- Home page
- Articles
- Everything, or almost everything, about obesity
The opinion that there must be a lot of good people has not been relevant for a long time. In today's society, no matter how civilized it may be, fat people are not treated very favorably. Job advertisements require applicants to be “good looking,” which implies at least a slim figure. The time is not far off when insurance companies will raise prices for health insurance for obese people - they say it is their own fault for exposing themselves to risk.
The United States of America is rightfully recognized as the most overweight country. Obesity in the United States is now reaching alarming proportions, and has already become the 2nd leading cause of death. 68% of those suffering from excess weight are very large numbers, and virtually every 4 Americans (23%) are diagnosed with real obesity, including infants and the elderly. Obesity in America is explained by an addiction to fast food - food that is eaten on the run, food that consists only of fats and carbohydrates, in other developed countries obesity is also very common, the statistics are terrifying, more and more people are getting sick with it already in childhood and adolescence age. And, unfortunately, society has a rather lenient attitude towards obesity; it is perceived more as a defect in appearance rather than a disease
.
Olga Grigoryan, senior researcher at the Institute of Nutrition of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences
: “In our country, the problem of obesity is no less acute than, say, in the United States.
Every third Russian is overweight, every second is obese. The aesthetic side of the issue is not at all the main thing. Obesity is a dangerous disease
that is accompanied by equally serious diseases, such as diabetes.
If we talk about the reasons that lead to the accumulation of excess body weight in us, I would highlight the following: a sedentary lifestyle, lack of nutritional culture and healthy lifestyle habits
. In addition, political and economic instability in Russia leads to people trying to “eat up” accumulated fatigue and stress. At the same time, we are also subject to general trends. Obesity in Russia, as well as throughout the world, has become significantly “younger”: there have been many more children and adolescents suffering from this disease in recent years. The number of calories required for a modern, sedentary city dweller is decreasing every year. Today, the daily energy requirement for women is 1800 kilocalories!, for men – 2000–2200! kilocalories."
However, obesity still has its own established objective reasons. People now spend more and more time in cars. Work, as a rule, is also sedentary. And at home, after a hearty dinner, sitting down for an hour or two in front of the TV or computer is a sacred thing. And we shouldn’t forget about genetics, poor ecology, stress, which we love to “eat up” with sweets.
Causes of obesity
The causes of obesity can be divided into 2 large groups: exogenous (dietary) and endogenous (morbid) obesity.
These forms of obesity differ from each other precisely in the reason that causes increased fat deposition. If nutritional obesity occurs due to excessive intake of calories from food due to appetite, eating habits, and poor nutrition, then morbid obesity is a disease based on a violation of metabolic processes and hormonal regulation of both eating behavior and fat metabolism.
Morbid obesity:
- Occurs as a result of infections, diseases and injuries of the organs of endocrine regulation of metabolism - adrenal glands, pituitary gland (pituitary obesity), thyroid gland, gonads.
- It is not of a family nature.
- It is a consequence of diseases, not their cause.
- Extremely difficult to treat, hormonal obesity must be treated together with the root cause - diseases of the endocrine glands.
This division is arbitrary and in advanced stages it is no longer possible to separate one from the other; if you have severe obesity, your hormones will inevitably suffer.
In any case, to succeed in the fight against the disease, you will first have to take control of your appetite.
Obesity and its effect on the body
Excess body weight determines a 2-3 times increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, coronary heart disease, hyperlipidemia, atherosclerosis and its clinical manifestations, varicose veins, thrombophlebitis, cholelithiasis, arthritis, osteochondrosis, flat feet, gout, fatty hepatosis and etc.
Obesity, especially its visceral type, in which fat predominantly accumulates in the abdomen and on the anterior abdominal wall, is the main and independent risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, a more reliable prognostic factor for the development of coronary heart disease than high blood pressure, smoking or impaired glucose tolerance .
