Pinworms are the most common type of roundworm that causes enterobiasis. This disease often occurs in children. The main cause of infection is unwashed hands and failure to comply with personal hygiene rules. After penetrating the body, pinworm larvae cause many negative symptoms and significantly worsen the quality of life.
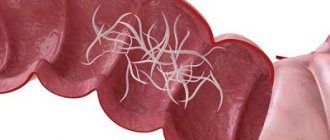
Adult pinworms
How can you become infected with pinworms?
Most often, pinworm infection occurs due to non-compliance with hygiene rules in everyday life. Washing your hands too often or carelessly is the first step to infection.
Pinworm eggs can be found literally anywhere. Females live in the human intestine. However, to lay eggs, they crawl into the anus in the evening and at night, which causes severe itching. Scratching, often unknowingly, causes parasite eggs to be transferred to the hands and under the nails, and from there to anything the infected person touches or directly into the mouth.
Itching in the anus
The source of pinworm infection can also be contact with the underwear or towel of a sick person, although it is no less likely that pinworm eggs will also end up on bed linen, a toilet seat, or a bathtub. Food products can also be contaminated with pinworm eggs.
Direct contact with eggs is not the only way to become infected. Infection is possible through airborne droplets. The eggs are very small and light, so they float in the air. Then they settle, for example, on dust that a person inhales. Adult worms live up to 2 months, but self-medication can cause the problem to persist much longer.
What do pinworm larvae look like?
Pinworms are small in size - an adult female grows no more than 1 cm, and a male up to 0.5 cm. The rear end of the female has a pointed shape, while that of the male is rounded. There is a vesicle on the head of the parasite, thanks to which it can attach to the intestinal walls and feed on its contents.
Pinworm larva and eggs
The appearance of the larva is not much different from the adult, with the exception of its size. To see pinworm eggs and larvae, special equipment is required because they differ in microscopic shape.
Cause of pinworm infection
Pinworm infection in humans occurs for the following reasons:
- poor sanitary and hygienic conditions;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- pinworms in family members.
The only source of pinworm infection is humans. The infection spreads very easily through the mouth, for example through contaminated hands or food. This problem especially affects children, who often do not follow basic hygiene rules and put various objects, toys or school supplies, such as pens and pencils, in their mouths, which facilitates the penetration of pinworms into the body.
Pinworm infection through contaminated hands
This is why it is so important that adults teach children basic hand hygiene rules and set an example of proper behavior themselves.
Clinical picture of enterobiasis
The most important symptom of a helminthic infection is itching in the anus ; it occurs mainly at night or in the early morning hours. The laid eggs irritate the skin in the anal area. Pinworms in children are accompanied by unbearable itching and the child cannot stop trying to stop scratching the skin. In this regard, scratches and scratches appear. Sometimes there is a violation of the integrity of the skin. This may be accompanied by an additional infection and symptoms of inflammation appear in the areas of scratching: hyperemia, swelling and soreness.
When a large number of parasites remain in the body for a long time, night sleep is disturbed due to a certain time of egg laying and the occurrence of specific symptoms at night.
Symptoms of pinworms
Among the symptoms of pinworms that may indicate an infection, the most common is persistent itching around the anus.
Patients are often irritable and have trouble concentrating. They often complain of abdominal pain and headaches. Teeth grinding is also a characteristic symptom that many parents pay attention to.
Pinworms may also be accompanied by:
- loss of appetite;
- weight loss;
- pale skin;
- dark circles under the eyes.
Dark circles under the eyes
Weight loss
It is worth noting that women may experience itching around the vagina. Pinworms can penetrate the female genitals and cause inflammation. There are also known cases of appendicitis caused by pinworms. In adults, the symptoms of pinworms are not very different from those in children. However, they are often much less serious.
Examination of stool for parasites (giardia, opisthorchid, roundworm, pinworm, whipworm)
Helminths
Helminths (colloquially worms) are the general name for parasitic worms that live in the human body. Helminthiasis is a series of diseases caused by parasitic worms. The causative agents of helminthic infection are:
- representatives of roundworms of the class Nematoda (nematodes);
- flat tapeworms (cetodes);
- fluke worms (Trematoda, trematodes).
