Cardiomyopathy is a primary myocardial lesion that is not caused by an inflammatory, tumor or ischemic process. Often the pathology has an unclear etiology. To diagnose a patient with cardiomyopathy, it is necessary to exclude other diseases: congenital developmental anomalies, valvular heart defects, damage caused by systemic vascular diseases, arterial hypertension, pericarditis, etc. Depending on the nature of the anatomical and functional changes in the heart muscle, the following types of cardiomyopathy are distinguished:
- dilatational (stagnant);
- hypertrophic (can be asymmetric and symmetric, obstructive and non-obstructive);
- restrictive (distinguish between obliterating and diffuse);
- arrhythmogenic right ventricular.
Causes
The etiology of this pathology has not been fully studied to date. There are a number of probable causes that can cause the development of cardiomyopathy:
- hereditary predisposition (genetic defect that causes improper formation and functioning of myocardial muscle fibers);
- various viral infections (Coxsackie, herpes, influenza, etc.);
- previous myocarditis;
- damage to heart cells by toxins and allergens;
- disturbances of endocrine regulation (negative effects of growth hormone and catecholamines);
- immune system disorders.
Types and symptoms of cardiomyopathy
Dilatational
There are no obvious symptoms of this type of cardiomyopathy until heart failure develops. Manifestations of the disease depend on the involvement of one or both chambers of the heart in the beginning pathological process. Due to the oxygen deficiency that occurs with cardiomyopathy, shortness of breath occurs, fatigue increases, and heart rate increases. At the initial stage of the disease, the listed symptoms are associated only with exposure to physical activity, and over time they appear at rest. Insomnia, dizziness, pain in the chest and under the left shoulder blade, and swelling occur.
Hypertrophic
With this pathology, relaxation (decreased extensibility) of the heart chambers is impaired, blood circulation worsens, the shape of the left ventricle changes, the septum thickens, as a result, pressure increases, and the walls of the outflow tract become thinner. Symptoms of hypertrophic type cardiomyopathy, along with shortness of breath and chest pain, are the patient’s tendency to faint and increased heartbeat. With this pathology, rhythm disturbance can even lead to sudden death.
Restrictive
At the initial stage, patient complaints are practically no different from those listed for other types of cardiomyopathy. But over time, leg swelling, shortness of breath and fatigue give way to more severe symptoms. The liver stops functioning normally, increases in size, and then dropsy develops. The instability of the heart rhythm reaches such a degree that it causes frequent fainting.
Arrhythmogenic
The most common symptom is ventricular arrhythmia. Among the complaints, patients name paroxysmal rapid heartbeat, most often during significant physical exertion. Patients with the listed symptoms, in whose family there have already been cases of early death with such manifestations, are considered to be at increased risk.
Treatment of cardiomyopathy at the Center for Pathology of the Circulatory Organs
At the Center for Pathology of the Circulatory Organs you can undergo a complete examination of the cardiovascular system. At the first symptoms of cardiomyopathy, our specialists will prescribe special diagnostic procedures that exclude suspicion of other diseases (differential diagnosis). This approach will help you quickly make an accurate diagnosis and begin timely treatment. For this purpose, our clinic is equipped with the latest diagnostic and therapeutic equipment in the world: the Cardiospec myocardial shock wave therapy system, the Vamed ECP System premium external counterpulsation device, the General Electric ergometric system, the MyLab 50 ultrasound system and much more.
The advantage of the Center for Pathology of the Circulatory Organs is the use of non-surgical methods of treating heart diseases: enhanced external counterpulsation, shock wave therapy of the heart, hypoxic therapy and much more.
After therapy, all patients of our clinic can undergo a rehabilitation course and remain under the supervision of experienced highly specialized specialists, relying on the experience of the best domestic cardiologists and foreign colleagues. This helps improve the prognosis of the disease and also minimizes the occurrence of postoperative complications.
Consequences and complications
For all types of cardiomyopathy, a characteristic complication is progressive heart failure. In addition, arterial and pulmonary thromboembolism, cardiac conduction disturbances, and severe forms of arrhythmia may develop. There is a high risk of sudden cardiac death. If the patient has bad habits, such as smoking and drinking alcohol, the prognosis worsens significantly. Life expectancy may also be affected by the presence of thromboembolism and tachycardia, especially if cardiomyopathy is untreated. Today, alleviating the course of the disease for such patients is becoming possible thanks to modern early diagnostic technologies.
Postoperative rehabilitation
Recovery after surgery usually takes from 2-3 months to six months, depending on the nature of the surgery. The exception here is recovery after a heart transplant or valve replacement - the recovery time after these operations is much longer.
This is a very important period in the treatment of cardiomyopathy, since with improper rehabilitation measures there is a possibility of a return of symptoms of the disease . A balanced diet and avoidance of physical activity, smoking and alcohol are recommended. You should temporarily refrain from driving.
Throughout the entire rehabilitation period, it is necessary to be observed by a cardiologist and undergo examinations. Only a specialist will be able to identify the development of pathologies, malfunctioning pacemaker or prosthetic heart valve and take timely measures!
Diagnostics
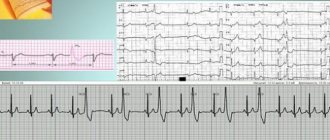
Diagnosis of cardiomyopathy necessarily includes a description of the clinical picture and data from additional studies. The most common method - electrocardiography (ECG) - allows you to record signs of hypertrophy of the heart muscle and identify various forms of rhythm and conduction disorders. Echocardiography (EchoCG) is especially informative, as it helps determine myocardial dysfunction. Thanks to X-ray data, dilatation (persistent increase in the lumen), hypertrophy (increase in volume and mass) of the heart muscle, as well as congestion in the lungs are detected. In some cases, as part of the diagnosis of cardiomyopathy, ventriculography (x-ray examination of the ventricular system), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the heart and multislice computed tomography (MSCT), as well as probing of the cavities of the heart to collect biomaterials for further morphological research are indicated.
