotional experiences, biologically active substances are released that cause the heart muscle to contract faster. “Pressor amines” are mediators synthesized by the adrenal glands (Adrenaline, Norepinephrine, Epinephrine, Norepinephrine), which cause vasospasm, tachycardia, and increased body temperature. During the day, their concentrations change, just like a person's mood.
- Abuse of bad habits and stimulants (nicotine, alcohol, tea and coffee) significantly changes the heart rhythm. Different substances have different effects on contraction frequency. In any case, it is strongly recommended to avoid bad habits due to their not always predictable harm to the cardiovascular system. There are a large number of fatal arrhythmias, in which it is extremely difficult to provide effective assistance to the victim due to the lack of medical personnel nearby. The lion's share of them falls on the state of intoxication.
- Hypoxia is a decrease in oxygen content in the blood. Occurs during prolonged stay in closed, hot rooms, in large crowds of people, or in the presence of respiratory diseases.
- Taking medications - glycosides, antidepressants, sympathomimetics.
- True cardiac causes : exacerbation of existing heart pathologies (coronary disease, developmental defects, cardiomyopathies, arterial hypertension).
- Endocrine pathologies (thyroid dysfunction), diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Idiopathic arrhythmia - occurs in the absence of an obvious cause.
Diagnostics
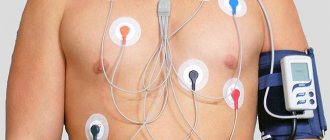
The stethoscope is still a valuable tool for identifying arrhythmias, but there are modern tests that can pinpoint the problem and signs of cardiac arrhythmias in women or men. An electrocardiogram (ECG) displays a graph of the heart's electrical activity using small electrodes attached to the chest. The curve on these graphs shows the type of arrhythmia. Since the arrhythmia may not occur in the hospital, there are portable ECGs that the patient wears at home. Some are turned on continuously over a period of time (called a Holter monitor), while others turn on when a person senses an arrhythmia (called an event monitor or loop recorder).
Certain arrhythmias may be associated with exercise, so patients may be asked to walk on a treadmill or ride an exercise bike while connected to an ECG machine.
Electrophysiological study (EPS) is a more complex test. Thin tubes are inserted into a blood vessel in the leg and directed toward the heart. They hold electrodes that can find muscle tissue that may be causing abnormal electrical activity.
What to do and how to relieve symptoms?
If the condition is accompanied by fear of death, loss of consciousness, or the person’s condition worsens significantly, it is necessary to call an ambulance. Before her arrival, at the pre-hospital stage, you should adhere to the following algorithm:
- Determine the presence and nature of arrhythmia by palpating the pulse in the carotid or peripheral arteries.
- Eliminate the impact of the factor, which provoked the arrhythmia:
- hypoxia - take to fresh air, free from tight clothing;
- physical overload - ensure complete rest;
- psychological stress - organize an emotionally comfortable environment, give a calming medicine (valerian tincture - 40 drops);
- known illness - for example, to stop the angina attack that caused the arrhythmia with Nitroglycerin.
- Carry out drug correction of arrhythmia (performed by qualified specialists).
Clinically it is possible to detect:
- Atrial fibrillation (fibrillation) (chaotic excitation and contraction of the muscle fibers of this part of the heart causes irregular functioning of the ventricles). The main clinical symptom is the phenomenon of pulse deficiency. The heart rate (determined by placing the hand on the middle third of the left side of the chest) exceeds the frequency of oscillations of the walls of the arteries at the periphery (to count on the inside of the wrist, press 3-4 fingers against the radius 0.5 cm below the end of the eminence of the thumb). Atrial fibrillation requires drug correction (antiarrhythmic drugs, cardiac glycosides, calcium antagonists, beta blockers), prescribed by a specialist after taking an electrocardiogram. Emergency care for fibrillation at the pre-medical stage is to give the victim a sedative (Valocordin, valerian) and provide comfort. You can try the hallux valgus tests described below, but their effectiveness in this case is low.
