Causes of the inflammatory process
Everyone has encountered the problem of gum inflammation: for some the process was more pronounced, for others less. However, the reaction to the inflammatory process is different - some people try not to make the disease worse and go to the dentist, while others let things take their course, hoping that “it will go away on its own.” Such an irresponsible attitude towards one’s health can ultimately lead to complications that will be difficult to cope with even with the help of a doctor.
To prevent inflammatory gum diseases, you need to know what can cause inflammation and what symptoms can be seen that it already exists.
What could be the reasons
1. Microbes
The human oral cavity contains a huge number of microorganisms that under normal conditions do not pose any danger. The body's general immune system and local immunity cope with the regulation of their numbers, growth and health effects until conditions favorable for microbes occur, when they become a serious threat.
2. Insufficient or poor oral care
In the absence of regular brushing of teeth, or the wrong choice of toothbrush, toothpaste, elixir or mouthwash, plaque accumulates on the surface of the teeth, which serves as an excellent breeding ground for pathogenic microorganisms.
3. Presence of tartar
Soft plaque under the influence of bacterial waste products turns into hard tartar. The appearance of these solid formations contributes to the development of the inflammatory process; The gums become injured and “sag,” and pathogens penetrate into the deeper layers of the soft tissue of the gums.
4. Other reasons
In addition to the above reasons, inflammatory gum diseases can occur:
- due to improper prosthetics and dental fillings
- smoking and vitamin deficiencies
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and endocrine system
Also, gum inflammation can be caused by a hereditary predisposition or weakening of the body's protective functions.
How do the symptoms manifest?
Inflammation does not occur immediately and is strong - it occurs in stages:
- swelling and redness of the gums, excessively soft tissue (this can be felt when palpating with a finger or touching a toothbrush)
- blood vessels are weakened, which is evident from the appearance of blood on the brush or dental floss (at first these are only traces, but later blood can appear at the slightest touch even with the tongue to the gum)
- tooth sensitivity increases, as the gums sag, the neck of the tooth is exposed, and since it is not as protected as the crown by enamel, any impact is noticeable
- the development of the inflammatory process can lead to the fact that the slightest irritation becomes a source of pain: it becomes difficult to chew food, and the contact of cold or hot, sour or sweet food on the inflamed area sometimes causes unbearable pain
- the surface and outline of the gums look uneven, the tissues become loose
- Bad breath becomes a constant unpleasant companion, which cannot be eliminated either by dental elixirs or by brushing your teeth.
General factors
The occurrence of inflammatory gum diseases is caused by a number of factors that weaken the functioning of the human immune system and make the gums susceptible to pathogens attacking them (gum inflammation begins - gingivitis). These factors are often:
- periods of hormonal changes (puberty, pregnancy, menstruation or menopause)
- stressful situations
- disorders of the body's protective functions
- active smoking
Inflammation of the gums can be caused by a disturbance in the composition of saliva, the balance of the bacterial flora in diabetes. Inflammatory gum disease can be caused by a lack of vitamins.
If these risk factors are present in your life, you should carefully monitor the formation of tartar and remove these unwanted deposits as quickly as possible.
Local factors
In addition to general factors, the occurrence of gingivitis is caused by poor oral care, dental plaque, poorly placed fillings and crowns, poor prosthetics, old fillings, malocclusion and the presence of orthodontic structures in the mouth that make normal teeth cleaning difficult. Increasingly growing deposits on teeth contribute to a greater accumulation of pathogenic microorganisms. Periodontal pockets may appear, which means inflammation moves to the gums.
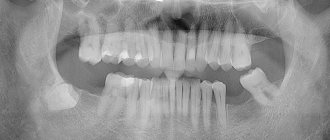
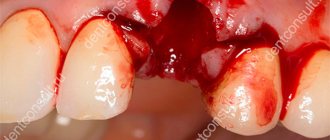
Symptoms of gingivitis, photos
There are general signs of developing gingivitis (see photo); of course, it is difficult to independently establish a diagnosis without special education and sufficient diagnostic experience. But every adult can determine that the inflammatory process is developing not in the tooth, but in the gum (the pathology can also manifest itself in children under three years of age).
