Photo: M24.ru/Mikhail Sipko
“Man is mortal, but his main problem is that he is mortal suddenly,” these words, put into Woland’s mouth by Bulgakov, perfectly describe the feelings of most people. There is probably no person who is not afraid of death. But along with the big death, there is a small death - clinical. What is it, why do people who have experienced clinical death often see divine light, and is this not a delayed path to heaven - in the material M24.ru.
General information
Clinical death is a transition period between life and biological death of a person.
At its core, it is a reversible stage of death, when the activity of the heart and breathing stops, and no signs of vital activity are observed. Characteristic signs of this condition are the absence of pulse and consciousness, dilated pupils. An objective sign is small-wave atrial fibrillation or isoline on the ECG. However, in this condition, oxygen starvation does not lead to the development of irreversible changes in systems and organs. The ICD-10 code for this condition is G93 (Other brain lesions). Speaking about how long clinical death lasts, it should be noted that the duration of clinical death is no more than 3-4 minutes. The maximum time during which the body can remain in such a terminal state is 5-6 minutes. In rare cases, a longer duration was recorded.
How to identify such a condition and properly provide first aid will be discussed in this article.
Biological death: irreversible death of cells, tissues, organs
One of the first signs of biological death is the drying of the cornea. It is determined by squeezing the eye from the sides - the pupil then takes the shape of a spindle or “cat’s” eye. It is known to doctors as Beloglazov’s symptom.
Next, the patient begins to exhibit the following symptoms:
- the mucous membranes of the nose, mouth, and genitals dry out;
- body temperature gradually decreases;
- characteristic cadaveric spots appear on the skin;
- rigor mortis is noticeable.
Although decomposition processes begin almost immediately, some organs are less susceptible to it. Thus, the heart can be implanted 1-2 hours after removal from a dead body, and the kidneys and liver can be preserved for about 4 hours. Skin transplantation from a deceased person to a living person can be performed within the first 6 hours. Bone tissue is considered the most resistant - due to its inertness to external factors, it can be implanted into the recipient within 1-2 days.
Pathogenesis
After clinical death occurs, tissue metabolism slows down sharply, but due to anaerobic glycolysis it does not stop completely. When breathing stops and blood flow stops, destruction processes begin very quickly in the body. Due to oxygen starvation, tissues are destroyed. In this case, the cells of the cerebral cortex experience the greatest sensitivity. As a result, when brain cells die, even after successful resuscitation, complete recovery does not occur.
When blood flow stops in the body, active blood clotting occurs, and microthrombi appear in the vessels. Due to toxic products of tissue breakdown entering the blood, metabolic acidosis . With prolonged absence of blood circulation, biological death occurs. In the case of urgent resuscitation, cardiac activity is restored, after which postresuscitation disease as a consequence of ischemia , thrombosis of the capillary network, and significant homeostatic changes.
The duration of the period of clinical death is determined by the period during which the cerebral cortex and subcortex can maintain viability under hypoxic . For 3-5 minutes, the higher parts of the brain can remain viable in the absence of oxygen supply under conditions of normal body temperature. The practice of doctors in all countries of the world indicates that if the specified period is exceeded, then the person can return to life, but in this case the phenomenon of decortication (death of the cerebral cortex) or decerebration (all parts of the brain die) is already noted.
However, in medicine there is a second period of clinical death, which can last longer, after which resuscitation measures allow the person to be revived. This is achieved by the fact that the processes of degeneration of parts of the brain due to hypoxia are slowed down due to the creation of certain conditions. Thus, it is possible to increase the duration of clinical death in a state of hypothermia , that is, artificial cooling of the body. This can also be done by physical influences - hyperbaric oxygenation , head hypothermia . Special pharmacological drugs are also used to ensure a sharp decrease in metabolic processes.
In the absence of resuscitation processes or the failure of such actions, biological death occurs, and all physiological processes in the body cease.
Post-resuscitation support
Monitoring
Auxiliary mechanical ventilation with 50% -100% oxygen
- alternative: auxiliary ventilation with an ambu bag » alternative: tracheal intubation
Reliable permanent connection with the central or peripheral vein
Correction of CLB (sodium bicarbonate w / w 4% 200.0 - 400.0 ml) alternative: sodium lactate
Prednisolone 90-120 mg IV
Furosemide 2.0-4.0 ml i.v. alternative: mannitol 200.0 i.v.
