Today's statistics are inexorable: every second woman has some kind of problem related to the mammary glands. The main conclusion that you should make by reading this article is that any lump in the breast that you discover during a self-examination is a reason to visit a doctor. He will make the correct diagnosis and will be able to assess the further danger of the identified compaction.
There are several factors influencing the occurrence of this pathology. During lactation, the appearance of lumps is provoked by blockage of the milk ducts, which occurs as a result of irregular or incomplete emptying of the mammary gland. Induration, accompanied by an increase in temperature, weakness, redness of the skin and the presence of pain signal the presence of an inflammatory process and the likelihood of developing mastitis.
Many girls and women experience painful sensations in the chest before each menstruation. In these cases, a lump may form in the mammary gland. Such dense areas are mobile and can change location and size. This is nothing more than mastopathy - a benign neoplasm in the mammary gland. It is also worth noting that the appearance of compactions may be associated with the onset of the development of the tumor process. But still, in most cases, the formations are benign. Quite common pathologies include cysts, adenomas, abscesses, blood clots, lipomas, and fat necrosis.
The appearance of lumps and knots in the chest is sometimes accompanied by discharge from the nipples. If they are brown or bloody in color, there is a risk of cancer occurring and developing, since discharge is one of its symptoms.
It is also worth noting that the appearance of compactions may be associated with the onset of the development of the tumor process. But still, in most cases, the formations are benign. Quite common pathologies include cysts, adenomas, abscesses, blood clots, lipomas, and fat necrosis.
Lump in the mammary gland: diagnosis, treatment
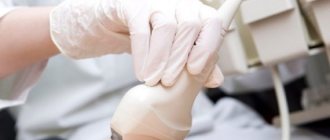
Already during the examination, the mammologist has an idea of the causes and nature of the detected breast lump. A preliminary diagnosis must always be confirmed by ordering additional studies. The algorithm for mammological examination is as follows: X-ray, ultrasound and laboratory diagnostics are performed. X-ray diagnostics includes mammography and ductography. Laboratory diagnostics involves the study of secretions from the mammary gland and its tissues.
The results of such a comprehensive examination allow us to make the final, most accurate diagnosis. In accordance with it, adequate treatment is prescribed and carried out. Its methods include conservative therapy aimed against diffuse tissue proliferation, removal of nodes if present, and complex oncological treatment in the case of breast cancer.
Taking care of your health involves regular examinations by specialists. Timely detection of breast cancer is a guarantee of recovery. Take care of yourself!
Healing procedures
The choice of treatment program is completely influenced by the cause of the problem.
The main task of combating lactostasis is to free the breasts from milk. A woman needs to massage her breasts, not get too cold, and feed the baby in a timely manner. It is important to eat well and rest; it is preferable to sleep on your side.
Mastitis is treated with antibiotic therapy. A properly selected treatment program can remove the seal.
When a doctor encounters purulent mastitis, surgical intervention is necessary.
For mastopathy, conservative methods are used. Various drugs, such as inhibitors, are used in therapy. Their task is to normalize hormonal levels.
When a doctor encounters a benign lump, a decision is usually made about surgical manipulation. This is more effective than therapeutic methods. Enucleation or sectoral resection is used.
Thrombocytopenia
Oncological tumors are treated only through surgery. Typically, a mastectomy is performed. In the process, regional lymph nodes are removed.
Sometimes the tumor is excised within healthy tissue.
As an alternative to treatment, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapy are used. The effect is enhanced if they complement each other.
Lumps in the chest: causes
Hormonal imbalance in the body, the occurrence of benign tumors and the development of breast cancer are the most common causes of lumps in the breast.
Doctors at our clinic always urge not to let diseases progress, not to self-medicate, but to turn only to professionals. After all, wasted precious time can lead to very sad consequences. For example, mastopathy often degenerates into breast cancer. Much less frequently, but still there are cases when benign tumors also turn into malignant cancerous ones.
Diagnostic techniques
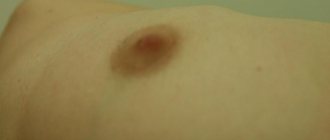
Each woman should palpate her breasts independently at different phases of the cycle. The lump can be detected at any age, but if you consult a doctor in time, you can defeat the disease, even oncology.
