Food poisoning is a pathological condition that occurs as a result of consuming low-quality, spoiled foods contaminated with pathogenic microorganisms and their waste products. The disease is not contagious, which means it is not transmitted from one person to another.
Most often, poisoning is caused by bacteria of the E. coli group, clostridia, staphylococci and salmonella.
Main symptoms of poisoning
When poisoned food enters the body, toxins enter the intestines, and from there through the mucous membrane they penetrate into the systemic bloodstream, causing clinical manifestations. The following symptoms are observed for food poisoning:
- Dyspeptic syndrome (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea).
- Weakness, malaise, decreased performance.
- Paleness of the skin.
- Increased heart rate and respiratory movements.
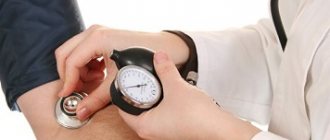
- Reduced blood pressure.
- Pain in the abdominal area.
- Increased body temperature.
In severe cases, the development of visual disturbances, the appearance of hallucinations and disturbances of consciousness (stupor, stupor, coma) are possible. If emergency assistance is not provided to the patient in such a situation, death is possible.
Enterosgel and food poisoning
Doctors consider Enterosgel sorbent one of the most effective drugs for combating intoxication! Scientists have proven the effectiveness of using this drug in patients with food poisoning.
Enterosgel has a positive effect on the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines, helps improve the processes of digestion and absorption of food and restores intestinal flora. Enterosgel has no side effects, has no contraindications, can be used in children and pregnant women in the complex treatment of food poisoning and does not change the color of stool, which is important for diagnosis.
First aid for poisoning
Providing emergency assistance for food poisoning is an extremely important event. This way you will cope with the disease faster and avoid complications.
Algorithm:
- Stomach cleansing. To do this, you need to drink a warm, weak solution of soda or potassium permanganate in a volume of 500 ml, and then induce vomiting. The procedure should be repeated until the wash water is clear.
- Taking sorbents (activated carbon, Filtrum) and enveloping drugs (Almagel).
- Drink plenty of fluids (clean water, warm tea, fruit infusions).
- Peace. The patient must be given a comfortable position in bed and ensure maximum comfort.
During the first day of illness, you should refrain from eating. Only drinking is allowed. Starting from the second day, you can start feeding the patient with vegetable soups and weak broths. When symptoms subside, the diet should be expanded, excluding fatty, smoked and salty foods from the menu. Carbonated drinks and coffee are also contraindicated.
When is it necessary to see a doctor?
The victim can survive some poisonings on his own if competent first aid is provided at home in a timely manner, or if the amount of food eaten was insignificant.
Calling an ambulance is mandatory if, during first aid measures for fish poisoning, the victim’s temperature rises to 39 degrees or higher.
In cases where initially a person felt mild signs of poisoning, washed his stomach, took sorbents, but over time he only gets worse, weakness, chills, dizziness, clouding of consciousness appear, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor.
In addition, you must call an ambulance if:
- elderly people and children were poisoned;
- poisoning is caused by poisonous fish species;
- there are increasing symptoms of dehydration;
- The victim shows signs of damage to the nervous system.
At home, it is impossible to fully cleanse the body of the poisons that have entered it, and compensate for the harm that intoxication has caused it. In a medical institution, doctors with a whole arsenal of medicines and manipulations enter the fight for the life and health of the victim.
Glucose solutions, vitamins, and saline solutions are administered intravenously.
Treatment
Treatment of food poisoning must be comprehensive. To do this, you must follow a strict diet and take the necessary medications. You can also turn to traditional methods.
Medications:
- Activated carbon (relieves symptoms of intoxication, relieves nausea).
- Enterosgel (adsorbs toxic substances and promotes their removal from the body).
- Rehydrog (a drug for preparing a water-salt solution necessary to combat dehydration).
- Linex (normalizes the functioning of intestinal microflora).
In severe cases, it is possible to take antibacterial drugs, but they must be prescribed by a specialist.
Folk remedies are also successfully used to treat food poisoning. The most commonly used decoctions are dill with honey, wormwood, marshmallow roots, yarrow, cinnamon tincture and ginger tea.
The diet involves fasting on the first day of illness. Then you should gradually introduce oatmeal in water, boiled, pureed vegetables, weak fish and meat broths, crackers, and lean meat into the diet. Drinks allowed include dried fruit compotes, herbal teas, jelly, fruit drinks, and boiled water.