The main symptoms of a developing inflammatory process will be:
- redness of the gums at the site of the outbreak of the disease, which indicates the beginning of the inflammatory process;
- swelling of the gums;
- bleeding;
- pain that intensifies as inflammation develops;
- the appearance of dental plaque, as a consequence of this process - an unpleasant odor from the oral cavity;
- an increase in the volume of periodontal papillae (this symptom can only be determined by a qualified specialist, as well as the formation of false pathological pockets);
- purple-blue tint.
It is important to remember that these are general symptoms that can appear all or in groups, depending on what type of gingivitis is present in the mouth and diagnosed by a specialist. In some people, symptoms may manifest themselves in completely different ways, which is why you should not even try to diagnose yourself and prescribe treatment.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums caused by local and general unfavorable factors, without a violation of the integrity of the tooth-gingival junction.
Although gingivitis is much easier to cure than periodontal disease or periodontitis, you should not relax: untimely contact with the dentist and delays in treatment can lead to very significant consequences. Firstly, you will need to spend more on treatment; secondly, it is unknown what side effects may appear on general well-being due to “simple” gum inflammation.
The main cause of gingivitis is still non-compliance with basic hygiene rules or a complete lack of oral hygiene. The disease can be caused by injuries of various types, improper installation of prostheses, and weakened immunity. Gingivitis is characterized by shallow inflammation of the gums around a tooth or several teeth. In dentistry, there are several forms of this disease.
Catarrhal gingivitis
There is redness of the gums around a tooth or several. Often the gums bleed, there may be slight itching, pain when eating or performing hygiene procedures. This is the most common form.
Ulcerative gingivitis
A severe form of the disease, when large areas of the gums are affected and a characteristic grayish coating is visible. At an advanced stage, the formation of purulent foci, necrosis of soft tissues, and bad breath may appear.
Hypertrophic gingivitis
In the clinic of this form, compaction and proliferation of the soft tissues of the gums are noted, sometimes leading to keratinization of its individual parts.
If the first symptoms of any form of disease appear, you should immediately see a doctor, because self-medication will not help in this case. Relieving the inflammatory process is not an end in itself; it is necessary to get rid of the cause that provoked the inflammatory process. Only a dentist can determine the cause of gingivitis and prescribe appropriate therapy. You may need to consult a specialized specialist, to whom a doctor will give a referral.
Classification
External manifestations of gingivitis are manifested by its appearance. According to the form and differences in the clinical picture, the disease is divided into four groups:
| ulcerative-necrotic | characterized by a severe course, the standard manifestations of gum inflammation are accompanied by deterioration of the condition, hyperthermia, and ulcers form on the mucous membrane. |
| catarrhal | the simplest form and manifests itself in inflammation of the interdental papillae and marginal gums. At the same time, it becomes smoothed, relief is lost, bleeding occurs during probing and a large amount of both soft and mineralized plaque is determined. |
| atrophic | a pathological process opposite to the previous one is observed - a loss of soft tissue occurs, which leads to the formation of recessions. The disease is common among children. |
| hypertrophic | There is an overgrowth of soft tissues, due to which the crowns of the teeth are partially or completely hidden by the gum, which hurts and is very itchy, and also bleeds. |
Inflammation of the gums is not only an independent disease - some of its forms are concomitant and indicate the presence of disturbances in the functioning of the body.
Inflammatory processes in the oral area
Today, there are a number of factors that can lead to inflammation of various types in the oral cavity.
Inflammation of the gums causes discomfort in the patient and does not contribute to improving communication with others: it is not very pleasant to talk with a person who has constant bad breath (and this accompanies any inflammation). However, one should not think that everything is limited only to the oral cavity: if infected saliva gets into the stomach, it can provoke quite serious systemic diseases.
Inflammatory process during pregnancy
Pregnancy for almost all women is problematic in terms of the condition of the oral cavity: tooth enamel weakens and begins to deteriorate; gums often become inflamed.
The causes of inflammation and pain in the gums can be different:
- weakening of the protective functions of the whole body and local immunity, as a consequence
- the diet changes, metabolic processes proceed in an unusual mode for the body, which leads to an acceleration of the formation of dental plaque
- neglect of the rules of oral hygiene during pregnancy
Ultimately, an impressive layer of plaque accumulates on the teeth during the day, which serves as an excellent breeding ground for pathogenic bacteria that cause inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity.