Excess visceral fat occurs in 57% of patients with type 2 diabetes, 30% with gallbladder disease, 75% with arterial hypertension, 17% with coronary heart disease (CHD), 14% with osteoarthritis, 11% with cancer breast, uterus and large intestine. At the same time, it has been proven that reducing body weight in the majority of hypertensive patients reduces blood pressure, and allows almost two-thirds of patients with type II diabetes to stop taking medications.
Among children, the incidence of obesity is also growing, and in childhood this disease is even more dangerous, because disrupts the formation of organs and systems, which continues into adolescence. There are prerequisites for the development of serious diseases in the future.
For example, obesity in girls significantly increases the risk of developing polycystic ovary syndrome, which often leads to infertility and menstrual irregularities. In addition, the presence of obesity in a teenager often indicates that he will suffer from this problem in adulthood. Thus, it is obvious that overweight and obesity are a problem that is widespread and requires a serious approach.
The negative effects of excess body weight on the body are extremely varied. However, although various diseases are important, they are not the only consequence of being overweight.
Another problem that obese people face are difficulties in the social sphere: it is difficult for them to move up the career ladder or even just get the job they want; they often have problems in relationships with the opposite sex, associated with both actual obesity and low self-esteem and the presence of a wide variety of psychological complexes.
Thus, even if a person is not critical of his appearance and does not consider excess body weight a problem that needs to be dealt with, he still has to deal with the sidelong glances of others and prejudiced attitudes towards himself. Therefore, it is better to think in time about choosing a competent plan for losing weight and maintaining normal body weight. Reducing body weight radically reduces additional risks of various complications.
Obesity is a very complex problem because there are many more causes than there are effective treatments to combat it.
Symptoms of obesity:
Signs of obesity are, of course, weight gain that is beyond what is normal for your height, gender, and age. Obese patients usually have other complaints, the severity of which depends on the degree of obesity.
As it progresses, shortness of breath, pain in the legs and back appear, the joints of the limbs and venous system suffer, and swelling appears. In severe cases, when the disease persists for a long time, atherosclerosis and hypertension are common, which become the killers of obese patients.
What is morbid obesity?
Morbid obesity is a chronic genetically determined disease. It is characterized by a BMI of 40 or more. When obesity reaches the morbid stage, excess weight begins to threaten the patient's life. Morbid obesity is associated with many dangerous diseases that affect both health and quality of life, reducing its average life expectancy. Type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, atherosclerosis, sleep apnea (stopping breathing), etc. appear. At the stage of morbid obesity, as a rule, neither diet nor physical activity leads to significant and lasting weight loss, namely weight loss is the only way to stop the development of severe concomitant diseases.
You can read articles and watch videos about the operations performed:
National Television and Radio Company of Uzbekistan. News. Master class by K.V. Puchkova Medical Newspaper. Traditional meeting place
Types of obesity:
There are visceral (also known as abdominal, also known as central) obesity and peripheral obesity. Often the first type of fat deposition is morbid in nature, if you have such obesity, losing weight will be a difficult task. Internal obesity is characterized by the deposition of fat mainly around the internal organs, liver, heart, stomach, pancreas. Abdominal obesity occurs most often, and while in women fat usually accumulates mostly under the skin, in men it is deposited in the area of internal organs.
Obesity classification:
A person’s normal weight depends on his body type (asthenics, people of a fragile physique with thin bones, normosthenics, averagely developed people, and hypersthenics, with massive bones and a strong physique). The Egorov-Levitsky table takes into account your gender, body type and height, from it you can find out the approximate range of normal body weight for you.
