Polyneuropathy is considered multiple damage to peripheral nerves, which is manifested by paralysis, sensory disturbances, trophic and vegetative-vascular disorders. Develops predominantly in the distal extremities. The disease is a common symmetrical pathological process, which is usually localized in the distal muscles and gradually spreads proximally.
What is polyneuropathy
Polyneuropathy is one of the most dangerous and severe neurological disorders, the main characteristic of which is damage to the peripheral nervous system.
Neuropathy is a condition of the body in which peripheral nerves, that is, those not included in the brain and spinal cord system, are partially or completely affected. The main disease has more than several dozen species, which are qualified by a variety of parameters:
- cause of occurrence;
- symptoms of illness;
- type of damaged nerve process.
Polyneuropathy is characterized by symmetrical damage, for example in both feet, and in more severe situations, symptoms are observed not only in the lower but also in the upper extremities. In rare cases, the disease has no manifestations or external signs, but is quickly diagnosed using hardware examinations and laboratory tests.
There are several forms of the disease:
- sensory;
- motor;
- sensorimotor;
- vegetative;
- mixed.
The first symptoms of neuropathy are tingling sensations and numbness in any part of the body; less often, pain occurs.
Expert opinion
Author: Irina Gennadievna Smolentseva
Head of the Research Center for Diagnosis and Treatment of Parkinson's Disease, Professor, Associate Professor of Medical Sciences
Polyneuropathy of the upper and lower extremities is a fairly common disease caused by dysfunction of the peripheral nervous system. The disease is classified according to the location of the source of symptoms into upper and lower polyneuropathy and into primary and secondary.
The causes of primary polyneuropathy are difficult to establish; it is mainly a hereditary pathology, while secondary polyneuropathy develops due to various factors. These include diabetes mellitus, deficiency of B vitamins, consequences of serious injuries, chemical intoxication, alcohol, drug and tobacco addiction, severe hypothermia of the extremities, hormonal imbalance, toxicosis of pregnant women, systemic and chronic complex diseases of the kidneys and liver.
Treatment of polyneuropathy requires an integrated approach; the tactics of therapy and recovery procedures are selected in accordance with the severity and neglect of the disease, the presence of side effects and concomitant diseases. Doctors at the Yusupov Clinic will conduct a full examination of the patient and, based on the diagnosis, prescribe comprehensive treatment.
Polyneuropathy (PNP) is a disease of the peripheral nervous system that develops as a result of diffuse damage to peripheral nerves—their axons (axonal polyneuropathies), the myelin sheath (demyelinating polyneuropathies) or the bodies of neurons (neuronopathies) [9]. The pathogenesis of axonal type polyneuropathies is based on generalized damage to the axial cylinders of peripheral nerves.
Pathogenesis
.
Axonal degeneration (axonopathy) is the result of impaired neuron metabolism due to insufficient energy production in mitochondria and/or impaired axonal transport. In axonopathies, the myelin sheath suffers secondarily (secondary demylinization). Myelin can be damaged as a result of nerve ischemia (damage to the vasa nevrorum
), deposition of substances or immune complexes toxic to the nerve in the endoneurium (which is typical, for example, of diabetes mellitus, especially type 1 - with high hyperglycemia and autoimmune disorders) [4]. Accordingly, among the causes of axonopathy of peripheral nerves are metabolic disorders, toxic effects, ischemia of nerve trunks, hereditary predisposition and autoimmune mechanisms [5]. According to the etiological factor, the vast majority of axonal PNPs are metabolic and toxic, among which the first place is occupied by diabetic (up to 50% among patients with diabetes mellitus and up to 90% of damage to the nervous system in diabetes [9, 12]) and alcoholic (up to 50% among patients alcoholism [2, 9]).
The cause of toxic-metabolic PNP is exo- and endogenous intoxication. Substances coming from outside or their own metabolites that are toxic to peripheral nerves cause their damage. The severity of this damage depends on the degree of toxicity of the agent (acute metabolic PSP is distinguished, developing against the background of severe general intoxication, for example, PSP with rapidly increasing liver failure or uremia, poisoning with organophosphorus substances, arsenic, lead, as an undesirable effect of treatment with lithium drugs, cytostatics ), the duration of its influence, the own genetic characteristics of the metabolism of nervous tissue, and the autoimmune factor also plays an important role [13].