To preserve their species, representatives of all classes of helminths leave the host’s body to reproduce. At the same time, to carry out intermediate stages of development, they move into the body of a new host or remain in the external environment. The movement of parasites from one host to another is carried out by vectors:
- mechanical (for example, arthropods (in particular houseflies), carrying parasite eggs over considerable distances);
- specific – intermediate hosts, in whose body one of the development cycles of the parasite occurs.
The transfer can be:
- contact (active), in which the penetration of parasites occurs through damaged/undamaged skin and mucous membranes;
- food (passive), when ingesting larvae or eggs of parasites with food or water.
The roundworm (Ascaris lumbricoides or stringworm) is a nematode (roundworm) of the order Spirurida that lives in the small intestine. Infection with roundworm differs from infection with other parasites in that fresh helminth eggs do not pose a danger to the owner. In order for them to become infectious, they need to ripen in the soil for 10-15 days, and sometimes for a month. Moreover, they can remain there for three years without dying due to significant drops in temperature and without reacting to exposure to ultraviolet rays.
The presence of adult parasites of both sexes in the body makes a person a source of infection for others. Fertilized females lay about 200 thousand eggs within 24 hours, which are excreted along with feces. If favorable conditions exist, their development begins.
When mature eggs enter the upper part of the small intestine of a new host, larvae begin to emerge from them. Migration follows: through the intestinal wall through a vein, through the vascular system of the liver and lungs, the parasite larvae enter the bronchi, and then into the lungs. Using the epithelium of the respiratory tract as a “ladder”, they rise to the pharynx, from where they are swallowed back into the stomach and returned to the intestines. There they develop (usually this period lasts up to 75 days), after which the larvae turn into adults capable of reproduction.
An adult worm lives on average for about a year, then dies and leaves the body in feces. Consequently, perennial ascariasis is caused by repeated reinfection with the parasite. Infection can occur through food, water or household items. An additional possibility of spreading infection is created by the consumption of greens, vegetables and fruits from land plots fertilized with feces that have not undergone disinfection treatment.
Ascariasis is a two-phase infection. The early phase is migratory and occurs during the advancement of larvae. The late phase is characterized by the presence of mature worms in the intestines and the development of complications. The symptoms of ascariasis are identical to those of pulmonary diseases: the infection may be accompanied by a dry cough, difficulty breathing, and chest pain. In addition, an increase in body temperature (up to 38⁰), the appearance of bright pink, very itchy blisters, headache, and weakness are possible. At the same time, the level of leukocytes and eosinophils in the blood increases significantly. Chronic ascariasis is accompanied by nausea, abdominal pain, intestinal dysfunction, and sleep disturbances. With a complicated course of the disease, pancreatitis develops, intestinal patency is impaired, and appendicitis becomes inflamed.
Pinworms (Enterobius vermicularis or Oxyuris vermicularis) are small roundworms, causative agents of enterobiasis, which got their name due to the presence of a pointed end in the female. The location of pinworms is the lower part of the small intestine, the cecum (the appendage at the junction of the small intestine with the large intestine, the first section of the large intestine) and the appendix (a blindly ending tubal formation - the appendage of the cecum). The worms feed on the contents of their intestines.
At night, pinworms crawl from the rectum to the exit of the anus to lay eggs, which require oxygen to develop. One individual is capable of laying from 5 to 15 thousand of them. After this, the females die. Eggs mature within 4-6 hours, which is accompanied by discomfort and severe itching in the anus.
When scratching this area, eggs get under the nails and, in the absence of proper hygiene, into the mouth, and then back into the intestines. Adults are formed inside the body within 10-12 days. Then the cycle repeats. The source of enterobiasis is a person infected with pinworms.
