Treatment of stage 2 hypertension, symptoms and causes
Stage 2 hypertension is arterial hypertension in moderate form. The upper blood pressure (systolic) is 160 - 179 mm Hg, and the lower blood pressure (diastolic) is 100 - 109 mm Hg. At this stage of the disease, periods of increased pressure are longer than with stage 1 hypertension. Arterial blood pressure in grade 2 hypertension rarely returns to normal.
Depending on the rate of change in the degree of hypertension, we can talk about normal and malignant arterial hypertension. In the second case, the disease progresses so quickly that it is often fatal. Hypertension is dangerous because an increase in the speed of blood movement through the vessels leads to thickening of their walls and an even greater narrowing of the arteries.
Risks of developing hypertension
The risk of developing hypertension or arterial hypertension - high blood pressure - consists of a number of factors. Accordingly, the more there are, the greater the likelihood that a person will become hypertensive.
Risk factors for developing hypertension:
- stress (stress hypertension) and mental stress. The stress hormone adrenaline increases your heart rate. It instantly constricts blood vessels;
- taking certain medications, for example, oral contraceptives, and various dietary supplements (iatrogenic hypertension);
- male gender;
- age over 35 years;
- pregnancy;
- diabetes;
- endocrinopathy of the adrenal glands, thyroid gland or pituitary gland;
- diseases of the hypothalamus;
- pyelonephritis;
- renal failure (nephrogenic hypertension);
- inactivity. Physical inactivity is accompanied by a slow metabolism - metabolism - and gradually weakens the body as a whole;
- excess salt in food. Table salt provokes arterial spasm and retains fluid in the body;
- excess body weight. Each extra kilogram increases blood pressure by 2 millimeters of mercury - mmHg;
- sudden change in weather;
- hereditary predisposition. The risk of getting sick is higher for those who have hypertension among first-degree relatives: father, mother, grandmothers, grandfathers, siblings. The more close relatives suffer from high blood pressure, the greater the risk;
- bad habits: smoking or drinking alcohol. Components of tobacco provoke spasms of blood vessels - involuntary contractions of their walls. This narrows the blood flow;
- atherosclerosis – blockage of blood vessels with plaques. Total cholesterol should not exceed 6.5 mmol/l of blood;
- chronic lack of sleep and other “provocateurs”.
Depending on the combination and degree of manifestation of the above factors, as well as the likelihood of cardiovascular complications in the next decade, there are 4 types of risk of developing arterial hypertension:
- low (risk less than 15%);
- average (from 15 to 20%);
- high (more than 20%);
- very high (more than 30%).
Risk factors for the appearance of arterial hypertension are also divided into 2 types based on the possibility of their elimination: correctable (correctable) and not. For example, a person may well quit smoking, but he is not able to change his ancestry. The amount of risk is summed up from a number of indicators. A patient with stage 1 hypertension who begins to abuse alcohol will significantly increase the percentage chance of developing complications.
What blood pressure is considered high?
Blood pressure is a factor that gives the specialist important information about the functioning of the circulatory system. Blood pressure levels are affected by:
- The magnitude of cardiac output, which in turn depends on the contractility of the left ventricle of the myocardium, heart rate and other parameters.
- Total peripheral vascular resistance (TPVR) is an indicator that reflects the ability of blood vessels to resist blood pressure from the inside. OPSS depends on the tone, stiffness of blood vessels, and blood viscosity.
- Circulating blood volume.
Blood pressure has upper and lower limits. The upper pressure is called "systolic", the lower - "diastolic". The first value reflects the force of blood pressure in the arteries during myocardial contraction, the second - at the moment of relaxation of the heart muscle.
The ideal pressure is considered to be 120/80 mm Hg. Art. Depending on the individual characteristics of a person (gender, age, physical activity), a slight deviation of these values down or up is allowed. However, in any person, blood pressure should not exceed 140/90 mmHg. Art. Higher levels are potentially dangerous and can lead to functional and organic damage to target organs.
The danger of high blood pressure
The main danger of hypertension is its complications, leading to disability and death.