To establish an accurate diagnosis, you will be offered examinations:
- Ultrasound;
- x-ray of glands;
- biopsy - puncture will allow you to obtain a sample of breast tissue for an accurate diagnosis. The technique is highly accurate and accurately determines the nature of the tumor;
- galactography is a type of mammography. To examine the tissues and compaction, a special contrast will be injected into the milk ducts, which is clearly visible on x-rays. The result is that compacted areas in the ducts can be easily identified.
The decision on the choice of technique is made by the attending physician, who evaluates the clinical picture of the disease.
Breast compaction in pregnant and lactating women
A woman cannot avoid hormonal changes during pregnancy. During this period, the mammary glands enlarge under the influence of estrogens, progesterone, prolactin and placental lactogen. The lactogenic effect of prolactin is blocked by increased production of estrogen and progesterone until the time of birth. After childbirth, the levels of these hormones in a woman’s body decrease significantly, and then, under the influence of a high level of prolactin production, lactation and milk production begin.
According to statistics, breast cancer develops in one out of 3000-4000 pregnant women. The course of this cancer is the same as that observed in the absence of pregnancy. Considering that the presence of a large formation or lump in the breast during pregnancy can be mistakenly attributed to ongoing hormonal changes, the tumor is often diagnosed at a later stage.
Therefore, for any large tumor that appears during pregnancy or lactation, it is necessary to undergo a detailed examination. It must include a biopsy performed under local anesthesia.
Fibroadenomatosis with a cystic component
It is characterized by the presence of round or oval formations (cysts) against the background of a heterogeneous pattern from the parenchyma of the gland.
In the upper-outer quadrant, areas of irregular round shape are identified, having a homogeneous MR structure, characterized by iso-, hypointense in T2 and isointense in T1
MRS with deformation of the architectonics of the mammary gland due to fibrosis around the glandular lobules. Similar areas are visualized in the central and upper-outer quadrants of the left breast (arrows).
With the advent of the ability to determine BRCA mutations and, thus, identify a population of women at high risk of breast cancer, the introduction of new modern and high-tech methods for the early detection of this disease has become especially urgent. This method is MR mammography, which is widely used all over the world and now, with the development of new technologies in Russia, can be a diagnostic method that complements routine mammography and ultrasound.
Breast compaction due to mastopathy
Mastopathy is a benign form of proliferation of breast tissue. This disease occurs and develops due to hormonal imbalances. The manifestation of mastopathy exists in two types: nodular and diffuse forms. The latter is more common.
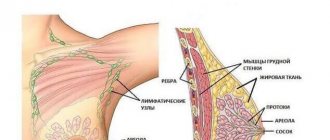
In the nodular form of the disease, areas of overgrown tissue appear in the form of nodes. On palpation, non-painful or slightly painful compactions are felt, which can be single or multiple. They are not fused to the skin and nipple. These lesions are mobile and cannot be felt in a lying position. Most often, with nodular mastopathy, there is no increase in nearby lymph nodes.
Diffuse mastopathy is expressed in the proliferation of tissue throughout the entire volume of the mammary gland. If there is a proliferation of glandular tissue that produces secretions, then adenous mastopathy is diagnosed. If the connective tissue grows, then we are talking about fibrous mastopathy. Cystic mastopathy is diagnosed when tissue grows with the formation of a large number of cavities, or cysts.
Quite often mixed forms of diffuse mastopathy are detected. Its main symptoms include swelling, heaviness and enlargement of the mammary glands, which is accompanied by nagging pain in the chest, and less often, discharge from the nipples. These signs appear approximately 5-7 days before the start of menstruation.
The growth of gland tissue is facilitated by the large amount of sex hormones estrogen in a woman’s body. The appearance and development of mastopathy is associated with this factor. The disease is quite common, every third woman suffers from one form or another. The risk zone also includes women with any gynecological diseases. Other factors that provoke mastopathy include late childbirth, abortion, early or late onset of menstruation, late or early menopause, disruption of the thyroid gland, injuries to the mammary gland and uterus, etc.
Why do fibroadenomas form?
This type of pathology belongs to the category of little-studied. There are only assumptions about the causes of fibroadenomas, the most recognized among them being hormonal disorders.
It has been proven that any factors associated with hormonal fluctuations contribute to the occurrence of fibroadenoma:
- Independent, uncontrolled use of oral contraceptives, emergency contraception;
- Pregnancy, frequent abortions, in which the body, which is in the gestation stage, is forced to sharply adjust to a new rhythm;
- Intermittent lactation, breast refusal or inability to feed;
- The presence of pathologies, stressful situations, overload;
- Menopause.
