Stenting of cardiac vessels is an expensive operation that helps normalize blood circulation, restore arterial patency and prevent the development of serious complications. The intervention involves the introduction of a special balloon with a metal shell into the affected vessel, which expands the lumen of the vascular bed, eliminates atherosclerotic plaques and promotes the proper functioning of the cardiovascular system. However, one operation is not enough for the treatment result to be stable and long-lasting. It is important to strictly follow all doctor’s recommendations, including nutrition. Otherwise, stenting will not give the desired result, and atherosclerosis will progress. This can lead to a number of undesirable consequences - coronary heart disease, acute cerebrovascular accident, myocardial infarction.
What is a heart attack
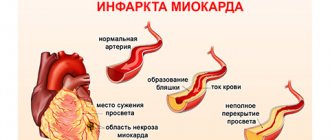
A heart attack is damage or destruction of the heart muscle resulting from insufficient blood supply. The main risk factors are high blood pressure, high cholesterol and smoking.
Modern medicine makes it possible to save patients after a heart attack, returning them to their previous state. However, damage to the heart muscle significantly affects the heart rhythm and its functions. Therefore, it is extremely important to control all risk factors to prevent another heart attack. And diet plays a major role in this.
Drug treatments for myocardial infarction
The purpose of using medications in the hospital is to restore and maintain circulatory functions, as well as relieve unbearable pain.
- Painful sensations can be eliminated with the help of analgesics, and the feeling of fear can be eliminated with tranquilizers.
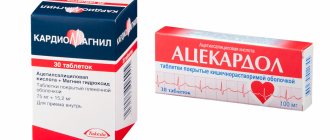
- To prevent the formation of a blood clot, acetylsalicylic acid and anticoagulants are used.
- If a blood clot has already formed, powerful thrombolytics are used to dissolve it.
In the treatment of acute myocardial infarction, a special place is given to thrombolytic therapy to eliminate the risk of new blood clots. Arrhythmia is a common occurrence in this disease, so the patient is offered antiarrhythmic drugs, adrenergic blockers, nitrates, and vitamin E.
Rehabilitation after acute myocardial infarction involves taking medications to maintain normal blood pressure and prevent blood clots.
Why is it important to diet
Nutrition after stenting and heart attack is an integral part of rehabilitation and prevention of further heart problems. The main task that needs to be solved is weight normalization. Obesity has a negative impact on the entire body, primarily on the cardiovascular system. Therefore, losing weight reduces the load on the heart.
Also, proper nutrition will prevent the emergence of new problems with the cardiovascular system and the progression of existing ones.
University
→ Home → University → University in the media → Unloading therapy after myocardial infarction
Patients who have suffered an acute myocardial infarction and have post-infarction cardiosclerosis should be taught the skills of unloading therapy, which reduces the load on the heart. Such therapy consists of drug and non-drug therapy.
Long-term controlled multicenter studies have proven the effectiveness and safety of the following groups of drugs for unloading therapy: 1) antiplatelet agents (aspirin) - reduce blood clotting; 2) β-blockers - normalize heart function and rhythm, reduce blood pressure; 3) angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) - protect the heart and blood vessels from the development of heart failure; 4) cholesterol-lowering drugs (statins) - normalize cholesterol levels in the blood.
A properly selected set of non-drug treatment for cardiosclerosis will help to sharply reduce the number of medications taken, slow down the evolution of atherosclerosis and the development of circulatory failure.
Non-drug treatment is an impact on manageable risk factors: total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, hypertension, glucose levels, etc.
Cholesterol in patients with coronary artery disease should not exceed 3.4 mmol/l, and in healthy people with risk factors (alcohol, smoking) - no more than 4 mmol/l. Smoking is unacceptable, it contributes to the rupture of the plaque, the formation of a blood clot on it with disruption of the lumen of the vessel and the development of ischemia.
The fight against cholesterol begins with a diet (up to 3 months) without lipotropic drugs. It is necessary: • consume a minimum of animal fats - white meat (poultry), lean beef. Limit dairy products; • introduce into the diet foods containing Omega-3 fatty acids (fatty fish, vegetable oils, nuts, seeds, etc.); • eat more vegetables (raw, stewed, boiled, baked); • reduce salt intake (3-4 g per day) to slow down fluid retention in the body and remove it; • exclude alcohol, smoked foods, fried and fatty foods; • include garlic, whole grains, cabbage, tomatoes, spinach, and apples in your diet.