| Height, cm | Men | Women | ||||
| Asthenics | Normosthenics | Hypersthenics | Asthenics | Normosthenics | Hypersthenics | |
| 148 | 42,0 — 44,8 | 43,8 — 48,9 | 47,4 — 54,3 | |||
| 150 | 42,7 — 45,9 | 44,5 — 50,0 | 48,2 — 55,4 | |||
| 152 | 43,4 — 47,0 | 45,6 — 51,0 | 49,2 — 56,5 | |||
| 154 | 44,4 — 48,0 | 46,7 — 52,1 | 50,3 — 57,6 | |||
| 156 | 45,4 — 49,1 | 47,7 — 53,2 | 51,3 — 58,6 | |||
| 158 | 51,1 — 54,7 | 53,8 — 58,9 | 57,4 — 64,2 | 46,5 — 50,2 | 48,8 — 54,3 | 52,4 — 59,7 |
| 160 | 52,2 — 55,8 | 54,9 — 60,3 | 58,5 — 65,3 | 47,6 — 51,3 | 49,9 — 55,3 | 53,5 — 60,8 |
| 162 | 53,2 — 56,9 | 55,9 — 61,9 | 59,6 — 66,7 | 48,7 — 52,3 | 51,0 — 56,8 | 54,6 — 62,2 |
| 164 | 54,3 — 57,9 | 57,0 — 62,5 | 60,7 — 68,8 | 49,8 — 53,4 | 52,0 — 58,2 | 55,9 — 63,7 |
| 166 | 55,4 — 59,2 | 58,1 — 63,7 | 61,7 — 69,6 | 50,8 — 54,6 | 53,3 — 59,8 | 57,3 — 65,1 |
| 168 | 56,5 — 60,6 | 59,2 — 65,1 | 62,9 — 71,1 | 52,0 — 56,0 | 54,7 — 61,5 | 58,8 — 66,5 |
| 170 | 57,9 — 62,0 | 60,7 — 66,7 | 64,3 — 72,9 | 53,4 — 57,9 | 56,1 — 62,9 | 60,2 — 67,9 |
| 172 | 59,4 — 63,4 | 62,1 — 68,3 | 66,0 — 74,7 | 54,8 — 58,9 | 57,5 — 64,3 | 61,6 — 69,3 |
| 174 | 60,8 — 64,9 | 63,5 — 69,9 | 67,6 — 76,2 | 56,3 — 60,3 | 59,0 — 65,8 | 61,3 — 70,8 |
| 176 | 62,6 — 66,4 | 64,9 — 71,3 | 69,0 — 77,6 | 57,7 — 61,9 | 60,4 — 67,2 | 64,5 — 72,3 |
| 178 | 63,6 — 68,2 | 66,5 — 72,8 | 70,4 — 79,1 | 59,1 — 63,6 | 61,8 — 68,6 | 65,9 — 74,1 |
| 180 | 65,1 — 69,6 | 67,8 — 74,7 | 71,9 — 80,9 | 60,5 — 65,1 | 63,3 — 70,1 | 67,3 — 75,9 |
| 182 | 66,5 — 71,0 | 69,2 — 76,3 | 73,6 — 82,7 | 62,0 — 66,5 | 64,7 — 71,5 | 68,8 — 77,7 |
| 184 | 67,9 — 72,5 | 70,7 — 78,1 | 75,2 — 84,5 | 63,4 — 67,9 | 66,1 — 72,7 | 70,2 — 79,5 |
| 186 | 69,4 — 74,0 | 72,1 — 79,0 | 76,7 — 86,2 | |||
| 188 | 70,8 — 75,8 | 73,5 — 81,7 | 78,5 — 88,0 | |||
| 190 | 72,2 — 77,2 | 75,3 — 83,5 | 80,3 — 89,8 | |||
| 192 | 73,6 — 78,6 | 77,1 — 85,3 | 81,8 — 91,6 | |||
| 194 | 75,1 — 80,1 | 78,9 — 87,0 | 83,2 — 93,4 | |||
If you have calculated your ideal body weight, how to determine obesity and its degree requires further calculations.
Subtract your ideal body weight from your actual body weight and divide by your ideal body weight. The resulting figure multiplied by 100 is % of excess body weight. Example: You weigh 87 kg, your ideal body weight is 63 kg. (87-63)/63=0.38X100=38% excess weight. Excess body weight - up to 10% 1st degree of obesity - 10-29% 2nd degree of obesity - 30-49% 3rd degree of obesity - 50-99% 4th degree of obesity - 100% or more of normal body weight.
