Salpingitis is a disease of the fallopian (uterine) tube of an infectious-inflammatory nature. It can be unilateral, when infection occurs in one of the fallopian tubes, often this occurs due to inflammatory processes of nearby organs - for example, the appendix, and depending on which of the tubes is infected, the disease is divided into left-sided salpingitis and right-sided salpingitis. Bilateral salpingitis can also occur when both fallopian tubes are affected as a result of the inflammatory process. In addition, according to the form of its course, it is divided into acute, subacute and chronic, and according to etiology - into specific and nonspecific.
Acute and chronic salpingitis can affect reproductive function in women and cause spontaneous miscarriages, inability to become pregnant, and constant pain in the lower abdomen. As an isolated inflammation, salpingitis appears quite rarely; most often it occurs against the background of an inflammatory process of the ovaries - oophoritis and the uterus - endometritis.
Causes of the disease
Fallopian salpingitis appears as a result of viral or microbial infection, which can occur in three ways:
- With the ascending transmission of infection from neighboring organs - the uterus (with a cyst, endometritis), vagina (with vulvovaginitis, vaginitis), urinary ducts.
- By contact, when infection occurs through organs of other systems that have become infected - for example, due to appendicitis.
- Hematogenously, when the infection is transmitted through the blood.
Factors that provoke the appearance of salpingitis may be:
- sexually transmitted diseases - trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, herpes, chlamydia;
- performing abortions with curettage;
- use of intrauterine devices;
- the occurrence of injuries during labor;
- carrying out metrosalpingography, salpingoscopy;
- inflammatory diseases of nearby organs – appendicitis, oophoritis, colitis, pelvioperitonitis
Causes and symptoms of acute salpingitis
Acute salpingitis occurs as a result of infection in the fallopian tubes along the ascending path or through an already existing focus - oophoritis, appendicitis. Very often, the development of this disease occurs against the background of an ectopic pregnancy and is accompanied by pronounced symptoms:
- increased body temperature;
- increased heart rate;
- general malaise, weakness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- headache;
- pain in the genital area - their localization is determined by the development of the inflammatory process in one of the fallopian tubes;
- specific discharge from the genitals - purulent, foamy, bloody, can be very copious and accompanied by itching and burning;
- disorders of stool and urinary function.
What it is?
Salpingitis is an isolated infectious and inflammatory disease of the uterine (fallopian) tube of one or two-sided nature, often leading to its obstruction and, as a result, infertility.
As an isolated inflammatory process, salpingitis occurs infrequently; in most cases, inflammation from the area of the fallopian tubes spreads to the ovaries (oophoritis), and acquires the features of a combined inflammation of the appendages (salpingoophoritis). Often inflammation of the uterine appendages (ovaries and tubes) is combined with endometritis (inflammation of the uterus).
Symptoms of chronic salpingitis
In most cases, chronic salpingitis does not have severe symptoms and does not cause the patient much discomfort. The woman feels well, the temperature is usually normal. Dull or aching pain in the abdomen and minor discharge may occur. Symptoms are wave-like, can subside and intensify as a result of stress and hypothermia. A characteristic sign of chronic salpingitis is disruption of the menstrual cycle, discharge during menstruation is profuse and accompanied by pain. A common prognosis for the development of this disease is the impossibility of pregnancy.
Classification of the disease
Based on the existing etiology, two forms of this disease can be distinguished:
- nonspecific salpingoophoritis, which is caused by microorganisms that are part of the microflora of the female body, which include Escherichia, staphylococci, enterococci;
- specific salpingoophoritis, which is caused by sexually transmitted pathogens already introduced into the female body, which include gonorrhea, chlamydia, and the like.
Depending on the nature of the course of this disease, the following three forms of the disease can be distinguished:
- Acute salpingoophoritis, which forms in the tube. Next, through this tube, microorganisms manage to penetrate the ovary. There is a release of inflammatory fluid in the lumen of the tube. If there is a large amount of fluid, the patient may feel pain in the abdominal area, and suppuration may occur. Depending on how badly the tissue is damaged, acute salpingoophoritis is accompanied by symptoms of peritoneal irritation and rupture of the tubo-ovarian formation.