Down with excess weight
The following rules must be observed: • sharply limit fats with saturated fatty acids; • increase the consumption of seafood, fish (2-4 times a week), seaweed; • reduce the amount of carbohydrates (due to sugar, honey, sweet fruits and berries). The source of carbohydrates can be cereals, wholemeal bread, and vegetables. It is necessary to reduce the consumption of saturated fats and cholesterol: • before cooking, remove fat from meat, remove skin from poultry; • cool the broth and soup to remove hardened fats from the surface; • vegetables absorb fat, so they should not be cooked together with meat; • replace whole milk with skim milk; • it is not advisable to add butter to rice dishes, pasta, or mashed potatoes; • reduce portions that contain a lot of fat and cholesterol, and increase portions of cereals and vegetables.
An appropriate daily caloric intake helps maintain normal body weight.
A special diet for correcting body mass index (BMI) is prescribed for BMI > 30, impaired glucose tolerance, diabetes or persistent hypertension. The diet of modern humans in developed countries has three components of atherogenicity - excess: 1) cholesterol, 2) saturated fats, 3) calories. The daily caloric intake is distributed as follows: 40% - breakfast, the last meal - no later than 19:00, less than 7% of calories should come from saturated fats.
After 60 years, you need to follow a diet close to vegetarian.
However, diet alone will not completely relieve the cardiovascular system.
Move to the max
An adequate motor regimen is needed that allows you to spend up to 2,000 kcal/day: walking at a fast pace (100–120 steps/min.) up to 8 km per day; do aerobics, physical exercise, swimming. The effectiveness of non-drug treatment is assessed by the clinic and lipid metabolism indicators after 3 months (lipid reduction should be 20% of the initial level). If the result is good, then therapy is continued; if not, lipid-modifying drugs are prescribed. You can increase physical activity, but you cannot work too hard. Work in the country is considered very difficult (you need to take breaks every 20–30 minutes). You can more accurately determine the patient’s load using a 6-minute test (walking at any pace for a specified time): • walked 100–150 m - low physical capabilities; • walked 300 m - average; • walked more than 500 m - good. In the first case, it is recommended to walk around the room and take 2-3 deep breaths every 5 minutes, devoting 1-2 hours a day to such exercises. In the second case - light loads, activity up to 8 hours a day, walking up to 30 minutes, 1 km in 15 minutes, up to 10 km per week. In the third case - daily activity 10-12 hours, combined loads, walking - 45 minutes, 1 km - in 12 minutes, up to 20 km per week. The degree of unloading of the cardiovascular system depends significantly on the state of the nervous system. In a normal state, a person adapts to the environment, successfully performs physical activity, professional and social functions - all this improves the quality of life. Particular attention should be paid to the development of depression in patients, which is often found in patients with cardiovascular pathology. Calming herbs can be recommended.
Raisa Novikova , Associate Professor of the 1st Department of Internal Medicine, BSMU; Natalya Polevkova , head of cardiology (infarction) department No. 2, 10th City Clinical Hospital of Minsk Medical Bulletin , July 17, 2014
Share
Nutrition rules after a heart attack and stenting of cardiac vessels
Diet after cardiac stenting involves limiting daily caloric intake. For men, this figure is a maximum of 2300-2500 calories, for women - 1800-2000 (depending on physical activity).
Let's highlight a few basic principles of nutrition:
- The emphasis in nutrition should be on proteins and carbohydrates. Products containing large amounts of fat, especially animal fats, should be completely excluded from the diet.
- Salt consumption should be minimized - no more than 5g per day in cooked dishes. Ideally, you can give it up completely.
- Drinking strong coffee and tea is strictly prohibited. There are various substitutes that can be drunk in moderation - chicory, herbal decoctions, mint, dried fruits, rose hips, flowers, dried citrus peels, etc.
- Half of the diet should be fruits, vegetables, and berries. It is advisable to consume them whole without heat treatment. Plant fibers saturate well, the body spends a lot of energy digesting them, which promotes weight loss.
- You need to eat small portions, 5-6 times a day. Fractional meals create an optimal load on the digestive system.
