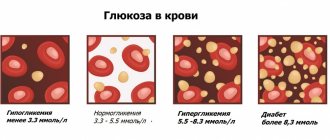
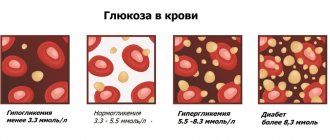
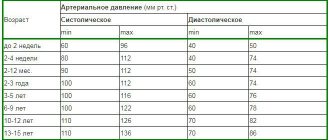
What is called pulse
When the heart muscles contract, the walls of the blood vessels vibrate in a certain rhythm and with a certain force.
These fluctuations are called the pulse, an indicator of the work of the heart and the condition of the blood vessels. Normally, there should be equal intervals between pulsations. Among the causes of disturbances in the rhythm of oscillations of the vascular walls:
- heart pathology
- problems with blood vessels
- endocrine system diseases
- intoxication
- tachycardia of a heavy smoker
- heavy physical activity
- trauma with blood loss
- acute cold
- severe stress, etc.
Any disturbance in heart contractions signals that something is wrong in the body. You should definitely consult a doctor. But first of all, learn how to measure your pulse correctly.
Pulse is an indicator of the work of the heart and blood vessels.
Indicators after waking up
The morning hours are the calmest, the time when people wake up in a peaceful state. But the pulse, both in adults and in children, is observed to be rapid. This is a completely normal situation due to a sudden awakening. After 5-10 minutes, the pulse beats normalize and stabilize.
After waking up, the body's functions switch to daytime mode and begin their activity. If the pulse quickens, this may be the result of restless dreams, which are most often caused by stress, anxiety, emotional arousal, or indicate cardiac problems responsible for blood circulation.
Cardiologists do not recommend a sharp rise to a vertical position; this puts a lot of stress on the heart muscle. Natural recovery consists of a gradual awakening; after waking up completely, you need to lie down for a few minutes to restore cardiac functions.
There are situations when, after waking up, weak pulse beats are observed. In order to raise them to a normal level, they do morning exercises and yoga. A pulse of 40 beats per minute is a reason to consult a doctor.
Athletes and those who are actively involved in physical education have larger hearts than those who are indifferent to training. This is due to the fact that the heart is a muscular organ. With moderate loads, it increases in size, as a result, it safely pumps blood, which normalizes blood pressure. The most important thing is that it strengthens the entire cardiovascular system.
How to measure your pulse manually
- The subject of measurement is the number of pulsations per minute, at rest. For more accurate calculations, use a stopwatch.
- Manual pulse measurements are usually taken from the inside of the wrists of the left and right hands, more precisely, in the area of the radial artery, close to the skin - at the base of the thumb.
- With rhythmic pulsations, you can count how many beats (oscillations of the vascular walls) there were in 30 seconds and double the result.
- For non-rhythmic pulsations, it is recommended to count the beats for a minute.
- In some cases, it is possible to measure the pulse in the area of other arteries located close to the skin on the neck (posterior edge of the sternocleidomastoid muscle), temple, thigh, elbow, under the collarbone, in the groin at the edge of the pubis.
Tachycardia and bradycardia
When the pulse rate changes up or down, they speak of a rhythm disturbance. Tachycardia is an increase in the number of heart contractions over 90-100 beats per minute. It can be physiological, occurring in response to a provoking factor, or pathological. In the first case, a rapid pulse is caused by stress, increased ambient temperature, physical activity, hard work or psycho-emotional experiences. If your heartbeat is normal at rest, there is nothing to worry about. Sometimes an increase in rhythm is provoked by eating, drinking caffeine-containing drinks or alcohol, since such factors are an external irritant for the human body.
The pathological form of tachycardia has no connection with the above reasons, which indicates a cardiovascular disease, an endocrine disorder or concomitant pathology. Often observed in persons with congenital or acquired heart defects, with hypertension, angina pectoris, thyrotoxic crisis or after bleeding. In this case, it is a symptom of the disease.