Often fibroadenoma forms during the childbearing period, and after entering menopause it resolves. This indicates the important role of female sex hormones in this process.
Breast compaction in benign tumors
A common benign neoplasm is breast fibroadenoma. There are nodular and leaf-shaped forms. Most often, nodular fibroadenoma is found in women under 35 years of age and is a single node. The tumor consists of glandular and connective tissue, has clear contours, a round shape and sizes ranging from a few millimeters to 3-5 centimeters. Usually painless. In women over 40 years of age, cases of malignant degeneration of nodular fibroadenoma occur.
A leaf-shaped tumor is a layered structure that rapidly increases in size. The skin of the breast over the leaf-shaped fibroadenoma becomes noticeably thinner, acquiring a bluish tint. Sometimes it undergoes malignant degeneration.
Ultrasound table with norms and deviations of fibroadenoma
| Glandular tissue thickness | Fibroadenoma size | ||
| Normal up to 40 years – up to 14 mm | Deviations - more than 14 mm | Normally does not exceed 2-3 cm | Deviations – up to 9 cm |
| The norm after 40 years is up to 20 mm | Deviations - more than 20 mm | ||
If cancer is suspected, a fine-needle biopsy is prescribed. This is quite unpleasant, but the only adequate procedure that allows you to accurately determine whether there is cancer in the mammary gland.
The mammologist, using a thin hollow needle, inserts it into the tumor, capturing a small amount of tissue. To avoid mistakes, the doctor monitors the process using ultrasound. The cells obtained in this way are sent to the laboratory for cytological (cellular) examination. Under a microscope, the structure of cells is clearly visible: it is different for benign and malignant ones.
After the tests obtained, the doctor will prescribe further treatment, and if necessary, surgery.
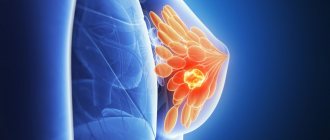
Lump in the mammary gland due to breast cancer
A lump in the breast is one of the signs of breast cancer. Most often, oncological pathology arises and develops due to the increased content of estrogen hormones in the body. This promotes the proliferation of the epithelium of the lobules and ducts and the formation of atypical, so-called immature cells.
Medicine distinguishes between two forms of breast cancer: nodular and diffuse. The nodular form is more common. It is characterized by the presence of a dense, painless node, marked by fuzzy contours and an uneven surface. This tumor grows towards the skin, growing into the subcutaneous tissue. This leads to changes in the skin over it, the skin of the mammary gland becomes wrinkled or retracted. Then swelling of the skin of the nipple and areola (peripapillary surface) appears. As the tumor spreads through the ducts of the mammary gland, nipple retraction is observed, and an “orange peel” appearance also appears due to swelling and expansion of the skin follicles above the tumor. If upon palpation the mammary gland
Young girls and women during pregnancy and lactation are susceptible to the diffuse form of cancer. This disease may be painless, but the tumor grows rapidly, metastasizing to nearby lymph nodes.
Another type of diffuse form is mastitis-like cancer, which occurs in older women.
In old age, any mastitis should be carefully examined. In some cases, the diffuse form takes on an erysipelas-like course. Then it is mistaken for erysipelas caused by streptococci. In the case of erysipelas-like breast cancer, uneven swelling and redness appear on the skin of the breast. With armored breast cancer, the breast decreases in size, becomes denser, and becomes inactive. The surface of the chest becomes uneven and resembles a shell in shape.
Prevention
To prevent the appearance of seals, you should give up bad habits, be physically active, and avoid nervous overload. Visit your mammologist periodically and have your breasts examined in the first week after bleeding stops. Alarming symptoms:
- the shape of the gland has changed;
- upon palpation, nodules and tubercles are felt; they appear in the armpit area;
- the presence of thickenings in the tissues, bulges, dimples and folds;
- obvious swelling.
Carry out the examination while standing in front of a mirror. Raise your opposite hand and slowly feel your breast with your fingertips. Move in a spiral from the armpit to the nipple, then from top to bottom.
Take a lying position, put your hand behind your head, palpate the base of the gland with your fingers, moving towards the nipple, squeeze it to make sure there is no discharge.
If lumps are detected, contact your doctor to treat the pathology at an early stage.