Gastroenterologist
Vinogradov
Dmitry Alekseevich
5 years experience
Gastroenterologist
Make an appointment
Ascariasis is damage to the small intestine of the body by helminthic infestations. The causative agent is roundworms - roundworms (hence the name), which parasitize the human intestinal tissue.
Intestinal nematodosis (another name for the disease) occurs everywhere in people of different ages and genders, regardless of climatic conditions.
Main symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of ascariasis depend largely on the extent of damage to the small intestine, as well as the age of the patient and the stage of development of the disease.
The primary phase can occur without clinical manifestations, especially during the period of larval migration. A person may experience one or more characteristic symptoms:
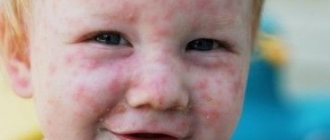
- an allergic reaction is manifested by numerous rashes on the limbs or torso. They itch intensely, causing serious discomfort;
- infectious syndrome is expressed by elevated body temperature, excessive sweating, loss of strength;
- a liver factor may be observed - ascariasis is manifested by an increase in the size of the spleen and liver and causes pain under the ribs on the right side.
In most cases, the patient suffers from a wet or dry cough and severe shortness of breath, and experiences pain in the chest area. All this can lead to pleurisy.
If ascariasis in children or adults is advanced, a sharp decrease in appetite, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, bloating, pain in the intestinal area, cramps, and weight loss may occur.
Are you experiencing symptoms of ascariasis?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Characteristics of pinworms
Today, all helminths can be divided into 3 classes. There are flatworms, tapeworms and roundworms. Pinworms belong to the class of nematodes (roundworms).
The disease in humans is caused by pinworms of the genus Enterobius vermicularis. Pinworms have a small, elongated body. The length of females reaches 10-12 mm, and males - 2-5 mm.
These organisms live in humans for 3-4 weeks, after which they die.
Pinworms live in the lower part of the small intestine, cecum and ileum. A special feature of these roundworms is the ability to actively move and exit the anus onto the human skin. In this case, the female lays several thousand eggs in the perianal area.
This happens at night when the anal sphincter relaxes. After laying, the pinworm dies. The second distinctive feature of these helminths is the high contagiousness of enterobiasis. Eggs can be transmitted from one person to another through close contact (a simple handshake).
This explains the outbreak of enterobiasis in children's institutions and adult groups.
The development cycle of pinworms is quite simple. Human infection occurs through contact, food, household or through self-infection. Eggs from dirty hands or food enter the human intestines.
Soon the eggs hatch into larvae that attach to the intestinal wall. After a month they can lay eggs.
After laying eggs, a person experiences itching, scratches the skin, and the eggs are brought back into the oral cavity with their hands.
Enterobiasis ranks 1st among all helminthiases in terms of prevalence. The main source of infection is a sick person. He is also the definitive host of pinworms.
Factors in the transmission of eggs can be food, various toys and household items, and contaminated hands. Eggs can be inhaled along with dust, but this mechanism of transmission is of minor importance.
With the development of enterobiasis, the following symptoms may be observed:
- itching in the anal area;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- loss of appetite;
- bowel dysfunction;
- pain in the abdominal area;
- rash;
- difficulty urinating (infantile enuresis);
- development of inflammatory diseases of the genital organs (in girls);
- fatigue;
- irritability.
The incubation period from the moment of infection is 3-6 weeks. Complications of this disease include purulent inflammation of the skin, paraproctitis, vulvovaginitis, enterocolitis, acute appendicitis, peritonitis, salpingitis.
Main causes of infection
The main cause of ascariasis is infection with helminth eggs, which occurs as a result of their entry into a person’s mouth after personal contact with an infected person, as well as with unwashed vegetables, fruits, berries, and household items.
Once inside the human body, the larvae hatch from the eggs and penetrate the circulatory system, spreading to the capillaries of the lungs. From there they reach the bronchi, trachea and pharyngeal area. There they are mixed with saliva, swallowed by a person and again enter the small intestine, growing there into full-fledged adults.
Parasite Information
Roundworms belong to the family of roundworms. The length of such a helminth rarely exceeds 40 cm in females, and 25 cm in males. The causative agents of ascariasis can live in the host's body for 1-2 years. Then they die and leave the human body, excreted in the feces. Female roundworms are capable of laying about 200 thousand eggs per day, which are also released in feces. Most often, adult worms can be found in the small intestine area - this is their favorite place to live.
Both people and animals suffer equally from the manifestations of ascariasis. The human roundworm, through its vital activity, can provoke serious disorders in the body of the host. Parasites cause acute intestinal obstruction, can damage the integrity of the mucous membrane of its walls, and provoke pathologies of the pancreas or liver.
