Arterial bleeding is one of the most dangerous to human health and life. Arteries supply blood to the heart and vital organs. Their damage leads to rapid blood loss, which often causes death. If the integrity of large arteries is compromised, a person can lose a significant amount of blood in a matter of seconds. It is important to know how to identify bleeding from an artery and provide first aid to the patient before doctors arrive. This will help save the victim’s life in emergency situations.
Symptoms of bleeding from an artery
There are several types of arteries in the human body, each of which plays an important role for the normal functioning of all organs and systems. The femoral, carotid, axillary and other arteries supply the body with blood and oxygen. With significant blood loss, the internal organs do not receive enough oxygen and nutrients, as a result of which the heart stops. It is not difficult to distinguish arterial bleeding from venous bleeding. Blood from the vein oozes slowly and has a brown tint.
In case of arterial bleeding, the following signs are observed:
- blood is scarlet, liquid;
- the flow of blood from the wound is rapid, often flowing like a fountain;
- the victim’s body temperature drops sharply;
- there is pulsation of blood with heartbeats, while below the site of injury the pulsation is impaired or completely absent;
- a person’s skin becomes pale and bluish;
- The patient’s general well-being worsens, blood pressure drops, dizziness, convulsions, and loss of consciousness develop.
By quickly identifying the signs of arterial bleeding and providing the person with the necessary first aid, his life can be saved. The reaction of others should be lightning fast, since when arteries are damaged, especially large ones, we are talking about a few minutes.
Bleeding. Types of bleeding. Methods to stop bleeding
Bleeding is the leakage of blood from blood vessels, most often occurring as a result of their damage. In this case, we are talking about traumatic bleeding (Training to stop traumatic bleeding is usually carried out on Maxim medical mannequin simulators, using pads that simulate various wounds and lesions, bleeding). Bleeding can also occur when a vessel is corroded by a painful lesion (tuberculosis, cancer, ulcer). Thus, non-traumatic bleeding occurs.
Traumatic bleeding is one of the main signs of every wound. A blow, cut, or injection breaks the walls of blood vessels, causing blood to flow out of them. Blood clotting. Blood has an important protective property - clotting; Thanks to the ability of blood to clot, any small, mainly capillary bleeding spontaneously stops. A clot of coagulated blood clogs the opening of the vessel caused by injury. In some cases, bleeding stops as a result of compression of the vessel.
Bleeding. With insufficient coagulation, manifested by disproportionately long, slow coagulation, bleeding occurs. Persons suffering from this disease can lose a significant amount of blood through bleeding from small vessels, small wounds, and even death can occur.
Consequences of bleeding. In case of bleeding, the main danger is associated with the occurrence of acute insufficient blood supply to tissues, blood loss, which, causing an insufficient supply of oxygen to organs, causes disruption of their activity; First of all, this concerns the brain, heart and lungs.
Types of bleeding.
Bleeding in which blood flows out from a wound or natural orifices of the body is usually called external bleeding. Bleeding in which blood accumulates in body cavities is called internal bleeding. External bleeding is divided into:
- Capillary - occurs with superficial wounds; blood flows out drop by drop from the wound;
- Venous - occurs with deeper wounds, such as cuts or stabs; with this type of bleeding, there is a profuse flow of dark red blood;
- Arterial - occurs with deep chopped, puncture wounds; arterial blood of a bright red color spurts from damaged arteries, in which it is under high pressure;
- Mixed bleeding occurs when veins and arteries bleed simultaneously in a wound.
STOPPING CAPILLARY AND VENOUS BLEEDING
The first goal when treating any significantly bleeding wound is to stop the bleeding. In this case, you should act quickly and purposefully, since significant blood loss during injury weakens the victim and even poses a threat to his life. If it is possible to prevent large blood loss, this will greatly facilitate the treatment of the wound and special treatment of the victim, and will reduce the consequences of injury and injury.
STOPING CAPILLARY BLEEDING
With capillary bleeding, blood loss is relatively small. This bleeding can be quickly stopped by placing clean gauze over the bleeding area. A layer of cotton wool is placed on top of the gauze and the wound is bandaged. If you have no gauze or bandage at your disposal, you can bandage the bleeding area with a clean handkerchief. It is impossible to apply shaggy fabric directly to the wound, since its villi contain a large number of bacteria that cause infection of the wound. For the same reason, cotton wool should not be applied directly to an open wound.