When excited, sodium thiopental IV before removal by the court, but not more than 1 g alternative: sibazon 2.0, sodium hydroxybutyrate IV is allowed
Heart rhythm correction
Correction of blood pressure (if necessary, dopamine intravenously)
Pathogenetic therapy of the underlying disease (cause of clinical death).
A living organism does not die simultaneously with the cessation of breathing and cessation of cardiac activity, therefore, even after they stop, the body continues to live for some time. This time is determined by the brain’s ability to survive without oxygen supplied to it; it lasts 4–6 minutes, on average 5 minutes. This period, when all the extinct vital processes of the body are still reversible, is called clinical
death
. Clinical death can be caused by heavy bleeding, electrical trauma, drowning, reflex cardiac arrest, acute poisoning, etc.
Signs of clinical death:
1) absence of pulse in the carotid or femoral artery; 2) lack of breathing; 3) loss of consciousness; 4) wide pupils and their lack of reaction to light.
Therefore, first of all, it is necessary to determine the presence of blood circulation and breathing in the patient or victim.
Definition of signs
clinical death:
1. Absence of pulse in the carotid artery is the main sign of circulatory arrest;
2. Lack of breathing can be checked by visible movements of the chest during inhalation and exhalation, or by placing your ear to the chest, hearing the sound of breathing, feeling (the movement of air during exhalation is felt by the cheek), and also by bringing a mirror, a piece of glass or a watch glass, or a cotton swab to your lips or thread, holding them with tweezers. But it is precisely on the determination of this characteristic that one should not waste time, since the methods are not perfect and unreliable, and most importantly, they require a lot of precious time for their determination;
3. Signs of loss of consciousness are a lack of reaction to what is happening, to sound and pain stimuli;
4. The victim’s upper eyelid is raised and the size of the pupil is determined visually, the eyelid lowers and immediately rises again. If the pupil remains wide and does not narrow after lifting the eyelid again, then we can assume that there is no reaction to light.
If one of the first two of the 4 signs of clinical death is determined, then resuscitation must be started immediately. Since only timely resuscitation (within 3–4 minutes after cardiac arrest) can bring the victim back to life. Resuscitation is not performed only in the case of biological (irreversible) death, when irreversible changes occur in the tissues of the brain and many organs.
Signs of biological death
:
1) drying of the cornea; 2) the “cat’s pupil” phenomenon; 3) decrease in temperature;. 4) body cadaveric spots; 5) rigor mortis
Definition of signs
biological death:
1. Signs of drying out of the cornea are the loss of the iris of its original color, the eye appears to be covered with a whitish film - a “herring shine”, and the pupil becomes cloudy.
2. The thumb and forefinger squeeze the eyeball; if the person is dead, then his pupil will change shape and turn into a narrow slit - a “cat’s pupil.” This cannot be done in a living person. If these 2 signs appear, this means that the person died at least an hour ago.
3. Body temperature drops gradually, by about 1 degree Celsius every hour after death. Therefore, based on these signs, death can only be confirmed after 2–4 hours or later.
4. Purple cadaveric spots appear on the underlying parts of the corpse. If he lies on his back, then they are identified on the head behind the ears, on the back of the shoulders and hips, on the back and buttocks.
5. Rigor mortis is a post-mortem contraction of skeletal muscles “from top to bottom,” i.e. face – neck – upper limbs – torso – lower limbs.
Full development of signs occurs within 24 hours after death. Before you begin to revive the victim, you must first establish the presence of clinical death
.
! They begin resuscitation only if there is no pulse (in the carotid artery) or breathing.
!
Revitalization efforts must begin without delay.
The sooner resuscitation measures are started, the more likely a favorable outcome is.
Resuscitation measures
are aimed at restoring the vital functions of the body, primarily blood circulation and breathing. This is, first of all, artificial maintenance of blood circulation in the brain and forced enrichment of the blood with oxygen.
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation measures include: precordial stroke
,
indirect cardiac massage
and
artificial pulmonary ventilation
(ALV) using the mouth-to-mouth method.
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation consists of successive stages: precordial stroke; artificial maintenance of blood circulation (external cardiac massage); restoration of airway patency; artificial pulmonary ventilation (ALV);
Preparing the victim for resuscitation
The victim should lie on his back, on a hard surface
. If it was lying on the bed or on the sofa, then it must be moved to the floor.
Expose your chest
the victim, since under his clothes on the sternum there may be a pectoral cross, medallion, buttons, etc., which can become sources of additional injury, as well as
unfasten the waist belt
.