In addition to this table and calculation, normal body weight can be calculated using the Broca index, as we wrote about how to do this, and of course, using the BMI calculation.
Next, you can estimate your BMI using special tables, the most detailed one is intended for the military registration and enlistment office, but this table is quite enough for us. Here are the degrees of obesity by BMI depending on age. Obesity table by BMI
| Level of excess of normal body weight depending on BMI | BMI for ages 18-25 | BMI for age over 25 years |
| Normal body weight | 19,5-22,9 | 20,0-25,9 |
| Excess body weight | 23,0-27,4 | 26,0-27,9 |
| Obesity of the first degree | 27,5-29,9 | 28,0-30,9 |
| Obesity of the second degree | 30,0-34,9 | 31,0-35,9 |
| Obesity of the third degree | 35,0-39,9 | 36,0-40,9 |
| Obesity of the fourth degree | 40.0 and above | 41.0 and above |
Obesity. Excess body weight. Overweight
The best price for an appointment with an endocrinologist in St. Petersburg.
Consultation with Doctor of Medical Sciences, endocrinologist E. L. Strukov. 2500 rubles.
The reception is conducted by:
Evgeniy Leonidovich Strukov – endocrinologist-oncologist, Doctor of Medical Sciences; work experience over 30 years. Graduated from St. Petersburg State Pediatric Medical University (LPMI) in 1984. In 1989-1993 — full-time postgraduate study in the laboratory of endocrinology of the Research Institute of Oncology named after. Professor N.N. Petrova. 1993 – defended his thesis for Candidate of Medical Sciences in the specialty “Oncology” (Research Institute of Oncology named after Professor N.N. Petrov) on the topic “Comparison of the content of polypeptide hormonal factors in tumor tissue and in peripheral blood in different types of malignant tumors.” his doctoral dissertation in the specialty “endocrinology” in 2003. The topic of the doctoral dissertation is “Hormonal regulation in cardiovascular diseases and some dysfunctions of endocrine organs in people exposed to the Chernobyl nuclear power plant accident and in the population of residents of St. Petersburg.” Topics of scientific interests: oncoendocrinology; neuroendocrinology.
Obesity is a disease of the body characterized by excessive deposition of fat in the subcutaneous tissue and tissues due to metabolic disorders. Obesity can be an independent disease (ordinary or true - alimentary obesity, constitutional-hereditary obesity) or act as a symptom of diseases, the cause of which is most often dysfunction of the endocrine glands or damage to the central nervous system. Regular obesity is a widespread disease that contributes to the development of various diseases and shortens life expectancy. In women, the incidence of obesity reaches 50%, in men - 30%, and in children - 10% (R. Shimonchikh). After the age of 70, a decrease in average body weight is usually observed.
Factors contributing to the development of regular obesity include:
- excessive consumption of food, especially rich in carbohydrates and fats;
- alcohol abuse;
- insufficient physical activity,
- age over 40 years, hereditary predisposition to obesity.
Symptomatic obesity develops most often as a result of endocrine diseases (adiposogenital dystrophy, Cushing's syndrome, hypothyroidism, hyperinsulinism, hypogonadism) or pathological processes in the central nervous system (brain injuries, encephalitis, tumors of the bottom of the third ventricle of the brain, etc.).
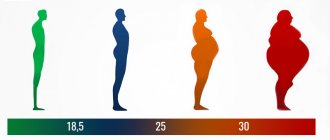
The World Health Organization considers excess weight dangerous if the body mass index (BMI, Quetelet index) is greater than 30 . Traditionally, body mass index is calculated using the formula: weight, measured in kilograms, divided by the square of height, measured in meters: BMI = weight (kg)/{height (m)}2; for example, if weight is 100 kg, height is 178 cm, i.e. 1.78 meters, BMI will be 32.