Most of the metabolic ASPs frequently encountered in the clinic are the result of long-term exposure to endo- and exogenous toxic agents (diabetic, hepatic, uremic, alcoholic, occupational, medicinal). The result of such intoxication is damage to the axial cylinder of the axon. Clinically, this is manifested not only by sensory disturbances and muscle weakness (which is also typical for demyelinating PSP), but also by muscle wasting and pronounced trophic disorders. All these signs indicate long-term suffering of peripheral nerve axons. Electroneuromyography (ENMG) reveals a decrease (sometimes to the point of complete absence) in the amplitude of sensory potentials and M-responses of peripheral nerves. In patients with axonal type PSP, motor functions are often sufficiently preserved (there are no pronounced paresis, patients retain the ability to walk, often without additional support), while sensory (pain and paresthesia) and trophic disorders are disabling. Thus, axonal sensorimotor PSP is one of the important pathogenetic factors in the development of diabetic foot syndrome [3]. Axonal nerve damage develops slowly and gradually, but with proper treatment it is potentially reversible.
With massive exposure to an agent toxic to the peripheral nervous system, the participation of the ischemic component (due to the suffering of the vasa neurorum
), autoimmune influences develop PNP of the axonal demyelinating type, such as uremic, lead, amiodarone, caused by exposure to substances highly toxic to nerves [9]. In the most common diabetic PSP, the demyelinating component is maximally present in insulin-requiring diabetes mellitus (characterized by higher hyperglycemia), and the severity of demyelination of peripheral nerves increases with sharp increases in blood glucose levels [4, 7]. The presence of the demyelinating component in metabolic PSP is influenced by hereditary factors (genetically determined myelinopathy, which would proceed subclinically without additional exposure to a toxic agent), autoimmune damage (for example, myelinopathy is more pronounced in type 1 diabetes mellitus, in which immunocompetent cells damage pancreatic tissue ) [4, 14].
PSP of the axonal demyelinating type are more severe, with severe paresis, sensory ataxia, and neuropathic pain syndrome, but often, with timely elimination of the toxic factor, they quickly regress. In case of a very severe and persistent course of the disease, given the role of the autoimmune mechanism in the development of this type of metabolic PSP, short-term administration of immunomodulatory therapy (usually glucocorticoids, sometimes cytostatics) is necessary [9, 11].
Clinical course of PSP.
As already mentioned, with prolonged exposure to an agent that is moderately toxic to nerves, axonopathy develops slowly, which is not always noticeable. Predominant damage to poorly myelinated vegetative and sensory fibers causes paresthesia, increased cold sensitivity of the hands and feet, and mild trophic disorders. With ENMG, it is not always possible to identify characteristic signs of sensory and motor axonopathy - a decrease in the amplitudes of sensory potentials and M-responses - if large, richly myelinated nerves are examined, the axons of which suffer later. Signs of secondary myelinopathy are revealed more quickly, both clinical - the addition of neuropathic pain, paresis, and myographic - a decrease in the speed of propagation of excitation (SRV) along the nerves.
Provided an adequate therapeutic strategy is eliminated the effect of the factor damaging peripheral nerves, the prescription of drugs that affect the metabolism of nervous tissue, remyelination occurs, which is reflected both in ENMG in the form of an increase in SRV, and clinically in the form of regression of paresis and neuropathic pain, improvement in sensitivity. However, if polyneuropathy developed under conditions of prolonged action of a toxic agent, damage to the axons of peripheral nerves, a decrease in the amplitudes of sensory potentials and M-responses to ENMG persists, since the axial cylinders of the nerves have a much lower ability to regenerate than myelin.