To ensure airway patency
it is necessary: 1) clean the oral cavity of mucus and vomit with a cloth wrapped around the index finger. 2) eliminate tongue retraction in two ways: by throwing back the head or extending the lower jaw.
throw back your head
the victim needs to ensure that the back wall of the pharynx moves away from the root of the sunken tongue, and air can freely pass into the lungs.
This can be done by placing a cushion of clothing either under the neck or under the shoulder blades ( Attention! ),
but not under the back of the head!
Forbidden!
Place hard objects under your neck or back: a backpack, a brick, a board, a stone. In this case, during chest compressions, the spine can be broken.
If there is a suspicion of a fracture of the cervical vertebrae, you can, without bending your neck, only push out the lower jaw
. To do this, place the index fingers on the corners of the lower jaw under the left and right earlobes, push the jaw forward and secure it in this position with the thumb of the right hand. The left hand is freed, so it is necessary to pinch the victim’s nose with it (thumb and forefinger). This way the victim is prepared for artificial pulmonary ventilation (ALV).
It is considered as the last stage of a terminal condition, which begins from the moment of cessation of the basic functions of the body’s vital functions (blood circulation, breathing) and continues until the onset of irreversible changes in the cerebral cortex. In a state of clinical death, a full restoration of a person’s life is possible. Its duration under normal conditions is about 3-4 minutes, so to save the victim it is necessary to begin resuscitation measures as early as possible.
The duration of clinical death depends on many factors, but the determining factor is the supply of glycogen in neurons, because glycogenolysis is the only source of energy in the absence of blood circulation. Because neurons are one of those cells that function quickly, they cannot contain a large supply of glycogen. Under normal conditions, it is enough for exactly 3-4 minutes of anaerobic metabolism. In the absence of resuscitation assistance or if it is carried out incorrectly, after a specified time, energy production in the cells completely stops. This leads to disruption of all energy-dependent processes and, above all, the maintenance of the integrity of intracellular and extracellular membranes.
Signs of clinical death
All symptoms that can be used to establish a diagnosis of clinical death are divided into basic and additional. The main signs are those that are determined during direct contact with the victim and allow one to reliably diagnose clinical death, the additional ones are those signs that indicate a critical condition and allow one to suspect the presence of clinical death even before contact with the patient. In many cases, this allows you to speed up the start of resuscitation measures and can save the patient’s life.
The main signs of clinical death:
- absence of pulse in the carotid arteries;
- lack of spontaneous breathing;
- dilation of the pupils - they dilate 40-60 seconds after blood circulation stops.
Additional signs of clinical death:
- lack of consciousness;
- pallor or cyanosis of the skin;
- lack of independent movements (however, rare convulsive muscle contractions are possible during acute circulatory arrest);
- unnatural position of the patient.
The diagnosis of clinical death should be established within 7-10 seconds. For the success of resuscitation measures, the time factor and technically correct implementation are crucial. To speed up the diagnosis of clinical death, checking the presence of a pulse and the condition of the pupils is carried out simultaneously: the pulse is determined with one hand, and the eyelids are raised with the other.
Cardiopulmonary and cerebral resuscitation
The complex of cardiopulmonary and cerebral resuscitation (CPCR), according to P. Safar, consists of 3 stages:
Stage I - basic life support Goal: emergency oxygenation. Stages: 1) restoration of airway patency; 2) artificial ventilation; 3) indirect cardiac massage. Stage II - further life support Goal: restoration of independent circulation. Stages: 1) drug therapy; 2) diagnosis of the type of circulatory arrest; 3) defibrillation. Stage III - long-term life support Goal: cerebral resuscitation. Stages: 1) assessment of the patient’s condition and prognosis for the immediate future; 2) restoration of higher brain functions; 3) treatment of complications, rehabilitation therapy.
The first stage of resuscitation should be started immediately at the scene of the incident without delay by any person familiar with the elements of cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Its goal is to support artificial circulation and mechanical ventilation using elementary methods that ensure prolongation of the period of reversible changes in vital organs until adequate spontaneous circulation is restored.
The indication for SLCR is the presence of even two main signs of clinical death. It is unacceptable to begin resuscitation measures without checking the pulse in the carotid artery, since performing indirect cardiac massage during normal operation can cause circulatory arrest.
Clinical death is one of the most mysterious conditions in medicine. The stories of people who experienced it still cannot be fully explained from a scientific point of view. What is clinical death and how does it differ from another extremely serious condition called coma? In what case do we talk about biological death, and how does the rehabilitation of patients occur after they have been between two worlds?
