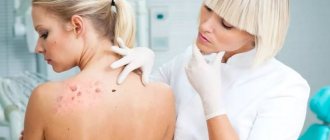
Molluscum contagiosum or contagious molluscum is a viral infection of the skin or mucous membranes. It is often called "water warts". It belongs to the group of sexually transmitted diseases. And although this is not a classic STD disease, sexual transmission is one of the most common.
The causative agent is a DNA poxvirus called molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV). It can only infect people. There are four types of MCV:
- MCV-1;
- MCV-2;
- MCV-3;
- MCV-4.
MCV-1 is the most common, while MCV-2 is more common in adults.
What is molluscum contagiosum
This is a viral skin pathology that mainly occurs in children under 10 years of age.
The disease also occurs in young people aged 20-30 years, during the period of their most active sexual life. This disease is characterized by the appearance of hemispherical nodules with a diameter of 2-5 millimeters on the skin or mucous membranes. Regarding the prevalence of this infection, rates in different countries vary from 1 to 22%. It is difficult to determine the exact incidence rate because the virus is easy to spread. To do this, you just need to come into contact with a patient or a virus carrier. The virus remains active for some time on the surface of objects, so infection is also possible when using things and objects shared with the patient.
Molluscum contagiosum is not considered a dangerous disease. It does not threaten the life and health of a child or adult. The presence of the disease, as a rule, indicates a reduced immune status. This is why the infection most often affects children whose immunity is just developing. The risk group also includes people with congenital or acquired immunodeficiency.
Important! You can become infected with molluscum contagiosum again. After illness, patients do not develop stable immunity, which makes reinfection possible. Minimizing the risk of infection is mainly associated with strengthening the immune system and compliance with preventive measures.
It is possible to defeat parasites!
Antiparasitic Complex® - Reliable and safe removal of parasites in 21 days!
- The composition includes only natural ingredients;
- Does not cause side effects;
- Absolutely safe;
- Protects the liver, heart, lungs, stomach, skin from parasites;
- Removes waste products of parasites from the body.
- Effectively destroys most types of helminths in 21 days.
There is now a preferential program for free packaging. Read expert opinion.
Read further:
How can you become infected with viral pneumonia?
Gram-variable coccobacilli in large and small quantities in a smear
Contagious helminthiasis: life cycle, mechanism of infection
Where can you get Lassa fever and what is the treatment?
How a person can become infected with ascariasis: ways of infection with these parasites
There are parasites and larvae in pork meat: how to avoid getting infected and what to do if infected
Causes of molluscum contagiosum
The causative agent of the disease is viruses of the orthopoxvirus family, which belong to the smallpox virus family. Molluscum contagiosum virus is abbreviated as MCV (Molluscum contagiosum virus). Today, 4 varieties of such viruses have been identified, but the most common viruses in the human population are MCV-1 and MCV-2. Moreover, if the first occurs in adults and children, the second occurs mainly in adults, since it is transmitted through sexual contact. Characteristic skin manifestations of infection appear in those areas where the virus has penetrated. Most often these are the limbs, face or genitals.
Molluscum contagiosum virus. Photo: PHIL CDC
All smallpox viruses, including orthopoxviruses, are large DNA viruses. This means that the mutation rate of such viruses is much lower than that of RNA viruses (for example, influenza viruses). This is due to the fact that when copying genetic material, DNA viruses use DNA polymerase, which also performs editing functions, clearing the genome of mutations.
The incubation period for this pathology ranges from one week to several months. Most often it is 2-8 months. In most adults and children, characteristic symptoms develop within a specified period of time after infection.
Important! A patient with molluscum contagiosum remains contagious until all skin manifestations disappear.
Medicines
Photo: chinastudy.it
After destruction of the molluscum contagiosum element, solutions of iodine, brilliant green, and fucorcin are used for reliable and relatively long-term disinfection of the skin.
