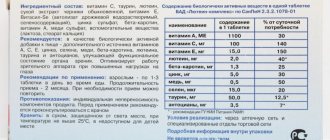
Composition and release form
| Capsules | 1 caps. (0.5 g) |
| lutein | 4.5 mg |
| zeaxanthin | 0.5 mg |
| ginkgo biloba extract | 20 mg |
| taurine | 100 mg |
| vitamin A | 1650 IU |
| vitamin C | 50 mg |
| vitamin E | 15 mg |
| selenium (in yeast) | 25 mcg |
| copper (as sulfate) | 1.5 mg |
| chromium (as picolinate) | 50 mcg |
| zinc (as sulfate) | 7.5 mg |
10 pcs in blister; There are 3 blisters in a cardboard pack.
Lutein Forte Capsules, 30 pcs., 500 mg, for oral administration, for adults
Description
LUTEIN FORTE is a source of carotenoids, flavonoids, vitamins and minerals necessary to maintain the functional state of the visual apparatus.
Properties of dietary supplement components for food LUTEIN FORTE:
Lutein and zeaxanthin
Accumulating in the macula (the central region of the retina) and the lens, they act as a light filter and protect important structures of the eye from the most aggressive, blue part of the daylight spectrum. Lutein and zeaxanthin are powerful first-order antioxidants that can neutralize the effects of free radicals and prevent retinal damage and lens clouding.
Taurine
An amino acid involved in the transmission of photosignals, stimulates the regeneration and metabolism of eye tissue. Helps normalize the function of cell membranes and activate the energy metabolic processes of light-sensing cells.
Vitamin A
Participates in the metabolism of the visual pigment rhodopsin. The disintegration of this complex under the influence of light plays a significant role in the mechanism of the appearance of visual sensation (photosignal). The restoration of rhodopsin and an increase in its content in the retina ensures the adaptation of the eye to low light levels (dark adaptation).
Vitamin C
It has the ability for rapid and reversible redox transformations, regulates the restoration of visual pigments, reduces increased intraocular pressure, reduces the risk of developing glaucoma and has significant antioxidant activity.
Vitamin E
Accelerates the regeneration of damaged cells, participates in tissue respiration and other important processes of tissue metabolism. Prevents increased fragility and permeability of capillaries.
Selenium, copper, chromium, zinc
A complex of vital microelements, which is a permanent component of eye tissue, ensuring normal metabolism and restoration of cellular structures.
Positive effect on body functions:
The retina, and especially its central part (macula), has a natural protection - a pigment layer containing carotenoids, lutein and zeaxanthin. Lutein is not synthesized in the human body and enters the body only with food (fruits and vegetables), while zeaxanthin is formed in the retina from lutein. The health of the retina depends on the level of lutein and zeaxanthin in the retina. To maintain good vision, a person should receive 5 mg of lutein and 1 mg of zeaxanthin daily from food - this amount is found in 250 g of spinach, 0.5 kg of sweet pepper or 1 kg of carrots. A typical diet contains less than 20% of the norm.
Component Properties
Lutein and zeaxanthin accumulate in the macula of the retina and protect it from the most aggressive, blue part of the daylight spectrum.
They partially reflect blue light from the central zone of the retina, where the light flux is most focused. In addition, lutein and zeaxanthin are able to absorb this part of the light spectrum and, being powerful antioxidants, suppress the formation of free radicals, which prevents retinal destruction and lens clouding.
Ginkgo biloba extract has antioxidant activity, as well as antihypoxic and cerebral circulation-improving effects. In addition, the components of the extract reduce the risk of thrombosis and reduce capillary permeability, which has a positive effect in diabetic retinopathy and other conditions accompanied by chronic ischemia of peripheral tissues.
Taurine is an amino acid. Participates in the transmission of photosignals, stimulates the regeneration and metabolism of eye tissue. Helps normalize the function of cell membranes and activate energy metabolic processes.
Vitamin A is involved in the metabolism of the visual pigment rhodopsin. The disintegration of this complex under the influence of light plays a significant role in the mechanism of the appearance of visual sensation (photosignal). The restoration of rhodopsin and an increase in its content in the retina ensures the adaptation of the eye to low light levels (dark adaptation).
Vitamin C has significant antioxidant activity; regulates the restoration of visual pigments, reduces increased intraocular pressure, reduces the risk of developing glaucoma.