As such, plaque on teeth does not pose any danger if it is removed on time and well enough. Morning and evening brushing of the oral cavity is enough to avoid the appearance of plaque. During pregnancy, special attention should be paid to the condition of the teeth and gums, without expecting that everything will go away on its own.
If left untreated, gingivitis can develop into periodontitis, which is much more serious and can lead to the loss of completely healthy teeth.
It is necessary to monitor the condition of the gums literally from the first days of pregnancy, since already in the first weeks the first signs of inflammation may appear. If there is pain in the gums, inflammation and bleeding, you should immediately go to see a doctor. You should not put off visiting the dentist and dental treatment until the postpartum period: you simply won’t have time, and most importantly, you will waste time, which will cause more serious consequences.
Prosthetics and installation of crowns
Orthopedic dental operations are not easy procedures in themselves, and additional complications arise against the background of gum inflammation. If prosthetics are necessary, then it is necessary to first treat the oral cavity, remove inflammatory processes, and then install orthopedic structures. In the initial stage, it is easier to get rid of any disease, so earlier treatment of inflammation will be more effective. If you need to install dentures for periodontitis, you need to know:
- the process will be longer due to the need for preliminary treatment
- “loose” teeth cannot be completely reattached to the gums, and if the teeth are too mobile, they will have to be removed; Even apparently healthy teeth, without traces of caries, are removed, since the dentures must have a strong, reliable support
- if you do implantation, then periodontitis will not be a contraindication
With periodontitis, the choice of dentures is small. Even in the remission stage of this chronic disease, one-piece metal-ceramic crowns, made of metal and ceramics, cannot be installed. For reliable installation of permanent dentures, it is necessary that the neighboring teeth are motionless, otherwise the denture will begin to loosen and the supporting teeth may become deformed.
Only an orthopedic dentist can determine which type of design is right for you. Based on examinations and examinations, he decides what kind of surgery is required: installation of a bridge, removable dentures, zirconium crowns or implantation. A good specialist will definitely have an option for you, no matter how difficult the dental situation may be!
Negative effects of wisdom teeth
Wisdom teeth begin to erupt after 18–19 years of age. This third pair of chewing teeth is not easy for a person: the gums become inflamed, swollen, and are literally “torn”. But if the pain or gum swelling is too severe, you should consult a dentist. Medical intervention or the use of special medications and hygiene products may be necessary.
Inflammation of the gums around wisdom teeth can occur for many reasons:
- it is difficult to clean with a toothbrush from food debris and plaque, which leads to the active proliferation of microbes
- the soft tissues of the gums are injured: eruption itself is difficult, plus improper growth of the wisdom tooth is possible
- inflammation around the figure eights can be caused by stomatitis, gingivitis, periodontal disease
In any case, inflammation of the gums around wisdom teeth requires treatment to prevent it from spreading further. Eights are often removed soon after they appear.
Bleeding gums when brushing teeth
Sometimes blood spots on the brush are perceived as a sign of inflammation, but this is not always the case. Often, the reason is trivial - incorrectly selected bristles or too zealous hygiene. To reduce the risk of injury, dentists remind you of the rules for brushing your teeth:
- Movements of the bristles along the vestibular side should not be from side to side, but up and down, as if sweeping away remnants of food and plaque.
- Medium hardness is optimal, but if you have pathological sensitivity, it is better to buy soft ones (Soft) and even ultra-soft ones (Ultra Soft).
- If the brush is positioned slightly at an angle to the teeth, the chance of better cleaning of gaps increases.
- It is advisable to move along the gum line in a circular motion - additional massage stimulates blood circulation.
- You should spend 40 seconds to a minute cleaning your tongue. Much more bacteria accumulates on its surface than on enamel, but many people ignore this fact.
- If you have an irrigator at home, it is recommended to put periodontal attachments on it at least once a week and clean out the gum pockets. Make sure that the water supply is turned on at minimum power at this moment, otherwise there is a risk of tissue rupture.
- For those who wear braces and other devices, it is better not to skimp on special brushes. A large amount of plaque accumulates under the ligatures and the corrective arch, which must be removed daily.