This is the formula for calculating body mass index that doctors often use. At the same time, the normal BMI ranges from 18.5 to 24 units. If the BMI is greater than 30 or a number less than 16, it is a serious threat to a person's health. ITM is necessary to assess the risk of dystrophy or obesity, as well as the high risk of developing cardiovascular pathology, hypertension and other diseases associated with the risk of death.
A new criterion for calculating body mass index was developed by Oxford mathematician Nick Trefesen. The scientist is confident that the index traditionally used to assess underweight or excess weight is incorrect. In his opinion, tall and short people should evaluate their weight differently. Weight compliance with health standards must also be assessed differently. The main criterion, from his point of view, is the ratio of body volumes . In this regard, tall people who believe that they are overweight may be wrong. The same applies to short people who are confident that they weigh little.
Professor Trefesen concluded that the following coefficients should be used in the calculation formula used:
- for weight - the number in kilograms is multiplied by 1.3,
- for height - the number in meters is multiplied by 2.5.
The scientist believes that the new non-academic formula concerns millions of people who are mistaken about their own weight, and therefore put their health at high risk. According to the new formula, people taller than 180 centimeters can easily subtract one from the calculated index, and those who are 150 centimeters tall must add the same unit to their body mass index (according to the newspaper “Arguments and Facts”).
Classification of obesity. There is no generally accepted classification of obesity. M.N. Egorov and L.M. Levitsky distinguishes the following forms of obesity.
Forms of general obesity: 1. Nutritional forms: a) habitually hyperalimentary; b) deregulatory; c) constitutional-hereditary; d) mixed. 2. Endocrine forms: a) hypothyroid; b) hypogenital; c) adrenal (cortical-adrenal); d) pituitary; e) mixed (polyendocrine). 3. Cerebral (nervous) forms: A. According to the type of local disorders: a) cortical (psychosomatic); b) hypothalamic (diffuse); c) hypothalamic-pituitary (Pechkranz-Babinsky-Fröhlich syndrome). B. According to etiological aspects: a) post-traumatic; b) post-infectious.
Classification of overweight and obesity by body mass index (BMI):
- BMI <18.5 Underweight
- BMI 18.5-24.9 Normal weight
- BMI 25.0- 29.9 Overweight
- BMI 30.0- 34.9 First degree obesity
- BMI 35.0- 39.9 Second degree obesity
- BMI >40 Third degree obesity
Along with BMI, an important indicator of excess weight is also an indicator such as waist circumference . If the waist circumference is more than 94 cm in men and more than 80 cm in women, then the patient should consult a doctor, as these figures indicate the possible presence of various diseases.
Why is obesity dangerous?
Obesity increases the risk of diabetes, cardiovascular disease, infectious diseases, heart attack, malignant tumors, musculoskeletal diseases and insomnia. Obesity is a significant cause of infertility and increases the risk of developing pregnancy pathologies and childbirth-related risks to the health of mother and child.
Methods for treating obesity
Obesity is a chronic disease that worsens a person's quality of life, increases the risk of developing many diseases and shortens life expectancy. Therefore, the treatment of obesity is very justified. Losing weight is easy—almost everyone has done it before. It is much more difficult, and often impossible, to maintain weight loss over the long term.
The body's hormonal system remembers stable excess body weight over a long period of time and reacts to weight loss not only by trying to restore the former weight, but also to store a little more just in case.
Therefore you need:
- First of all, change your lifestyle. To do this, you will also need to conduct a series of consultations with an endocrinologist and gastroenterologist on proper nutrition.
- It is necessary to take into account the fact that physical activity should be regular and appropriate to your age and concomitant diseases.
- You may need cognitive behavioral therapy (the help of a psychotherapist).
- Drug treatment.
- Surgical treatment (bariatric surgery). A 2007 New England Journal of Medicine study found that bariatric surgery reduced overall mortality by 40%, including a 92% reduction in diabetes-related mortality and a 56% reduction in cardiovascular disease-related mortality. from cancer - by 60%.