- Subacute salpingoophoritis, which is a disease that occurs for the first time, but has not very pronounced symptoms. This form of salpingoophoritis is not characterized by severe pain; rather, it is aching and dull. The pain does not occur specifically in one place, but spreads to different parts of the abdomen.
- Chronic salpingoophoritis occurs if acute salpingoophoritis is not cured. This form of this disease can lead to the formation of adhesions in the pelvis, which lead to obstruction of the fallopian tubes and infertility. Chronic salpingoophoritis is characterized by a long course, accompanied by relapses, as well as menstrual irregularities.
According to their localization, two forms of salpingoophoritis are distinguished:
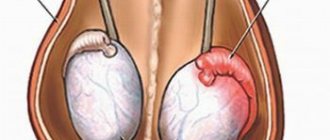
- Unilateral salpingo-oophoritis, which is characterized by inflammatory processes of the uterine appendages on only one side: left or right. Left-sided salpingo-oophoritis is much less common, in contrast to right-sided one. If only one tube is affected, a woman can become pregnant without special treatment.
- The most complex form of this disease is chronic bilateral salpingoophoritis. This form of the disease is a serious threat to a woman’s health. Bilateral salpingoophoritis often becomes the cause of female infertility. If pregnancy does occur, there is a possible risk of intrauterine infection. Bilateral salpingoophoritis can cause miscarriage. It can also lead to ectopic pregnancy, which poses a great danger to the woman's life. When diagnosing bilateral salpingoophoritis, timely treatment is necessary.
Causes and symptoms of right-sided salpingitis
Right-sided salpingitis is characterized by inflammation in the right fallopian tube, caused by the activity of various pathogens - for example, chlamydia. The causes of infection can be sexual activity without using condoms, poor personal hygiene, and traumatic injuries as a result of gynecological surgical interventions. When infection penetrates the fallopian tube, swelling and disruption of blood outflow occur, severe thickening of the appendages and the formation of adhesions. A woman may have a fever, pain in the pelvic organs, and discharge. If right-sided salpingitis is diagnosed and treated in a timely manner, the consequences can be avoided and a complete recovery will occur.
Prevention of relapse
- Maintaining personal hygiene
The most obvious and important measure is the daily use of hypoallergenic intimate care products. Washing gel “Ginocomfort” is perfect as an addition to the course of treatment. One of the components of the gel - tea tree oil - is a natural antiseptic and perfectly fights germs and pathogens in the vulnerable environment of the vagina, without allowing them to penetrate deeper.
- Delicate conduct of any gynecological procedures
After severe inflammation, it is necessary, if possible, to allow the fallopian tubes to fully recover. The restorative intimate gel “Gynocomfort”, created to support women after suffering infectious diseases, will help heal microcracks in the vagina and return to its previous healthy state. - Using “barrier” contraception
In order not to provoke a conflict of microflora in an even weakened reproductive system, it is better to use condoms for the first time after recovery and, if necessary, use a lubricant, for example, Gynocomfort intimate gel-lubricant, which reduces friction. - Visit a gynecologist at least 2 times a year.
It is timely diagnosis of the condition of the internal and external genital organs that will help detect all possible diseases in the early stages and prevent complications. - Avoid self-medication
Salpingitis is a rather dangerous disease. If any of the above signs appear, make an appointment with a gynecologist and do not put off the visit. Otherwise, the risk of unpleasant complications increases significantly.
Causes and symptoms of purulent salpingitis
Purulent salpingitis usually occurs as a result of infection with gonorrhea. It can also be triggered by a miscarriage, an abortion performed outside the walls of a medical institution, or the use of expired uterine devices. A large amount of pus forms in the cavity of the fallopian tube, and when it penetrates into the abdominal cavity, peritonitis develops. The symptoms of purulent salpingitis are very noticeable. Body temperature rises, severe pain occurs in the lower abdomen, which can radiate to the lower back and rectum, purulent vaginal discharge, chills, and fever. This disease must be treated surgically; conservative methods are ineffective.