To treat molluscum contagiosum, topical agents containing antiviral and immunomodulatory components can be prescribed. For example:
- Cycloferon, Viferon, Infagel. The drug has an anti-inflammatory effect and inhibits the ability of the virus to reproduce. Effective in the fight against viruses of molluscum contagiosum, herpes, as well as infectious diseases of the oral cavity and genital organs. Apply twice a day for a week.
- Imiquad. An immunostimulant cream that enhances the body's production of interferons - special substances necessary to fight viral infection. It should be applied to previously cleansed skin and not washed off for a long time, for example at night.
- Oxolinic ointment. Has a pronounced antiviral effect. Apply two to three times a day until the elements of molluscum contaginosis disappear.
- Acyclovir. In the form of an ointment, it is also applied to the nodules 2-3 times a day until recovery. Used in children over 3 years old. To enhance the antiviral effect, it can be used in a mixture with oxolinic ointment in a 1:1 ratio.
To strengthen the immune system and better fight infection, the following may be prescribed for internal use:
- Isoprinosine tablets. The medicine has anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties, helps the body fight infection.
- Viferon in the form of candles. Has similar effects. Convenient for use in children.
Acyclovir and other antiviral drugs are prescribed only to patients with impaired immunity.
Methods of infection and provoking factors
Infection with the virus occurs through contact with a patient or carrier of the virus. Using things and objects shared with the patient also poses a danger, since orthopoxviruses remain active for some time on various surfaces. For this reason, children often become infected when visiting sports sections, where the likelihood of infection spreading is especially high due to the large crowd of people who use the same sports equipment. Contact sports (such as combat sports) also pose a risk because close contact increases the likelihood of transmitting the virus.
Children's judo section. Photo: nomadsoul1 / freepik.com
In young people who are sexually active, infection most often occurs through sexual contact. As in young children, in older people the provoking factor for infection is weakened immunity. HIV-infected people, as well as people suffering from atopic dermatitis, are at risk. One of the factors in the development of the disease is long-term use of glucocorticoid drugs and cytostatic agents that reduce the activity of the human immune system.
Important! If molluscum contagiosum is sexually transmitted, many people mistakenly believe that they can protect themselves from the virus by using a condom. This is a big misconception, since a condom is only effective in protecting against infections concentrated directly in the urethra, penis, semen or vagina. It is impossible to completely protect yourself from sexually transmitted infections such as molluscum contagiosum, syphilis or genital herpes using a condom.
Main transmission options
The virus that causes the disease is transmitted from one person to another. Representatives of the animal world are not carriers of orthopoxvirus. There are 3 main infection options:
- Due to sexual intercourse with an already infected person;
- through water;
- contact-household method.
The last case occurs most often. You can become infected through tactile touch (hugs, travel on public transport, massage of a sick subject). This explains why children are often treated for this disease.
The indirect contact route is dangerous because a person cannot be sure that infection will not occur even in the absence of obvious signs (an incubation stage is possible).
You can simply walk into an unfamiliar room, sit on the sofa and become a carrier of the virus. After all, it is wonderfully preserved in various materials. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out thorough disinfection in residential premises and public places.
Another situation is frequent change of sexual partners. In this case, the person takes responsibility for his health. You need to understand that contraception cannot protect against all diseases.
In this case, even a hug will be enough to cause health problems. Although the virus foci are predominantly located in the genitals, so a condom can still protect against infection.
The waterway is often not classified as a separate group. In fact, infection occurs through water, but viral particles enter it from an infected subject. Therefore, many experts are inclined to believe that this is also a household contact route.
A similar outcome of events is possible when visiting swimming pools, saunas and public beaches.
In addition, a person who has previously suffered from molluscum contagiosum may become self-infected again. This happens when the skin rubs. But regardless of the method of infection, the clinical symptoms are very similar.
Some people are immune to this infection.