The most severe complications:
- from the heart - heart attack, development of arrhythmia, heart failure;
- in the brain - stroke, loss of memory and intellectual abilities (dementia);
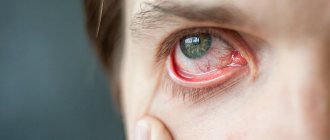
- from the eyes - severe vascular disorders in the retina;
- kidney – the occurrence of failure;
- vessels - aneurysm (sac-like expansion) of the aorta, the rupture of which leads to almost instant death.
Healthy lifestyle
Exercises and physical activity for hypertension play an important role, and the patient must constantly maintain a correct lifestyle. It includes quitting smoking, regular exercise, and simple sports activities. The patient must completely eliminate sources of stress from his environment, heavy physical work, reduce the time spent in noisy rooms, and refuse to work in the evening and at night.
Slow walks are recommended for hypertensive patients. Walking saturates the lungs with oxygen, makes the heart work, has a tonic effect, and promotes weight loss. You can do special cardio yoga or breathing exercises, swim, do water aerobics, or hippotherapy.
What is stage 2 hypertension
Stage 2 hypertension is a condition characterized by a persistent increase in blood pressure to 160/100 and above. However, blood pressure rarely returns to normal on its own; drug treatment is required to correct the patient’s condition.
Stage 2 hypertension is more common in patients over 50 years of age and this is understandable. With age, changes occur associated with the deposition of cholesterol plaques and narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels, the load on the heart increases, which has to make more efforts to pump blood, and conditions arise for increased blood pressure.
Stages of pathology
Depending on the degree of increase in blood pressure, three stages of hypertension are distinguished ⇓⇓⇓
First stage of headache
In the first stage of hypertension, high blood pressure can independently return to normal values. As a rule, at this stage of the disease, target organs are not affected and there are no complications.
Second stage of headache
At the second stage of hypertension, a person may experience various pathological changes:
- thickening of the walls of the left ventricle of the myocardium, which often leads to heart failure and coronary heart disease;
- atherosclerosis - the formation of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of blood vessels that impair blood circulation;
- retinal angiopathy is a violation of the tone of the vessels that supply the iris of the eye.
At the second stage of hypertension, normalization of blood pressure is possible only with the help of medications.
Third stage of headache
The third stage of hypertension can lead to severe complications:
- stroke - acute disruption of blood supply to the brain;
- aortic dissection - rupture of the largest artery. If the aortic wall is completely ruptured, massive blood loss occurs;
- myocardial infarction - necrosis of a section of the heart muscle;
- renal failure - decreased excretory capacity of the kidneys.
In the third degree of hypertension, blood pressure is difficult to normalize even with the help of medications. A person may experience hypertensive crises, during which blood pressure rises sharply and urgent medical attention is required.
Symptoms of stage 2 hypertension
Stage 2 hypertension has ambiguous symptoms and treatment. Increased blood pressure may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Throbbing pain in the temporal region;
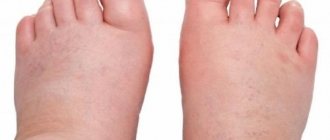
- Swelling of the face, especially the eyelids;
- The facial skin is hyperemic, and spider veins appear over time;
- Hands swell;
- It gets dark in the eyes, “spots” periodically flicker;
- At the same time, there is aching pain in the back of the head;
- After waking up, there is no cheerfulness, fatigue and apathy persist throughout the day;
- Periodic noise in the head;
- Emotional lability – low threshold of excitability;
- Dilated blood vessels of the eyes (sclera);
- Compaction of the ventricular wall (resistance to blood flow is compensated);
- Involuntary urination due to renal failure;
- Heart rate increases with the slightest exertion;
- There are problems with remembering.
Hypertension of the 2nd degree, symptoms can change depending on its characteristics: a primary independent form or a secondary one, as a complication of another disease.
Etiology
In 90 out of 100 patients, the cause of the constant increase in pressure remains unknown - this is primary (essential) hypertension, which is considered as an independent pathology. In other cases, there is some kind of premorbid background (another disease), one of the manifestations of which is high blood pressure - this is symptomatic or secondary hypertension. Depending on the etiology, it is divided into four types.
- Hypertension of renal origin develops against the background of congenital anomalies of the genitourinary system (hydronephrotic transformation, polycystic disease) or with severe acquired diseases (various forms of glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, chronic renal failure). Characteristic is stable hypertension of at least the second degree, high diastolic pressure numbers.