- It is necessary to change the brush every 2 months, and if you are prone to inflammation - monthly.
An integrated approach to treatment
To stop the further development of the disease and eliminate discomfort, you must do the following:
- diagnose the disease to prescribe appropriate therapy
- remove deposits and stones from teeth
- treatment of inflammation
- sanitize the oral cavity
If necessary, loose teeth are splinted, dentures are placed, and teeth that cannot be treated are removed. After completing the treatment course, maintenance therapeutic procedures are prescribed. Only an integrated approach guarantees complete cure of inflammation, and following the recommendations will avoid relapses.
Consultation and initial examination of a specialist
At the first visit to the dentist, the patient undergoes an initial examination and receives advice on possible treatment methods for the identified disease. After a thorough examination of each tooth, the doctor records data on the condition of the teeth and gums in the patient’s medical record. The visitor is given information about which and how teeth need to be treated, and the approximate cost of the necessary procedures can be calculated.
Anti-inflammatory therapy
The problem of gum inflammation is a common phenomenon, however, self-medication cannot get rid of it. In order not to start the disease and not lose teeth, you should promptly seek the help of a dentist.
The combined use of conservative local therapy and physiotherapy gives good results. Medications used in the treatment of periodontitis are divided into several categories:
- antibacterial agents (antifungals, antiseptics, antibiotics)
- enzymatic, steroidal and non-steroidal drugs
- hormonal, immunostimulating agents, vitamins
If the inflammation worsens, an operation may be prescribed to open the gums so that the accumulated pus can be released. For periodontitis, planned operations are performed:
- patchwork
- gingivectomy
- curettage
Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed after getting rid of severe inflammation.
Treatment of inflammation caused by injury
There are two types of gum injuries - chronic and acute. The former are a consequence of the action of a constant irritating factor - an incorrectly installed prosthesis, unsuccessfully made bridges, crowns, etc. In this case, you cannot do without contacting an orthopedic doctor. Acute injuries can occur when using cutlery, dental floss or a hard brush, as well as in fights and falls.
Anti-inflammatory treatment is carried out by a periodontist. First, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of the inflammatory process:
- replacement of old or low-quality fillings is carried out
- uncomfortable dentures are removed
- It is recommended to buy a soft toothbrush
Next, the treatment course is carried out in stages:
- acute pain is relieved
- anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed
Features of choosing toothpaste and brush
A toothbrush is a personal hygiene item; it should be individual for everyone. The brush should not be used for more than two to three months.
If there are no problems with your gums, a medium hardness toothbrush will do. If there are any gum diseases, then the brush should be soft to avoid injury to the gums.
If you are used to using an electric brush, then you need to know that you should not brush your teeth for more than 3 minutes, and the brush movements are the same as when brushing with a regular brush. To reduce the load on the teeth, the electric brush should be applied to the surface of the teeth with less force compared to a regular one.
The choice of paste and the rules for using it are of great importance. Don’t think that the more toothpaste you squeeze out of the tube, the better you can clean your teeth. The volume of the paste does not affect the quality of the procedure - just squeeze out a little paste, the size of a pea.
The selection of toothpaste is also individual and depends on the condition of the gums and teeth. If your gums are bleeding, then the toothpaste should contain antibacterial and anti-inflammatory components. Most often these are medicinal plants: chamomile, eucalyptus, oak bark, sage, coniferous extracts, echinacea and others. Paste with propolis works well.
As a prophylactic paste, you should use those containing zinc citrate and aluminum lactate. They have an astringent effect and prevent periodontal disease and periodontitis. To restore mucous membranes, you need to buy pastes containing allantoin and bisabolol.
To choose the most suitable paste for your case, it is better to seek the help of a dentist. After examining and assessing the condition of the oral cavity, the doctor will be able to recommend exactly the paste that you need to prevent disease or as part of a treatment course for existing inflammation.
Treatment of ulcerative gingivitis
The treatment regimen is as follows:
- Treatment of ulcers: first, anesthesia is performed, then with the help of enzymes and instruments, the gums are cleared of ulcers;
- Fighting dental plaque. This stage includes mandatory antiseptic treatment of the entire oral cavity and superficial anesthesia using a gel;
- Taking antibiotics (metronidazole orally);
- Local antibacterial therapy with metronidazole;
- After healing begins, local wound-healing preparations are used (oil solutions of vitamins A, E, sea buckthorn);
- Anti-inflammatory therapy;
- Antiallergic drugs;
- After recovery – treatment of diseased teeth;
- General restorative therapy: vitamins, possible prescription of immunomodulators.