Under the influence of waste products and, especially, the remains of parasites, the body is poisoned, allergic reactions occur, which causes an increase in the level of eosinophils (a subtype of white blood cells secreted by the immune system during the development of allergies or infection with parasites). In addition, the disease may be accompanied by metabolic disorders and vitamin deficiency. Pinworm larvae that attach to the skin cause the development of inflammatory processes. Also characteristic features of enterobiasis are intestinal dysfunctions:
- motor – aimed at mixing and promoting its contents;
- secretory - a violation of the release into the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract of secretions involved in digestion.
Severe perianal itching can cause anxiety, worsening or complete loss of appetite, weight loss, irritability, and insomnia. In children with severe and prolonged enterobiasis, deviations in mental development may occur.
Opisthorchiasis is another special case of helminthiasis. Its causative agent is opisthorchid , a small flatworm of the trematode class of the family Opistorhidae. The source of human infection is cyprinids infected with worm larvae that have not undergone sufficient heat treatment. Infection is also possible when cutting infected fish. The location of parasites in the human body is the bile ducts of the liver and the pancreatic ducts. The incubation period for infection is approximately 2-3 weeks. The disease may occur without symptoms, or may be accompanied by weakness, jaundice, fever, and chills. One of the reasons for the development of the disease is the ingestion of waste products of worms into the body (they cause an allergic reaction). In addition, health problems arise due to:
- mechanical effects of parasites on the walls of the pancreatic ducts, as well as on the ducts and the wall of the gallbladder;
- irritation of elements of nerve tissue located in these ducts;
- creating favorable conditions for the development of secondary biliary tract infections;
- proliferation of the glandular epithelium of the bile and pancreatic ducts.
The disease is often asymptomatic, which increases the risk of developing its chronic form, which can last for many years. The most characteristic consequences of opisthorchiasis infection are damage to the pancreatic ducts and chronic cholangitis (chronic inflammation of the bile ducts). As a result of a complicated course of the disease, the following diseases can develop:
- purulent cholangitis;
- pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas);
- cholelithiasis;
- cholangiocarcinoma (a cancerous tumor formed from mutant cells of the bile duct epithelium).
The most common cause of the development of chronic opisthorchiasis is repeated infections, causing relapses of inflammatory processes. With a single infection, the likelihood of developing severe complications is much lower.
Whipworm is a representative of roundworms (nematodes) 2-5 cm long, which parasitizes only in the human body. It is the causative agent of the disease trichocephalosis. The worm owes its name to its unusual shape: the front part of its body is much thinner than the back, and resembles a thread in appearance. It contains only the esophagus, and the remaining organs are located in the back. Whipworm eggs are transparent, barrel-shaped, with caps at the ends.
The female worm lays from 2 to 10 thousand eggs during the day, which are excreted from the intestinal lumen along with feces. When eggs fall into moist soil, larvae begin to develop. The optimal temperature for this process is +25-30°C. Development lasts 3-4 weeks, after which the eggs become invasive. Human infection is caused by ingestion of eggs with larvae, which can be on vegetables, berries, fruits, and also in water. In the human body, under the influence of digestive enzymes, the egg shell dissolves and the larva is released. The process of her reaching puberty continues for several weeks. The parasite lives for about 6 years.
The worm’s habitat is the initial section of the large intestine, where it “drills” deeply into the wall with its thin end. The parasite feeds on the host's blood and tissue fluid. Violation of the integrity of the intestinal wall can cause the development of an inflammatory process and, with massive invasion, the addition of a secondary infection at the site of damage (in particular, cause the development of pathological processes in the appendix). Also, a significant increase in the number of parasites can lead to anemia. The waste products of the worm cause poisoning of the body. The most common complaints of patients with trichuriasis are abdominal pain, headaches, and dizziness.
Diseases caused by parasite infection have a number of common symptoms. In particular, any of them can occur in acute or chronic form.
Acute helminthic infestation is usually characterized by:
- general allergic reaction;
- fever;
- leukocytosis (increased levels of white blood cells in the blood);
- eosinophilia (increased concentration of eosinophils (a subtype of leukocytes) in the peripheral blood more than 500/μl).
Symptoms of the chronic form of infection depend on the number of helminths and their location. In the vast majority of cases, infection with worms is accompanied by metabolic disorders, abnormalities in neuropsychic activity, and weakened immunity.