Thus, in a study [8] devoted to the treatment of alcoholic PSP, the leading ENMG sign of damage to peripheral nerves in most patients was a decrease in ERP. Under conditions of elimination of the toxic factor (in this case, alcohol intake) and treatment with α-lipoic acid (berlithion in a daily dose of 600 mg), patients quickly, within 1 month, regressed ENMG and clinical signs of myelinopathy - the severity of paresis and pain syndrome (in points on a visual analogue scale from 5.2±1.0 to 2.6±0.5) significantly ( p
<0.05) SRV increased (for motor fibers
n. tibialis
from 36.93±1.12 to 42.22±0.8 m/s, for sensory fibers
n. suralis
from 32.45±0.70 to 38 .24±0.50 m/s), but signs of axonopathy (decrease in the amplitudes of sensory and motor responses of peripheral nerves, sensory loss of the polyneuritic type, trophic disorders) persisted even after 6 weeks of treatment.
Thus, we can imagine the following scheme for the development and course of metabolic PSP (see table)
: highly toxic, highly concentrated toxic agents lead to the development of polyneuropathy of the axonal demyelinating type (in the development of which hereditary, vascular, and autoimmune factors also play a significant role), long-acting endo- and exogenous poisons lead predominantly to axonal suffering with moderately severe secondary myelin damage (so how the process of remyelination constantly occurs) [7].
Treatment.
Axonal damage to nerves, both primary and secondary, is reversible due to the regeneration of damaged axons and the terminal sprouting of surviving axons, but this process proceeds slowly (months), often axonal regeneration is incomplete. To regress axonopathy of peripheral nerves, it is necessary to neutralize the effects of the toxic agent (correction of metabolic and nutritional disorders, detoxification, influence on autoimmune mechanisms); pathogenetic therapy aimed at restoring impaired axonal metabolism (mitochondrial disorders, damage caused by oxidative stress) is also of great importance.
Thus, in the pathogenetic treatment of axonal PSP, depending on their nosological and clinical-electrophysiological variant, detoxification and correction of metabolic and nutritional disorders should be present; vascular therapy (disaggregants, venotonics, pentoxifylline, vasoprostan); drugs that affect the universal mechanisms of axonal damage (vitamins and vitamin-like drugs); if necessary, influence on autoimmune components (glucocorticoids, plasmapheresis). In some cases, when the representation of myelinopathy in the structure of damage to peripheral nerves is large and it is difficult to distinguish toxic-metabolic polyneuropathy from inflammatory (for example, Guillain-Barré syndrome in a patient with alcoholism or the debut of chronic inflammatory demyelinating PSP in a patient with diabetes), it is necessary to conduct a trial of immunomodulatory therapy , its rapid effectiveness will allow us to speak in favor of the prevalence of the autoimmune mechanism of damage to peripheral nerves in the patient [7, 11].
In the treatment of all metabolic PNP, it is necessary to eliminate (if possible) the poison that affects the peripheral nerves and use drugs that improve the metabolism of the nervous tissue of the peripheral nerves. The latter must be used for a long time, since the first effect of these drugs will be to accelerate remyelination, but the restoration of the axons themselves - and these APNs are axonal - requires a significantly longer amount of time.
α-lipoic (thioctic) acid is a vitamin-like substance that is endogenously formed in the body; as a coenzyme, it participates in the oxidative decarboxylation of α-keto acids. The main function of endogenous lipoic acid in the body is to participate in the aerobic metabolism of the glycolysis product pyruvate. Thioctic acid is a coenzyme in the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvic acid to acetyl-CoA and α-ketoglutaric acid to succinyl-CoA in the Krebs cycle. By facilitating the conversion of lactic acid into pyruvic acid with subsequent decarboxylation of the latter, α-lipoic acid helps eliminate metabolic acidosis [6]. Thioctic acid has a complex complex effect: hypoglycemic, lipotropic, hepatoprotective, anti-atherosclerotic, and is a powerful antioxidant. Lipoic acid can exist in oxidized (-SS-) and reduced (SH-) forms, due to which its coenzyme and antioxidant functions are realized. The reduced form, dihydrolipoic acid, serves as an electron donor for the restoration of other antioxidants (vitamins C, E and glutathione), and recycles vitamin E when it is depleted. Dihydrolipoate increases intra- and extracellular levels of glutathione, an endogenous antioxidant.