Symptoms
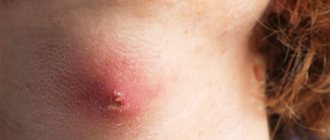
The main symptom of a skin infection is painless nodules 2-5 mm in diameter with a small dimple in the center. Let's take a closer look at the main characteristics of rashes and other symptoms.
- The rashes have the appearance of dome-shaped papules. The surface of the papules may be smooth or waxy. The consistency of the papules is dense, and as the tumor grows it softens. In patients with HIV infection, as well as in people with weakened immune systems, the diameter of the rash reaches 10-15 mm.
- Papules are flesh-colored, pink, or darker in color. When pressed, curdled contents come out of the papule. Sometimes pearlescent stains, like a pearl, are clearly visible on the papules.
- Papules form at the sites of viral infection penetration - in various parts of the body. They are often grouped into one or two areas, but diffuse distribution of papules over a specific area of the skin is also possible. Often in people with weakened immune systems, the rash affects large areas of the skin.
- The rash is painless, but the area of the rash may become inflamed, which is accompanied by itching.
- In approximately 10% of cases, patients develop eczema in the affected area - an inflammatory skin lesion (dermatitis).
- Papules never appear on the palms or soles. Very rarely, rashes form on the mucous tissues of the oral cavity.
- Skin tumors with molluscum contagiosum grow slowly. The papule increases in size and is filled with a light, cheesy mass consisting of skin cells, sebaceous gland secretions, as well as dead leukocytes and the viral particles themselves.
- Around the 12th week, papules reach their peak size, after which their growth stops. Then the tumors gradually die off.
Figure 1. Molluscum contagiosum rash on the face. Source: Ben Naafs/Community Eye Health/Flickr
Symptoms in women
In adults, rashes most often affect the genital area. This is due to the predominance of transmission of infection through sexual contact. For infection, genital contact itself is not at all necessary; just contact with the infected area of the partner’s skin is sufficient.
Most often in women, papules form in the lower abdomen, on the thighs, pubic area or external genitalia.
It is noteworthy that pregnant women are especially susceptible to infection due to a natural decrease in immunity. The manifestations are indistinguishable from the classic clinical picture of the disease. The virus does not pose a threat to the life and health of the fetus. However, if the baby comes into contact with the mother's infected skin, the child runs the risk of becoming infected.
Symptoms in men
In men, as in women, the rashes are predominantly located in the genital area. This is the groin area, penis, inner thighs. Men are more likely than women to rub papules on clothes, which leads to the release of viral particles and re-infection. Therefore, the rash affects not only the area of contact with the infected partner, but also nearby areas.
How does the infection manifest in children?
Skin manifestations in children mainly affect the face, limbs and chest area. The rashes do not cause any inconvenience to children other than aesthetic ones, especially if they are located on the face. Papules in children do not hurt and very rarely cause itching. It is important to ensure that the child does not scratch or rub the affected areas. Otherwise, secondary infection with the virus will occur.
Important! In children, rashes are extremely rarely observed in the genital area. If a child has papules on the genitals, pubis, buttocks or inner thighs, the circumstances of possible infection should be especially carefully examined, since sexual abuse cannot be ruled out.
Folk remedies
The most effective means for treating the disease in question from the category of “traditional medicine”:
- Prepare a concentrated solution of potassium permanganate - it should be dark purple. A cotton swab is moistened in it and applied (cauterized) to the papule. Please note that after using potassium permanganate, burns may form on the skin - be extremely careful, treat the papule specifically, acting on it point by point.
- The string grass is crushed and a decoction is made - 300 ml of water per 100 grams of raw material, cook for 3 minutes. Then the broth should brew for 60-90 minutes. Only after this can you strain it through a strainer or several layers of gauze. A decoction of the string is used as a lotion and for wiping off papules. There are no restrictions on the number of procedures per day.