Until complete recovery, you should exclude pickles, spices, fatty and fried foods, mushrooms, sweets and various sauces from your diet.
What is fish poisoning and why is it so dangerous for humans?
Content:
- What is fish poisoning and why is it so dangerous for humans?
- Main types of fish poisoning
- Symptoms of poisoning: how to recognize
- Providing first aid to a victim of fish poisoning
- When is it necessary to see a doctor?
- Botulism and fish poisoning
Fish is considered a nutritious and healthy product, which doctors and nutritionists advise to include in the diet, especially for children and the elderly. It contains fatty acids, proteins, a complex of vitamins and minerals, including phosphorus. Sea fish is rich in bromine and iodine, unlike its river “sister”. Its benefits for the brain, cardiovascular system and musculoskeletal system have long been known to both doctors and ordinary people.
Does this mean that fish in the human diet always brings only benefits? Unfortunately, it is not. It is known that fish, like meat, is a perishable product. In addition, fish can live and be caught in a variety of water bodies, even those that are heavily polluted and saturated with harmful waste. Living in dirty, poisoned water, the fish absorbs all the toxic elements from it, and itself becomes a source of poisons. In addition to the results of human activity, which poison many water bodies on the planet, various bacteria, microorganisms, and pathogens also live in water bodies.
In fatty varieties, chlorinated hydrocarbons, mercury, polychlorinated biphenyls, and dioxin can accumulate in large quantities.
Another danger is that even normal, healthy fish caught in a clean reservoir, before it reaches the buyer, may have time to deteriorate due to improper storage or processing conditions, due to the expiration date, or violation of the temperature regime. Parasites, helminths, poisons and toxins may appear in such a product as a result of the vital activity of such “inhabitants”. However, this fact practically does not bother sellers and manufacturers of fish products, so both in the market and in the supermarket you can find fish of the so-called “second freshness”, or even completely spoiled.
Separately, canned fish should be mentioned - an ordinary can of sprat in a tomato, if the process of fermentation and bacterial growth has begun in it, can cause the death of a person. The combination of “fish + canned food” is especially dangerous, since under conservation conditions the product is in a sealed, almost vacuum-sealed form, and all processes, including pathogenic ones, develop concentrated in it. The growth of botulism bacteria in canned food is especially dangerous.
Possible consequences and prevention
Fish poisoning is always accompanied by vomiting and loose stools, which causes dehydration.
This condition requires urgent hospitalization and comprehensive treatment. In addition, many chronic diseases of the digestive system and intestinal tract may become aggravated in the victim after poisoning.
To prevent the occurrence of various complications, at the first signs of intoxication you should seek medical help.
Prevention
Despite the high probability of fish poisoning, you should not give up this tasty and healthy product. To avoid intoxication, you must follow the following rules.
Prevention measures:
- You should buy fish fillets only from trusted retail outlets, avoiding spontaneous markets along the road.
- The required temperature conditions must be maintained in the sections selling fish products, otherwise the fish will quickly spoil.
- Fish should not be re-frozen.
- There is no need to order dishes from exotic varieties of fish in unknown restaurants.
- Use salted fish when preparing sushi.
Rotten fish has a pungent odor, cloudy eyes and a soft consistency. If you have the slightest suspicion of poor quality of the product, you should refuse to purchase.
Fish poisoning is a serious illness that requires immediate treatment. The faster first aid is provided to the victim, the fewer complications will arise.
How to recognize botulism
The main symptoms of botulism include:
- dry mouth, nausea, change in voice, hoarseness, pain when swallowing;
- double vision, blurred vision (fog, spots before the eyes);
- drooping of the upper eyelid, dilated pupils, strabismus, ptosis;
- lack of facial expressions, pale skin, unsteady gait, poor coordination;
- symmetrical paresis and paralysis of the limbs, respiratory muscles (feeling of chest compression);
- bloating and abdominal pain, diarrhea 3-5 times a day.
If a person experiences at least one or two of the listed signs of botulism, it is necessary to immediately consult a doctor. Delay is fraught with the most serious consequences, since rapidly developing paralysis of the muscles of the respiratory system inevitably leads to the death of the patient.
Diagnosis of botulism in a medical facility includes laboratory tests aimed at detecting botulinum toxin and bacteria in the patient's vomit and blood. In addition, products that are believed to have caused poisoning are necessarily examined for the presence of a toxin.