What is bariatric surgery?
Bariatric surgery is the most effective treatment for obesity today. After surgery, patients begin to feel fuller by eating less food, thus consuming fewer calories. A person's preferences and habits when choosing food change significantly. As a result, body weight is steadily reduced, multiple concomitant diseases are cured (type 2 diabetes, high blood cholesterol, etc.), and life expectancy increases. A persistent change in the patient’s eating habits and lifestyle is the key to success in getting rid of concomitant diseases. Bariatric surgery provides a very powerful tool that helps the patient stay on the chosen path.
Why is bariatric surgery needed?
Gaining weight is very easy - many of us have done it at some point. It is much more difficult, and most often impossible, to maintain the weight achieved after losing weight at the same level for a long time (we all have a similar experience). Research shows that weight loss achieved with the best conservative treatments is 3-5% of body weight. Only one person out of seven can lose more than 10% of weight and maintain this result for more than a year. With the use of additional medications, the long-term weight loss achieved is 6-8%. Bariatric surgery can achieve significant and sustainable weight loss. For example, according to the results of the Swedish SOS study, operated patients 15 years after surgery weighed 27% less than before it.
Weight loss is a very important part of the whole process, but by no means the only one. Many weight-related diseases are cured or their symptoms are noticeably alleviated (type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, heart failure, etc.). All this has a positive effect on health, as a result of which the life expectancy of operated patients is longer than that of non-operated patients who initially had the same weight. First of all, mortality from cardiovascular diseases, diabetes and cancer is reduced.
Is bariatric surgery right for you?
Bariatric surgery is indicated if your BMI is 30 kg/m2 or is in the range of 30-39.9 kg/m2 if you have obesity-related diseases. After the operation, persistent weight loss is achieved, which has a beneficial effect on the course of concomitant diseases (type 2 diabetes, arterial hypertension, heart failure, sleep apnea, hypercholesterolemia, degenerative joint diseases, female infertility).
In other words, you must understand that obesity is a chronic disease and surgery is one of the best treatments to achieve long-lasting and satisfactory results. At the same time, you must be ready to change your lifestyle and diet. Patients should try other weight loss methods before undergoing surgery; surgery should never be the first choice for treating obesity!
The patient must understand that after the operation he will have to regularly visit a doctor (nutritionist, endocrinologist, therapist) for a long time. As a result of bariatric surgery, depending on the method, patients lose on average 40-70% of their excess weight. It is very important to understand that this is an average weight loss. There are patients who lose 100% of their excess weight, and those whose excess weight drops below the average, or even those who begin to gain weight.
Bariatric surgery is not cosmetic surgery like liposuction. Bariatric surgery is a radical surgical intervention (majorsurgery) with consequences for life.
How does bariatric surgery work?
To understand how bariatric surgery works, you need to understand the anatomy and function of the digestive tract. (A diagram of the alimentary tract is shown below.)
Conventionally, three sections of the digestive tract are distinguished: the anterior section (oral cavity, pharynx and esophagus), where mechanical processing of food is carried out mainly; middle section (stomach, small and large intestine, liver, pancreas). It is in this department that the chemical processing of food is carried out, the products of its breakdown are absorbed and feces are formed. Third part: the posterior part of the caudal part of the rectum, which ensures the excretion of feces from the body.
Food initially enters the oral cavity, after which it moves through the esophagus and enters the stomach and then the intestines. As food moves through the alimentary tract, it undergoes mechanical and enzymatic processing.
The esophagus (1) is a long, muscular, tube-like organ whose purpose is to transport absorbed food from the mouth to the stomach. The stomach (2) is an organ with a volume of up to 1500 ml, in which food, after absorption, is retained for some time, then mixed with gastric juice, and its breakdown begins.
Stretching the walls of the stomach is what causes the feeling of fullness.
