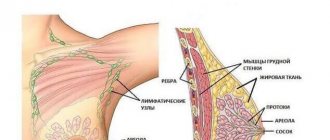
The female breast is an unusually complex part of the body, consisting of a large number of different components: glandular cells, ducts, fatty and connective tissue. In a woman's normal state, depending on the menstrual cycle, the components that make up the breasts grow and decrease in size again. During pregnancy and lactation, the breasts enlarge to fulfill their main “purpose”. Breast tissue grows the most during the third trimester of pregnancy. At the same time, several hormones influence the preparation of the breast for feeding: progesterone, estrogen and prolactin.
But if breast tissue grows incorrectly, or at different rates, grows constantly or does not decrease during the appropriate period of the cycle, then we are talking about mastopathy. Mastopathy can occur at any condition and age, and not only in a nursing mother, as is often believed.
What is mastopathy of the mammary glands and why is it dangerous?
Breast mastopathy is a pathological proliferation of breast tissue. There are different types of disease depending on the type of expanding breast tissue.
- Fibrous mastopathy is an excessive proliferation of connective tissue.
- Cystic mastopathy is excessive growth and obstruction (blockage) of the ducts, the formation of cysts.
- Adenomatosis is an excessive proliferation of glandular ducts.
There are also mixed types of mastopathy, for example, fibrocystic.
It is also important how exactly the tissue begins to grow. There are diffuse and nodular mastopathy. When it is not possible to determine clear boundaries of tissue changes, such mastopathy is called diffuse. And when the heterogeneity is clearly localized, they speak of nodular mastopathy.
It is important to understand that mastopathy can be benign (when the compaction does not threaten the body) or malignant. To determine the type of tumor, a biopsy or puncture is usually done. The sooner the type of compaction is established, the easier it will be to cope with the problem, especially in the case of a malignant neoplasm. Therefore, it is so important to consult a doctor at the first symptoms of mastopathy.
Diagnosis: which doctor to contact
To carry out diagnostics, you need to see a mammologist. The specialist conducts a visual examination and analyzes the patient’s complaints. The first step is palpation. The patient stands up, raises her arms, then lies down on the couch and does the same. The doctor determines not only the appearance, but also the presence of signs of asymmetry, enlargement of one gland relative to another
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo one or more diagnostic procedures:
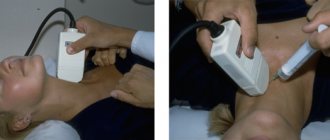
- Ultrasound examination;
- CT;
- mammography (not performed for women under 35 years of age or for pregnant and lactating women);
- pneumocystography;
- checking hormonal status;
- performing a biopsy (sampling of biological material) of the mammary glands.
Symptoms and signs in women
Diagnosing mastopathy is quite easy.
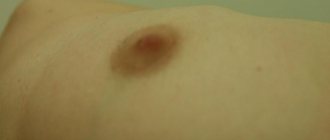
Firstly, it can be detected independently by palpation of the chest. It is advisable to carry out palpation at least once a month. If you can feel heterogeneity in the breast, most likely the lump will be a sign of mammary gland mastopathy. In some women, this heterogeneity is accompanied by chest pain during menstruation, and sometimes engorgement of the mammary glands occurs during menstruation.
To confirm the diagnosis, you should consult a doctor. A mammologist and most gynecologists can professionally palpate the breasts and detect mastopathy. But for an accurate diagnosis, equipment is used: ultrasound to detect relatively large objects, as well as mammography. By the way, it is advisable for women who have relatives with breast cancer to have a mammogram annually for early diagnosis.
Treatment of mastopathy
The treatment regimen for mastopathy should be selected individually for each woman. When prescribing a regimen, the reasons for the development of mastopathy, examination data, and changes in blood tests should be taken into account. If necessary, a woman should consult such specialists as a neurologist, gynecologist, endocrinologist, or therapist. Also, according to the doctor’s decision, if a nodular formation is identified, surgical treatment can be performed in the oncology department with histological examination of the removed area of the mammary gland.
In her life, almost every woman has at least once felt pain, discomfort in the mammary glands, or independently discovered a lump in the mammary gland. In such a situation, each woman behaves differently. One goes to a mammologist or oncologist, explains the sensations that are troubling her, undergoes an examination and, in the future, either receives a course of treatment or simply receives recommendations on self-examination and the frequency of visits to the mammologist. The other suffers pain, is tormented by doubts, and every time she hears from friends or acquaintances about a cancerous tumor, she thinks, “after all, not everything is all right with me either,” but due to her own fear of hearing a terrible diagnosis or simply from the eternal “not up to herself” continues to put off visiting the doctor.
You can find out more about the work of the hospital by calling +7 (495) 292-39-72.
Causes
The causes of mammary gland mastopathy are not fully understood; it is often believed that it is caused by excessive or insufficient amounts of hormones produced by the body. The most common hormonal disorder in mastopathy is an excess of estrogen with a deficiency of progesterone. It's not just a matter of changing the hormonal balance, but also an excessive growth of hormonal receptors in the breast tissue. However, the reasons for these processes are currently unknown. Sometimes the cause of mastopathy cannot be detected, but quite often the cause of the disease is inflammatory diseases of the endocrine and neuroendocrine sphere.
The risk of the disease increases with age. Factors that increase the likelihood of disease also include:
- heredity;
- overweight;
- hormone replacement therapy;
- late labor or absence of labor;
- late menopause;
- early onset of menstruation.