- Endocrine hypertension is a mandatory symptom in thyrotoxicosis, Itsenko-Cushing's disease, pheochromocytoma, obesity, etc.
- Hemodynamic hypertension occurs due to disturbances in normal blood flow, which is a constant companion to many heart diseases (congenital and acquired malformations, atherosclerosis, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy). A significant increase in systolic pressure is characteristic.
- Neurogenic hypertension - in the medical history of such patients there are indications of severe traumatic brain injury, acute cerebrovascular accident, encephalitis, brain tumors, etc. This type of hypertension is characterized by attacks of increased blood pressure, which are combined with dizziness, headaches, neuropsychiatric disorders.
As an independent pathology, stage 2 hypertension does not arise out of nowhere; for its development, the presence of certain predisposing factors is necessary, namely:
- excess weight - pressure increases by an average of 2 mm Hg. Art. when gaining just one extra kilogram of body weight, especially with abdominal obesity (excess fat in the chest and abdomen);
- habit of eating a lot of salty, fried and fatty foods;
- smoking tobacco and drinking alcohol - ethanol promotes the gluing of red blood cells and the formation of blood clots, which can clog any small blood vessels, and nicotine causes vascular spasms, so even one cigarette increases blood pressure by 15-20 mmHg. Art.;
- low physical activity – physical inactivity increases the risk of hypertension by 20-30%;
- psycho-emotional factors - stressful situations increase blood pressure, especially with the modern busy pace of life in large cities;
- hereditary burden - early onset of cardiac diseases in close relatives;
- diabetes mellitus of any type;
- age.
Risk 2 for stage 2 arterial hypertension
When establishing the risk of a characteristic illness, doctors take into account the age, gender, and presence of chronic diseases in the body of a clinical patient. This information helps predict clinical outcome and reduce the likelihood of serious health complications and disability. Risk 2 for arterial hypertension of the 2nd degree means that irreversible processes in internal organs under the influence of surges in blood pressure are observed only after 10 years, the probability of stroke and heart attack is 20%.
How is the disease diagnosed?
To diagnose arterial hypertension, a doctor needs to take several blood pressure measurements at different times of the day. If necessary, a specialist can prescribe ABPM - an instrumental study in which blood pressure is monitored throughout the day using a special device.
Differential diagnosis of hypertension occurs as follows:
- An examination of organs whose pathologies could cause increased blood pressure is performed. For example, the examination may include an ECG, ultrasound of the kidneys, and fundus examination.
- If secondary hypertension is excluded and a specific cause for the increase in blood pressure is not found, then a diagnosis of hypertension is made.
Arterial hypertension 2 degrees risk 4
Risks of arterial hypertension 2 degrees The presence of a “bouquet” of diseases (atherosclerosis, diabetes, ischemia) allows us to state that the patient has acquired a diagnosis of hypertension 2 degrees, 4 risk. Arterial hypertension at this stage only complicates the situation. This diagnosis is given to patients who have survived 1-2 heart attacks, regardless of the affected area.
It should be clarified that one hundred risk is a predictable concept, not an absolute one. It only indicates the likelihood of a complication developing. If the patient understands the danger of his situation and takes appropriate measures, the diagnosis can be corrected. Hypertensive patients who adhere to a healthy lifestyle and constantly monitor their condition can live a long and fulfilling life.
While with a burdened anamnesis and high risk, life expectancy is significantly shorter. Timely diagnosis and adequate treatment aimed at reducing blood pressure can extend your life and improve your quality of life.
What causes the disease?
The diagnosis of “arterial hypertension stage 2, risk 2” usually comes with age, because the body wears out, the lumens in the vessels narrow and blood circulation becomes difficult. But in recent years, this diagnosis has been made to patients just over 30 years old, and, what is more surprising, even very young people can find some symptoms of this disease. Why is the pressure unstable, what causes such high numbers?
- Atherosclerosis: because of it, blood vessels lose their elasticity and the lumens in the arteries narrow.
- Hereditary factors and genetic predispositions.
- Bad habits: smoking and alcohol.
- Lifestyle: People move too little.
- High body weight.
- Increased blood sugar, hormonal changes in the thyroid gland.
- Kidney diseases.
- Stressful situations.
- Excessive salt intake causes water retention in the body.
