Oxytocin is both a hormone that affects various organs (including the breasts and uterus) and a neurotransmitter (a chemical messenger in the brain). It controls key aspects of the reproductive system, including childbirth and lactation, as well as human behavior.
English name:
Oxytocin
Synonyms:
syntocinon and pitocin (synthetic versions of oxytocin), carbetocin (an analogue of oxytocin with a similar structure), “love hormone”
See also:
October 16-18, 2021
Expert school
Advanced level
Participate
What is oxytocin: main functions
Oxytocin is produced in the hypothalamus and secreted into the bloodstream by the posterior pituitary gland. For example, the ability of the uterus to contract during childbirth and breastfeeding depends on it.
Artificial oxytocin is sometimes given to induce labor if labor has not started naturally. It is also used to strengthen contractions during weak labor and to reduce the risk of heavy bleeding after the birth of a child. During breastfeeding, oxytocin helps milk move through the ducts in the breast, allowing it to exit through the nipples.
In the male body, oxytocin is responsible for the movement of sperm and the production of testosterone by the testicles.
In the brain, oxytocin acts as a chemical messenger and influences people's behavior and emotions, including:
- For sexual arousal;
- Confession;
- Confidence;
- Romantic affection;
- Bonding between mother and baby.
Therefore, oxytocin is often called the “love hormone” or “cuddle hormone.”
Oxytocin: the hormone of love and social cohesion
A lot of information about hormones has accumulated over the past decades, and not only purely scientific. Ordinary people also know about hormones. Probably anyone will say that these are products of the endocrine glands, which control metabolism. Some will also add that hormone levels affect health. When there are more or less of them than necessary, illness may occur. However, these substances have not yet revealed all their secrets. Every year, scientists discover new functions of hormones. Oxytocin especially brings many unexpected surprises.
Oxytocin became known many years ago mainly as a substance that “guides” childbirth, and therefore was considered a female hormone. Of course, oxytocin was also detected in the blood of men, but at first scientists did not pay much attention to this fact.
Hormone of love and affection
However, it soon became clear that the functions of oxytocin in the body are associated not only with childbirth. Both men and women need the hormone because it can create affection between people: it not only makes them stick together, but also triggers a chain of reactions in the brain, as a result of which they enjoy spending time together.
It is believed that this oxytocin mechanism was developed in the times of prehistoric animals. Thanks to him, the mother felt attached to the child, animals of the same group flocked and were ready to protect each other, and sexual partners stayed close.
It's the same in the human world. Friends, lovers and parents release a fair amount of oxytocin when they are around each other. Hugs and kisses initiate an additional surge of the hormone. For this reason, we are happy with the people close to us and our life is full of joy.
Sex
During physical intimacy, oxytocin is also released, but very briefly. Immediately after orgasm, the hormone level begins to drop, but, naturally, not to zero, but to the value that was before sex. That is, the person’s attitude towards his partner, which was before intimacy, will return. However, it happens that sex lays the first brick in a close relationship being built.
Broken heart
Oxytocin can be produced not only with intimacy and pleasure. If a relationship breaks down, this hormone can trigger very unpleasant experiences and severe stress. According to modern research, during such mental suffering, the activity of the pain centers in the brain is as high as if the person were experiencing real physical pain.
There is an opinion that this is also a reaction developed by evolution: we must stay close if we break away from a group or a loved one, putting ourselves and others in a difficult position. So oxytocin does not allow us to run far, it drives us back. Of course, life is not so simple. Sometimes a person doesn’t mind returning, but they no longer accept him, which causes suffering.
Me and them
Thanks to oxytocin, we separate ourselves and others, that is, we know that we are capable of being the same as them, but we cannot be them. We also understand that our mental processes, thoughts, desires and emotions belong to us, and not to others.
In addition to separating ourselves and others, oxytocin helps us perceive others positively. We see their good sides and intentions and, accordingly, behave friendly with them. It is believed that this is also a rather ancient mechanism that helps the group stay close and live in peace with each other.
Generosity and generosity
In order to feel close to others and feel safe, having a good relationship with each other is not enough. Oxytocin stimulates expressions of generosity and generosity. This process is two-way. Oxytocin is released both when we please our loved ones and when they please us, that is, if they themselves are kind to others and if they are kind to us. In addition, any generous act is again rewarded with a portion of oxytocin. This makes it possible to feel a sense of community with the society in which we live.