Worms are able to move throughout all organs of the digestive tract, but sometimes they even get into the organs of the respiratory system. As a result of such a lesion, a person may develop bronchitis, focal pneumonia, perforated peritonitis, hemoptysis and a feeling of suffocation may occur. Adult roundworms are sometimes found in the nasolacrimal canal, frontal sinuses, eustachian tubes and middle ear, appendix, urinary organs, and in the outer ear canal. The parasite secretes substances that can trigger allergies. In such a case, the patient experiences attacks similar to bronchial asthma, and skin rashes that resemble urticaria are possible. The constant residence of worms in the cavity of the small intestine causes inflammatory processes.
Preventive measures
Prevention of ascariasis is based on timely detection of the disease and adequate treatment under medical supervision.
Of particular importance in this process is compliance with all hygiene rules: it is necessary not only to keep your hands and the hands of children clean, but also to instill in them proper hygiene habits.
Regular hand washing after a walk, visiting the toilet, before eating, as well as proper sanitary treatment of food that comes on the table can significantly protect the body from infection with roundworms.
Ascaris reproduction and penetration into the body
This parasite, like many other worms, reproduces by laying a huge number of eggs (24,000 at a time) and it is these that a laboratory technician identifies by examining stool analysis under a microscope. (helminth larvae cannot be seen without special equipment). On average, the size of a worm larva is 70.0 microns.
Most often, roundworms in feces are detected in children of school and preschool age because they spend most of their time in crowded places and do not realize how important personal hygiene is. They can touch the excrement of infected animals in the sandbox, come into contact with the ground, or take the hand of other infected children, in whom helminth eggs accumulate under the nail plate. As a result, they do not wash their hands before eating or put them in their mouths, allowing the larvae to penetrate the esophagus and digestive tract.
As a rule, adults become infected from their children because in their sleep, children's anus begins to itch. As a result of scratching, helminths get under the nails, and then gradually throughout the day they are localized on things, furniture, door handles, cutlery, etc.
What to do in such a situation? To get started, we recommend reading this article. This article describes in detail methods of controlling parasites. We also recommend that you consult a specialist. Read the article >>>
Diagnostic features
If you notice one or more symptoms of this disease in yourself or your child, you should seek help from an infectious disease specialist (in the case of a child, a pediatrician or pediatric infectious disease specialist).
Diagnosis of ascariasis involves a general blood test: the presence of the disease will be indicated by an increase in ESR and eosinophils, a slight increase in the number of leukocytes and a decrease in hemoglobin.
In addition, an X-ray of the lungs may be prescribed, which, in the presence of helminths, reveals foci of infiltration.
The presence of roundworms can be confirmed by microscopic examination of sputum.
It is important to seek help from a center with a truly competent specialist and high-quality equipment, since helminths tend to demonstrate themselves not in all tests. Only an experienced doctor is able to see their presence in the patient’s body.
Appearance of roundworms
The body of the parasite is long, oval in shape with a ring-shaped cut. The sharp ends give it a spindle-shaped appearance. The color is pale pink. The length of the roundworm varies from 10 to 50 cm. The worm is covered with a multilayer cuticle that protects it from enzymes and toxic substances. Roundworms do not have devices in the form of hooks and suction cups designed for attachment to the host’s body. Adults are retained in the intestines by constantly moving towards the food masses. Reproduction is possible when a female and a male are present in the intestines. The latter can be distinguished by the end bent towards the ventral side and by its size.
This parasite, like many other worms, reproduces by laying a huge number of eggs (24,000 at a time) and it is these that a laboratory technician identifies by examining stool analysis under a microscope. (helminth larvae cannot be seen without special equipment). On average, the size of a worm larva is 70.0 microns.
Treatment
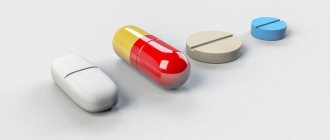
Drug therapy based on the use of anthelmintics is prescribed. They are selected depending on what stage the disease is currently at. In some cases, a single dose for ascariasis may not be enough, and the drug will need to be taken 3 times with a pause between doses prescribed by the doctor.
If allergic manifestations are present, the doctor will additionally prescribe antihistamines. If a patient has stool upset, bloating and abdominal pain, and other intestinal disorders, then enzymes and probiotics are also selected for him.
At the end of the main treatment, over the next 3 months the patient is registered at the dispensary with periodic blood and stool tests.
Therapeutic measures
When roundworm is detected in the human body, treatment usually involves taking anthelmintic medications: Mebendazole, Albendazole or Ivermectin.