STOPPING VENOUS BLEEDING
A dangerous aspect of venous bleeding, along with a significant amount of lost blood, is that when the veins are wounded, especially the cervical ones, air can be sucked into the vessels through the areas damaged by the wounds. The air that has entered the vessel can then enter the heart. In such cases, a fatal condition occurs - air embolism.
Venous bleeding is best controlled with a pressure bandage. Apply clean gauze to the bleeding area, on top of it an unrolled bandage or gauze folded several times, or, in extreme cases, a folded clean handkerchief. Means used in this way act as a pressure factor that presses the gaping ends of damaged vessels. When such a pressing object is pressed against the wound with a bandage, the lumens of the blood vessels are compressed and the bleeding stops.
If the person providing assistance does not have a pressure bandage at hand, and the victim is bleeding heavily from a damaged vein, then the bleeding area should be immediately pressed with your fingers. When bleeding from a vein of the upper limb, in some cases it is enough to simply raise your hand up. In both cases, a pressure bandage should be applied to the wound after this.
The most convenient for these purposes is a pocket pressure bandage, an individual package that is sold in pharmacies.
STOPPING ARTERIAL BLEEDING
Arterial bleeding is the most dangerous of all types of bleeding, since it can quickly lead to complete bleeding of the victim.
Arterial bleeding can be stopped with a pressure bandage. If there is bleeding from a large artery, you should immediately stop the blood flow to the damaged area by pressing the artery with your finger above the wound site. However, this measure is only temporary. The artery is pressed with a finger until a pressure bandage is prepared and applied.
When bleeding from the femoral artery, applying a pressure bandage alone is sometimes insufficient. In such cases, you have to apply a loop, a tourniquet, or an improvised tourniquet.
If the person providing assistance does not have a standard loop or tourniquet at hand, then instead you can use a scarf, handkerchief, tie, or suspenders. A tourniquet or loop is placed on the limb immediately above the bleeding site. For these purposes, a pocket bandage (individual package) is very convenient, acting simultaneously as both a covering and a pressure bandage. The area where the tourniquet or loop is applied is covered with a layer of gauze to avoid damaging the skin and nerves. The applied tourniquet completely stops the flow of blood into the limb, but if the loop or tourniquet is left on the limb for a long time, it may even die. Therefore, to stop bleeding, they are used only in exceptional cases, namely on the shoulder and thigh (when part of a limb is torn off, during amputations).
When a loop or tourniquet is applied, the victim must be taken to a medical facility for special surgical treatment within two hours.
Bleeding of the upper limb can be stopped with a bag of bandage placed in the elbow or armpit, while simultaneously tightening the limb with a tourniquet. In case of bleeding of the lower limb, proceed in a similar way, placing a wedge in the popliteal fossa. True, this method of stopping bleeding is used only occasionally.
If there is bleeding from the main cervical artery - the carotid artery - you should immediately compress the wound with your fingers or fist; After this, the wound is stuffed with a large amount of clean gauze. This method of stopping bleeding is called packing.
After bandaging (using an IPP-1 dressing package) of the bleeding vessels, the victim should be given some non-alcoholic drinks and taken to a medical facility as soon as possible.
INTERNAL BLEEDING
Bleeding into the abdominal cavity. This type of bleeding occurs when there is a blow to the stomach; in most cases, rupture of the liver and spleen is observed. In women, intra-abdominal bleeding occurs during ectopic pregnancy. Intra-abdominal bleeding is characterized by severe bleeding and pain in the abdominal area. The victim falls into a state of shock or loses consciousness. He is placed in a semi-sitting position with his knees bent, and a cold compress is placed on the abdominal area. The victim should not be given anything to drink or eat. It is necessary to ensure his immediate transportation to a medical facility.
Bleeding into the pleural cavity. This type of bleeding occurs when there is a blow or injury to the chest. Blood accumulates in the pleural cavity and in the affected half compresses the lungs, thereby preventing their normal activity. The victim breathes with difficulty, and with significant bleeding even suffocates. He is placed in a sitting position on the floor with his lower limbs bent, and a cold compress is placed on his chest. It is necessary to ensure immediate transportation of the victim to a medical facility.