The effect of exogenously administered α-lipoic acid on polyneuritic syndrome was first discovered in diabetes mellitus. Hyperglycemia caused by diabetes mellitus leads to the deposition of glucose on the matrix proteins of blood vessels and the formation of advanced glycosylation end products, resulting in a decrease in endoneural blood flow and endoneural ischemia. α-lipoic acid leads to a decrease in blood glucose levels and an increase in glycogen content in the liver, and has a hypoglycemic effect. The effect of the drug reduces the severity of sensory symptoms of polyneuropathy - pain, burning, numbness and “crawling” in the limbs.
The use of α-lipoic acid has a positive effect on universal mechanisms of axonal damage, such as the damaging effects of oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction, due to its antioxidant effect and increasing glutathione content. The energy-correcting effect of α-lipoic acid, which is tropic specifically to nerve axons, ultimately promotes rapid axonal regeneration [18].
The drug not only reduces the manifestations of oxidative stress, but also affects the vascular component of peripheral nerve damage, normalizing endoneurial blood flow (which is of great importance, for example, in diabetic microangiopathy) [16, 17]. The complex mechanism of action of α-lipoic acid explains its effectiveness against all axonal PNP, the pathogenesis of which is associated with toxic-dysmetabolic and vascular factors. Thus, the effectiveness of thioctic acid has been shown in uremic and alcoholic PSP, and in damage to peripheral nerves induced by cytostatics [15]. For the regeneration of peripheral nerve axons against the background of toxic and metabolic influences, the detoxification and hepatoprotective effects of α-lipoic acid are also important. The positive effect of the drug was noted in relation to liver diseases, hepatic coma, and some intoxications, including alcohol [6, 10].
With significantly severe axonopathy, given the slow rate of axon regeneration, long-term use of fairly high doses of α-lipoic acid is necessary. Usually its daily dose is 600 mg. It is preferable to start treatment with an intravenous drip of the drug - 600 mg (24 ml of solution) diluted in 200 ml of physiological solution, the duration of the infusion is from 2 to 4 weeks, depending on the severity of PSP. In especially severe cases, the drug is administered intravenously at a dose of 1200 mg per day. Then they switch to oral administration of α-lipoic acid - in tablets of 600 mg for at least 2 months [1].
In accordance with this clinical need - the need for long-term administration of fairly high doses of α-lipoic acid, given the potentially reversible, but slow nature of axonal regeneration - pharmaceutical forms of the drug have been developed. For example, Berlition 300 and Berlition 600, produced in the form of a solution for intravenous infusion of 12 and 24 ml, respectively (for the initial stage of treatment of PSP), and tablets of 300 and 600 mg (for continued therapy).
Compliance with all conditions of pathogenetic treatment of PSP - normalization of glycemia, cessation of the intake of exogenous poison, detoxification, correction of autoimmune disorders, long-term use of drugs that normalize axonal metabolism, promotes gradual regeneration of axons, reducing the severity of sensory and motor disorders, pain, paresthesia, paresis. Further studies are needed to clarify the dynamics of various types of metabolic ANPs against the background of such a therapeutic approach.
Causes of polyneuropathy
The disease can occur due to various factors. In most cases, the cause of the disease is diabetes mellitus type I or II, since the pathology affects the functioning of the vessels that feed the nerves and causes disruption of metabolic processes in the myelin sheath of nerve fibers, which leads to their damage. In diabetes mellitus, the lower extremities are primarily affected.
In rarer situations, the causes are considered to be:
- elderly age;
- AIDS virus;
- AIDS;
- negative environmental conditions or prolonged exposure to toxins on the body;
- alcoholism;
- smoking;
- drug use;
- hereditary and genetic predisposition.
The level of B vitamins is no less important. Long-term deficiency can lead to the development of polyneuropathy. Since vitamins are vital for the proper functioning of the nervous system.
There can be several causes of damage to the nerves themselves:
- poor blood supply to the nerves;
- abnormal deformations of nerve processes.
Mechanism of occurrence
The exact mechanism of damage to nerve cells is unknown; it is assumed that the drug penetrates from the blood into the intercellular fluid, from there it diffuses into the cell, where it damages the protein tubulin and other proteins.
Each drug has its own “point of application” to tubulin: taxanes break up its microtubules, platinum derivatives denature it, vinca alkaloids are disassembled into components.