Salpingitis along with oophoritis
The most common form of the pathological process is simultaneous inflammation of the fallopian tube and ovaries. Most often, the lesion occurs unilaterally, bilaterally occurs much less frequently. The inflammatory process originates on the mucous membrane of the fallopian tube and is then transmitted to the epithelium of the ovary. As a result, a pathological conglomerate is formed. It is necessary to begin treating salpingitis and oophoritis as quickly as possible in order to preserve the possibility of pregnancy in the patient.
How life-threatening are the consequences of salpingitis?
Inflammation of the fallopian tubes in itself is not a deadly disease; the prognosis for treatment is almost always positive, unless complications arise: “sealing” of the fimbriae and the formation of hydro- (sacto-, hemato-) salpings or their suppuration (pyosalpings) involving the ovaries - “ tubo-ovarian tumors”, which may entail surgical treatment with removal of the fallopian tubes, and sometimes the appendages entirely or together with the uterus.
It should be noted that the speed of treatment and final restoration of the reproductive function of the female body may vary depending on how quickly the disease was stopped and therapy was prescribed.
In any case, this diagnosis is common, which means that modern gynecology, coupled with medicinal cosmetics based on effective ingredients, can help recover even after a serious illness.
Sources:
- POSSIBILITIES OF PRESERVING REPRODUCTIVE FUNCTION IN YOUNG WOMEN WITH ACUTE SALPINGITIS. Pokinchereda T.V. Chertovskikh M.N. Kulinich S.I. // Siberian Medical Journal. – 2009. – No. 7. – P. 70-73.
- MAGAZINE A MODERN VIEW ON THE ANATOMY AND FUNCTION OF THE FALLOPY TUBES. // Aketaeva A.S. – Clinical medicine of Kazakhstan. – 2021. – No. 2 (40). – pp. 14-21.
- Basic research methods and surgical interventions in gynecology. Kolgushkina T.N., Korshikova R.L., Peresada OA, etc. - Minsk, 1999. - 124 p.
- Hyperandrogenism syndrome in women. // Methodological manual for doctors, ed. Academician I.I. Dedova. M., 2003.
- Post-stroke cognitive impairment. Vakhnina N.V., Parfenov V.A., Yakhno N.N. // Journal of Neurology and Psychiatry. Stroke. - 2008. - No. 22. - P. 16-22.
- Mini-mental state: a practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. Folstein M., et al. // Journal of Psychiatric Research. - 1975. - No. 12. - R. 189-198.
- Pathologic correlates of incidental MRI white matter signal hyperintensities. Fazekas F., et al. // Neurology. - 1993. - Vol. 43. - P. 1683-1689.
- https://www.healthline.com/health/womens-health/salpingitis
- https://www.pubfacts.com/search/Salpingitis/2
- https://www.lecturio.com/magazine/salpingitis/
- https://research.omicsgroup.org/index.php/Salpingitis
Diagnosis of salpingitis
Diagnostic methods include:
- conducting a gynecological examination;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (ultrasound examination is performed transvaginally and transabdominally);
- bacteriological examination of a smear taken from the cervix, bacterial culture, smear analysis using the PCR method - one of the mandatory methods aimed at identifying sexually transmitted infections;
- performing laparoscopy;
- carrying out metrosalpingography.
During a gynecological examination, a vaginal examination using fingers and a speculum examination are performed. This ensures visualization of the vaginal walls and fornix, and the cervix. The presence of salpingitis is characterized by purulent mucus on the walls of the vagina and uterine cervix, as well as possible erosions, dysplasias, and neoplasms on the mucosa. During a digital examination, the gynecologist evaluates the shape and position of the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries. With salpingitis, soreness of the fallopian tubes and adhesive formations are detected.