Protozoa
The Protozoa group includes microscopic unicellular organisms (which, however, can unite into multicellular colonies). Although their body is represented by only one cell, the protozoa are absolutely full-fledged organisms with all the characteristic features - their life activity is coordinated, orderly, which is confirmed by:
- the process of nutrition and the release of decay products;
- carrying out the reproductive function.
Protozoa differ from prokaryotic bacteria (single-celled living organisms that do not have a formed cell nucleus and other internal membrane organelles) by the presence of a cell nucleus surrounded by a membrane and containing DNA molecules.
For most protozoa, as well as for animals, food comes from ready-made organic substances present in their environment. However, some protozoa, like plants, contain chlorophyll and, using solar energy, are able to convert inorganic substances into organic ones (carbohydrates). In connection with this division, protozoa were classified either as plants or animals, or as a separate group. Ultimately, they, together with a number of organisms, form a group of protists (Protista), within which they are separated into an independent subgroup.
To date, about 30,000 species of protozoa have been described. There are many of them that are dangerous to humans, but three are recognized as the most significant:
- lamblia (Lamblia intestinalis);
- dysentery amoeba (Entamoeba histolytica);
- balantidia (Balantidium coli).
Giardia (Giardia intestinales, also known as Giardia lamblia or Giardia duodenalis) is the most common single-celled parasite that is found almost anywhere on the planet, both in humans and animals. Giardia is protected on the outside by a shell that allows them to survive in the external environment for a long time. Infection with the parasite occurs through the oral-fecal route, through dirty hands, through water (the presence of Giardia in it is the most common cause of infection) and contaminated products.
Giardia is the causative agent of the pathology - giardiasis and lives mainly in the duodenum and bile ducts of the host. There they can move freely using flagella or attach to the epithelium through an adhesive disk, which is located in their lower part. Up to a million lamblia can stick to 1 cm^2. In this case, a violation of the villi occurs, which disrupts the absorption of nutrients and provokes the development of inflammation of the mucous membrane.
The most characteristic manifestations of the disease are diarrhea with watery stools and stomach cramps. The onset of symptoms is observed 7-14 days after infection. The active phase usually lasts from 2 to 6 weeks. If the infection affects the bile ducts, the disease is accompanied by jaundice.
Dysenteric amoeba is the causative agent of amoebiosis. It is distributed everywhere, but especially widely in the tropical zone. Infection with the parasite most often occurs through ingestion of cysts - a temporary form of existence of the infectious agent, in which it can exist for several years.
Amebiasis is a deadly disease, from which, according to available data, about 100 thousand people die every year. Once in the human blood, the amoeba is able to penetrate the tissues of the liver, lungs, kidneys, brain, heart, spleen, and genitals. The food for this protozoan is epithelial cells, food fragments, bacteria, erythrocytes, and leukocytes.
Dysenteric amoeba lives in the intestines and has two forms - tissue and luminal. In countries with temperate climates, it usually remains in the intestinal lumen, so the infection does not manifest itself visibly. In subtropical and tropical climates, the amoeba becomes active and begins to attack its walls. The reasons for the transition of amoebas to a pathogenic tissue form remain unclear, but it is known that it can attack in several ways. First of all, the amoeba secretes substances that dissolve the mucous membrane, which allows it to kill the cells of the host body. The parasite presumably kills cells in one of the following ways:
- by launching the process of apoptosis (programmed death) in them, which occurs in a few minutes;
- through trogocytosis (gnawing off pieces from the cell), which today explains the amoeba’s ability to penetrate the blood, liver and other areas of the body.
Balantidia are the largest protozoa that parasitize the human body - they are much larger than the intestinal cells among which balantidia live. They are the causative agent of an infectious disease - balantidiasis. Infection with the parasite occurs through consumption of food and/or water contaminated with its cysts.