The process of protein damage by cytostatics in all cells is the same, its consequences are varied:
- degeneration of nerve processes - axonopathy;
- degenerative changes in neuron cell bodies—neuronopathy;
- destruction of the myelin sheath of the nerves - myelinopathy throughout or partially.
The first signs of polyneuropathy
One of the very first signs of polyneuropathy is a feeling of tingling and numbness in the toes and hands. Then pain may appear. In most cases, symptoms rise from the lower extremities up to the legs and knees, and then appear in the upper extremities.
Most often, the patient’s condition is characterized by the following symptoms:
- sharp pain;
- increased sensitivity of the affected areas;
- burning;
- itching.
In this case, there is no tactile sensitivity of the limbs. It is necessary to regularly check the affected areas, since you can easily burn or overcool the skin, but still not notice the damage at all.
In rare cases, the patient loses a sense of balance and coordination, and therefore cannot move independently. In an advanced situation, the patient suffers from constant pain, which causes insomnia and depression, as the psychological state is shaken. Therefore, at the first symptoms of illness, you must immediately consult a doctor for qualified examination and treatment.
Symptoms of polyneuropathy
The causes of polyneuropathy are different, the symptoms in most cases are similar and do not depend on what caused the disease. The main features are:
- weakness in the upper or lower extremities;
- decreased sensitivity, which may worsen until sensations disappear completely;
- lack of a reflex reaction;
- crawling;
- burning;
- swelling of the distal areas;
- trembling fingers;
- uncontrollable muscle twitching;
- increased sweating, which does not depend on the environment and body temperature;
- dyspnea;
- cardiopalmus;
- severe dizziness;
- lack of sense of balance;
- lack of coordination;
- delayed wound healing.
The severity of symptoms varies from patient to patient and depends on the condition of the body. Sometimes the disease takes years to develop, but it can also occur in a matter of weeks.
The following symptoms are characteristic of motor polyneuropathy:
- weakness in the limbs;
- amyotrophy;
- delayed manifestation of reflexes or their complete absence;
- muscle spasms.
If the disease is left untreated and ignored for a long time, the situation may result in complete or partial paralysis.
Sensory polyneuropathy is more characterized by such symptoms as:
- loss of sensation in the limbs;
- sensation of vibration;
- deterioration in perception of temperature changes;
- causeless itching;
- tingling;
- strong burning sensation.
The disease can develop not only against the background of diabetes, but also with systemic diseases such as malignant tumors, injuries, arthritis, and vitamin deficiency.
Dynamics of manifestations
In patients suffering from sensory polyneuropathy of the lower extremities, positive sensory symptoms (burning sensations and other paresthesias) first appear in the feet, most often in the fingertips. Over time, negative sensory symptoms (numbness and decreased sensitivity) appear. As shorter and shorter nerve fibers are affected, they gradually spread proximally (to the lower leg and thigh).
After the symptoms in the legs rise to the middle of the legs, a violation of superficial sensitivity appears in the arms. This leads to the classic "socks and gloves" look. If the sensitivity disorder has risen to the middle of the thigh on the legs and to the level of the elbow on the arms, you can expect the appearance of an area of reduced sensitivity in the lower part of the anterior abdomen. It is caused by damage to the longest trunk nerves and has the shape of an irregular semicircle with the apex directed towards the sternum. In contrast to the level of damage in diseases of the spinal cord, sensory disturbances in sensory polyneuropathy are detected only on the anterior surface of the body and are absent on the back. Their upper border is curved rather than horizontal.
With porphyritic polyneuropathy, sensory disturbances are not detected on the feet and hands. And in the proximal parts of the limbs and on the trunk. If deep sensitivity fibers are involved in the pathological process, sensitive ataxia develops - a disorder of sensory perception of pressure, vibration and body position in space. It leads to incoordination and movement disorders. It manifests itself as a disorder of coordination and gait, decreased tone of skeletal muscles and distal limbs. Patients experience constant worm-like hyperkinesis of the upper extremities (slow movements of the fingers) with outstretched arms, which intensify with closed eyes.