- Ventricular fibrillation (chaotic excitation and contraction of myocardial fibers). It is manifested by asystole - the absence of heartbeat and pulse in the peripheral (radial) and central (common carotid artery - located in the upper half of the neck, you need to slide your fingers from the Adam's apple up and to the sides) vessels. First aid: resuscitation measures . Before the ambulance arrives, you should press on the middle part of the sternum with straight, clasped hands at a frequency of 2 times per second. If you don't have the skills, you don't need to take breaths . Emergency assistance consists of defibrillation.
- Paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia (rhythmic heart contractions with a frequency of 140-220 per minute). The attack suddenly begins and ends. Symptoms include the sudden onset of a strong heartbeat, a feeling of pulsation in the head and neck, and tightness in the chest. Abrupt cessation gives the illusion of cardiac arrest. Treated with Lidocaine and Amiodarone.
- Paroxysmal sinus tachycardia (attack of heartbeat with a frequency of 150-240 beats per minute). Accompanied by sweating, dry mouth, dizziness, pain in the pit of the stomach. You can help with arrhythmia at home by performing vagal tests (their essence is the reflex activation of the vagus nerve, which causes bradycardia):
- squatting on your toes with tension in your abdominal muscles;
- massage of the carotid sinus (at the angle of the lower jaw);
- pressing on the root of the tongue (stimulating the gag reflex);
- imitation of a coughing attack;
- muscle tension at the height of a deep breath.
Symptoms
When the heart beats faster than normal, it is called tachycardia . Symptoms and signs of arrhythmia include:
- chest discomfort
- cardiopalmus,
- dizziness,
- sometimes fainting.
When the heart beats slower than normal, it is called bradycardia . It can cause fatigue, dizziness, lightheadedness and fainting as it usually causes low blood pressure.
Almost everyone's heart will flutter from time to time, and it usually doesn't mean anything. More often, symptoms of cardiac arrhythmia occur in men and treatment is not always necessary. But if a person has chest pain, feels weak, or notices that the pulse is irregular, either very fast or very slow for a long period, it is time to see a doctor. Source: Insider's View Focus on the Arrhythmia Patient. Boqueria O.L. Annals of Arrhythmology, 2014. p. 196-199.
Symptoms of this disease may not appear. Arrhythmia can be detected by a specialist during a routine clinical examination: before any of its signs appear. But predominantly, heart rhythm disturbances are characterized by the following symptoms:
- pain in the chest;
- increased feeling of heartbeat;
- accelerated heartbeat;
- slow heartbeat;
- dyspnea;
- loss of consciousness or fainting.
In most cases, in a person who has a certain type of arrhythmia, such arrhythmia occurs repeatedly.
Some types of arrhythmias are initially asymptomatic or with few symptoms. Other types of arrhythmias, on the contrary, manifest themselves in pronounced symptoms, but do not have serious consequences. Typically, the nature and severity of the underlying heart disease that causes the arrhythmia are more important than the arrhythmia itself.
Prevention of complications
Rhythm disturbances are dangerous due to the possibility of blood clots forming and breaking off. The most unfavorable in this regard is atrial fibrillation.
To avoid thromboembolic complications, the following drugs are used:
- Anticoagulants (reduce blood clotting):
- with a direct mechanism of action (heparin and heparinoids);
- with indirect (hydroxycoumarin and phenylindanedione derivatives).
- Antiplatelet agents (reduce the ability of platelets to stick together):
- acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin), Clofibrate, Anturan, Dipyridamole.
The drug regimen is selected by the attending physician based on the number of risk factors present in the patient.
How does arrhythmia manifest?
Arrhythmia may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- a feeling of interruptions in the work of the heart;
- a feeling of somersault, a jolt in the heart;
- accelerated heartbeat;
- suffocation;
- dizziness;
- general weakness, fatigue;
- exercise intolerance.
The most severe manifestations of arrhythmia are presyncope and loss of consciousness, which are most often associated with a very high heart rate (more than 200 beats/min).
In addition, there are “silent” arrhythmias that are asymptomatic. They are usually diagnosed by electrocardiography.
conclusions
Paroxysm of arrhythmia occurs with the active use of compensatory capabilities.
This happens with physical or emotional overload, exacerbation of the disease. You can relieve an attack of arrhythmia at home by ensuring complete rest, sometimes using light sedatives. For sinus tachycardia, vagal tests will be effective, while ventricular fibrillation requires resuscitation measures. The diagnosis of arrhythmia is confirmed by an electrocardiogram.