Bradycardia is a slow heart rate of less than 60 per minute. Normally, it can only manifest itself in physically trained individuals, professional athletes who exercise regularly and for a long time. Pathological indicates a heart rhythm disturbance, atrioventricular block, weakness of the sinus node or a complication of coronary artery disease (CHD), a consequence of a heart attack, intoxication, or valvular disease. In both cases, an examination is required to identify the causes of the disorder and treatment by a specialist.
Pulse measurement with a tonometer
You can conveniently and quickly measure fluctuations in the vascular walls using a special electronic tonometer, which displays blood pressure and pulse indicators on the screen. Depending on the type of model, it can be worn on the wrist or shoulder.
For an untrained adult, a normal heart rate is considered to be between 60 and 80 beats per minute.
It is necessary to strictly follow the instructions for the device. Regardless of the type of tonometer, when measuring your pulse, follow the following important rules:
- do calculations at rest, being relaxed
- take a sitting position
- empty your bladder beforehand
- an hour before measurement, do not consume caffeine, alcohol, or nicotine
- keep your elbow approximately at heart level
- If you want to measure your pulse again, do so after at least 5 minutes.
Remember that when a serious illness is detected, the doctor will not limit himself to simply counting the pulse and recommends more in-depth examinations, for example, undergoing an electrocardiography procedure or doing a so-called treadmill test, that is, a study of the functioning of the heart and blood vessels on a treadmill.
A tonometer will help you accurately determine your heart rate.
What is pulse
Pulse is a jerky oscillation of the walls of blood vessels that occurs as a result of the flow of blood after it is expelled from the cardiac cavities and enters the large main and then peripheral arteries.
The nature of the pulse wave propagation and the number of its repetitions depends on the cardiac cycle, due to which, when indicators change, disorders in the human body are judged. Unlike the heart rate (HR), which reflects only the number of heart beats in one minute, the pulse shows the number of waves and impulses occurring in the arteries in the same unit of time. Pulse diagnostics are widely used in modern medicine. In addition to the traditional manual method of determination by palpation on the radial, carotid, femoral or temporal artery, a hardware examination is carried out. To do this, use a pulse oximeter, heart rate monitor or electrocardiograph, each of which helps to anticipate the number of wave oscillations per minute.
Normal heart rate in adults and children
Heart rate can depend not only on diseases, but also on many other factors. In particular, on gender and age, body weight and temperature, diet and even the environment. For example, people who are professionally involved in sports have a faster heart rate than untrained people; The pulse quickens in the afternoon and slows down at night.
In order for anyone to determine whether their pulse is normal, they should first take into account their age.
The norm for children is:
- in newborns - from 110 to 160 beats per minute
- in infants from 1 month to 1 year – from 100 to 150
- children from 3 to 8 years old – from 70 to 125
- children from 9 to 11 years old – from 60 to 100
- teenagers from 12 to 15 years old – from 55 to 95
in adults:
- up to 50 years – from 64 to 84
- up to 60 years – from 64 to 84
- after 60 – from 69 to 89
Features of bradycardia
A slowing of the heart rate to 50 beats or below is called bradycardia. It is a sign of physiological and pathological factors. In the first case, the list of reasons for a decrease in heart rate is as follows:
- During sleep, a person's metabolism slows down, body temperature drops slightly and heart rate decreases by about 10% of normal. The reason for the change in indicators is the complete relaxation of the body.
- Stimulating reflex zones (eyeballs, carotid artery) can inadvertently cause a slight slowing of the pulse.
- In older people, bradycardia can be a consequence of age-related cardiosclerosis. Areas of connective tissue scattered throughout the myocardium impair cardiac contractility, which contributes to a decrease in heart rate
- When exposed to cold for a long time, the heart rate slows down as a protective reaction. The body begins to save resources in order to resist adverse effects longer.
- Constant physical activity forces the heart to work harder than it should. Tissue hypertrophy begins, against the background of which bradycardia develops. For professional athletes, a heart rate in the region of 40-45 beats per minute is considered normal.