- Grind a few cloves of garlic (in a blender or on a fine grater), add 30-50 grams of butter (soft) to them and mix everything thoroughly until a paste-like mixture is obtained. The product must be applied to the affected areas of the skin 2 times a day. Please note that garlic can cause burning and even irritation on healthy areas of the skin, so try to use this product with extreme caution.
You can also use some plants that will help get rid of papules in a short time. For example, the juice from bird cherry leaves copes with this task perfectly (it is squeezed out and stored in a cool, dark place) - a cotton pad is moistened in it and the skin is treated after removing the nodules. Moreover, this remedy can be used for a long period, until all wounds are completely healed.
Types of molluscum contagiosum
There is no generally accepted classification for molluscum contagiosum. At the same time, in addition to the “classical” papules, atypical forms of rashes are distinguished. These include:
- giant clams, the size of which is 3 cm or more;
- cystic molluscs - the appearance of cysts (cavities, with a wall and contents) instead of papules of the same size;
- ulcerated mollusks - instead of nodules, small areas of erosion appear, which subsequently turn into bleeding ulcers;
- molluscs in the form of eels or warts;
- pendicular mollusks - neoplasms are located on a thin stalk above the skin.
Depending on the prevalence of lesions, two forms of the disease are distinguished:
- Localized - affects only a specific area of the body, such as the face, genital area, upper or lower extremities.
- Generalized - rashes are observed over a large surface of the body. In some cases, neoplasms are noted throughout the body.
Could there be complications?
The development of molluscum contagiosum in the normal course does not lead to the formation of any problems over time, and often the elements can gradually disappear from the skin without leaving any traces on it. This can happen even without treatment for about three to four years.
- Some treatments may cause scarring on the skin.
- Sometimes the infection can reactivate, in which case a larger area of skin is affected.
- In the presence of severely weakened immunity, the development of molluscum contagiosum can take a generalized and pronounced form.
When the elements appear abundantly on the face and body, or become large in size and can change in appearance, treatment becomes difficult. In such cases, active therapy with drugs, both local and to stimulate systemic immunity, is indicated.
Treatment of molluscum contagiosum
Source: Fantasy Children's Clinic
Before starting treatment, a diagnosis is carried out, which is not difficult for molluscum contagiosum. The diagnosis is made based on the external manifestations of the disease. For atypical forms, specific laboratory tests are used to identify viral particles. This is staining of the contents of nodules according to Romanovsky-Giemsa, Papanicolaou or Wright. Instrumental diagnostics for molluscum contagiosum are not used.
There is no specific treatment for molluscum contagiosum. Treatment is aimed at eliminating skin lesions as quickly as possible. The disease is treated on an outpatient basis by a dermatologist.
Treatment for molluscum contagiosum is not always carried out, since within 6-18 months the papules “go away” on their own. Treatment measures are resorted to based on aesthetic considerations, as well as in severe cases of the disease (when a significant part of the body is affected by rashes) and when patients at risk are infected (people with HIV and a weakened immune system).
Drug treatment
Drug therapy is ineffective. However, to eliminate papules, salicylic acid is used as an external agent. The healing of rashes in this disease is also facilitated by topical preparations with retinoids (in particular, tretinoin).
To eliminate rashes, cantharidin is used, a poison contained in the hemolymph of some types of beetles. Currently, cantharidin is used as a blister agent. In particular, one drop of cantharidin is applied to the papule of molluscum contagiosum. In this case, blisters may appear at the application site. Cantharidin has not yet been registered in the Russian Federation and cannot be used.
Cytostatic drugs (podophyllotoxin) and potassium hydroxide are also used for medicinal purposes. However, the effectiveness of these drugs, as well as the above, for molluscum contagiosum is extremely low.
Antiviral drugs
Since molluscum contagiosum is a viral disease, it is logical to assume that antiviral drugs can help in treatment. Unfortunately, here too the existing arsenal of antiviral drugs turned out to be powerless against the molluscum contagiosum virus. Some doctors prescribe acyclovir and oxolinic ointment to such patients, but these drugs are ineffective against the molluscum contagiosum virus. Currently, antiviral drugs acting directly against the molluscum contagiosum virus have not yet been developed.