The duodenum (3) is the first part of the small intestine, the length of which is approximately 20 cm. The length of the small intestine (5 in the diagram) is 5-6 meters. This is where most of the digestion of food and absorption of nutrients occurs. Different micro- and macronutrients are absorbed by different parts of the intestine. In the large intestine (6), water is absorbed and formed elements of feces are formed. Unprocessed food debris is excreted through the caudal part of the rectum.
Before resorting to surgery, patients should try other, more conservative methods of weight loss. Although this is usually ineffective, it demonstrates the patient's desire and motivation to solve their problems. Practice shows that patients who tried to reduce their weight before surgery achieve better results after surgery.
Obesity is a complex and severe chronic disease, the treatment of which continues throughout life. Bariatric surgery is the only surgery that provides lasting results that last a lifetime. Not all overweight patients are candidates for surgery. The decision to resort to surgery is always made individually, after a thorough consultation with a surgeon and endocrinologist.
Types of bariatric surgeries. Their comparison Contraindications to bariatric surgery Complications during bariatric surgery Nutrition before and after bariatric surgery Proper and improper nutrition after surgery Consistent postoperative diet Nutritional features after gastric bypass surgery Additional vitamin treatment Physical activity What else does a patient need to know after bariatric surgery Postoperative follow-up
The partner of the Dominanta Medical Center in matters of surgical treatment of obesity is the North-Estonian Regional Hospital (Tallinn). We are happy to help you in this difficult struggle for a quality and fulfilling life.
Obesity treatment
This is always a lot of work, and first of all on the part of the person concerned, the person who decided to lose weight.
Obesity is a disease, the doctor who treats it is a nutritionist, usually other doctors are also involved, for example, an endocrinologist and a therapist.
Treatment of obesity depends on the causes that caused it, the degree and presence of complications. If we sought help early, with not significant degrees of this disease, everything would be solved much easier and faster, but if you are overweight or grade 1-2 obesity, this only bothers you as a cosmetic defect, and it seems that you can cope on your own. One begins to exhaust oneself with diets, which leads to breakdowns and gaining even more weight, and when the patient finally consults a doctor, the fight against obesity becomes a real problem.
In case of obesity, the advice of your friends should not become a direct guide to action for you; first, go to an appointment. You will have to undergo an examination to identify hormonal imbalances and the presence of complications, for example, diabetes.
Anti-obesity treatment methods imply an integrated approach consisting of a specially selected diet, exercise, and changes in lifestyle. Medicines are used as an aid to help cope with excessive appetite, speed up metabolism, and normalize the function of the hormonal system.
If you have stage 1 obesity, treatment may only include a light diet and a moderate increase in physical activity, and this is enough for your weight to normalize within 3-4 months.
Treatment of stage 2 obesity is already more difficult, because excess weight leads to poor exercise tolerance by the patient, and the diet turns out to be less effective. The reason is the patients’ weak will; it is difficult for them to give up their usual diet; they often require medicinal support.
Treating grade 3 obesity on your own is almost impossible. Most patients have hormonal imbalances, leading to profound metabolic disorders. I don’t eat anything, but I still get fat, how often do you hear this phrase from patients with advanced obesity! And if we take into account that physical abilities are sharply reduced, minimal physical activity tires, energy consumption in this way becomes minimal, and losing weight is extremely difficult.
In all cases, help with obesity cannot be done without dietary restrictions.
What is obesity? Treatment in Butovo
Obesity (excess body weight) is a complex chronic disorder of lipid metabolism with excessive accumulation of fat in different parts of the body, accompanied by an increase in body weight and the subsequent development of various complications, resulting, as a rule, from the excess of calorie intake into the body from food over calorie expenditure, especially with a lack of movement. Except in cases of very developed muscles, obesity is considered to be an excess of body weight by 20% or more from the standard values indicated in generally accepted height and weight tables. A more accurate assessment is made by determining your body mass index (BMI) by dividing your weight (in kilograms) by the square of your height (in meters).