- The diet should include boiled, steamed or baked dishes. Fried foods should be completely avoided. As a last resort - occasionally, in small quantities and in coconut oil.
- Give preference to foods rich in polyunsaturated acids.
- The last meal of the day is no later than 3 hours before bedtime.
A diet for heart problems is prescribed in order to normalize metabolic processes in the body and reduce the load on the heart, liver and kidneys. A healthy diet reduces the load on the heart, slows down the development of atherosclerosis, and prevents the occurrence of coronary heart disease.
Ultraviolet irradiation of blood
This method of treating the consequences of myocardial infarction, used in CBCP, also improves the quality of life after this disease. Does not require any surgical intervention in the patient's body. In this case, no blood is drawn: a special needle connected to a UV emitter is inserted into the patient’s vessel. The device affects a small volume of blood with low-power radiation, which is not felt at all by the patient.
Under the influence of UV radiation, a photochemical reaction occurs in the blood and plasma, as a result of which their composition and functionality improves. It is possible to achieve a significant reduction in blood viscosity (eliminate the risk of blood clots), activate metabolism, improve oxygen delivery to heart tissue, and dilate blood vessels.
Ultraviolet irradiation of blood attracts, first of all, its restorative effect. If you want to “rejuvenate” your heart without resorting to surgery, this method opens up wide possibilities for you.
Is it necessary to contact a nutritionist or can you create a diet yourself?
Cardiologists strongly recommend contacting nutritionists with appropriate qualifications, who will select a suitable diet for each patient individually. Each person's body is unique, and there is no universal diet. Moreover, many patients are convinced that the diet means serious restrictions and a very meager menu. A nutritionist will help you create a varied, nutritious diet so that proper nutrition does not cause discomfort.
Authorized Products
After myocardial infarction and coronary artery stenting, the daily menu must include:
- vegetables, fruits, berries;
- nuts, beans, greens;
- homemade fermented milk products;
- lean fish, seafood (seaweed, mussels, shrimp);
- unrefined vegetable oil (preferably olive, flaxseed);
- chicken, turkey;
- lean meat - veal, beef tenderloin;
- whole grain cereals.
Important! You should not buy low-fat fermented milk products. They are significantly inferior in taste, are repeatedly processed, and contain a lot of synthetic additives.
Prohibited Products
Men and women who have had a stent or heart attack should completely avoid:
- coffee, cocoa, chocolate, spices;
- fatty fermented milk products - cheese, sour cream, cream;
- fatty meat, fish;
- puff pastries;
- mushrooms and even mushroom broths;
- canned, smoked products;
- mayonnaise, margarine, butter.
It is also worth removing from the menu store-bought sauces, sausages, various chips, crackers, nuts and other products that are not recommended for consumption even by absolutely healthy people.
Foods to eat in moderation
The menu after stenting and heart attack may contain the following products, but in limited quantities:
- semolina, rice cereal;
- whole grain pasta, bran bread;
- honey, sugar;
- grapes, raisins, bananas.
This is a difficult food for the body, the consumption of which should be minimized.
Prohibited Products
The diet for myocardial infarction is aimed at reducing body weight and is therefore low-calorie.
Products with a high content of purines are excluded, as they have a stimulating effect on the nervous and cardiovascular systems, which leads to impaired blood circulation and kidney function and aggravates the patient’s condition.
Animal fats, as well as other foods high in cholesterol, are completely excluded.
It is necessary to reduce the load on the digestive tract, so it is forbidden to eat large amounts of food at one time. Also for this purpose, foods that promote fermentation and cause flatulence are prohibited.
Difficult to digest foods, as well as foods with carcinogens (fried, baked goods, grilled, smoked) are also prohibited, because they require increased energy consumption, which aggravates the course of the disease.
Salt causes fluid retention, so foods with a high salt content are prohibited.
It is not recommended to eat dishes that impede intestinal motility and reduce its tone (since the patient is on bed or semi-bed rest).