Immunomodulators
Some doctors may prescribe immunomodulatory and immunostimulating drugs to patients. For example, this is imiquimod, a drug that enhances local immunity; Local drugs with inducers of interferons, proteins that have antiviral activity, are also prescribed. However, there are no studies confirming the effectiveness of such drugs for molluscum contagiosum.
Thus, in the treatment of molluscum contagiosum, medications and folk remedies are either ineffective or useless. An effective way to eliminate rashes are methods of direct papule removal.
Surgery
The following surgical techniques are used to remove molluscum contagiosum papules:
- Cryosurgery is treatment using liquid nitrogen. The papule is exposed to liquid nitrogen for a few seconds, which leads to its deep freezing and destruction. Since new papules may form over time, the patient will have to undergo several cryotherapy sessions. Among the disadvantages of this treatment is the painfulness of the procedure. Therefore, it is not used to treat young children. In addition, after exposure to liquid nitrogen, blisters may form, and then barely noticeable scars.
- Evisceration is the removal of a papule using thin tweezers. The advantage of the method is that the removed papule is not destroyed, which means it can be sent for laboratory testing.
- Curettage is the removal of lesions using a curette. This is a tool that resembles a long metal fork with a loop instead of teeth. This technique is painful, and after removal scars may form. As a rule, curettage is used for a small number of papules. If there are a lot of rashes, then curettage is ineffective, since after the procedure there is a high risk of new rashes appearing.
- Laser therapy - laser exposure to molluscum contagiosum papules. As a rule, one session is enough for laser removal of papules, but in some patients the rash may persist, which requires re-treatment after 2-3 weeks.
- Electrocoagulation is the removal of skin lesions using electrical cauterization. For this purpose, an electrocoagulator is used - a device that supplies high-frequency current. Under the influence of current, the proteins of the papules are destroyed, which leads to its destruction.
Diagnostics
The symptoms are quite specific, so once symptoms appear, diagnosis is not difficult. For example, a rash with an umbilical depression and crust-like contents is typical of molluscum contagiosum.
After examining the nodules, a dermatologist can immediately make the correct diagnosis.
Additional examinations are extremely rarely required. To do this, a small amount of skin is taken from the neoplasm. Next, it is studied under a microscope.
Such a biopsy of the biopsy thoroughly shows all the features of the disease. Molluscum contagiosum nodules are often confused with similar formations, which happens with certain diseases.
Among them are the following formations:
- Flat warts. They usually appear on the face or the back of the hands. They are small in diameter and smooth.
- Keratoacanthomas are convex-shaped formations. They are usually hemispherical in shape and slightly reddish in color.
- Milia are small white dots located in the sebaceous glands of the skin. They occur when excessive amounts of dense sebum are produced. It is not completely released from the layers of the skin and the pores begin to clog.
- With scabies, small pink papules appear on the skin.
- Basal cell carcinoma actually resembles a clam on the skin. They are also lightly pearlescent in color and protrude above the surface of the skin. The main difference is the single location. But the “contagious mollusk” appears in plural quantities. Moreover, these rashes are nearby.
But the risk of confusing this disease with warts or lichen ruber is minimal.
Prevention of molluscum contagiosum
Source: Jesselton Medical Center
There is no specific prevention against molluscum contagiosum (a vaccine against the pathogen has not yet been developed). Basic preventive measures involve isolating patients to avoid infecting other people. To minimize the spread of infection, doctors recommend:
- isolate the sick person until complete recovery;
- observe the rules of hygiene;
- conduct preventive examinations for children of preschool and school age;
- be more attentive to your sexual partners - a quick examination of the person can help you avoid infection, and motivate your partner to undergo examination.