Types of polyneuropathy
Researchers identify several types of disease:
- sensory. It is expressed to a greater extent by a disorder of sensory fibers, that is, sensitivity in the damaged limbs, for example, a sensation of crawling, tingling, numbness, burning;
- motor. It manifests itself as severe muscle weakness, which worsens to the point of absolute inability to move arms or legs. This can lead to muscle atrophy;
- vegetative. Unlike other types of disease, symptoms of damage to the autonomic nervous system appear in the foreground: increased sweating, excessive pallor of the skin, dizziness, disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and digestive system, constipation, rapid heartbeat, difficulty breathing. With vegetative-sensory polyneuropathy, several types of symptoms are combined at once;
- sensorimotor. Combines symptoms of motor and sensory polyneuropathy. In most cases, it is this form that is diagnosed;
- mixed. All the symptoms of the above forms are observed.
However, according to etiology, the following nosological forms of polyneuropathy are distinguished, which cannot be determined from a photo:
- hereditary;
- paraneoplastic, which is associated with malignant neoplasms in the body;
- for systemic diseases such as sarcoidosis, dysproteinemia, etc.;
- toxic, which occurs with alcohol dependence, long-term use of medications, long-term exposure to any other toxic substances on the body;
- for infectious diseases and vaccination, for example, diphtheria, influenza, measles, borreliosis, etc.;
- for metabolic disorders in the body, which include diabetic, uremic abnormalities, prolonged vitamin deficiency;
- inflammatory;
- non-inflammatory, such as Guillain-Barré syndrome, or chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy.
As the disease progresses, polyneuropathy is divided into the following categories:
- spicy. Develops over a short period of time, that is, several days or weeks;
- subacute. Symptoms increase in the patient over several weeks, but not longer than 2 months;
- chronic. The course of the disease occurs almost imperceptibly, covering several months or years at once, while the victim does not consult a doctor and does not relieve the symptoms.
Clinical phenomenology of chronic renal failure
Symptoms of damage to the nerve process - axonopathy - manifest several weeks and even months later than damage to the neuron - neuronopathy.
Platinum derivatives predominantly cause sensory disturbances in the legs, which destabilizes the gait, does not give the foot a feeling of the floor, which is why the patient has to use his eyes to choose a place to place the foot. It is possible that a motor component may be associated with muscle spasms. After completion of chemotherapy, the manifestations of polyneuropathy decrease very slowly, perhaps even increasing over 3 months - a symptom of inertia.
Pactitaxel initiates sensory disturbances, usually “pins and needles” and numbness, more often in the legs than in the arms. The feeling of “burning” soles is typical, especially after high-dose chemotherapy. Motor disorders are as atypical as autonomic ones. Normalization may take up to a year.
Docetaxel affects sensory fibers, the frequency of symptoms increases with a total of 500 mg, but severe polyneuropathy is practically impossible. Every 5-6 patients develop asthenia - weakness.
Vinorelbine does not begin to ruin your life right away - after a month of weekly injections, the sensitivity of the fingers is often impaired, gastrointestinal motility decreases, which is manifested by constipation, but the most common complication is asthenia in six out of ten patients, when they complain of severe fatigue precisely from the treatment.
Oxaliplatin changes the sensitivity of the hands with tingling of the fingertips, and the disturbances appear very early - literally after the first dose, reaching a maximum on the 3rd day. Between administrations everything seems to return to normal, but in the next course it is repeated and more intensively. The peculiarity is that 3 months after chemotherapy, the symptoms of polyneuropathy are the brightest, then improvement begins, six months after chemotherapy, symptoms of impaired sensitivity in the legs come to the fore, and the hands are less bothersome.
Fluorouracil “hits” the brain, causing gait instability - cerebellar ataxia and spasmodic eye movements - nystagmus, and changes speech due to sluggishness of the tongue. High doses and multi-day infusions may be complicated by encephalopathy. The frequency and intensity of manifestations increases many times in the absence of an enzyme in the cells that destroys fluorouracil metabolites.
During administration, irinotecan
With all the variety of clinical manifestations of polyneuropathy after chemotherapy and the absence of a clear diagnostic algorithm, the neurological complication can be recognized in time, but it is absolutely impossible to predict its duration.