ACUTE ANANAMIUM DUE TO BLOOD LOSS
Acute anemia occurs when the body loses a significant amount of blood. The loss of even one and a half liters of blood poses a great danger to the life of the victim.
In acute anemia, the victim complains of weakness, pallor, sunken eyes, a weak and rapid pulse, the patient looks haggard, apathetic, and cold sweat appears on his forehead. Sometimes involuntary urination and stool leakage occurs. In short, shock occurs due to acute anemia caused by loss of blood. Finally the victim collapses and loses consciousness.
WHAT HAPPENS IN THE HUMAN BODY DURING SIGNIFICANT BLOOD LOSS?
As a result of a decrease in blood volume in the circulatory system, the body's organs suffer due to insufficient oxygen supply to the body; Most of all, this affects brain activity and general metabolism. Despite a number of adaptive protective mechanisms, the brain and hormonal system are not able to balance the pathological changes occurring in the body. If in this phase the victim is not provided with appropriate assistance, then as a result of paralysis of the respiratory and circulatory centers located in the medulla oblongata due to lack of oxygen, the patient’s death occurs.
First aid. A patient who has lost a significant amount of blood can be saved, but this requires urgent first aid measures. First of all, it is necessary to stop the bleeding, if it has not yet stopped spontaneously as a result of loss of vascular tone, which is observed with significant blood loss. Even if the bleeding has stopped, a pressure bandage should still be applied to the wound. Then the victim’s dress and collar are unbuttoned; If consciousness is maintained and there are no injuries to the digestive tract, the patient should be given tea. Giving black coffee in such cases is not recommended. Then the victim is placed on his back with his head slightly lowered, his arms and legs are raised and even suspended. This position promotes blood supply to the brain and thereby supports its activity. After this, the victim must be urgently transported to a medical facility.
What is the danger
As already mentioned, blood is the transporter of oxygen molecules and other nutrients throughout the human body. Saturating the tissues of the heart, brain and other organs, the blood takes carbon dioxide and other metabolic products from them. The heart and central nervous system are most sensitive to disruption of this process. If there is no blood supply to the brain for more than 6 minutes, death will occur in most cases.
In addition, there is such a thing as vascular collapse. Vascular tone is ensured by the continuous flow of blood through them. If this process is disrupted due to a sharp drop in the volume of circulating blood in the body, vascular shock or collapse occurs.
Important! Failure to help a patient with arterial bleeding leads to death due to oxygen starvation as a result of severe blood loss.
Causes of bleeding
In medical practice, a distinction is made between mechanical and pathological bleeding from an artery. In the first case, we are talking about mechanical damage to healthy vessels due to injuries, bone fractures. Pathological implies a violation of the integrity of the artery due to changes in the structure of their walls. These can be various vascular diseases, tumors, systemic diseases of the body.
Road traffic accidents and other accidents are common causes of arterial bleeding.
Common causes of arterial bleeding include:
- injuries received in road accidents, railway and plane crashes, piercing wounds, damage to the walls of blood vessels as a result of domestic or industrial emergencies;
- vascular pathologies, for example, oncological formations, tissue suppuration affecting the arteries, hemangiosarcoma, atherosclerosis;
- blood diseases, which include hemophilia, von Willebrand disease, cirrhosis, hepatitis, fibrinogen deficiency and others;
- systemic pathologies such as diabetes mellitus, viral infections, sepsis, vitamin deficiency. As a result, blood plasma leaks through damaged vascular walls and bleeding develops.
Regardless of the causes of damage to the artery, it is necessary to provide first aid to the patient as soon as possible and call a medical team.
Features of first aid
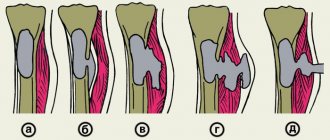
In order to stop bleeding from an artery, you should know how the vessels are located in the body. If arteries in the legs or arms are damaged, it is recommended to apply a tourniquet. If the carotid artery is damaged, a splint or digital pressure is used. The figure shows the location of arteries in the body.
Help with arterial bleeding involves squeezing the damaged vessel.