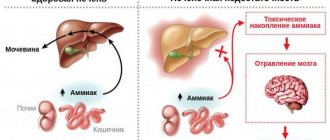
In case of stage 2 hypertension, damage is primarily caused to the main excretory organ - the kidneys. First of all, the smallest vessels of the organ suffer. As they narrow, they are unable to ensure normal blood flow, and at first a slight inflammation occurs in the kidney. In response to this, the hormone renin begins to be produced. Further, the process worsens, the renin-angiotensin system is activated, causing an even greater increase in pressure. The kidneys gradually become deformed and atrophy, becoming wrinkled and unable to perform their functions.
Hypertrophied muscle tissue requires more oxygen and nutrients to function. Therefore, in patients with myocardial hypertrophy, hypertension is often combined with coronary heart disease, and in some cases myocardial infarction may develop.
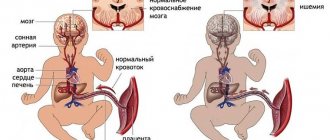
The brain is also susceptible to pathological changes due to high blood pressure levels. Even with the first degree of the disease, patients may note the presence of symptoms such as headache, tinnitus, and fatigue. Damage to the vascular wall leads to impaired blood circulation in the brain, as a result of which microscopic zones of necrosis appear in it, the tissue mass of this organ decreases, which leads to impaired cognitive functions, memory, and the development of dementia of vascular origin.
Treatment of stage 2 hypertension
How to treat stage 2 hypertension? The scheme is drawn up by the local therapist. If necessary, a consultation with a cardiologist and neurologist is scheduled. Traditional methods of treating stage 2 hypertension include:
- To eliminate blood thickness (thin the blood flow), you should take Aspirin, Cardiomagnyl, Heparin, Aspicard.
- To normalize blood pressure, diuretics (diuretics) are prescribed, such as Diuver, Furosemide, Piretanide, Torasemide, Veroshpiron, Ravel.
- For this diagnosis, thiazides (thiazide drugs) such as Arifon, Chlorthalidone, Indapamide are recommended.
- To reduce blood cholesterol, you should take lipid-lowering drugs such as Atorvastatin, Atoris, Liprimar, Zovasticor.
- In order to dilate blood vessels, antihypertensive drugs of different groups are prescribed, such as Physiotens, Artil, Bisoprolol, Lisinopril.
It is important to consider that the quality of treatment largely depends on compliance with the instructions for their use. Self-medication for hypertension is dangerous. Such experiments can result in disability. The therapist selects the treatment regimen individually, taking into account the age, build and other health characteristics of the individual patient.
Diet
Hypertensive patients must follow a constant diet, which they create together with a nutritionist or attending physician. Taking medications without lifestyle changes is not enough when treating hypertension grade 2, risk 1,2, 3 or 4. The patient should exclude from the daily diet:
- Fatty fish and meat dishes,
- Baking, sweets,
- Fast food,
- Alcohol, tonics and carbonated drinks,
- Strong tea, coffee, cocoa,
- Hot spices,
- Smoked meats,
- Pickles,
- Canned foods,
- Sour cream, fatty varieties of cottage cheese and cheese.
You can eat greens (especially parsley and dill) and dried fruits in unlimited quantities. Your daily menu should include garlic and a variety of cereals. It is recommended to make broths for soups from vegetables or turkey. And cook meat no more often than once every 10-12 days. The diet should include as many vegetables, fruits, seafood, lean fish, and beef liver as possible. You need to cook food with a minimum amount of salt and oil. The ideal option is for a couple. But you can both stew and cook.
The diet must be followed constantly, and not just until the pressure normalizes and symptoms disappear.
Diet for hypertension
In order for the kidney vessels to function normally, hypertensive patients with any stage of the disease must adhere to certain nutritional rules. For example, it is important to control the water and salt balance of the body, to prevent the formation of stagnation and, as a consequence, stage 2 hypertensive crisis. Fatty, fried, sweet and smoked foods are prohibited.
Seven foods that lower blood pressure:
- Blueberries – Blueberries are rich in natural substances called flavonoids.
- Fresh leafy greens such as fenugreek leaves, kale, mint leaves, patchouli, dill greens, mustard leaves, curry leaves, beet greens, Swiss chard, arugula, broccoli, celery and spinach are high in potassium
- Potatoes - contain a lot of potassium and magnesium
- Beets – Nitrates in beet juice are known to lower blood pressure
- Skim milk is an excellent source of calcium plus low fat levels
- Oatmeal is a high-fiber, low-fat, low-sodium food.