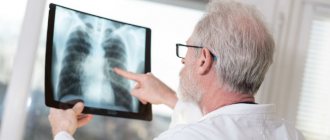
Diagnosis of polyneuropathy
In some cases, when making a diagnosis, the doctor initially relies on the patient’s description of the sensations and problems. In rare cases, a nerve conduction velocity test may be ordered.
Electromyography is a way to study the bioelectric potentials that arise in human skeletal muscles. The stimulation method makes it possible to determine the speed of propagation of nerve impulses in the patient’s nerve and muscle tissue.
The procedure is performed to find out the cause of muscle weakness. It can be performed on specific areas of the body, for example on the sciatic or gastrocnemius nerve, arm or forearm muscles. The examination is carried out by a qualified neurologist, as the doctor must examine the damaged limbs and check reflexes. It brings quite a lot of discomfort, so it is important to have a positive attitude in advance. Additionally, a nerve biopsy and consultation with an endocrinologist may be required.
Diagnosis can be difficult because the cluster of symptoms may correspond to many different diseases. Additionally, it is recommended to pass a set of laboratory tests:
- general blood test for comparison with reference indicators of hemoglobin level, coagulation rate, cellular composition;
- determination of sugar levels in biological fluids such as blood and urine to refute or confirm the presence of diabetes;
- biochemical analysis for indicators such as creatinine, urea, total protein, liver enzymes, vitamin B12 levels.
To exclude paraneoplastic syndromes, oncological screening is performed:
- carefully examine the mammary glands (ultrasound and mammography);
- lungs (CT);
- gastrointestinal tract (endoscopic examinations are performed); Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, pelvis, genital organs;
- if necessary, PET-CT.
It is necessary to understand that drawing up an examination plan is individual for each patient. The polyetiology and different mechanisms of development of the disease, the diversity of the clinical picture require a detailed and comprehensive examination, but despite this, it is still not always possible to identify the cause of the disease. In this case, the diagnosis of idiopathic polyneuropathy is established.
Treatment of polyneuropathy
A patient who has been diagnosed with polyneuropathy of the upper or lower extremities needs to prepare for long-term complex treatment, since the matter is not limited to the fight against symptoms that are not visible in the photo. When the disease occurs, nerve fibers are destroyed. It will take a lot of time and effort to restore them.
Initially, therapy begins with an impact on the cause that caused the disease, that is, with treatment of the main disease or stabilization of the patient’s condition. For example, if the cause is diabetes, then it is first important to reduce the sugar level in the body, and with an infectious-allergic cause of polyneuropathy, you should first fight the infection, and only then relieve the symptoms. If there is a deficiency of B vitamins, doctors first compensate for the deficiency, then treat polyneuropathy. If the cause of the disease is disturbances in the proper functioning of the endocrine system, hormone therapy is indicated. If the disease is accompanied by severe pain, then an anesthetic is prescribed orally and locally.
The most common treatment for polyneuropathy is vitamin therapy. A positive result is given by medications that improve blood microcirculation, thereby affecting the quality of nutrition of nerve fibers. Physiotherapeutic techniques, including electrophoresis, are widely used during treatment.
If the treatment is successful and the nerve fibers are restored in full, it is too early to relax and return to your normal lifestyle. It is necessary to conduct a course of rehabilitation therapy, since the disease affects the muscles, because lack of movement leads to a rapid weakening of muscle tissue. To regain your former mobility, you need to spend a long time and put in a lot of effort, and use the help of several specialists at once.
During rehabilitation, therapeutic massage is indicated. It may last 30, 40 or 60 minutes, depending on the severity of the problem and the need. A high-quality massage improves elasticity and tone of muscle and other tissues, reduces tension, has a positive effect on joint mobility, improves metabolic processes and lymph circulation, reduces stress levels and improves immunity.
Various physiotherapeutic methods also provide good results. They also improve microcirculation, relieve pain and restore muscle cells. For serious injuries, when full restoration of the upper or lower extremity is impossible, sessions with an occupational therapist will help. Occupational therapy is treatment by action. The specialist helps the patient adapt to the new condition, develop a new movement algorithm for performing everyday activities. The scheme of rehabilitation measures is prescribed individually for each patient. It may also include vitamin therapy, work with a psychologist, diet therapy and other methods.