A connection between breastfeeding and mastopathy has not been identified.
We invite you to cooperation
Treatment of fibrocystic mastopathy
To ensure that the symptoms of the disease are relieved, it is advisable to conduct a competent diagnosis and consult a doctor. An integrated approach is used to treat this disease, including changes in diet, the use of comfortable underwear, the use of vitamins, anti-inflammatory and sedatives, and in some cases the use of hormonal and homeopathic medications.
Nutrition correction
It is advisable to completely eliminate products that can affect the formation of fibrous tissue and the appearance of fluid in the structure of the cyst. Doctors often recommend giving up coffee completely and limiting the consumption of tea, chocolate, and sweets. Many experts believe that any pathology of the mammary glands occurs as a secondary phenomenon after the formation of disorders in the intestines. It is advisable to completely eliminate constipation and normalize the bacterial flora.
If you have been diagnosed with mastopathy, it is advisable to eat foods that contain the maximum amount of fiber. Eat vegetables and fruits, greens daily. Drink enough water. Get rid of bad habits, in particular, drinking alcoholic beverages.
On a note! Do not cook foods that are too fatty; it is advisable to completely exclude from your diet foods that can irritate the gastrointestinal tract.
Using the correct underwear
If you suffer from mastopathy, it is advisable to review your entire wardrobe, in particular your underwear. Measure your measurements carefully to avoid purchasing clothes that are uncomfortable. Pay attention to all elements of the underwear, make sure that the clothes do not cause discomfort.
Vitamins
Useful microelements are necessary to improve the condition of the immune system, stabilize hormonal levels, and also activate the endocrine system. Experts recommend primarily using vitamins B, A, and E for mastopathy. Use the drug Aevit
(dosage: 1 capsule per day for 30 days) or
Triovit
(dosage: 1 capsule per day for 2 months).
Diuretics
If the disease is not treated in time, most patients suffer from edema. They may spread throughout the body. To get rid of negative effects, it is enough to use light diuretics. It is advisable to stop using medications and replace them with special teas based on medicinal herbs.
On a note!
You should reduce the amount of salt you consume daily.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Doctors often advise using Nise
,
Diclofenac
, allowing you to completely get rid of pain. Unpleasant sensations intensify before menstruation. It is advisable to use these drugs if you experience severe discomfort. A course of therapy with nonsteroidal drugs for mastopathy is not provided.
Sedative drugs
Necessary to eliminate psychological stress factors, which allows you to reduce the intensity of the symptoms of the disease in a short time. Use valerian infusion
or
motherwort
.
You can use special teas. Many people use sage tea
. To prepare it, place 1 tsp. chopped herbs in 1/2 tbsp. boiling water, brew, then take 2-3 times a day.
Hormone therapy
If a hormonal imbalance occurs in the body, the functioning of the mammary glands without disturbances is impossible. It is necessary to monitor the level of estrogen and progesterone. With mastopathy, the amount of hormones increases, which causes the mammary glands to grow. Medicines necessary to suppress estrogen activity should be used. Doctors often prescribe Toremifene
and
Tamoxifen
.
To suppress the secretion of excessive amounts of hormones, oral contraceptives are used, in particular Marvelon
. With their help, you can eliminate the increased production of almost all female hormones and stabilize the functioning of the endocrine system.
Tactics and methods of treatment
Some forms of mastopathy do not require treatment, they just need to be monitored. If the disease progresses, then conservative treatment is prescribed. It is necessary to treat not mastopathy itself, but to eliminate its causes: inflammation of the female genital organs, endocrine pathologies, liver diseases.
For the conservative treatment of diffuse mastopathy, hormonal drugs that normalize the balance are prescribed (as a rule, with mastopathy, an excess of estrogen and a deficiency of progesterone) and drugs that normalize metabolism are prescribed. vitamin and mineral complexes.
For nodular mastopathy, conservative treatment is ineffective. Cysts, fibroids, and large fibroadenomas are removed surgically. Many operations are performed using a minimally invasive method through mini-punctures.
Diffuse FAM
NB! This abbreviation is very often used after any examination of the breast (ultrasound, mammography, examination). This is due to the fact that in budget clinics, if the doctor does not find any pathology during the examination and does not make at least some diagnosis, the insurance company does not pay for this consultation and examination to the institution. Therefore, there is an unspoken instruction to doctors to “put at least something.” This is how it is implemented. It is impossible to write “Normal variant” or “No pathology detected”!
In private centers, in most cases, there is an unobtrusive recommendation to encourage repeat visits of patients and their additional examinations. Therefore, they also “find” FAM, FCM or mastopathy during a simple preventive examination without the patient’s complaints - in order to be able to prescribe a “control” examination, examination or even treatment with dietary supplements (which are often sold right there) with a second “appearance in 3-4 months” .
Breast tumor
If a biopsy of a benign breast tumor reveals proliferation or atypia , this is just an alarming factor: with this process, the risk of cancer is higher than without it (maximum 4 times). Without proliferation and atypical hyperplasia, all benign breast tumors - papilloma, fibroadenoma, cyst, FAM or FCM - have no higher risk of cancer than all other women .
- Operations for fibroadenoma
- Treatment of breast cysts
- Breast papilloma
- Surgeries for gynecomastia
- Plastic surgery for benign breast diseases
- Mastitis or inflammation of the breast