Treatment
Due to the lack of specific therapy, treatment of cardiomyopathy is aimed at preventing complications incompatible with life. If the disease is in a stable phase, all measures are prescribed and carried out on an outpatient basis. Must be under the supervision of a cardiologist. The indication for periodic planned hospitalization is the presence of severe heart failure, for emergency - the development of intractable paroxysms of arrhythmias, as well as thromboembolism and pulmonary edema.
Drug treatment. For various manifestations of cardiomyopathy, it is advisable to prescribe:
- diuretics, which reduce pulmonary and systemic venous congestion;
- cardiac glycosides, which help combat disorders of contractility and pumping function of the myocardium;
- antiarrhythmic drugs that help regulate heart rhythm;
- anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents to prevent the occurrence of thromboembolic complications of cardiomyopathy.
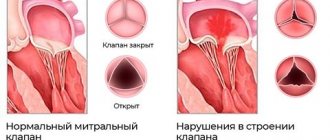
Surgery. Indicated in extremely severe cases. Among the methods practiced today are septal myotomy (resection of an enlarged portion of the interventricular septum) and mitral valve replacement, as well as whole heart transplantation.
In addition, experts emphasize the need to reduce physical activity and adhere to a diet, an important condition of which is limiting the consumption of animal fats and salt. It is strongly recommended to eliminate bad habits and exposure to negative external factors. Compliance with these recommendations will significantly reduce the load on the myocardium and slow down the progression of heart failure.
Restrictive cardiomyopathy
Restrictive cardiomyopathy is the least studied of all forms of the disease. To date, there is no effective surgical treatment for this type of disease. Heart transplantation also does not work, since the same pathological processes occur in the donor organ some time after the transplantation. All surgical methods are aimed at prolonging the patient’s life: the weakened myocardium is supported by a pacemaker, and if the functions of the heart valves are impaired, their prosthetics are performed.
Prognosis for cardiomyopathies
With regard to cardiomyopathy, the prognosis is unfavorable: the steady progression of heart failure causes a high probability of arrhythmic, thromboembolic complications, as well as sudden death of the patient. According to statistics, with dilated cardiomyopathy, the 5-year survival rate is 30%. Systematic treatment can stabilize the patient’s condition indefinitely. There are also cases of exceeding 10-year survival after heart transplantation. Surgical treatment, for example, for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, gives a positive result, but is associated with a high risk of death of the patient during or after surgery. Women who have been diagnosed with cardiomyopathy are not recommended to become pregnant, since pregnancy and childbirth are associated with a high probability of maternal death.
Dilated cardiomyopathy
One of the ways to treat dilated cardiomyopathy is cardiomyoplasty . For this operation, the surgeon takes a muscle flap from the latissimus dorsi muscle and then wraps it around the heart, thus partially replacing the affected myocardial tissue with it. During the operation, a pacemaker is installed, with the help of which muscle contractions are synchronized. Cardiomyoplasty helps many patients avoid hospitalization and increases life expectancy with the disease.
There is also a technique for dual-chamber electrical stimulation of the heart using an implantable pacemaker. The operation is indicated for patients with atrial and ventricular fibrillation. After installing the device, the internal circulation of the heart improves and the functions of the ventricles develop.
Another method of treating dilated cardiomyopathy is the installation of an extracardiac mesh frame. This frame is made individually for each patient, depending on the size and anatomical features of the heart. The purpose of the operation is to prevent pathological growth of the ventricles.
A radical surgical method used to treat dilated cardiomyopathy is heart transplantation. Indications for transplantation are considered to be low chances of survival (less than 50%) within a year. The prognosis is conditionally favorable. Today, patients with a donor heart live more than 10 years. The disadvantage of this method is the long queue for transplantation. The wait often takes several years, which is not the case for a patient with a severe stage of the disease.
Prevention
To date, there are no preventive measures for hereditary (congenital) cardiomyopathy. However, some recommendations have been developed to reduce the risk of developing concomitant diseases that worsen its course - myocardial infarction, arterial hypertension. In general, prevention comes down to maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including physical exercise and giving up tobacco and alcohol. To identify the underlying disease (arterial hypertension, hypercholesterolemia or diabetes mellitus) at its early stage, it is important to follow the following recommendations:
- regularly visit a doctor and undergo examinations prescribed by him;
- follow all the specialist’s recommendations regarding lifestyle changes, daily routine, diet, etc.;
- take medications and other medications in strict accordance with the doctor’s prescription.
For patients at high risk of sudden cardiac death, timely implantation of a cardioverter-defibrillator, a device for stopping threatening arrhythmias, is of great importance.
If you want to undergo diagnosis or treatment of various types of cardiomyopathy under the supervision of highly qualified specialists, contact the ABC-Medicine clinic. To sign up for a consultation or ask clarifying questions, please call +7.
Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy
To treat arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy, implantation of pacemakers, cardioverter-defibrillators (autonomous defibrillator for electrical discharge during cardiac arrest), as well as radiofrequency ablation are used. During this operation, a vein (femoral or subclavian) is punctured to the patient under local anesthesia and electrodes are inserted into the heart through catheters, which affect some of its areas that cause arrhythmia.
Also, in some cases of arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy, ventriculotomy is used - opening the ventricles of the heart and heart transplantation.