Last update: 02/21/2021
Hemorrhagic diathesis is a category of diseases that are in one way or another associated with increased bleeding of the body.
If a person has hemorrhagic diathesis, deviations in the functioning of the hematopoietic system are observed, leading to disruption of the blood clotting process, frequent external, subcutaneous and internal bleeding. The diagnosis of hemorrhagic diathesis and their treatment should be carried out exclusively by a doctor - self-medication is inappropriate here.
Hemorrhagic diathesis: classification
There are two groups of hemorrhagic diathesis, caused by hereditary (primary) and acquired (secondary) deviations from the norm. In the first case, the main role is given to congenital genetic defects (for example, problems with platelet development, as well as abnormalities in plasma clotting factors).
In the second case, the trigger for the development of hemorrhagic diathesis is autoimmune diseases, taking certain medications, damage to the walls of blood vessels by toxins, and so on.
As for the mechanism of development of the disease, the following forms of hemorrhagic diathesis are distinguished:
- Caused by disruptions in the functioning of platelet hemostasis (autoimmune thrombocytopenia, thrombasthenia).
- Caused by a violation of the integrity of blood vessels (hemorrhagic vasculitis, Randu-Osler disease).
- Appeared as a result of a violation of the plasma hemostasis (congenital and acquired coagulopathies).
- Hemorrhagic diathesis caused by combined disorders (von Willebrand disease).
Hemorrhagic diathesis in children
Quite often, hemorrhagic diathesis occurs in childhood. Viral and bacterial infections and medications (sulfonamides, butadione, quinine, dopegit, etc.) contribute to the development of the disease.
However, there are also congenital forms of diathesis, when problems with blood clotting can be caused by heredity.
You cannot let hemorrhagic diathesis take its course, even if you are sure that this is an age-related disorder that will go away over time. It is necessary to undergo a laboratory blood test and carefully monitor the manifestations of this functional abnormality.
Diagnosis of diathesis
In order to make a diagnosis of atopic dermatitis, you must have:
- Allergy burden.
- A typical rash, which is located in typical places.
- A clinical blood test shows eosinophilia (increased levels of cells responsible for allergies).
- An increase in the blood level of allergen-specific IgE antibodies, which also increase with allergies.
- Positive skin tests with allergens (so-called “prick tests”). They are the gold standard in confirming allergies. The essence of the method is that a healthcare worker applies small punctures with allergens to the patient’s skin and evaluates the reaction. If a reaction occurs, the test can be considered positive.
Hemorrhagic diathesis: causes
Most often, problems associated with bleeding are based on abnormalities in the process of blood clotting - the so-called disaggregation forms of thrombocytopathy. A tendency to hemorrhagic diathesis may be due to the presence of diseases such as leukemia, hemorrhagic vasculitis, hemophilia, and so on.
In addition, common causes of hemorrhagic diathesis include the following:
- Taking certain medications (for example, anticoagulants that thin the blood).
- Congenital pathologies of blood vessels and hematopoietic system.
- Violation of the permeability of the walls of blood vessels.
- Vitamin C deficiency.
- Deviations in the functioning of the liver and spleen.
- Some autoimmune, infectious and viral diseases.
- Damage to the vascular system during fever.
Diagnosis of hemorrhagic syndrome
A timely diagnosis will help a specialist prescribe effective treatment, and you will be able to make your blood vessels healthy once and for all. The diagnosis can be confirmed or refuted by passing a series of laboratory tests aimed at obtaining detailed information about the state of the blood. You will also need to conduct coagulation tests; during controversial situations, the diagnostician may perform a sternal puncture for in-depth diagnostics.
After obtaining a complete picture of the disease, determining its stage, causes and severity of hemorrhagic syndrome, treatment will be prescribed.
Treatment of hemorrhagic syndrome
The basis for choosing a treatment method for hemorrhagic syndrome is determining the cause of the disease, but there are the following key principles:
- Regardless of the cause, the patient is provided with emergency medical care to stop the bleeding. For this, vikasol, calcium chloride, vitamin C, and thromboplastin solution are used.
- If pathology occurs while taking potent medications, their discontinuation is mandatory.
- Local therapy for hemorrhages is carried out using dry thrombin, homeostatic sponges, aminomethylbenzoic acid (Amben).
- In case of heavy blood loss, transfusion of blood or its fractions may be necessary, preferably directly from the donor.
- Also, for hemorrhagic syndrome of various etiologies, serotonin preparations, for example, Dynaton, are used.
Prevention of hemorrhagic syndrome
The most important and fundamental part of the prevention of hemorrhagic syndrome is a complete medical examination for the timely identification and elimination of its possible causes.
Newborn premature babies need subcutaneous vitamin K and breastfeeding as soon as possible after birth.