Vitamin E accelerates the regeneration of damaged cells, participates in tissue respiration and other important processes of tissue metabolism. Prevents increased fragility and permeability of capillaries.
Selenium, copper, chromium, zinc are a complex of vital microelements that are a permanent component of the eye tissue and ensure its normal metabolism and restoration of cellular structures.
pharmachologic effect
Lutein and zeaxanthin
They are deposited in the central region (macula) of the retina and lens, endowed with the functions of a light filter, protecting important structures of the organ of vision from the particularly aggressive blue spectrum of daylight. They are powerful antioxidants that can neutralize free radicals and prevent the destruction of the retina with clouding of the lens.
Taurine
The amino acid is a participant in the transmission of photosignals and activates the metabolism and regeneration of eye tissue. Stimulates the normalization of cell membrane functions and promotes the activation of energy processes.
Ginkgo biloba extract
A powerful antioxidant with antihypoxic effect. Improves cerebral circulation, reduces the risk of thrombosis and reduces capillary permeability. Indispensable for diabetic retinopathy, as well as other conditions accompanied by ischemia of peripheral tissues.
Selenium, copper, chromium, zinc
Vital microelements are a permanent component of the eye tissue, which ensures its normal metabolism and restoration of structures.
Vitamin A
It is an obligatory component of the exchange of the visual pigment rhodopsin. Disintegrating under the influence of light, this complex plays an important role in the mechanism of formation of the visual sensation (photosignal). An increase in the content of rhodopsin in the retina ensures the adaptation of the eyes to low light levels (dark adaptation, twilight vision).
Vitamin C
An obligatory participant in reversible redox transformations, regulates the processes of restoration of visual pigments, reduces intraocular pressure, and reduces the risk of developing glaucoma. Is an antioxidant.
Vitamin E
Capable of activating the regeneration of damaged cells by participating in tissue respiration and other important processes of tissue metabolism. Protects against capillary fragility and permeability.
The retina and macula, its central part, have natural protection. This is a pigment layer that contains lutein and zeaxanthin (natural carotenoids). Lutein can be ingested exclusively through foods (fruits and vegetables), while zeaxanthin, in turn, is formed from lutein. The level of these components affects the condition of the retina and its health. To maintain good vision, a person should receive 5 mg of lutein daily, as well as 1 mg of zeaxanthin - this amount can be contained in 250 g of spinach, 1 kg of carrots, 0.5 kg of sweet pepper. The normal human diet contains less than 20% of this norm.
Radiation from computer and TV screens and intense light have a damaging effect on the macula, the most important area of the eye. Over time, this can lead to the development of a serious disease - age-related macular degeneration (AMD). AMD is the most common cause of blindness in the elderly. However, the incidence is rapidly becoming younger, and today people who have barely reached 50 years of age face it. Currently, it is impossible to cure this disease and a person completely loses vision due to atrophy of the optic nerve. Therefore, it is necessary to do everything possible to slow down the development of pathology, which Lutein Forte contributes to.
Lutein Forte vitamins for eyes VITAMIR tablets No. 30
Product description
Dietary supplement for improving vision.
Action
Biologically active food supplement. Not a medicine. Lutein and zeaxanthin. Accumulating in the macula (central region) of the retina and lens, they act as a light filter and protect important structures of the eye from the most aggressive, blue part of the daylight spectrum. Lutein and zeaxanthin are powerful first-order antioxidants that can neutralize the effects of free radicals and prevent retinal damage and lens clouding. Ginkgo biloba extract. It has antioxidant activity, as well as antihypoxic and cerebral circulation-improving effects. The components of the extract reduce the risk of thrombosis and reduce capillary permeability, which has a positive effect in diabetic retinopathy and other conditions accompanied by chronic ischemia of peripheral tissues. Taurine. An amino acid involved in the transmission of photosignals, stimulates the regeneration and metabolism of eye tissue. Helps normalize the function of cell membranes and activate energy metabolic processes. Vitamin A. Participates in the metabolism of the visual pigment rhodopsin. The disintegration of this complex under the influence of light plays a significant role in the mechanism of the appearance of visual sensation (photosignal). The restoration of rhodopsin and an increase in its content in the retina ensures the adaptation of the eye to low light levels (dark adaptation). Vitamin C. Has the ability for rapid and reversible redox transformations, regulates the restoration of visual pigments, reduces increased intraocular pressure, reduces the risk of developing glaucoma and has significant antioxidant activity. Vitamin E. Accelerates the regeneration of damaged cells, participates in tissue respiration and other important processes of tissue metabolism. Prevents increased fragility and permeability of capillaries. Selenium, copper, chromium, zinc. A complex of vital microelements, which is a permanent component of eye tissue, ensuring normal metabolism and restoration of cellular structures.