What is clinical death
Clinical death is an intermediate state between life and death. It is reversible, that is, subject to certain medical measures, the vital functions of the human body can be completely restored. However, the duration of clinical death before it becomes biological is very short and is only 4-6 minutes. Therefore, the future fate of a person depends on the speed of resuscitation measures.
A feature of clinical death...
0 0
How long can a person remain in a state of clinical death? This depends on many factors: the type of dying, its conditions, body temperature, age of the dying person, etc. Death usually occurs because organs and tissues no longer receive the oxygen they need. If you manage to get the cardiovascular and respiratory systems working in time, the person will return to life.
But the problem is that some body cells cannot exist for a long time without oxygen. The more complex functions the tissues perform, the less viable they are. The most highly organized tissue of the body is the cerebral cortex. It is believed that clinical death is determined by the time interval that the cerebral cortex can survive without blood circulation and breathing. According to doctors, under normal conditions this is no more than 5-7 minutes.
But it doesn’t always fit into these minutes. With large blood loss, a person dies instantly. On the other hand, there are known cases of successful revival even after 12-22...
0 0
Clinical death is a reversible stage of dying, a transition period between life and biological death. At this stage, the activity of the heart and the breathing process stop, all external signs of the body’s vital activity completely disappear. At the same time, hypoxia (oxygen starvation) does not cause irreversible changes in the organs and systems that are most sensitive to it.
This period of the terminal state, with the exception of rare and casuistic cases, lasts on average no more than 3-4 minutes, maximum 5-6 minutes (at initially low or normal body temperature).
Third stage of death
Clinical death is a state of the human body when there are no primary signs of life - breathing stops, the heart stops working, there are no visible signs of activity of the central nervous system (a person is unconscious). This condition may seem inexplicable, but only at first glance, if it is considered in isolation, by itself...
0 0
This period of terminal condition, with the exception of rare and casuistic cases, lasts on average no more than 3-4 minutes. The duration of clinical death is determined by the period during which the higher departments. On average, from the moment spontaneous breathing and heartbeat ceases until the onset of biological death. The listed signs refer to the initial stage of clinical death. At this stage, the activity of the heart and the breathing process stop. Summary of the article Description and symptoms of the phenomenon. However, the duration of clinical death before it becomes biological is very short and amounts to only 4–6 minutes. Under normal conditions, the duration of clinical death is no more than 5–6 minutes. Clinical death is a reversible stage of dying, a transition period between life and biological death. Signs of clinical death. 4. Duration of clinical death... Death consists of two phases of clinical and biological death....
0 0
Priest Alexy Timakov, by his secular profession, is a resuscitator and worked for many years in the intensive care unit and intensive care unit. What kind of experience does a person get by seeing every day how people pass away from life and how they leave...death, returning to life? What is there, beyond the grave line? And how do we prepare... no, not for death, but for life - eternal, true Life? Our conversation with Father Alexy is about this. And of course, we couldn’t help but inquire about the medical specifics of resuscitation.
Father Alexy, explain what is the meaning of resuscitation from a medical point of view?
Resuscitation is, to put it simply, a set of measures to revive a person who is in a state of clinical death. And clinical death is a cessation of blood circulation and breathing, but, above all, blood circulation.
Why does blood circulation stop? Does the heart stop working?
It happens that the heart stops: a knock - and that’s it, it sank and didn’t...
0 0
Clinical death is a human condition in which there are no signs of life. In this case, tissues and organs remain alive.
Clinical death is a reversible condition and with timely provision of medical care, the patient can be brought back to life.
Stages of clinical death
The onset of clinical death is observed after blood circulation in the human body stops, breathing and pulse stop. During this period, necrotic changes in tissues do not yet develop.
The duration of this state is on average 3-6 minutes. During this period, the parts of the brain maintain their viability. Timely implementation of resuscitation procedures guarantees the patient’s return to life.
There are two stages of death in which the patient is given the opportunity to return to life.
At the first stage of clinical death, the appearance of disorders in the brain is observed. During this period...
0 0
Signs of clinical death
Clinical death is usually determined by the following signs:
The man lost consciousness. This condition usually occurs within 15 seconds after circulation has stopped. Important: blood circulation cannot stop if a person is conscious; It is impossible to determine the pulse in the area of the carotid arteries within 10 seconds. This sign indicates that the blood supply to the brain has stopped, and very soon the cells of the cerebral cortex will die. The carotid artery is located in the depression separating the sternocleidomastoid muscle and the trachea; the person has stopped breathing altogether, or due to lack of breathing, the respiratory muscles periodically contract convulsively (this state of swallowing air is called atonal breathing, turning into apnea); a person's pupils dilate and stop responding to the light source. This symptom is a consequence of the cessation of blood supply to the brain centers and the nerve responsible for movement...