Disruption of blood flow can lead to the formation of a clot in the heart cavity (detected by ultrasound), its rupture and thromboembolic complications. For prevention, anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents (Warfarin, Xarelto, Dabigatran) are used as continuous medications.
Treatment methods for arrhythmia
Treatment of arrhythmia depends on its type, the cause of the arrhythmia, and the individual condition of the patient.
For any arrhythmia, actions aimed at normalizing lifestyle and general health are useful, including proper nutrition, healthy sleep, quitting smoking and other bad habits, dosed physical activity, such as therapeutic walking, swimming, cycling.
Drug treatment
The basis of drug treatment is antiarrhythmic drugs. In some cases, the doctor may decide that drug treatment is not required. Under no circumstances should you use medications at your own discretion, without consulting a doctor.
Specialist consultation
To treat arrhythmia, you should contact a cardiologist. Cardiologists at Family Doctor JSC have extensive experience in diagnosing and treating arrhythmias. If you need an in-depth examination of the condition of your heart, contact the high-tech divisions of our network - the Rehabilitation Center (Polyclinic No. 5) and the Hospital Center.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
How is cardiac arrhythmia treated?
There are several methods for treating arrhythmia:
- drug therapy. The patient can be prescribed both drugs that have antiarrhythmic properties and drugs that do not directly affect the electrophysiological properties of the myocardium. The latter are called upstream therapy. It includes ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists, statins, corticosteroids, polyunsaturated fatty acids and other drugs. Upstream therapy is aimed at eliminating the causes that lead to arrhythmia: inflammatory processes, high blood pressure, myocardial remodeling;
- implantation of a pacemaker - a medical device that affects the heart rhythm. Most often, a pacemaker is used for slow heart rate and AV block;
- radiofrequency ablation of the heart (RFA) is a surgical intervention during which an electrode is used to destroy the focus of pathological excitation of the myocardium or areas of abnormal impulse conduction.
Classification
In medicine, there are several types of arrhythmias - each of them has different symptoms and course, so it is necessary to diagnose not just the arrhythmia, but also its specific type - the choice of therapeutic therapy will depend on the results.
- Sinus arrhythmia. Most often diagnosed in childhood and adolescence, it is characterized by an abnormal alternation of heart beats. With this type of disorder in question, no specific treatment is required, the patient’s condition is not disturbed, and the normal rhythm of the heartbeat can be quickly restored by simply holding the breath for a few seconds.
- Sinus tachycardia is diagnosed if the heart rate exceeds 90 beats/min, of course, for no apparent reason (running, exercise, excitement). Typically, with such tachycardia, the heart rate does not exceed 160 beats per minute under calm conditions, and only during intense exercise can it reach up to 200 beats. It is caused by many factors associated with pathological processes in the body, therefore the treatment of such tachycardia is aimed at the underlying disease;
- Sinus bradycardia. This type of arrhythmia is manifested by a decrease in heart rate - in a patient this figure may be less than 55 beats per minute.
- Paroxysmal tachycardia, similar to extrasystole, developing suddenly and also suddenly stopping, is characterized by a regular, strict rhythm, although the contraction frequency can reach 240 beats/min (atrial) or pronounced changes in hemodynamics (ventricular);
- Flickering arrhythmia. Doctors characterize this type of arrhythmia as fluttering in the chest - the heart begins to contract faster (up to 150 beats per minute), then even faster (up to 300 beats per minute), the atria do not contract completely, and the ventricles do so irregularly.
Ventricular flutter and fibrillation are considered the most life-threatening manifestations of arrhythmia. This usually occurs against the background of heart pathologies, electric shock, or taking certain medications.
Clinical signs of atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation, or atrial fibrillation, is the most common disorder, characterized by an increase in heart rate up to 600 beats per minute.
It can be constant, persistent and paroxysmal. The most common symptoms of atrial fibrillation include rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, discomfort or stabbing pain in the heart area, increased sweating, increased urination and muscle weakness. Patients complain of a feeling of unreasonable fear, a state of panic, and dizziness and fainting are often observed.