List of prohibited products:
- bread and flour products: fresh bread, baked goods, baked goods from various types of dough, pasta;
- fatty meats and fish, rich broths and soups made from them, all types of poultry, except chicken, fried and grilled meat;
- lard, cooking fats, offal, cold appetizers (salted and smoked foods, caviar), stewed meat;
- canned food, sausages, salted and pickled vegetables and mushrooms;
- egg yolks;
- confectionery products with rich cream, limited sugar;
- legumes, spinach, cabbage, radish, radish, onion, garlic, sorrel;
- fatty dairy products (whole milk, butter, cream, high-fat cottage cheese, sharp, salty and fatty cheeses);
- coffee, cocoa, strong tea;
- chocolate, jam;
- seasonings: mustard, horseradish, pepper;
- grape juice, tomato juice, carbonated drinks.
Additional recommendations
Patients with cardiovascular problems should avoid alcoholic beverages. It has been proven that excessive alcohol consumption significantly increases the risk of developing cardiomyopathy, arterial hypertension, arrhythmia, and stroke. The maximum permissible daily alcohol intake is 100 ml of wine\30 ml of spirits. Smoking is strictly contraindicated. It puts a tremendous burden on all systems of the body, including the cardiovascular system. If you cannot quit cigarettes on your own, contact your doctor. He will help you choose the correct nicotine replacement therapy - patches, chewing gum, etc., thanks to which you will be able to give up your addiction without stressing the body.
Moderate physical activity plays an important role. You need to spend at least 30 minutes a day outdoors. Strength exercises are contraindicated for patients with cardiovascular problems. It is recommended to practice Nordic walking or swimming.
If after stenting or a heart attack you experience discomfort in the heart area, shortness of breath and other unpleasant symptoms, consult a doctor immediately.
Angioplasty and coronary artery stenting
One of the effective and widespread methods of treating acute myocardial infarction throughout the world is coronary angioplasty with the possibility of installing a stent. The advantage of the operation is that it is extremely minimally traumatic: a small puncture is sufficient to insert a catheter into a peripheral vessel (usually the femoral artery serves as a transport vessel). The goal of high-precision manipulation is to widen the coronary artery in the place where it is blocked.
The catheter, under the control of X-ray equipment, is passed through the vascular system to the site of narrowing of the coronary artery. At the end of the catheter there is a miniature balloon, which is in a compressed state. An X-ray contrast agent is injected into the vessels, and the doctor has the opportunity to observe the manipulations on monitors in the operating room. The cardiac surgeon places a balloon in the affected area of the vessel and inflates it with special equipment, thereby restoring blood flow.
To prevent the walls of the artery from narrowing again, a cylindrical stent is inserted into it in the same way and secured. Thus, it replaces the affected area of the vessel.
Diet effectiveness
The main goal of nutrition according to special principles is to improve blood circulation, improve intestinal function, and accelerate metabolism.
What processes are affected by therapeutic nutrition:
- Improvement of heart rhythms.
- Normalization of weight.
- Restoration of the heart muscle.
- Getting rid of puffiness.
The benefits of diet after myocardial infarction in men are expressed in the prevention of pathologies leading to the appearance of pathology, atherosclerosis, hypertension. Providing the body with vitamins and minerals will affect the functioning of other organs.
Products for the heart
After a heart attack, men are advised to eat foods rich in heart-healthy substances:
- cabbage of different varieties;
- eggs;
- spicy herbs;
- whole grains;
- vegetables, fruits, berries;
- fatty fish (mackerel, salmon);
- vegetable oils;
- almonds, sunflower seeds, walnuts and other nuts;
- dark chocolate;
- lentils.
Dishes prepared from carrots, pumpkin, and turnips are beneficial. During the first month, it is recommended to consume vegetables after heat treatment.
Unwanted Products
Products that require avoidance in case of cardiac pathology primarily include sausages and canned food. This is due to the presence of salt, fats, and various preservatives in them. Their use causes a sudden surge in blood pressure and other complications.
The amount of table salt in the daily menu extremely weakens the effectiveness of medications taken and increases the load on the myocardium. As a result, the threat of re-development of the pathology increases.
The second category of contraindications are products containing cholesterol. They include offal: offal, liver, brains, heart, kidneys of animals. In case of acute pathologies of the brain, you need to give up fish from the sturgeon family, fatty meats, lard, and butter. This also applies to eggs, due to their cholesterol content.
The diet after a heart attack and stenting for men should exclude:
- fresh baked goods;
- white cabbage;
- salty food;
- cucumbers;
- legumes;
- grape juice;
- whole milk;
- soft drinks, other sweet drinks, coffee, strong tea.