The dietary nutrition of patients prone to this pathology should be based on increased consumption of vitamin K, as well as proteins, vegetables and fruits. In addition, such people need to avoid physical activity that leads to injury and injury.
You may also be interested in
Acute intestinal obstruction
A pathological condition that is characterized by a violation of the passage of the contents of the gastrointestinal tract in the direction from the stomach to the anus
More details
Intestinal paresis
Intestinal paresis is a condition that accompanies many serious diseases and is characterized by a gradual decrease in the tone of the intestinal wall and paralysis of the intestinal muscles
More details
Symptoms of hemorrhagic diathesis
The clinical picture usually looks like this:
- The appearance of reddish-pink rashes on the body and mucous membranes.
- Hematomas of unknown nature.
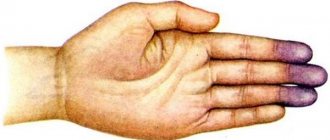
- Subcutaneous bleeding.
- Ulcers may appear.
- Presence of blood in the urine.
- Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting.
- Hemorrhage in the joint cavity is also possible.
- Redness of the retina.
- In especially severe cases, hemorrhages into internal organs occur.
As for the types of bleeding with a particular type of hemorrhagic diathesis, we can distinguish:
- Hematoma type. It manifests itself as painful, intense hemorrhages in both soft tissues and joints - typical for hemophilia A and B.
- Microangiomatous type. Most often occurs in the presence of a hereditary hemorrhagic form of diathesis. Manifests itself in the form of frequent recurring bleeding.
- Mixed type. The clinical picture with this type of bleeding is the appearance of a small red rash and extensive hematomas.
- Petechial-spotted (bruised) - characteristic of thrombocytopenia, thrombocytopathies and some bleeding disorders (exceptionally rare) - hypo- and dysfibrinogenemia, hereditary deficiency of factors X and II, sometimes VII;
- The vasculitic purpuric type is characterized by hemorrhages in the form of a symmetrical pinpoint rash, possibly associated with nephritis and intestinal bleeding; observed in infectious and immune vasculitis.
On our website you can find photos of hemorrhagic diathesis that clearly demonstrate the different types of manifestation of this reaction of the body.
Hemorrhagic diathesis: treatment
Before starting treatment, it is important to successfully diagnose. This may require the following:
- Conducting general laboratory and biochemical tests of blood and urine.
- Determination of the time required for blood clotting and the duration of bleeding. Carrying out a coagulogram.
- Carrying out immunological, as well as thromboplastin generation, prothrombin and thrombin tests.
After passing these examinations, the doctor can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment. It may include taking certain medications (for example, iron supplements, corticosteroids) and vitamin complexes and supplements, as well as more radical methods: for example, joint puncture, transfusion of plasma or red blood cells, or surgical removal of the spleen.
When diagnosing hemorrhagic diathesis, it is important to carry out preventive measures that can strengthen the body and increase its protective functions. These include hardening, moderate physical activity and exercise, a balanced diet with a carefully selected vitamin composition. In addition, it is especially important to protect the body from the possibility of infection with viral diseases in the autumn-spring period. To do this, it is recommended to take specially selected vitamin complexes.
Pharmacy products from La Cree cannot be considered fully medicinal, but they can provide high-quality care for skin damaged by hemorrhagic diathesis. Since La Cree skin products are made from natural ingredients and do not contain dyes, parabens or fragrances, creams and gels of this brand help to delicately cleanse the skin and relieve signs of redness and irritation.
Prevention
The following measures are recommended as preventive measures: strengthening the body’s defenses by hardening, playing sports or doing physical exercises, and organizing a balanced diet. It is also recommended to use multivitamin complexes or individual vitamins during the period of seasonal deficiency of these substances in food (in winter and early spring) and to maintain personal hygiene in order to prevent infection with viral or bacterial infections.
Clinical researches
The effectiveness, safety and tolerability of La-Cri products have been clinically proven. The products are recommended by the Union of Pediatricians of Russia; many products can be used in children from birth.
Sources:
- B.A. Shamov, I.G. Safiullina, A.B. Beshimova, T.B. Shamov, Differential diagnosis of atopic dermatitis, journal of Practical Medicine, 2011 https://cyberleninka.ru/article/v/differentsialnaya-diagnostika-atopicheskogo-dermatita
- Fokina R.A., Atopic dermatitis: stages of development of classification forms, Siberian Medical Journal, 2007 https://cyberleninka.ru/article/v/atopicheskiy-dermatit-etapy-razvitiya-klassifikatsionnyh-form
- A.N. Pampura, A.A. Chuslyaeva, Modern approaches to the treatment of atopic dermatitis in children https://cyberleninka.ru/article/v/sovremennye-podhody-k-terapii-atopicheskogo-dermatita-u-detey
Photos of diathesis
Photo album on the disease