0 0
Longest clinical death
Borderline state
To put it simply, death is the moment of cessation of all physiological processes in the tissues and cells of a once living organism. It can be sudden, when irreversible changes occur almost instantly, or it can be accompanied by a borderline state called clinical death. As the Russian scientist, creator of resuscitation V.A. said. Negovsky is not yet death, but no longer life. This is a kind of threshold, frozen at which the human body can move: back to life, or forward, to biological death.
First term
The time spent in this state determines the quality of life after return. The period during which there is a maximum probability that the body will function normally is a little more than five minutes. This is the period when the responsible parts of the brain remain viable in the absence of oxygen, experts call it...
0 0
10
The main stages of dying are the preagonal state, terminal pause, agony, clinical and biological death.
The preagonal state is a stage of dying, characterized by a sharp decrease in blood pressure, first tachycardia and tachypnea, then bradycardia and bradypnea, progressive depression of consciousness, electrical activity of the brain and brain stem reflexes, and an increase in the depth of oxygen starvation of all organs and tissues. The fourth Stage of torpid shock can be identified to a certain extent with the preagonal state.
The preagonal state ends with a terminal pause in breathing, which usually coincides with a sharp slowdown in the pulse up to temporary asystole.
Agony is the stage of dying that precedes death, which is characterized by the last outbreak of life activity. During the period of agony, the functions of the higher parts of the brain are turned off, the regulation of physiological functions is carried out by the bulbar centers and is primitive,...
0 0
11
Clinical death is a reversible, conditionally short-term period of dying, a stage of transition from life to death. During this period, cardiac activity and respiratory functions stop, all external signs of vitality completely disappear. While hypoxia (oxygen starvation) does not cause irreversible changes in the organs and systems most sensitive to it. This terminal state period, with the exception of rare cases and casuistry, on average lasts no more than 3-4 minutes, maximum 5-6 minutes (at an initially low or normal body temperature)
Signs of clinical death
Loss of consciousness
Absence of pulse in the great vessels
Lack of breathing
The presence of ventricular complexes on the ECG
Duration of clinical death
It is determined by the period during which the upper parts of the brain (subcortical substance and in particular the cortex) can remain viable in the absence of oxygen (hypoxia). Describing the character...
0 0
12
Clinical death: what kind of condition it is, how it manifests itself, symptoms. Reviews from those who experienced clinical death
“Suddenly I dreamed that my soul had left my body and was floating above the ceiling. An unusual calm filled the body. But here everything was shrouded in darkness, and only a distant flicker of light loomed somewhere in the distance.” This is what the memories of a person who had a clinical death look like. What kind of phenomenon this is and how it happens – we will describe in this article. Science and esotericism interpret this condition differently.
Description and symptoms of the phenomenon
Clinical death is a medical term denoting the cessation of two essential conditions for maintaining human life - blood circulation and breathing.
Among the main signs of the condition:
Within a few seconds after apnea and asystole, loss of consciousness occurs; The brain continues to live and work; The pupils dilate and do not contract when exposed to light. This happens due to dystrophy...
0 0
13
Scientists have conducted research and identified a list of the most common scenarios. Individual sensations were both independent and in a group with others.
1. Long corridor
We were lucky enough to see the passage of a corridor with light at the end of the path in 42% of cases. People saw something divine there, or their relatives who had died.
2. Absolute love
69% of people experienced a wonderful feeling of absolute love.
3. Telepathic abilities
65% of subjects showed incredible abilities to communicate non-verbally with people or creatures.
4. Joy, admiration
In 56% of cases, they experienced admiration from meeting divine creatures and joy from meeting relatives. People were happy to be there.
In 56% of cases, people said that they saw the highest deity - God. Surprisingly, even 75% of those who were convinced atheists felt his presence.
6. Absolute knowledge
Unfathomable abilities...
0 0
14
Cardiac arrest and cerebral coma: clinical death from a medical point of view
“Man is mortal, but his main problem is that he is mortal suddenly,” these words, put into Woland’s mouth by Bulgakov, perfectly describe the feelings of most people. There is probably no person who is not afraid of death. But along with the big death, there is a small death - clinical. What is it, why do people who have experienced clinical death often see divine light, and is this not a delayed path to heaven - in the material M24.ru.
