General information
Pediculosis is an infestation of the hairline with lice.
Parasites settle mainly on the head, feed on human blood and are easily transmitted to others. Pediculosis in children is a parasitic disease. Caused by body, pubic or head lice. Cases of head lice infestation are more common. The danger of lice lies in the fact that scratching the itchy areas creates wounds through which the infection penetrates. In schools and kindergartens, nurses regularly examine children. At the first signs of head lice, the child is isolated until complete recovery; the parents of the remaining children are informed about the disease in the group. Treatment begins immediately to prevent infection of others and protect the baby from complications.
Where does pediculosis come from in children?
You can only become infected with lice through direct contact, since the insects cannot jump or fly. Insects hold on to the hair with special hooks on their legs, and when the opportunity arises, they move from one person to another. It takes a little time to change the host, since, as already said, lice move quite quickly. Pediculosis is more often observed in children and adolescents because they often interact closely during play, joint projects, and physical exercise.
Interesting fact!
An unusual study was recently conducted in Argentina. After the World Health Organization declared COVID-19 a pandemic in March 2021, the Argentine government imposed a mandatory lockdown involving distance learning in schools. After the end of quarantine, a survey was conducted, according to which the prevalence of head lice during this period decreased by 25%. This confirms that the main route of lice infection is through close contact between children.
Head lice do not live long outside their host. Several studies in schools have shown that even in classrooms where children with head lice were identified, no live lice were found on surfaces or floors. In addition, it has not yet been scientifically proven that parasite infection can occur through combs, hairpins and headphones. However, infectious disease specialists admit that there is still a small probability of such a transmission route.
A common myth is that children in kindergarten become infected with lice through carpets, play mats and soft toys. If children bring lice from preschool institutions, it is only because during play they come into close contact, giving lice an excellent opportunity to crawl from head to head.
Symptoms of lice
The first signs of lice are increasing itching of the scalp. When examining the hair, nits (lice eggs) are found, which are whitish in color and difficult to remove. There are especially many nits on the back of the head or behind the ears. If there are few parasites, parents cannot always detect them on their own, so the help of qualified doctors is mandatory. Pediculosis is characterized by the following features:
- increasing itching, which leads to significant wounds and scratching;
- increased irritability, sleep disturbance;
- hair tangling, brittleness and dryness;
- the appearance of an allergic rash on the face and other parts of the body;
- the presence of reddish spots from bites on the scalp.
If the disease is not treated, then under the influence of lice waste products, the hair becomes tangled.
Against the background of decreased immunity, another infection occurs, pyoderma and eczema occur, lymph nodes become enlarged, and the temperature may rise. In addition to head lice, pubic lice also occurs. Its frequency in the population is lower, but parents should still be aware of the symptoms. The disease is characterized by itching in the genital area; after an insect bite, bluish nodules up to 1 cm in diameter appear on the stomach and thighs.
Even less common is body lice, when infection occurs with body lice living in bedding and clothing. The main symptoms of this disease are itchy reddish spots and papules on the body. As the disease progresses, the skin becomes rough, peels, and pigmented spots appear that do not go away and remain for life.
Available treatments for head lice in children
To treat head lice, use the products available in pharmacies. Lice preparations may contain chemical compounds that have an insecticidal or physical effect.
Insecticidal preparations contain permethrin (for example, Medilis-Bio) which has neurotoxic properties, that is, it changes nerve conduction in arthropods, which leads to paralysis of the central nervous system in lice.
Head lice - treatment for children
Preparations with permethrin (for example, Medifox Super should not be used for children under 3 years of age, and caution should be exercised in case of allergies. They can cause irritation and redness of the scalp.
Physical preparations contain silicones - dimethicone and/or cyclomethicone. They work by penetrating the lice's respiratory system, thereby cutting off the air supply and suffocating the lice. Products with this composition are non-toxic and do not irritate the scalp. They can be used for small children from approximately 3-6 months.
Medicines for the treatment of head lice are safe and easily available in pharmacies without a prescription, so there is no need to prepare lice rinses yourself. Firstly, they may turn out to be ineffective, and secondly, harmful.
Popular herbs (rosemary, thyme, mugwort, larkspur) or essential oils such as tea tree oil, which allegedly contain insecticides, can irritate the scalp and do not cure lice. Natural products are not always effective or safe.