Balantidium is essentially a ciliate (the only one of all protozoan parasites). It lives in areas where pigs live, which are its main carriers. The habitat of balantidia in the human body is the submucosal layer of the large intestine, although the parasite is also able to penetrate the epithelium of the lungs. Balantidia feed on bacteria, pieces of food and fragments of the epithelium of the host organism. They can cause both mild colitis and severe illness with the formation of ulcers in the walls of the colon, which are accompanied by severe diarrhea with blood and mucus. Deaths from balantidiasis are extremely rare, but severe disease leads to chronic exhaustion.
Complications due to the activity of worms
Warning symptoms should not be underestimated. Unfortunately, an untreated problem can cause many complications, the most common of which are:
- problems with concentration, which leads to problems with learning and remembering;
- sleep disorders;
- inflammation of the female genital organs;
- colitis;
- appendicitis;
- dermatitis (caused by constant scratching around the anus);
- weight loss.
What are pinworms and why are they dangerous?
Pinworms are representatives of roundworms.
This type of helminth is dangerous and can lead to many negative consequences in the body:
- disrupt their own beneficial intestinal microflora due to the production of their metabolic products and the formation of harmful toxic substances;
- in girls, young women and women, due to the close anatomical location of the anus and vagina, pinworms can spread to the female genital organs, causing gynecological inflammatory diseases;
- as the number of parasites in the body increases, they populate different parts of the intestine; if they enter the cecum, where the appendix is located, it may become inflamed and appendicitis may begin;
- helminths are able to rob the body by feeding on blood, the level of red blood cells and iron decreases, and as a result anemia occurs. This condition is accompanied by lethargy, drowsiness, fatigue, lethargy, brittle hair and nails, pale complexion and skin;
- When parasites enter a child's growing body, they affect the child's immune system, he gets sick more often, and lacks vitamins and microelements.
When pinworms enter the human body, they parasitize primarily in the intestines.
Analysis for pinworms
Testing for pinworms is recommended for people of any age every six months. The occurrence of severe itching around the anus, which worries mainly in the evenings and at night, is an immediate indication for testing.
It also happens that pinworms are visible in the stool. This is possible with global pinworm infection. However, you should not wait until the disease becomes visible to the naked eye.
Pinworms are detected using a smear from the anal area, based on which it can be determined whether there are parasite eggs in the body. The material is collected using self-adhesive cellophane tape, which is glued to the skin around the anus in the morning before hygiene procedures and bowel movements. The tape is sent to the laboratory. The test may need to be repeated (only 3 tests performed in a row detect 90% of infections).
Analysis for pinworms
Doctors often decide to conduct a general stool examination, which can reveal possible infection not only with pinworms, but also with other parasites. This is a more accurate and effective test for worms.
Diagnosis of pinworms
To confirm the presence of enterobiasis, the child must undergo certain diagnostics.
Since pinworm eggs are localized in the folds of the anus, the main method of studying the disease is perianal scraping, which is subsequently subjected to careful analysis under a microscope. It should be noted that to obtain a reliable diagnosis, the study must be carried out several times with an interval of 3-5 days. The sticky tape method is also practiced. During the examination, a special tape is applied to the perianal area, after which the tape is examined under optical magnification. There are other methods for studying helminthic infestation:
- General blood analysis. Elevated levels of eosinophils may indicate the presence of pinworms in the body.
- Coprological analysis - examination of stool can help identify worms and determine their type, however, this method is not always reliable (pinworms are not in a fixed position, but move freely through the intestines, which complicates the diagnostic process).
Treatment of pinworms
Treatment for pinworms is generally not very complicated and consists mainly of taking appropriate medications and maintaining personal hygiene. Regardless of age, the drugs are usually taken immediately - a single dose of a prescription antiparasitic drug is determined by the doctor.
Treatment of pinworms
Treatment must be repeated after 2 weeks due to possible recurrence of helminth infestation. This repetition of the dose of the drug is aimed at completely eliminating all parasites. It should be emphasized that if pinworms were found in a child, then in order to avoid cross-infection, the whole family must undergo diagnostics and drug therapy. Often in adults, along with pinworms, a whole “bouquet” of parasites is detected.