Albendazole for oral administration is usually prescribed in an amount of 400 mg per day. The use of Mebendazole can be divided into 2 times a day, 100 mg at a time, or a one-time dose of 500 mg, therapy continues for 3 days. The dosage of Ivermectin is calculated based on the patient’s weight at 150 or 200 mcg per kilogram. It should be mentioned that these medications are dangerous to take during pregnancy, so the risk of their use during this period must be justified by the indications.
Nitazoxanide shows good results in the treatment of mild to moderate ascariasis. The previously used drug Piperazine, due to its toxicity, has now been replaced by more advanced analogues.
In case of intestinal obstruction by adult helminths, in addition to anthelmintic drugs, surgical intervention to remove the worms may be required.
Answers to common questions
Is it possible to drive away roundworms with herbs?
Many medications contain herbal ingredients. Herbs also have a certain effect, but we must not forget about the serious adverse reactions that their thoughtless use can lead to.
It is strictly not recommended to treat ascariasis yourself with herbs.
Can I get rid of roundworms myself without seeing a doctor?
No, this is strictly prohibited, as it is fraught with poisoning of the body and the occurrence of serious complications in the functioning of internal organs, in particular the organs of the pulmonary system and intestines.
How is ascariasis transmitted?
The disease can be transmitted by shaking hands, as well as by other types of bodily contact.
The most common infection is through contact with poorly washed fruits, vegetables, berries and herbs. You should also remember about hand hygiene after returning from the street and visiting the toilet.
What foods can serve as a source of disease?
Absolutely any, if they are not processed properly.
Why does a cough develop with ascariasis?
Cough appears due to the penetration of larvae through capillary vessels into the area of the lungs and bronchi.
What is the prognosis after treatment for ascariasis?
The prognosis is generally favorable. After adequate treatment, complications can occur only in people with weak immunity and serious chronic diseases.
At-risk groups
By eating unwashed vegetables or fruits, and even simply taking a clean apple with dirty hands, a person can introduce parasite eggs into his own body. After entering an environment favorable for the worm to live in, it quickly grows and multiplies - this is how ascariasis develops. The following categories of people most often suffer from this disease:
- children under 6 years of age (can become infected when visiting a kindergarten, where the risk of transmitting helminthiasis from one child to another is so high);
- plumbers;
- personnel of wastewater and sewerage treatment plants;
- agricultural workers;
- Gardeners also often get sick.
List of sources
- Avdyukhina T.N. Laboratory diagnosis of helminth infections / T.I.Avdyukhina, T.N.Konstantinova, Yu.P.Gorbunova // Part I. Nematodes: Textbook. allowance. -M., 1993. -60 p.
- Astafiev B. A. Achievements of domestic science in the study of helminth pathogenesis // Med. parasitology and parasitic diseases. - 1998. - No. 2. — P. 8.
- Vasiliev Yu.V. Diseases of the digestive system / Yu.V. Vasiliev. M.: “Dubl Freig Publishing House”, 2002. -93 p.
- Sergiev V.P. Parasitic diseases, their prevention and treatment //Epidemiology and infectious diseases. - 1997. - No. 2. — P. 8 — 12.
Diet
Diet 5th table
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 14 days
- Duration: from 3 months or more
- Cost of products: 1200 - 1350 rubles per week
During the treatment of ascariasis, you should adhere to diet Table No. 5 . It is necessary to minimize fats, while increasing the consumption of protein foods. It is very important not to drink raw water and wash vegetables and fruits thoroughly.
The basic nutritional rules during this period are as follows:
- You need to consume a lot of vegetables, fruits, and grains.
- Minimize fatty foods, but still consume normal amounts of protein and carbohydrates.
- Drink enough fluids.
- Eliminate pasteurized foods from your diet.
- Do not eat chocolate and other sweets, and do not drink soda.
The following foods should be excluded from the diet:
- Muffins, pastries, pasta.
- Fatty fish and meat.
- High fat dairy products.
- Marinades, mushrooms.
- Sweets.
- Alcohol.
Classification
Ascariasis is divided into several types based on different characteristics.
By type of disease there are:
- typical or manifest – occurs with the usual symptoms;
- atypical - asymptomatic form.
Taking into account the severity of the disease, the following forms of ascariasis are distinguished:
- light;
- medium-heavy;
- heavy.
Taking into account the characteristics of complications of the disease, the following forms are distinguished:
- without complications;
- with intestinal complications - possible complications include appendicitis , peritonitis , obstruction , pancreatitis , cholangiohepatitis ;
- with extraintestinal complications - liver abscesses, purulent cholangitis or pleurisy , sinusitis, abdominal abscess, etc.
There are two stages in the development of the disease:
- Migration – during this period the larva moves through the human body.
- Intestinal - during this period the larva finds itself in the intestine and grows rapidly.