Place of application of a tourniquet or splint depending on the location of the wound:
- the carotid artery is compressed in the area of the 7th cervical vertebra in the region of the cleidomastoid muscle;
- if the jaw artery is damaged, the person providing assistance must clamp the area on the lower jaw in the area of the masticatory muscle;
- if blood comes from the temporal artery, the temple area is compressed;
- the femoral artery must be pressed against the pubic bone in the area of the inguinal ligament;
- the popliteal artery is compressed in the middle of the popliteal cavity;
- the shoulder is compressed in the area of the inner surface of the shoulder hand, under the biceps;
- when blood comes from the subclavian artery, a tourniquet should be applied to the tibia along the back of the leg.
You can more accurately see which areas are pinched when specific arteries are damaged in the figure.
Schematic representation of the place where arteries are clamped during bleeding
Important! The effectiveness of first aid and the patient’s life depend on the correct application of a tourniquet, splint or finger pressure.
Instructions for performing digital compression of the wound
The actions of the person providing assistance must be quick and concentrated. You must not panic, you must concentrate and strictly follow the following instructions:
- if the exact location of the wound is not clear, it should be pressed with your palms, this will help determine the source of bleeding;
- if necessary, remove clothing by tearing it or cutting it with scissors;
- It is recommended to squeeze the artery with your thumb or covering hand;
- You cannot remove your hand until the victim is bandaged;
- If you hold your fingers for a long time, cramps and numbness may develop; in such a situation, you should replace it with the other hand.
If the situation allows, before squeezing the wound with your fingers, it is recommended to wash them with soap or treat them with an antiseptic, this will avoid infection of the wound and the development of complications. This advice does not apply to situations where the main arteries are damaged and minutes are counting.
General classification
The division of bleeding into different types is of great expediency due to the ease of determining treatment tactics at different stages of medical care. Wherever she finds herself, all doctors know her clear algorithm. This approach minimizes the time spent and minimizes the amount of blood loss. People who are not involved in medicine should also know the main features and possible types of bleeding in order to help themselves or their loved ones if necessary.
The classification is given in table form.
| External bleeding (bleeding with direct contact with the external environment) | Internal bleeding (the spilled blood does not have direct contact with the environment) |
|
|
| According to the amount of blood loss during any bleeding | |
| |
How to stop bleeding with a tourniquet
Applying a tourniquet for arterial bleeding helps stop the bleeding until the victim receives medical attention. During the procedure, you should adhere to the following algorithm of actions:
- the damaged artery must be pressed with a finger above the wound;
- a tourniquet is applied 2 cm above the affected vessel;
- A tourniquet cannot be applied to a naked body, as this can injure the dermis. A cotton swab or soft cloth (towel, scarf, etc.) must be placed under it;
- After applying the tourniquet, you need to write down the exact time and name of the victim. This will help doctors in further treatment of the patient.
It is important to remember that the time for applying the tourniquet is limited, otherwise there is a risk of necrosis. In summer, it is allowed to compress the artery for 1 hour, in winter - 30 minutes.
When applying a tourniquet, be sure to indicate the time
If the ambulance has not arrived by this time, the bandage must be removed and reapplied. In this case, you need to be careful, especially when removing the last turn, as there is a risk of a blood clot breaking off and re-bleeding. After removing the tourniquet, it is applied again 1.5–2 cm above the wound. After the bleeding has stopped, all measures should be taken to transport the patient to the hospital.
First aid for external bleeding
Ask others to call an ambulance
1. Make sure that neither you nor the victim is in danger. Use medical gloves to protect the victim from body fluids. Carry (take) the victim out of the affected area.
2. Check the victim's consciousness.
3. If the victim is conscious, quickly (within a few seconds) conduct a physical examination to determine if there is severe external bleeding.
4. Stop bleeding if there is any.
Wound tamponade
Emergency care for a person with bleeding in the head or neck area, when a tourniquet cannot be applied, is to pack the wound. To do this, use a sterile bandage or cotton wool; if you don’t have them at hand, you can take napkins. The tampon is pressed tightly to the wound site and a bandage is applied. The bandage should be made tight to avoid blood leakage. This method can be used in case of damage to the vessels of the upper and lower extremities. To do this, the wounded arm or leg must be raised to drain the blood, a tampon placed in the area of the affected artery, and a tight bandage applied to secure it.