In case of ulcerative gingivitis, they are required to issue a certificate of incapacity for work (sick leave) for several days.
Preventive actions
It is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it. To prevent gum inflammation, a whole range of hygienic and general health measures is necessary. It is necessary to prevent the appearance of tartar; maintain favorable microflora of the oral cavity; prevent the proliferation of microbes that cause inflammation and properly carry out hygienic procedures for caring for the oral cavity.
Comprehensive prevention includes the following measures:
- maintaining oral hygiene, using properly selected care products and a toothbrush for regular care
- mandatory doctor visits twice a year; When the first signs of inflammation appear, go to an appointment with a dentist outside of your plan
- treatment of general somatic diseases
- maintaining a proper diet with the introduction of a large number of foods containing a lot of fiber and vitamins into the menu (it is advisable to consume fruits and vegetables without heat treatment)
- introduce celery, apples, carrots into your daily diet
- the use of mouth rinses with antiseptic properties that do not destabilize the balance of microflora in the mouth
Nutrition rules
The diet of a person suffering from gingivitis should include as many fresh fruits and vegetables as possible.
- Apples and pears contain pectin and microelements that accelerate the regeneration process.
- A large amount of vitamin C, which helps strengthen blood vessels and reduce bleeding, is found in citrus fruits.
- Vegetables are rich in fiber and antioxidants. By including cabbage, carrots and zucchini in the menu, you can speed up metabolic processes in the body and reduce the time of gum regeneration (healing).
- Berries (blackberries, currants, raspberries) enrich the body with vitamins and minerals, increasing its overall immunity.
You should not eat food containing fast carbohydrates (flour products, potatoes, sweets) in large quantities, as they contribute to the formation of soft plaque.
Antiseptic rinses against inflammation
They are good at removing microbes and the toxins they produce, partially destroying pathogens, protecting the enamel and reducing the enzymatic activity of various types of rinses.
Rinses used for inflammatory processes can be divided into:
- antimicrobial action;
- anti-inflammatory action;
- mixed (or combined) action.
Antimicrobial solutions include antiseptics or antibiotics. They don’t just temporarily remove inflammation, they act on the root cause of inflammation – pathogenic microflora.
Important note: when using rinses with anti-inflammatory agents, it is recommended to simultaneously use gum gels containing antibiotics or antiseptics.
How not to do it
Patients often self-medicate and try to get rid of gum disease with hydrogen peroxide. Despite the fact that this is a good antiseptic, it is not suitable for use in the treatment of inflammatory gum diseases and does not give any effect other than foam in the mouth. It is not possible to rinse periodontal pockets on your own using a syringe; certain knowledge and skills are required.
How to quickly relieve gum inflammation
Different approaches are used to combat this disease. It is important to eliminate the original problem, then relieve the symptoms and take care of prevention so that the inflammation does not return again.
Let's consider proven areas of treatment.
Gels, solutions and ointments
The principle of use is application to the gum surface. A gentle and gentle rubbing is required.
Among the most effective drugs:
- Holisal . Apply to inflamed areas twice a day. The course of treatment is from 7 to 10 days. The product has a mild soothing effect and quickly relieves swelling from the affected area.
- Periodonticide . The principle and duration of administration are the same as for Cholisal. The composition is effective due to the large number of essential oils in the composition.
- Metrogil denta . Fights germs. Used with the same frequency as the two drugs above.
- Heparin ointment . Twice a day, gently rub into the gums. Relieves swelling, kills germs, soothes tissue and reduces pain.
- Traumeel S. Used as an application for four weeks. A natural drug with a pronounced effect.
The patient always has a question - what to choose, ointment or gel. Ointments are less absorbed, but give a better effect.
The gel is easier to use, but it will take longer to apply. The level of effectiveness differs depending on the characteristics of the human body and the course of the disease.
Traditional medicine
Despite the fact that many are skeptical about traditional medicine, the components used have a pronounced calming, antiseptic and anesthetic effect.