Us versus them
If the social group to which we consider ourselves is in danger, oxytocin again comes to the rescue. He helps group members close their ranks more tightly and mobilize for defense. In this case, the peace-loving hormone can initiate defensive aggression towards the enemy.
Anxiety and depression
The fact that oxytocin helps with depression has been known for quite some time. Back in the 70s, articles were published describing the effect of this drug when instilled into the nose. The substance showed its effectiveness, but publications were few. Oxytocin really got its start in the 2000s. A series of studies have confirmed that the hormone improves mood. At the same time, the adaptation of depressed patients to society increases: it is easier for them to build connections with others, easier to get along with relatives.
Memory
It was noted that oxytocin can improve memory, but only social memory, that is, memory of events or objects related to human interaction. Thanks to this hormone, we easily recognize standard social situations and can understand how to behave in society under certain conditions. Memory for faces is also realized under the influence of oxytocin. This substance helps us remember our childhood, our mother. Although the beneficial effects of oxytocin are one-sided, it is currently being tested for use against Alzheimer's disease.
Dark side of the force
For a very long time, oxytocin was viewed solely as a “soft and fuzzy” hormone that provided pure pleasure and helped people connect. However, not all so simple. Every positive function has a downside.
The substance helps communicate, enhances a sense of unity, and reduces social stress. But this does not always happen. In some cases the opposite may be true. People become more anxious, suspicious, and feel that society is pushing them away. It was found that a person’s reaction to oxytocin depends on the circumstances and the person’s mood for communication. In this case, the hormone triggers a chain of physiological reactions that activate the neural pathways responsible for fear. The activity lasts about six hours. So, in an unfavorable situation, oxytocin may not help, but harm.
Oxytocin enhances social memory, but recent research suggests it may impair aspects of memory unrelated to communication. For a time, it was considered as an aid to student learning, but retention of material not related to human interactions suffered somewhat with the use of this hormone.
dietary supplements
As soon as the first studies began to be published about the positive effects of oxytocin on mental function, dietary supplement manufacturers quickly took action. Dietary supplements do not need to be patented, and clinical safety is not required to be tested. You can simply write about the “miracles of oxytocin” and even provide links to good articles in scientific journals.
Moreover, oxytocin is a drug with a long history and has been produced by pharmaceutical companies for a long time. There's even a nasal spray. It was used in all studies of the effect of oxytocin on mental processes. However, the spray was created for obstetrics and not for other purposes. Therefore, it is worth remembering that, despite the long list of positive effects of the hormone, the doses of its use outside of obstetrics and gynecology have not yet been clearly defined.
If you read reviews about the drug, people who have taken it have very different opinions about its effectiveness. It was good for some, and very bad for others.
Those who have decided, despite the lack of evidence, to try the obstetric spray on themselves, should know that the hormone is quite capricious to the temperature environment. In your hands, it can lose all its activity, and you will put a solution equal in activity to water into your nose. In addition, the obstetric spray is not designed for long-term use. It is used during labor and delivery. Of course, no one imagined that it would be used for weeks and months. For this reason, all sorts of troubles from the nasal mucosa are possible.
Happiness is at arm's length
Oxytocin is much easier to obtain through social interactions, especially physical ones. When communicating with children, mutual hugs and any friendly interactions, it is produced in much larger quantities. In this case, the hormone does not deteriorate during storage and acts immediately.
Natalia Stilson
Photo thinkstockphotos.com
Related product: [product](oxytocin)
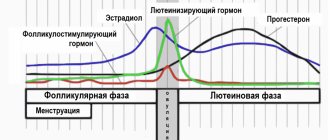
How is oxytocin controlled?
The production and secretion of oxytocin is controlled by a positive feedback mechanism, where the release of the hormone causes an action that stimulates its own production. For example, when the uterus begins to contract during labor, oxytocin is released. This stimulates contraction activity and the release of more oxytocin. Thus, contractions increase in intensity and frequency.
Another example of positive feedback: stimulation of the nipple during breastfeeding leads to an increase in the production of oxytocin and its secretion into the blood, resulting in milk flowing into the breast.
Oxytocin gives a person self-confidence
Produced in sufficient quantities, this hormonal substance gives a person self-confidence, develops a sense of satisfaction with life, good nature and sociability. A person becomes generous, sociable, ready to show participation and compassion.