Measures related to the removal of sources of re-infection from the environment are also of great importance in the treatment of pinworms. Therefore, on the day of treatment, it is necessary to very carefully clean the entire apartment, change and wash, or even boil linen, bed linen, towels, and then iron them with a hot iron.
These steps are necessary to get rid of parasite eggs. You also need to take care of your baby’s toys, which may contain pinworm eggs. If a child puts a toy contaminated with eggs into his mouth or hands that held the toy, reinfection may occur.
You should clean your apartment every day to remove dust that may contain pinworm eggs. In addition, you should change your underwear, bed linen and towels every day, shower every morning and wash the anal area with warm soapy water. Also don't forget to trim your nails.
Many people change their eating habits after learning about the infection. Because diet can help with drug treatment. A diet limited in carbohydrates (sugars) and rich in protein and fiber is recommended, sourced from vegetables, fruits, and whole grain breads and cereals.
Please note that home remedies cannot replace a visit to the doctor and appropriate diagnosis and pharmacotherapy. They can only support the healing process.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Prevention of pinworms
In order to prevent infection by parasites, parents should follow preventive measures:
- From a very early age, develop basic personal hygiene skills in your child.
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap after visiting the restrooms, returning home from the street, or contacting domestic and street animals.
- Process raw vegetables and fruits before consumption.
- Change your child's underwear daily and wash it in hot water.
- Regularly trim your baby's nails to prevent infectious agents from getting under them.
- Conduct timely deworming of animals in the same house as the child.
If it was not possible to prevent the disease, you should not self-medicate. Be sure to show your child to a qualified specialist. At the SM-Doctor clinic, doctors with many years of experience will help identify parasitic diseases and quickly treat them without harming children's health.
Diagnosis of enterobiasis
First of all, the doctor interviews the child or his parents. We need to focus on issues such as
- detailed explanation of all complaints;
- time of onset of symptoms;
- whether other family members have similar complaints;
- how the rules of personal hygiene are observed (washing hands after going to the toilet, after going outside, before eating, using an individual towel);
- The doctor can see if your child or you have pinworms in your stool.
This is followed by laboratory diagnostics. The patient's stool and scraping of the perianal area are taken for analysis.
The next stage of diagnosis is taking blood for a general analysis. For helminthic infestation, certain changes in the general blood test are characteristic:
- an increase in the number of eosinophils is the main indicator of the presence of a disease caused by parasites;
- anemia - decreased hemoglobin concentration.
This happens infrequently, when the disease is advanced, when the number of parasites in the body is quite large and they feed on blood in the intestines.
Harm from pinworms in humans
Infection with pinworms occurs through accidental ingestion of eggs that fall from the patient’s hands onto food (fecal-oral transmission mechanism). Therefore, the disease often spreads spontaneously and in outbreaks, especially often it can be found in kindergartens, swimming pools, and medical institutions.
The harm caused by helminths is caused by several factors:
- Mechanical damage to the mucosa. Pinworms have sharp wing-shaped processes that literally cut the walls of the gastrointestinal tract. The wounds become inflamed and may become infected. This is why helminth infestations are so often accompanied by the development of fungal and bacterial infections (development of candida, streptococcus).
- Toxic effects. Any type of pinworm (and three types of these worms can parasitize the human body) has a serious toxic effect, releasing waste products into the gastrointestinal tract. In addition, after their death, pinworms remain in the intestines, affecting it with decay products. Gradually, toxins accumulate and symptoms of intoxication worsen.
- Deficiency of micro- and macroelements. Like any parasites, pinworms in adults and children feed on the body of their host, literally “eating” it. As a result, the body does not receive enough micro- and macroelements, the imbalance of which disrupts endocrine processes.
- Disruption of the usual way of life. One of the most unpleasant (from a psychological point of view) symptoms of pinworm infection is associated with its migration to the anus. During these periods, the patient experiences severe obsessive itching in the perineal area. As a rule, pinworms become active in the evening and at night. Irritation of the anus does not allow the patient to sleep peacefully; as a result, the usual routine is disrupted, psychological fatigue accumulates, performance decreases, and irritability increases.