The effectiveness and success of treatment, regardless of the pharmaceutical composition of the product, depends on strict adherence to the instructions and method of application. Therefore, before using the drug, be sure to read the attached leaflet.
In addition to head lice and scabies, the doctor recommends paying attention to where the child is walking. Children often relax in wooden country houses with bedbugs, and it turns out that the child returns from the trip completely bitten. Then you should contact a dermatologist, who will adjust the therapy - drugs that relieve itching, sometimes steroid ointments or antihistamines will be required.
Causes of lice
The cause of lice in children is lice that live on the human body in the hairline.
The source of infection is the patient; transmission of parasites occurs through close contact. In this regard, children attending kindergartens, schools, and clubs are at risk for head lice. Girls with long hair are especially susceptible. Infection is also possible through the use of hygiene products that belong to the patient. This is how lice get onto a child’s skin in a hairdresser’s salon (if the workers do not properly handle the tools). There is a risk of infection in transport, bathhouses, and swimming pools.
Doctors also identify factors that increase the likelihood of developing head lice:
- weakened immune system;
- unfavorable living conditions;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules.
Most people believe that lice are a sign of a dysfunctional family in which a child lives. But that's not true. Children living in normal conditions can also become infected. It is important what environment the baby is in and what his state of health is.
What are lice?
The life cycle of these insects lasts approximately three weeks (12-28 days). During her life, a female can lay up to 300 eggs (8-10 per day). These insects cannot fly, jump or swim. They crawl, moving along the hair with the help of pointed hooks on their legs.
The mobility of lice depends on the ambient temperature. In conditions close to the temperature of the human body, they move quite quickly, covering about 33 cm per minute, which is a very good speed considering their millimeter size.
Without a host, parasites can live only 2-3 days. Again it all depends on the temperature. At 35–37 °C, a human louse can survive one day without feeding. At a temperature of 10-20 °C, when the metabolic processes of insects slow down, it takes a little longer. It is believed that lice die at a temperature of -20°. Insects calmly survive hair washing. They cling tightly to the hair and close the holes on the body through which they breathe
Interesting fact!
Human lice have an amazing resistance to ionizing radiation (radiation) compared to other insects. A radiation dose of 150,000 rads can kill a louse in only a week. For comparison, exposure of a person to a radiation dose of 200-400 rad causes radiation sickness.
Diagnosis of pediculosis
No special tests are required to detect lice in hair.
Parents and nursing staff should regularly examine their child's hair. The diagnosis of lice is confirmed by the detection of nits in the hair of adults. Nits are often confused with dandruff. An important difference is that lice eggs do not separate from the hair with a light touch; force is required. When nits are crushed, a clicking sound is heard. To make a final diagnosis in doubtful cases, a Wood's lamp is used: in its rays, nits glow blue. When pediculosis is accompanied by skin lesions, differential diagnosis with other dermatological diseases is required: seborrheic dermatitis, pyoderma, psoriasis, etc. Only a qualified dermatologist can carry it out.
Causes of lice: main methods of infection
The causes of head lice depend on the type of parasite. The main route of infection with head lice is through close head-to-head contact with an infected host. That is why lice most often occur in children, who, due to their age, spend a lot of time being close to each other.
Lice infestation in adults also occurs through close contact. The risk is especially high in places with large crowds of people in small areas. These could be boarding schools, dormitories, military barracks, correctional institutions. Children most often become infected with lice in preschool or school institutions, summer camps during joint games or activities.
There is a certain risk of infection when sharing bed linen, towels, and other household items. Bed lice can be transmitted through clothing and bedding. The main route of infection with pubic lice is through sexual contact.
The causes of lice are not related to contact with pets, visits to swimming pools, water parks or ponds, or stressful situations. Compliance with the rules of hygiene and cleanliness do not guarantee protection against head lice - lice can penetrate dirty and clean hair with equal success.
Treatment of pediculosis
To treat head lice in children, special shampoos and medications are used. The hair is treated with medications, and then the dead lice and nits are combed out. For children, drugs in the following forms are suitable:
- soap;
- cream;
- shampoo;
- spray;
- cleaning liquid;
- lotion.
Antiparasitic agents attack the nervous system of insects and paralyze them, after which the adults die and are easily combed out.