Such food stimulates increased flatulence, which is harmful in the presence of heart pathologies. The diet should also not consist of refined, processed grains and carbohydrates. For example, breakfast cereals, white bread and white rice stimulate weight gain, and processed grains increase blood pressure along with cholesterol levels. This can worsen vascular function and increase the feeling of hunger, which causes the number of meals to increase and excess volumes to increase.
The acute form of ischemic pathology has a harmful effect on the heart and the activity of the nervous system. For this reason, during rehabilitation, dishes containing purines are removed from the patient’s menu. These are mostly protein products, yeast. Their use will worsen the patient's condition.
Stages and terms of rehabilitation of patients with myocardial infarction
In cardiological practice there are three stages:
- inpatient - the patient is in the intensive care unit for up to three days, he spends about two weeks in the cardiology department;
- inpatient-outpatient – its duration depends on the severity of the condition (usually 28 days);
- remote (supportive, outpatient) – people who have had a heart attack are monitored by a cardiologist.
Hospital treatment
The inpatient treatment stage begins from the moment the patient is admitted. It involves being under constant observation, first in the intensive care unit, then in the cardiology department. During this period, intensive treatment is carried out. On the first day, physical exercise is contraindicated. From the second, primary physical skills begin to be restored with the help of exercise therapy (under the supervision of a therapeutic exercises instructor).
The first 2-4 days of exercises are performed in a lying position. The patient can:
- bend/extend fingers and toes (up to eight times);
- Without lifting your feet from the bed, bend your knees and straighten them (up to six times);
- lower your legs bent at the knees to the left and right (up to six times);
- perform other simple exercises recommended by the instructor.
The patient must rest before starting the next exercise - it takes from 10 to 30 seconds.
After transfer to the cardiology department, physical activity expands. From days 4 to 12, the second stage of exercise therapy begins. The patient performs the complex in a hospital, sitting in bed. It is recommended to do:
- not sharp turns of the head left and right (up to 10 times);
- raising your arms forward and up, then returning to the starting position (up to five times);
- movement of the feet forward/backward without lifting off the floor (up to 15 times);
- other simple movements included in the exercise therapy complex.
At home, the patient also performs a set of exercises with a dosed and systematic increase in load. It is convenient to use special mobile applications.
Along with physical treatment, psychological support is provided. The patient learns about his disease, the correct lifestyle and the changes that have occurred in the body.
Inpatient-outpatient recovery
The patient is ready for the inpatient-outpatient stage after discharge from the hospital. By this time:
- his condition becomes stable;
- motor activity expands (the patient can walk up to 500 m in steps).
Recovery from illness is possible in a specialized sanatorium or in a cardiac rehabilitation center. The patient is referred for sanatorium-resort treatment by a doctor and a medical advisory commission based on a conclusion from the hospital. There he goes:
- training at the health school - individual and group classes are provided;
- psychotherapy;
- drug therapy - special medications, metabolic agents, vitamin and mineral complexes are prescribed;
- physiotherapy (electrophoresis, baths, thermal power station) – the course includes 10-15 procedures.
An important stage in the patient’s recovery is physical rehabilitation after myocardial infarction. Massage, exercise therapy according to a more intensive program, classes on special simulators, and measured walking are indicated. To select exercises, at the first stage the patient undergoes a test:
- a load is prescribed - walking for six minutes, an exercise bike, a treadmill (walking);
- The body's reaction to it is monitored - the patient's degree of fatigue, the presence of shortness of breath, blood pressure and pulse indicators, ECG.
In accordance with the results obtained, the doctor determines the type of response:
- physiological – moderate fatigue, blood pressure within normal limits taking into account the load;
- intermediate – slight shortness of breath, fatigue disappears within five minutes, moderate changes on the ECG, disturbances in blood pressure and pulse with recovery within 10 minutes;
- pathological – severe shortness of breath, fatigue, chest pain, ECG changes, prolonged increase in blood pressure/pulse limit.
Self-recovery
The long-term (maintenance) stage begins from the moment the patient’s condition is completely stabilized. The doctor’s recommendations on lifestyle, quality of nutrition, and physical activity must be strictly followed. During the first year, the patient visits a cardiologist every three months and undergoes coagulogram and lipidogram monitoring. In the future, the frequency of visits and tests will be once every six months. Blood pressure should be measured daily.