To identify acute salpingitis, laparoscopy is one of the main diagnostic techniques, the accuracy of which is approximately 80-90%. This surgical intervention is performed under local anesthesia. Using a laparoscope, the fallopian tubes and ovaries are visualized and the presence of inflammatory processes in them is detected. You can also see purulent and blood accumulations in the oviducts.
Metrosalpingography is one of the radiopaque methods aimed at assessing the patency of the fallopian tubes. A contrast agent is injected into the uterine cavity and tubes, which is subsequently monitored on x-rays. Photos are taken with a delay. In the presence of obstruction, the contrast does not fill the fallopian tube at a certain level, which is most often caused by adhesions against the background of chronic salpingitis.
Treatment of salpingitis
Treatment of salpingitis in Moscow clinics is carried out using medicinal and surgical methods.
The following are prescribed as therapy:
- antibiotics – Ceftriaxone, Azithromycin, Doxycyline, Cefotaxime, Ampicillin, Metronidazole;
- anti-inflammatory drugs - Ibuprofen, Acetaminophen, Butadione, Paracetamol, Terzhinan suppositories, Hexicon;
- immunomodulatory agents – Imunofan, Polyoxidonium, Groprinosin, Humisol;
- antipyretics and antihistamines;
- vitamin complexes containing cocarboxylase, vitamins E, C;
- probiotics, antioxidants.
It is also possible to carry out physiotherapeutic procedures - electrophoresis with lidase, treatment with pulsed low-frequency ultrasound, reflexology, infusion therapy, heat therapy, diadynamic therapy, autohemotherapy. During treatment, it is advisable to adhere to a healthy diet and avoid the consumption of alcoholic beverages, which leads to a deterioration of the immune system and the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
It is possible to add traditional methods to drug therapy - taking baths with valerian, sage, juniper, rosemary, milk, douching with a herbal solution, using tampons with a decoction of plantain, aloe, cabbage, and consuming various herbal teas.
In cases of ineffectiveness of drug and physiotherapeutic treatment, as well as in the presence of tumor formations in the uterine appendages, adhesions causing obstruction of the fallopian tubes, accumulation of pus, and infertility, the patient is prescribed surgical intervention. First of all, adhesions and neoplasms are eliminated and normal patency of the fallopian tubes is restored. Surgical intervention is carried out by laparoscopy (the surgeon makes a small incision through which a miniature camera is inserted and the affected areas of the tubes are excised and their patency is restored) or laparotomy (the abdominal cavity in the area of the projection of the affected fallopian tube is dissected, the infected areas are eliminated, sanitation, dissection of adhesions is carried out formations).
Salpingitis and the possibility of getting pregnant
If the patient suffers from unilateral salpingitis and treatment was started in a timely manner, her chances of becoming pregnant on her own without undergoing additional medical procedures and manipulations are very high. If the inflammatory process is traced in both uterine appendages, the probability of spontaneous pregnancy is one in ten. About twenty-five percent of women suffering from a chronic form of salpingitis receive a conclusion about the occurrence of infertility. Through the use of laparoscopic surgery, complete elimination of intrauterine adhesions is possible; competent drug therapy helps eliminate the inflammatory process. After long-term treatment, spontaneous pregnancy may occur.
In case of obstruction of the fallopian tubes, which cannot be restored, or in the case of removal of the oviducts, a woman’s opportunity to become a mother is realized using the IVF technique.
Most Frequently Asked Questions
What type of anesthesia is used during surgery?
For more complete information, you should visit the special section of this site.
Is there any special preparation for surgical treatment for fallopian tube pathologies?
Those patients planning surgical treatment should study the section on preoperative preparation.
In which clinic can the operation be performed?
The initial consultation is carried out at the Swiss University Clinic in Moscow. You can also familiarize yourself with clinical sites located in Moscow or Switzerland.
Useful links to various sections of the site on surgical treatment of intrauterine diseases:
preparation for surgery for diseases of the fallopian tubes ... pain relief during surgery for diseases of the fallopian tubes ... simultaneous (simultaneous) operations for diseases of the fallopian tubes ... clinical sites ... reviews of other medical specialists