The same calendula extracts are actively used in ointments and gels, so why not use the plant directly.
The main thing is not to self-medicate until the doctor has approved the remedies you have chosen and has determined the cause of the problem.
3 proven products:
- Chamomile solution. Used for rinsing. You need to buy dried flowers of the plant, pour a glass of water over them and boil for at least 10 minutes. After straining, rinse your mouth up to three times a day.
- St. John's wort solution. You will need two tablespoons of dry plant. They are poured with two glasses of already heated water and boiled for 10 minutes. The frequency of rinsing is the same as for chamomile.
- Aloe. Apply a paste of plant leaves wrapped in a sterile bandage to the site of inflammation twice a day.
The classic solution of soda and salt also works well.
Special toothpastes
Your doctor may advise you to use specially selected toothpastes that contain a high percentage of beneficial plant components, as well as chlorhexidine, bisabol, and allantoin.
Among the most common recommendations are pastes such as Lacalut active, Parodontax, President Exclusive.
They have a pronounced antiseptic effect, help get rid of germs, soothe gums and significantly reduce inflammation.
It is important to remember that such products are used for a limited time - usually up to two weeks. After this, you should stop taking it.
Rinse
There are also several special solutions that doctors recommend rinsing your gums on a set schedule.
These include:
- Chlorhexidine. Copes with bacteria. The frequency of rinsing is up to 4-6 times a day.
- Furacilin. You will have to prepare the solution yourself. To do this, it will be enough to simply dissolve one tablet in 200 ml of water. The frequency of rinsing per day is 2-3 times.
- Rotokan. An important feature of this product is that it contains many natural ingredients that perfectly relieve inflammation. You will need to rinse your mouth up to three times a day. In this case, it is enough to simply dilute a tablespoon of Rotokan concentrate in a glass.
You can also use Stomatofit. Add two tablespoons to 50 ml of water.
As with all other remedies, you should not self-medicate - all rinses are performed only in consultation with your doctor.
Other treatments
Depending on the patient’s condition, dentists may recommend other remedies to relieve gum inflammation.
These include the following methods:
- Massage. It is carried out at home to reduce inflammation and restore normal blood circulation in the gum area. Massage can be carried out either with your fingers or using special brushes recommended by the dentist.
- Taking vitamins. The three most popular types of vitamins are A, PP and D. The patient may also need to consume complexes with a high content of calcium and phosphorus.
- Drug treatment. It is used only on the recommendation of a doctor - he prescribes the necessary medications. These include such as Flemoclav, Metronidazole, Ciprofloxocin and others.
In the most complex and advanced cases, surgical treatment is used. There are several options for work - open curettage method, patch surgery, excision of the hood.
In order not to end up with surgery, you need to be attentive to your body and promptly contact your dentist at the first sign of problems with your gums.
Gels and ointments against the inflammatory process
To treat periodontitis, applications with various therapeutic agents are used. Each has its own recommendations for use, however, during all procedures one should strictly adhere to one rule: hands must be clean (processing can be carried out with cotton swabs)
After eating, you should brush your teeth and squeeze out a small amount of gel from the tube. Apply the product to the affected part of the gum, then do not eat or drink for half an hour. You should not take a lot of gel or ointment: the effect will not increase, and a reaction to the swallowed drug may follow.
However, no ointments or gels used at home can replace dental treatment. They can become a good auxiliary component of a complex of treatment measures prescribed by a doctor. They can relieve discomfort, prevent gingivitis or periodontitis, but cannot replace treatment.
Treatment of gums and oral cavity with periodontitis
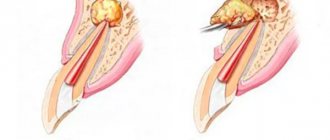
When gums hurt, treatment of periodontitis is almost always complex and depends on the severity of the disease and its specific manifestations. The difficulty is that periodontitis can be treated well only in the early stages: when the disease is in severe form, it is very difficult to cure it. Below are the current techniques that are used to effectively treat gums today.