However, nits turn out to be resistant to these agents, so after 1-2 weeks the treatment must be repeated. The traditional treatment regimen involves applying the medication to the hair. Then the head is wrapped in polyethylene and a towel and left for 1-2 hours (be sure to read the instructions). The product is washed off with regular shampoo, then the paralyzed lice are combed out from damp hair.
Not all medications are suitable for children. Therefore, how to treat pediculosis in children, check with a specialist. Products containing permethrin and phenothrin should be avoided in children under 3 years of age with sensitive skin. Medicines containing malathion are quite toxic, so they are not suitable for skin allergies when the permeability of the dermis is increased. A dermatologist will help you choose the right drug.
Does your child have pediculosis? What should we do?
Category: Prevention.
Pediculosis or lice is a specific parasitism of a person by lice that feed on his blood. There are three types of lice: body lice, head lice and pubic lice.
Body lice are the most dangerous epidemiologically, as they can become carriers of typhus, relapsing fever, and Volyn fever. Feeding on the blood of a sick person, body lice, when bitten, are able to transmit the causative agents of these infections to a healthy person.
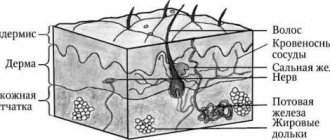
The body louse is the largest (size up to 5.0 mm), lives in the folds and seams of linen and clothing, where it lays eggs that stick to the fibers of the fabric, as well as to the hair on the human body. The average lifespan of adult lice is 35–45 days. During its life it lays up to 400 eggs. Body lice remain viable outside the human body for 2–3 days, when the temperature drops to 7 days. Fortunately, body lice is not that common. Basically, people with a low level of personal hygiene (homeless people, alcohol abusers, etc.) are affected by this type of lice.
Currently, head lice is the most common problem.
This disease has become widespread, mainly among organized children's groups. The causative agent of head lice, the head louse, is up to 3.5 mm in size, lives and reproduces in the scalp, preferably on the temples, back of the head and crown. The life cycle from egg (nit) to adult is 25–35 days; it lays up to 140 eggs during its life. Outside the host's body, it dies within a day. The source of infection is a sick person. It is impossible to become infected with lice from animals, because these parasites are species-specific, i.e. human lice can only live on humans. The main symptoms of lice are itching accompanied by scratching. Scratching often contributes to the occurrence of secondary skin diseases: pustular lesions, dermatitis, skin pigmentation, eczema, and some people develop allergies. In advanced cases, a “tangle” may develop—tangling and sticking together with purulent-serous discharge of the hair on the head, the skin surface is covered with crusts, under which there is a weeping surface.
To prevent the widespread spread of head lice in children's groups, regular examinations are carried out by medical workers in preschool, secondary school and vocational education institutions.
The frequency of such examinations is regulated by orders of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation and the Department of Health of the Tyumen Region. If head lice is detected in a child in a children's group, he is excluded from attending kindergarten or school until he is completely cured. The medical worker who has identified pediculosis must explain to relatives or the patient himself (if he has reached 15 years of age) the rules and methods of treatment for pediculosis and issue a reminder. A child will be considered healthy if he is completely free of lice and nits. If there are even a small number of nits, a child is not allowed to join the children's group.
What to do if you yourself discover head lice in your child?
First of all, please calm down and choose any option that is convenient for you:
First option:
- Buy any product for treating pediculosis (lice) at the pharmacy. Do not use folk remedies (kerosene, DUST, hellebore water) - most often they are toxic, and their effectiveness is questionable.
- Treat the child’s scalp with the chosen product strictly in accordance with the attached instructions.
- 3. Wash your baby using baby soap or shampoo. For boys, a haircut is possible.
- Remove dead insects and nits mechanically (pick with your hands or comb out with a fine-toothed comb). To remove nits, you need to wet strands of hair in a solution prepared from equal amounts of water and 9% table vinegar. You can place cotton wool soaked in the same solution on the comb to improve the peeling off of nits. Rinse your hair with warm water.
- Put on clean underwear and clothes for your child.
- Wash bedding and baby's clothes separately from other things, iron them using steam.
- Examine and, if necessary, treat all family members. Don't forget about yourself.