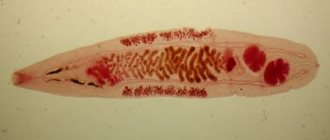
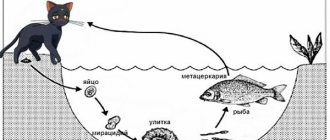
Prevention of helminthic diseases
- cook the fish for 15-25 minutes;
- cooking cutlets, meatballs, etc. - 15-25 minutes;
- baking pies with fish for at least 45-60 minutes;
- cold smoking of fish must be carried out either after pre-salting for 2-3 days, or after freezing;
- fry large pieces of fish spread out and always in fat for at least 20 minutes, fry small fish whole for 15-20 minutes;
- salt the caviar (at a temperature of 5-6°C), the ratio of the amount of salt is 6% to the weight of the caviar for 12 hours, for example: 60 g of salt per 1 kg of caviar, or salting the caviar in a 5% solution (50 g of salt per 1 kg of caviar ) at least 2 days with periodic mixing of caviar;
- salt: small fish for 14 days, large fish (over 25 cm) for 40 days with the addition of 2 kg of salt per 10 kg of fish;
- drying of fish for at least 3 weeks with preliminary salting for 2-3 days; d freezing: at 40°C-7 hours, at 35°C-14 hours, -28°C-32 hours.
The danger of contracting opisthorchiasis and diphyllobothriasis does not disappear all year round.
How does intoxication occur?
Fish is considered a perishable product, the preparation and storage of which must be treated with great care. Smoked, salted and even freshly cooked fish can cause intoxication. Also, the use of fresh fillets in the preparation of sushi and rolls is currently gaining great popularity. (sushi and roll poisoning)
Causes of intoxication:
- Eating expired red fish, herring, and canned fish. Many sellers try to make an expired product marketable in various ways, thereby putting the lives of customers in danger.
- Using fresh seafood when preparing sushi. A real Japanese delicacy is prepared from raw fish, which is soaked in a special solution before serving. Restaurants in our country mainly use chilled or salted fish for sushi, so for safety reasons, nutritionists recommend buying the seafood delicacy only in trusted places.
- Violation of the technology of smoking and salting fish, in which bacteria do not die, but rather multiply.
- Content of heavy metal salts in the product. Fish caught in polluted waters is potentially dangerous to humans.
- Repeated defrosting of a fish product significantly increases the risk of food poisoning. After the fish has been defrosted, it is necessary to start cooking it, otherwise the number of bacteria increases every hour.
- Poisoning from poisonous fish. The most dangerous seafood delicacy is fugu fish, the improper preparation of which can lead to death.
Types of toxemia:
- Smoked fish intoxication. The cause of the disease may be an incorrectly selected smoking temperature or incorrect dosage of salt during the production process. As a result, parasites and other microorganisms remain on the surface of the product and cause food poisoning in children and adults.
- Poisoning from fried fish occurs due to insufficient heat treatment of the raw materials. During prolonged frying, most bacteria die and the dish does not cause poisoning. A spoiled product can be recognized by the strong ammonia smell emanating from the fish fillet.
- Intoxication with salted and pickled fish occurs due to improper salting technology for the fish product. An insufficient amount of salt in the marinade cannot rid the fish of all bacteria and parasites that cause poisoning.
We recommend: Poisoning of a child and an adult with expired condensed milk - symptoms and consequences
Despite all the possible options for fish poisoning, you should not give up this useful product, because it contains many vitamins and minerals necessary for humans.
Causes
Often food poisoning can be caused by a number of reasons:
- Improper storage - at inappropriate temperatures, in warehouses with high humidity
- Fruits, berries and vegetables treated with chemicals
- Eating poisoned or spoiled fish and raw seafood
- Meat that has not been stored properly or has not been properly cooked.
- Products with a disrupted preservation process: in this case, bacteria penetrate into the airless space and multiply there. An example of a food poisoning that develops in this case is botulism, a disease with frequent fatal outcomes.
- Poisoning by mushrooms - poisonous by nature or edible , but which grew in unfavorable environmental conditions
- Poor quality and expired food products with damaged packaging
- Storing dairy products without refrigeration promotes the growth of staphylococcus in them
- Raw water, especially from unverified sources. It may contain Vibrio cholerae, E. coli, animal feces with parasites, and hepatitis A virus.
- Pre-cut fruits and vegetables may contain various microorganisms