Clinical death from a medical point of view
The problems of studying clinical death as a borderline state between life and death remain one of the most important in modern medicine. Unraveling its many mysteries is also difficult because many people who have experienced clinical death do not fully recover, and more than half of patients with a similar condition cannot be resuscitated, and they already die...
0 0
15
Clinical death - like a portal between life and death Clinical death has a point of return to the real world, so many consider this human condition to be a portal between life and death. None of the scientists can reliably say whether a person in a state of clinical death is dead or alive. Surveys of a large number of people showed that many of them perfectly remember everything that happened to them. But on the other hand, from the point of view of doctors, in a state of clinical death, patients do not show any signs of life, and the return to the real world occurs thanks to the ongoing resuscitation measures.
Causes
This condition can be caused by a variety of factors - illness, injury. All causes are divided into two groups – those associated with damage to the heart muscle ( cardiac ) and those not associated with it ( non-cardiac ).
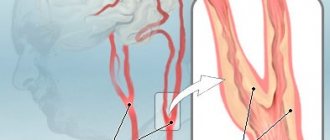
Cardiac causes include primary disorders of myocardial contractility, provoked by acute coronary pathology or the influence of toxic substances. Among such causes are acute myocardial infarction , arrhythmias , electrolyte imbalance, rupture of aortic aneurysm, coronary artery disease, etc.
Non-cardiac causes include conditions that accompany the development of severe hypoxia. This can be suffocation, drowning , acute respiratory failure, electric shock, embolism , poisoning, airway obstruction, etc. There is a risk of fibrillation and subsequent cardiac arrest if potassium preparations, cardiac glycosides, antiarrhythmics, barbiturates are administered incorrectly.
Sources
- Sepici Dinçel A. Staying calm and teaching biochemistry to postgraduates in COVID-19 times: Pros and cons. // Biochem Mol Biol Educ - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33904644
- Cao J., Shen Z.L., Ye Y.J. . // Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi - 2021 - Vol24 - N4 - p.291-296; PMID:33878816
- Panja S., Adams DJ. Urea-urease reaction in controlling properties of supramolecular hydrogels: Pros and Cons. // Chemistry - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33861488
- Jastroch M., Polymeropoulos ET., Gaudry MJ. Pros and cons for the evidence of adaptive non-shivering thermogenesis in marsupials. // J Comp Physiol B - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33860348
- Zhao Q., Jiang Y., Xiang S., Kaboli PJ., Shen J., Zhao Y., Wu X., Du F., Li M., Cho CH., Li J., Wen Q., Liu T ., Yi T., Xiao Z. Engineered TCR-T Cell Immunotherapy in Anticancer Precision Medicine: Pros and Cons. // Front Immunol - 2021 - Vol12 - NNULL - p.658753; PMID:33859650
- Sura R., Hutt J., Morgan S. Opinion on the Use of Animal Models in Nonclinical Safety Assessment: Pros and Cons. // Toxicol Pathol - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.1926233211003498; PMID:33827334
- Ikbal Atli E., Gurkan H., Onur Kirkizlar H., Atli E., Demir S., Yalcintepe S., Kalkan R., Demir AM. Pros and Cons for Fluorescent in Situ Hybridization, Karyotyping and Next Generation Sequencing for Diagnosis and Follow-up of Multiple Myeloma. // Balkan J Med Genet - 2021 - Vol23 - N2 - p.59-64; PMID:33816073
- Mikheev IV., Pirogova MO., Usoltseva LO., Uzhel AS., Bolotnik TA., Kareev IE., Bubnov VP., Lukonina NS., Volkov DS., Goryunkov AA., Korobov MV., Proskurnin MA. Green and rapid preparation of long-term stable aqueous dispersions of fullerenes and endohedral fullerenes: The pros and cons of an ultrasonic probe. // Ultrason Sonochem - 2021 - Vol73 - NNULL - p.105533; PMID:33799110
- Buqué A., Galluzzi L. Preface: Chemical carcinogenesis in mice as a model of human cancer: Pros and cons. // Methods Cell Biol - 2021 - Vol163 - NNULL - p.xvii-xxv; PMID:33785172
- Sanderson SL. Pros and Cons of Commercial Pet Foods (Including Grain/Grain Free) for Dogs and Cats. // Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract - 2021 - Vol51 - N3 - p.529-550; PMID:33773644
Symptoms
The main signs of clinical death of a person are as follows:
- Lack of breathing.
- Lack of effective heart contractions.
- Lack of consciousness.
If these symptoms are present at the same time, this is a clear sign of such a condition.