So, for example, if your weight is 80 kg and your height is 160 cm (1.6 m), then your BMI = 80: (1.6 x 1.6) = 31.25.
Obesity is considered to be a BMI exceeding 29.9 kg/m2 (normal is from 18.5 to 25, overweight is up to 29.9), which is divided into three degrees. An important indicator of the risk for abdominal obesity is waist circumference - with a normosthenic body type, it should be no more than 102 cm in men, and no more than 88 cm in women.
In some countries, including Russia, the proportion of people suffering from this pathology is very large. According to statistics, in the United States, 34% of men and 37% of women are obese, and our figures are approximately the same. The prevalence of this disease varies depending on age, socioeconomic status and race, but has a steady upward trend of 5-9% annually!
Diet for obesity
Diet for obesity is most important because it is much easier to lose weight through caloric restriction than through exercise. Just imagine, 100 ml of vegetable oil contains 800 calories, and an hour! jogging burns only 300 calories.
Nutrition for obesity primarily excludes foods rich in calories, but poor in substances beneficial to the body, such as sweets, white bread and other sources of quickly burning carbohydrates. That is, whether you want it or not, whether you like it or not, you will have to switch to vegetables and protein foods, and the menu for obesity is always meager, a slight feeling of hunger is constantly simply unavoidable.
Products for obesity must completely cover your daily protein needs, otherwise, instead of fat, muscles, minerals and vitamins will begin to be lost, otherwise there will be vitamin deficiency states and mineral metabolism disorders. You can achieve what you need using not only a limited set of products, but also methods of preparing dishes; recipes for obesity involve limiting fats, using cooking, stewing and baking, and steaming.
The higher the degree of obesity, the more limited the diet, since there is less opportunity to use exercise to burn fat due to a decrease in physical activity and exercise tolerance of patients. For example, a diet for grade 1 obesity may be lower than the daily calorie requirement by only 10-15% in order to begin to lose weight intensively, but a diet for grade 3 obesity will require a reduction in calories by 30% or more for the same result. The fatter you are, the more hungry you will have to be.
The diet for obese children should be prepared especially carefully, because it is dangerous to deprive them of many nutrients. A lack of calcium will lead to disruption of the formation of the musculoskeletal system, a deficiency of fatty acids will affect the development of the brain...
Treatment of obesity in a sanatorium becomes an excellent choice.
Under conditions of strict control over the fulfillment of prescriptions and a clearly drawn up menu, it is possible to boost your metabolism and begin to lose kilos. If you decide to go to a sanatorium, the treatment will provide you with the most important things: you will believe that you can cope and understand how to do it, and after completing the course of treatment, all that remains is to follow the diet and exercise regimen that you will be taught. Anti-obesity pills
Of course, anti-obesity pills, which are now so widely advertised as unrivaled means of weight loss, are in fact far from a panacea...
Anti-obesity drugs work in a variety of ways, from suppressing appetite to impairing the absorption of nutrients in the gastrointestinal tract. Now there are quite a lot of them, and some of them, in fact, are not a means to lose weight in the literal sense, but were created to treat hormonal disorders or to correct metabolism. Something used as a cure for obesity is actually intended for bodybuilders (building muscle mass), something in theory should have compensated for hypothyroidism or deficiency of sex hormones. Be that as it may, you must understand that medications for obesity act deeply, affecting the very foundations of metabolic regulation, and if used incorrectly, they can cause an endocrine disaster, simply destroying your metabolism forever. They are dangerous.
Exercise for Obesity
Regular gymnastics (fitness is not indicated until weight loss), swimming under control of pulse and blood pressure - “without fanaticism”, but the most necessary thing at the first stage of the fight against excess weight is walking, once again avoid traveling in public transport or a car.
Whatever treatment method you would like to use, we recommend that you decide how to deal with obesity with your doctor. Many techniques have contraindications that are simply not taken into account when trying to self-medicate.