When treating acute polyneuropathy, it is important to maintain joint mobility in the patient, even if he has already developed bedsores. Therefore, passive or active therapeutic exercises aimed at increasing the range of motion should be performed several times a day. It is important to pay attention to replacement therapy in bed and stretching. During the acute phase, it is necessary to control pain and relieve it with painkillers.
Patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome should receive respiratory support if necessary. You should also take time to learn how to use various aids.
Treatment of chronic polyneuropathy consists of walking support and progressive training. A special place in therapy is occupied by the elimination of complications. With the help of a physiotherapist, special exercises are performed to strengthen the muscles and prevent overexertion. Additionally, the following treatment methods are used:
- manual;
- isokinetic;
- isotonic;
- isometric.
During active therapy, it is necessary to learn the correct use of aids, including prostheses that compensate for weak muscle function. The therapist also teaches proper behavior at home, which reduces the risk of falls and household injuries and allows you to safely cope with everyday activities.
Consequences
If the function of the nerves that regulate the functioning of the heart is impaired, the rhythm of cardiac activity is disrupted, which can result in sudden death. In cases of severe muscle weakness, patients cannot move without assistance. In some polyneuropathies (Guillain-Barré syndrome), the function of the nerves that provide movement of the respiratory muscles is impaired.
The consequences of polyneuropathy can be different. In some patients, the symptoms of the disease reverse under the influence of medications. In others, despite timely initiation of adequate complex therapy, the disease progresses. The clinic's neurologists make every effort to stabilize the patient's condition.
Make an appointment
Prognosis of polyneuropathy
The disease is very dangerous for human health. Since it never goes away on its own and requires long-term treatment and rehabilitation. If the disease is allowed to develop, the consequences will be quite severe.
Prolonged muscle weakness quickly leads to a decrease in muscle tone, and then to complete muscle atrophy. In turn, this is dangerous with the risk of ulcers.
If the disease is ignored for a long time, polyneuropathy can result in complete paralysis of the limbs or respiratory system. A progressive disease causes a lot of inconvenience to the victim, forcing him to change his usual lifestyle, as people lose the ability to move independently and take care of themselves in everyday life. This can lead to problems with nerves, increased anxiety and depression. Therefore, it is important for the patient to receive timely help from a specialist - a psychologist.
2. Mononeuropathy
Damage to one peripheral nerve is called mononeuropathy
. The most common cause of mononeuropathy is domestic or accidental injuries. Prolonged pressure on the nerve caused by prolonged sedentary activities (such as in a wheelchair or in bed), as well as continuous repetitive movements, can also cause mononeuropathy. Damage to the intervertebral discs can cause pressure on the nerve and cause this type of neuropathy.
Carpal tunnel syndrome
is a common type of mononeuropathy. This is an injury caused by overuse when the nerve running through the wrist is compressed. People whose jobs require repetitive movements of the wrist (such as assembly line workers or those who constantly type on a computer keyboard) are at greatest risk of developing this syndrome.
Nerve damage can lead to numbness, tingling
, unusual sensations and pain in the first three fingers of the hand on the thumb side, especially during sleep.
Over time, carpal tunnel syndrome can weaken the muscles
in your hand.
With this condition, you may also experience pain, tingling, or burning in your arm and shoulder.
Here are examples of other mononeuropathies
which can cause weakness in affected parts of the body (arms and legs):
- Ulnar nerve neuropathy
occurs when the nerve that runs close to the surface of the skin at the elbow joint becomes damaged; - Radial nerve neuropathy
is caused by damage to the nerve that runs along the underside of the arm; - Peroneal nerve neuropathy
occurs when the nerve behind the knee becomes compressed. This results in a condition in which it becomes difficult to lift one or both legs.
Neuropathy can affect the nerves that control muscle movement ( motor nerves
), and those responsible for the perception of sensations - cold or pain (
sensory nerves
).
In some cases, the disease can cause problems with internal organs
- the heart, blood vessels, bladder or intestines.
Neuropathy that affects internal organs is called autonomic neuropathy
.
Visit our Neurology page