- Be sure to inform the doctor (nurse) of the child care facility your child is visiting about the situation so that they can carry out a set of anti-pediculosis measures.
- Repeat examinations of the child and all family members after 7, 14, 21 days and, if necessary, carry out repeated treatments until insects and nits are completely eradicated.
Second option:
It is carried out in cases where your child has skin or allergic diseases and if the child is under 3 years of age.
- Comb out live insects with a fine-toothed comb, preferably in the bathroom, and rinse with hot water.
- Treat strands of hair carefully, without touching the child’s scalp, with 9% table vinegar diluted in half with water and remove nits from the hair with your hands or a comb. You can put cotton wool soaked in the same solution on the comb to improve the peeling off of nits.
- Wash your child's head and body with baby soap or shampoo.
- Wash your child's underwear, bed linen and things separately from other things, iron with a steam iron.
- Inspect and if insects are identified, treat all family members. To treat adult family members, use anti-pediculosis agents, which can be purchased at the pharmacy chain.
- Repeat examinations of the child and all family members after 7, 14, 21 days and carry out repeated treatments if necessary. If insects and nits are detected, carry out repeated treatments until they are completely exterminated.
Prevention of head lice includes educating the population in hygienic skills. In terms of personal hygiene, children should be told about lice in an accessible form adapted for them. Usually, a child with head lice becomes subject to
ridicule from peers. Such mental trauma is difficult to bear in a group of children, and, knowing this, the child can hide the discovery of lice from others, including parents, and try to cope with the problem on his own. It is necessary to explain that this is the same disease as others that are transmitted from person to person, and that it also needs to be fought, because it will not go away on its own. You should draw the child's attention to the fact that lice cannot tolerate clean, neatly trimmed hair and combing it daily with a fine comb. You should not use other people's combs, hats, clothes, and especially other people's underwear. Children's teams should be encouraged to be neat and observe the rules of personal hygiene.
Prevention of head lice
Preventive measures are based on careful attention to the child’s health:
- regular head examination;
- use of personal hygiene products;
- Regular washing and combing of hair.
Remember, if lice is confirmed, all family members will have to be treated.
If there is constant itching of the scalp, consult a dermatologist about head lice. SM-Doctor employs qualified specialists who will quickly establish the correct diagnosis and prescribe the necessary treatment.
How to properly diagnose lice?
When checking a child's head for lice, it is not enough to simply examine the hair and scalp. It is best to use a fine-toothed comb for this purpose. This method is much more efficient and will save your time. The distance between the teeth of the comb should not exceed 0.2 mm and be the same along the entire length (such combs are often sold in pharmacies complete with pediculicides).
You can comb both dry and wet hair. You can also use hair conditioner. It makes hair smooth and slippery, making it difficult for lice to move around and making combing much easier
It is better to inspect and comb the child's head in daylight or good artificial lighting. If you have poor eyesight, you can use a magnifying glass. It is necessary to comb your hair over a bathtub or a white towel, so insects are easier to spot.
How dangerous are lice?
Skin damage due to insect bites is an extremely unpleasant occurrence. But lice can also cause more serious problems:
- Typhus – is a complication of pediculosis, accompanied by high fever, severe damage to the nervous system, and can lead to disturbances in the functioning of the heart and blood vessels;
- Relapsing fever - develops due to the entry of pathogenic bacteria into an open wound, causes severe pain in the joints, fever, vomiting, and also affects the liver and heart up to a microinfarction;
- Pyoderma is an infectious complication in the form of purulent skin lesions caused by the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms through bite sites;
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes, primarily behind the ear and cervical;
- Severe allergic reactions;
- Disturbances in the functioning of the immune system due to the penetration of foreign proteins with lice saliva;
- Folliculitis – damage to the hair follicles, hair loss.
Due to constant scratching, pustules appear, the rash may spread, and skin pigmentation may occur. Pediculosis harms the scalp and provokes the formation of dandruff. Streptococcus, staphylococcus can get into the wounds, and it can even lead to sepsis. Scratching can cause the development of eczema and dermatitis.
Pediculosis is more common in children. Doctors attribute this to the imperfection of the child’s immune system, as well as to behavioral characteristics, for example, the exchange of things and personal hygiene items, and close contact in children’s groups. After infection, the child becomes restless, sleeps poorly, and has trouble concentrating.