Important! Despite the fact that the methods described above are only temporary help for the patient, and the patient still requires treatment in the hospital, clear actions of the helper can save a person’s life.
Prevention of DMK
In order to avoid pathology at an early stage, prevention must begin during the development of the fetus in the womb. Next, you need to monitor the health and condition of the immune system in childhood and adolescence. It is especially important to prevent abortions and acute diseases of the reproductive system.
But following all the specialist’s recommendations does not always lead to the desired result. When intrauterine bleeding occurs, all efforts must be directed toward restoring the menstrual cycle and preventing exacerbations in the future. For this purpose, experts use the following treatment regimen:
- During the first three cycles, oral contraceptives are taken (from 5 to 25 days).
- During cycles 4, 5, 6, medications are taken from 15 to 25 days.
- Progestin agents are taken from 15 to 25 days of the cycle for no more than 5-6 months.
Fact: oral contraceptives reduce the number of abortions and disruptions in the hormonal system, and also eliminate the development of breast cancer and other serious diseases.
How to help a patient with major blood loss
If a person has lost a large amount of blood, all measures must be taken to prevent vascular shock before the ambulance arrives. To do this, you should free the patient's chest and throat from clothing, give access to fresh air, and avoid crowding. The person should lie on his back, arms and legs raised, head slightly lowered. This position of the body will ensure proper blood supply to the brain, which will help maintain its activity. If there are no injuries to the abdominal area and the patient is conscious, it is recommended to give him water or weak sweet tea. In case of loss of consciousness and respiratory arrest, it is necessary to perform resuscitation measures in the form of cardiac massage and artificial respiration.
If there is significant blood loss, the patient must ensure correct body position
Health care
After the victim has been taken to the hospital, his treatment is carried out by a general or vascular surgeon. The choice of therapeutic tactics always depends on the diameter of the artery damage and the location of the wound. To completely stop bleeding in a hospital, the following methods are used:
- plastic surgery of the damaged artery, that is, its suturing;
- tightly bandaging the wound. This method is used for minor damage;
- arterial replacement. The tactic involves replacing damaged artery walls with the patient’s own tissues; it is used for extensive lesions.
To prevent wound infection, local and general antibacterial therapy is carried out.
Arterial bleeding is one of the most dangerous. Lack of treatment leads to large blood losses and death of the patient. The quick reaction of others and competent emergency care ensure the safety of the victim’s life and prevent serious consequences.
Uterine bleeding in postmenopause
DUB in postmenopause is primarily considered as a symptom of a malignant process of the endometrium or cervix. The cause may also be hormonally active ovarian tumors. Without connection with malignant transformation, the cause of DUB can be endometrial hyperplasia, polyps and atrophic colpitis. Examination of the vagina and cervix in the speculum allows you to clarify the condition of the mucous membrane of the lower parts of the gynecological tract.
In atrophic colpitis, the cause of scanty bleeding is the thinned and eroded vaginal mucosa. The main complaint before the appearance of bleeding in such patients is dryness and discomfort, and more often in those who practice sexual intercourse. Treatment consists of local (intravaginal) use of drugs with estrogens, lactobacilli, and bacteriophages.
Treatment of DUB
Uterine bleeding in postmenopause in the vast majority of cases is an indication for hysteroscopy and endometrial curettage, followed by histological examination to determine the diagnosis and further tactics. In severe cases, complete removal of the uterus is performed. Often, gynecologists expect relief over time without surgical treatment, but this does not lead to a positive result. You should remember the need for an annual examination by a gynecologist and ultrasound control for all menopausal and postmenopausal women. If there are no complaints, the M-echo is more than 5 mm - there is an indication for hysteroscopy and histological evaluation of the endometrium.
Diagnosis of DMC
At this stage, it is necessary to differentiate uterine bleeding from menstruation. At this age they occur very rarely. Specialists perform hysteroscopy before and after curettage. Polyps, fibroids and endometriosis are often discovered after the procedure. Less commonly, the pathology is associated with a neoplasm in the ovary, which causes hormonal imbalance. Ultrasound can also accurately determine the presence and size of a tumor. The exact diagnostic strategy is selected by the attending physician based on medical history.