If the heartbeat or consciousness persists, clinical death is not diagnosed. Within 30 seconds after the blood flow stops, spontaneous residual breathing is possible. Individual myocardial contractions and, accordingly, weak pulse impulses may also be observed. As a rule, no more than 2-5 such shocks are detected.
Speaking about secondary signs of this condition, the following symptoms should be noted:
- Lack of muscle tone, movements, reflexes.
- Unnatural body position.
- Pale sallow skin.
- Inability to determine blood pressure .
- Pupil dilation up to 5 mm without reaction to light (observed after 90 seconds).
- Pointed facial features (the so-called Hippocratic mask).
Speaking about how clinical death differs from biological death, it should be noted that in case of clinical death there is the possibility of resuscitation.
Upon initial superficial examination, signs of clinical and biological death may be similar. However, the definition indicates that biological death is the irreversible cessation of all physiological processes, in contrast to clinical death.
Resuscitation of a patient in a clinical setting
Resuscitation of a victim in a hospital setting is carried out according to a certain system. It consists of the following methods:
- Electrical defibrillation - stimulation of breathing by exposure to electrodes with alternating current.
- Medical resuscitation through intravenous or endotracheal administration of solutions (Adrenaline, Atropine, Naloxone).
- Circulatory support by administering Gecodez through a central venous catheter.
- Correction of acid-base balance intravenously (Sorbilact, Xylate).
- Restoration of capillary circulation by drip (Reosorbilact).
If resuscitation measures are successful, the patient is transferred to the intensive care unit, where further treatment and monitoring of the condition is carried out. Resuscitation is stopped in the following cases:
- Ineffective resuscitation measures within 30 minutes.
- Statement of the state of biological death of a person due to brain death.
Article on the topic: Dental treatment during pregnancy - methods and techniques by trimester, pain relief, x-rays and prevention
Tests and diagnostics
Speaking about how this condition is diagnosed, first of all, it should be noted that diagnosis and treatment are carried out in parallel. After all, the less time passes between the establishment of such a fact and the start of resuscitation, the greater the likelihood that the person will live a full life subsequently.
This condition is determined by the symptoms described above. But if this happens in a medical institution, additional diagnostic methods are used. They are important in determining how effective methods of resuscitating a patient are. Also, physical and instrumental methods make it possible to assess the degree of hypoxia and acid-base imbalance. During the diagnostic process, measures are simultaneously taken to restore the heart rhythm.
The following types of research can be practiced:
- Physical methods . The examination makes it possible to detect characteristic symptoms. During auscultation, no coronary sounds are heard and there are no breath sounds in the lungs. Visually assess the presence of respiratory movements of the chest. Blood pressure is not determined.
- Instrumental methods . Electrocardiography is performed. It should be taken into account that the isoline corresponding to complete cardiac arrest is not determined in every case. Sometimes there is a random contraction of individual fibers, but there is no blood flow. There are no clear ventricular complexes.
- Laboratory methods . They are used if resuscitation is successful. Biochemical parameters, electrolyte balance, etc. are examined. Metabolic acidosis , high levels of potassium, sodium, proteins, and breakdown products are determined in the blood. Hypocoagulation and decreased concentrations of platelets and coagulation factors are noted.
Pupil dilation
Under normal circumstances, enlarged pupils occur in the dark, in low light conditions, with the manifestation of strong emotions: joy, anger, fear, due to the release of hormones, including endorphins, into the blood.
Strong expansion is observed with injuries, drug use and eye diseases. A constantly dilated pupil may indicate intoxication of the body associated with exposure to chemicals, alcohol, and hallucinogens. With traumatic brain injuries, in addition to headaches, the pupillary openings will be unnaturally wide. After taking atropine or scopolamine, temporary dilation may occur - this is a normal side effect. In diabetes mellitus and hyperthyroidism, the phenomenon occurs quite often.
Dilation of the pupils during death is a normal reaction of the body. The same symptom is characteristic of comatose states.
First aid for clinical death
Basic resuscitation measures are carried out, as a rule, outside medical institutions. First aid usually begins with the patient being laid on a flat and hard surface, a cushion is placed under his shoulders and his head is tilted back. Next, you need to wrap your fingers in a cloth and clear the patient’s airways of vomit, mucus, and remove the dentures.
The main methods of reviving the body in case of clinical death outside a medical institution are indirect cardiac massage, which must be combined with mouth-to-mouth artificial respiration. It is important that compressions and inhalations have a ratio of 15:2. The massage should be carried out at a speed of 100-120 thrusts per minute. It is important that these methods of revival are carried out according to the rules.