- Bananas – Adds potassium to your diet.
Therapeutic nutrition for stage 2 hypertension allows boiled lean meats, cereals, vegetables and fruits on the menu. Green tea and diuretic herbal decoctions have beneficial properties.
Hypertension 4 degrees
Some experts also identify stage 4 of the disease, which is very severe. In most cases, death is close. They try to alleviate the patient’s suffering as much as possible, and with each hypertensive crisis they provide first aid. The patient is laid down, raising his head. He is urgently given medications that sharply lower his blood pressure.
Without treatment, new complications appear. Some of them provoke others, and diseases increasingly overcome a person. To stop this destructive process in time, you just need to monitor the dynamics of changes in your blood pressure, at least using a regular tonometer.
Author of the article:
Mochalov Pavel Alexandrovich |
Doctor of Medical Sciences therapist Education: Moscow Medical Institute named after. I. M. Sechenov, specialty - “General Medicine” in 1991, in 1993 “Occupational diseases”, in 1996 “Therapy”. Our authors
Folk remedies
When treating illness at home, many people prefer to use folk remedies. This therapy involves the use of medicinal plants that have a positive effect on the cardiovascular system.
You can treat the disease with the following recipes:
- Treatment can also be carried out with peppermint, cinquefoil, chamomile, and yarrow. These herbs go well together.
- Prepare a decoction of motherwort, horsetail, marsh cudweed, and valerian root. All plants must be taken in the same quantity. This remedy has diuretic effects and allows you to cope with single surges in blood pressure.
- Bee products and citrus fruits are actively used in the treatment of hypertension.
- You can treat with viburnum juice. To reduce blood pressure, it should be consumed three times a day, a quarter glass.
Folk remedies help cope with unpleasant symptoms of the disease and speed up the effectiveness of traditional therapy. Such recipes have proven their benefits over many centuries. People whose bodies do not tolerate medications well turn to this type of therapy. But it is important to remember that treatment of the disease with traditional recipes can only be carried out after consultation with a doctor.
Prevention of hypertension
To prevent hypertension and possible complications of this disease, the cardiologist at the A-Media clinic recommends taking the following measures:
- quit smoking
- minimize alcohol consumption
- control body weight
- be sure to get eight hours of sleep
- establish proper nutrition
- engage in physical activity daily.
Contact the A-Media clinic for the treatment of hypertension, and our experienced cardiologist will help you avoid severe complications of this disease and significantly improve your quality of life.
Prevention
Your healthcare provider will likely also suggest a variety of lifestyle changes, including:
- Maintaining a healthy weight;
- A diet rich in fruits, vegetables and low-fat dairy products;
- To give up smoking;
- Limiting salt intake in the diet;
- Limit alcohol consumption. For most adults, this means that it is normal to drink up to one drink per day for women of all ages and men over the age of 65, and up to two drinks per day for men 65 or younger;
- Exercise at least 30 minutes a day. These include walking, jogging, strength training, yoga, and cardio exercises such as cycling.
On your part, methodical adherence to medical recommendations and organization of the correct regimen are required. A healthy lifestyle is the path to recovery. Remember this.
Prevention of arterial hypertension
Giving up bad habits and normalizing lifestyle are the basis for preventing hypertension. Knowledge of the principles of preventing hypertension allows you to prevent the disease, facilitate its course, and also eliminate possible complications. Experts distinguish between primary and secondary prevention.
Primary prevention is to prevent the development of hypertension. People at high risk of developing arterial hypertension should not only fight bad habits and adhere to the principles of proper nutrition, but also monitor their physical activity.
Secondary preventive measures are carried out for people with an established diagnosis, for example, gestational hypertension. The efforts of doctors and patients are aimed at preventing complications. Secondary prevention consists of two components: arterial hypertension (treatment with tablets) and non-drug treatment.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital have extensive experience in treating arterial hypertension. The quality of services provided in the hospital is at the European level. All diagnostic and treatment procedures are performed using the latest medical equipment. The rooms are equipped with maximum comfort for patients. You can make an appointment with a doctor by phone.