| Stage of gum disease | Treatment |
| Easy stage | Cleansing teeth from plaque and tartar, as well as antiseptic treatment. Additionally, antibiotics, vitamin complexes and special hygiene products may be prescribed. |
| Stage of gum disease | Treatment |
| Middle stage | At more serious stages, it is almost always necessary to take antibiotics (lincomycin, clindamycin and others), and periodontal pockets are also treated (deephalization). A carbon laser is best suited for this purpose, as it effectively clears the affected tissue from the area and promotes faster healing. |
| Stage of gum disease | Treatment |
| Severe stage | The stage of the disease that is most difficult to treat. The most effective method of treating severe periodontitis is curettage. This is a surgical procedure where the doctor makes an incision along the gum line and cleans out the pockets of granulation tissue and dental plaque. Often, when teeth are loose, splinting is required, and in case of extensive damage to bone tissue, bone grafting is required. However, even such measures do not always provide a positive result. |
Patients often note that their gums hurt after treatment. This is normal, especially after surgery, but if the pain is much worse than usual and does not go away for a long time, we recommend notifying your doctor.
Toothpastes against gum disease
If your gums are bleeding, you should choose the right toothpaste. Aluminum lactate has a good hemostatic effect; chlorhexidine and mineral salts are slightly inferior to it.
As for the other components included in the toothpaste for gums - bisabolol, allantoin, medicinal plant extracts - they do not directly affect bleeding gums. They have an anti-inflammatory effect, as a result of which bleeding is reduced and may disappear. Thus, we can only talk about their indirect effect on bleeding gums, which is why a positive result is observed later than when using a paste with aluminum lactate or chlorhexidine.
At the same time, you need to know that even the best paste only temporarily removes bleeding, but in no case is a remedy. To get rid of the disease, you need to see a dentist.
Traditional methods of treating gum inflammation
Alternative medicine offers many ways to treat inflammation in the oral cavity. Gingivitis, periodontitis and periodontal disease are treated with ointments, tinctures, rinses and special “masks”. In addition to medicinal plants, honey, salt, soda, and peroxide are used to prepare medicinal compositions.
But we must understand that traditional medicine cannot seriously become a full-fledged treatment. When you notice the first signs of inflammatory diseases, you should go to see a dentist, and use folk remedies only on his recommendation.
Gum disease - periodontal disease
Although periodontal disease is a gum disease, it has nothing in common with either gingivitis or periodontitis. Periodontal disease is especially often confused with periodontitis: this is due to the fact that periodontal disease also exposes the necks of the teeth. However, with periodontal disease there is no dental plaque, purulent inflammation and periodontal pockets. Moreover, these diseases have completely different pathogenesis. The exact causes of periodontal disease have not yet been determined, but most experts believe that the disease is formed as a result of metabolic disorders, chronic diseases of internal organs, lack of normal blood supply to soft tissues and poor heredity. One thing is good: periodontal disease is considered a fairly rare disease that occurs in no more than 10% of people. Since the disease is not inflammatory in nature, the treatment of periodontal disease has its own characteristics.
Prices for treatment of gum inflammation in our clinic
We can talk about the cost of treatment for any inflammatory gum disease only after clarifying the diagnosis, determining the cause and level of neglect of the disease. With a timely visit to the dentist, professional teeth cleaning is often sufficient. In severe cases, surgery may be prescribed. If the examination reveals the presence of concomitant diseases of the oral cavity that complicate the therapeutic treatment of gingivitis, periodontal disease, periodontitis, consultation with a specialized dental specialist - an orthopedist, surgeon or therapist - will be required. This also affects the final cost of treatment.
You should not delay the treatment of periodontitis and gingivitis, because they can quickly develop into a more severe form. If your gums become swollen, red, or begin to bleed; there is pain and itching when eating; If stones and heavy plaque appear on your teeth, you should immediately visit a dentist.
A competent doctor is always aware of the most modern treatment methods and, after examination, will give recommendations and, if necessary, prescribe an appropriate course of treatment.
Treatment of hypertrophic gingivitis
In this case, the treatment plan corresponds to the treatment plan for catarrhal gingivitis, but after the stage of sanitation of pathological teeth, surgical removal of excessive gum growth occurs.
Moreover, before the operation, fibrous hypertrophic gingivitis is treated as chronic catarrhal, edematous – as acute catarrhal. In the presence of leukemia, only symptomatic treatment is performed; gum overgrowth is not removed.