The pathological form of bradycardia is a consequence of the following factors:
- inflammatory diseases of the heart muscle;
- myocardial infarction;
- taking antihypertensive medications;
- impulse conduction disturbance;
- hypothyroidism (thyroid hormone deficiency);
- hypotension (low blood pressure);
- stomach ulcer;
- high intracranial pressure.
If it is not possible to identify the causative factor, a diagnosis of “idiopathic bradycardia” is made. If it is not accompanied by other disorders and the symptoms are not particularly pronounced, then it is also equated to physiological forms.
Slow and fast heartbeat
The heart muscle can contract at an increased (tachycardia) or decreased (bradycardia) rhythm. If the pulse does not correspond to the norm, there is no need to immediately sound the alarm: the reason may be not only in pathology, but also in the physiology of the female or male body. Thus, some increase in heart rate is observed when women reach menopause, or when estrogen levels decrease; slowing of the pulse - when taking certain medications.
Various physical and mental stress affect the heart rate, even the difficult digestion process after a heavy holiday dinner and the use of energy drinks. Typically, physiological causes of abnormal heart rate are temporary. After 45 minutes, the pulse readings can return to normal.
Record your heart rate readings on both hands - this will allow you to get more accurate data when measuring this indicator manually.
Clinical practice shows that the pulse often increases when the nervous system is damaged, cardiac pathology, or hormonal system disorders. It is possible that with high readings a tumor or some kind of infection develops in the body.
The pulse slows down if the body experiences intoxication, peptic ulcer disease, or increased intracranial pressure, myocardial infarction develops. Perhaps this signals a lack of thyroid hormones, organic damage to the heart, or poor oxygen supply to tissues.
Only a specialist can answer the question why your pulse is too fast or too rare. In any case, consult a doctor immediately if your pulse is abnormal:
- dyspnea
- my head is spinning
- fainting or presyncope
- heart pain
- vision problems
When playing sports, it is important to regularly measure your pulse.
Features in men and women
An important factor that is taken into account when making a verdict about the normal or pathological pulse is the gender of the person. Due to anatomical and physiological characteristics, the number of pulse oscillations per minute differs, which is due to:
- Different heart sizes . In men, the size of the heart cavities is slightly larger, due to which a larger volume of blood is expelled into the great vessels in one minute and fewer contractions are required for this. Normally, women's pulse is 7-10 beats faster. The exception is professional athletes, who, due to constant training and frequent exercise, develop compensatory bradycardia and the indicator is equal to the norms of men.
- Hormonal imbalance can provoke changes in heart rate in women as they age. Pregnancy, especially in the second and third trimester, physiologically represents a significantly increased load on the cardiovascular system and the entire body, which is manifested by an increased heart rate and, as a consequence, a frequent pulse rhythm. During menopause and menopause, an imbalance of estrogen, progesterone, luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormone occurs, which has a provoking effect on the cardiovascular system. Symptoms of hot flashes, nervousness, and sleep disturbances appear.
- Frequent, heavy menstruation with loss of a larger volume of blood is the cause of anemia, the main symptom of which is rapid heartbeat and pulse.
- Mental characteristics , susceptibility to frequent mood swings and experiences in the fairer sex are more pronounced, which is manifested by changes in pulse during stress. In men, the provoking factor is often physical activity, overwork due to lack of rest and sleep, or caffeine/alcohol consumption. Another cause of tachycardia or bradycardia is vegetative-vascular dystonia, in which a disorder of the nervous system manifests itself as a more frequent or rare pulse.
- Another indicator that should be taken into account when assessing heart rate norms is body weight . Anatomically, an increase in the load on the heart and the need to deliver blood to a larger area of cells, tissues and muscles requires an increase in heart rate and, as a result, a more frequent pulse rate. Therefore, individuals with obesity and concomitant hypertension have an extremely high risk of developing cardiac complications.