Compound
Active ingredient: Lutein, mg 4.5 90 Zeaxanthin, mg 0.5 50 Vitamin A, ME 1650 50 Vitamin E, mg 15.0 150 Vitamin C, mg 50 70 Zinc, mg 7.5 50 Copper, mg 1.5 150 Chromium, mcg 50.0 100 Selenium, mcg 25.0 35 Taurine, mg 100.0 25 Flavonoids, mg 10.0.
Indications for use
This dietary supplement is an additional source of carotenoids - lutein, zeaxanthin, flavonoids, vitamins A, E, C, minerals (zinc, selenium, copper, chromium) and taurine. Helps improve the functional state of the visual organ.
Recommendations for use
Adults and children over 14 years of age: 1 capsule 2 times a day with meals. Duration of treatment: 1 month. If necessary, the reception can be repeated.
Side effects
Allergic reactions.
Overdose
Cases of drug overdose have not been reported to date.
special instructions
It is recommended to consult a doctor before use.
Contraindications
Individual intolerance to product components.
Buy Lutein Forte vitamins for eyes VITAMIR, tablet. 618 mg No. 30 in the pharmacy
Price for Lutein Forte vitamins for eyes VITAMIR, table. 618 mg No. 30
Instructions for use for Lutein Forte vitamins for eyes VITAMIR, table. 618 mg No. 30
LUTEIN FORTE VITAMIR VITAMINS FOR EYES, TABLETS No. 30
A dietary supplement containing lutein and zeaxanthin, vitamins, and microelements that help maintain the normal functioning of the visual organs.
Lutein is a natural pigment that is very useful for the organs of vision, especially for the retina, is responsible for vigilance and prevents some age-related eye diseases. Lutein takes care of the condition of the eyes, maintains visual acuity, helps the visual analyzers adapt to sudden changes in light, and promotes the normal functioning of the visual organs.
Zeaxanthin is a carotenoid pigment. It is responsible for the health of the retina and its normal functioning. Zeaxanthin protects the organs of vision from harmful ultraviolet radiation and from the effects of free radicals, improves intercellular metabolic processes, and, consequently, nutrition of the eyes, strengthens the walls of blood vessels and capillaries of the organs of vision, improves visual acuity and color perception, keeps the eye muscles in good shape and relieves fatigue.
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) is involved in carbohydrate metabolism and redox reactions. It stimulates collagen synthesis, tissue regeneration, and also improves capillary permeability, improves the condition of the fundus vessels, prevents increased eye pressure and hemorrhages in the retina. Vitamin C is a strong antioxidant, so it can stop the oxidative processes of visual pigments. Ascorbic acid maintains the mobility of the eye muscles and is responsible for preserving the functions of the optic nerve. Vitamin deficiency leads to rapid eye fatigue and poor vision.
Vitamin A regulates the functioning of the immune system and is one of the most effective vitamins for protecting vision. It is necessary for night vision, it moisturizes the cornea of the eyes, keeps it from dryness and damage
Vitamin E belongs to a class of antioxidants that neutralize free radicals in the body, which are one of the main causes of aging. Vitamin E is able to penetrate into cells and protect the integrity of cell membranes from damage by free radicals. It is involved in the functioning of all body systems.
Vitamin E reduces the progression of age-related vision degeneration, prevents retinal detachment, and supports eye function.
Rutin (Vitamin P) forms a group of substances called flavonoids. The high biological activity of flavonoids is due to the presence of antioxidant properties. Regular use of vitamin P normalizes the condition of capillary walls, increasing their strength and elasticity, and helps reduce intraocular pressure.
Zinc (Zn) is good for vision and is used to prevent eye diseases. Actively participating in biochemical processes, it helps to absorb vitamin A, which is necessary for normal eye function. Zinc deficiency leads to impaired color vision and the development of eye diseases.
Selenium (Se) is a powerful antioxidant, the deficiency of which can cause clouding of the eye lens, decreased visual acuity, and early development of cataracts. This is one of the components that converts the light signal into a nerve impulse. For better absorption, selenium must be taken together with vitamin E.