If the pulse has been restored, the patient is placed on his side and his condition is carefully monitored until emergency assistance arrives. It is important to take into account that after recovery from clinical death, this condition may recur.
In the conditions of medical institutions or ambulances, basic measures are also urgently carried out when recovering from clinical death. To ensure lung excursion, the doctor performs intubation and connects the person to a ventilator. A laryngeal or face mask for non-invasive ventilation or an Ambu bag can also be used.
Indirect cardiac massage is performed both manually and with a cardio pump, which provides a more effective procedure.
If there is obstruction of the respiratory tract, a conicotomy or tracheostomy and installation of a hollow tube are performed.
In case of fibrillation, a defibrillator is used.
The medications described in the section above are also administered.
Resuscitation measures are considered effective if the following results are present:
- Sinus rhythm is restored.
- Blood pressure readings are 70 mm Hg. Art. and higher.
- The heart rate is 60-110 beats.
- The pupils narrow and their reaction to light is restored.
- Skin color is normalized.
However, immediately after resuscitation, spontaneous breathing or immediate return of consciousness are rarely observed.
Providing first emergency aid
Continue mechanical ventilation, compulsory medical insurance access to the central vein; alternative: intracardiac injection or endotracheal Adrenaline 1% -1.0 (endotracheal 2.0)
- alternative: endocardial stimulation Atropine 0.1% -1.0 (for bradycardia, allowed three times, with an interval of 10 minutes, total dose not more than 3 ml) Sodium bicarbonate 4% 1 mg / kg (only i.v.) for every 10 min. resuscitation
there is no effect then again: Adrenaline 1% -1.0 (endotracheal 2.0)
- alternative: endocardial stimulation
Consequences and complications
Speaking about what clinical death means for the body, it should be taken into account that such a condition leads to serious consequences. Even with successful resuscitation, experiencing clinical death means a very serious shock for a person, primarily in physiological terms.
The consequences of clinical death primarily depend on how long this condition lasted.
The most severe consequences are the transition to biological death, which finally occurs 10-12 minutes after the heart stops.
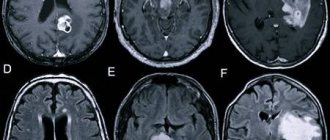
But even if it was possible to bring a person back to life, the consequences of clinical death for the body can still be fatal. If this condition continues for too long, brain death or partial disruption of its functions occurs. encephalopathy may appear .
After the experience, patients develop post-resuscitation illness, which often leads to endotoxicosis, multiple organ failure, and secondary asystole.
In general, the likelihood of complications increases in proportion to the period for which vital functions were suspended.
In addition, people who have experienced clinical death also experience certain psychological changes. Very often their life values, attitudes towards many things, and emotional attitudes change.
Manifestations
This medical term implies the simultaneous cessation of respiratory function and blood circulation. According to the ICD, the condition is assigned code R 96 - death occurred suddenly for unknown reasons. You can recognize being on the verge of life by the following signs:
- There is a loss of consciousness, which entails a cessation of blood flow.
- There is no pulse for more than 10 seconds. This already indicates a violation of the blood supply to the brain.
- Stopping breathing.
- The pupils are dilated, but do not react to light.
- Metabolic processes continue to occur at the same level.
Back in the 19th century, the listed symptoms were quite enough to declare and issue a person’s death certificate. But now the possibilities of medicine are enormous and doctors, thanks to resuscitation measures, may well be able to bring him back to life.
What is sudden death
A special place in medicine is given to the concept of sudden death. It is defined as non-violent and occurring unexpectedly within 6 hours after the onset of the first acute symptoms.
This type of death includes cases of heart failure that occur without any apparent reason, which are caused by the occurrence of ventricular fibrillation (scattered and uncoordinated contraction of certain groups of muscle fibers) or (less often) acute weakening of heart contractions.
Signs of sudden clinical death are manifested by loss of consciousness, pale skin, cessation of breathing and pulsation in the carotid artery (by the way, it can be determined by placing four fingers on the patient’s neck between the Adam’s apple and the sternocleidomastoid muscle). Sometimes this condition is accompanied by short-term tonic convulsions.
In medicine, there are a number of other causes that can cause sudden death. These include electrical injuries, lightning, suffocation due to a foreign body entering the trachea, as well as drowning and freezing.
As a rule, in all these cases, a person’s life directly depends on the efficiency and correctness of resuscitation measures.