- With the help of the influence of this substance, we can very vividly imprint various events, positive and negative, in our memory.
Partner birth
The neuropeptide plays an important role in the regulation of maternal behavior. During childbirth, a strong emotional bond arises between mother and child. Surprisingly, when the father is present at birth, a similar effect is observed in him (only a little weaker).
Autism
Oxytocin may be associated with autism and may be an effective treatment for autism and autism-related behaviors. Oxytocin treatment increased emotional behavior abilities in autistic adults. Two relevant studies in adults, in 2003 and 2007, found that oxytocin reduced the repetition of autistic behaviors and improved the expression of emotions in autistic people. Recently, intranasal administration of oxytocin was found to improve emotional recognition in children aged 12 years diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder. Oxytocin has been linked to autism in the sense that autism is determined by deletion of the gene containing the oxytocin receptor gene (OXTR). Studies involving Caucasians and Chinese Mongoloids have provided evidence for the association of OXTR with autism. After inhalational oxytocin treatment, autistic patients exhibit more active social behavior. The benefits and side effects of oxytocin treatment for autism have not been thoroughly studied at this time - therefore, oxytocin treatment is recommended[ by whom?
], if possible, be carried out in conditions relevant to a clinical hospital.
Increased trust and decreased fear. In the experimental group, subjects who received nasal oxytocin showed “high levels of trust” twice as often as the control group, which did not receive oxytocin. Nasal administration of oxytocin demonstrated a reduction in fear, possibly due to suppression of the amygdala (which is thought to be responsible for fear of communication). Some researchers argue that oxytocin has a general effect on enhancing other social emotions: after intranasal administration of oxytocin, feelings of envy and schadenfreude increase.
Decreased trust in outsiders and increased cultural and racial prejudice.
- Showing generosity by increasing trust.
- Some learning and memory functions are impaired after oxytocin use.
Oxytocin also has weak vasopressin-like antidiuretic properties.
Melatonin
Let's end today's story on a happy note - let's go to bed.
Melatonin, a sleep hormone, is produced by the pineal gland in the brain when it gets dark (which is why shining a smartphone screen into your eyes before bed is a bad idea). It regulates the “internal clock” - circadian rhythms - and helps all body systems go into rest mode. During the day, the highest levels of melatonin occur between midnight and 5 a.m. during daylight hours; throughout the year, melatonin levels increase in winter. In the body, melatonin is preceded by the amino acid tryptophan, which also plays the role of a precursor to serotonin. Melatonin slows down aging and reproductive functions and increases serotonin levels. The interaction of melatonin with the immune system plays a special role - the hormone’s action reduces inflammation. Melatonin has an antioxidant effect and protects DNA from damage.
Thanks to melatonin, the daily routine is restored after a change in time zone or night work. Decreased melatonin production—for example, due to bright light or changes in daily routine—can cause insomnia, which increases the risk of depression. To help your body get a good night's sleep and regain its routine, try sleeping in the dark—with the lights off and the curtains drawn if you have to sleep during the day.
Life in a big city sometimes consists entirely of stress, chronic lack of sleep, traffic jams, delays, meaningless work meetings and tasks of exaggerated importance and urgency. In such a rhythm, it is very difficult to find time to recover, so we simply begin to take the state of chronic fatigue for granted. But nature did not prepare us for this, and the same cortisol will not be released forever: if you are constantly under stress, cortisol is depleted over time - and then the body is forced to respond to stress in other ways.
To make sure your health matches your stress load, consult with your endocrinologist: your body may need support. And I definitely need rest.
Why is a lack of oxytocin dangerous?
A lack of oxytocin negatively affects a person’s overall well-being. The main signs of its deficiency are:
- menopause;
- depressive states;
- disorders of the central nervous system;
- decreased thyroid function;
- depressed state;
- high likelihood of developing AIDS;
- feeling of loneliness;
- anxiety disorders;
- certain forms of schizophrenia.
A person with a deficiency of oxytocin feels depressed. He is in a bad mood, has no strength or desire to do anything. This negatively affects the overall quality of life. In this situation, complex therapy is required.
Directions for use and dosage
Important: the use of the hormone is allowed only under the supervision of a doctor, in a hospital setting. The specialist administers the drug so that the rate of cervical dilatation does not differ from the rate observed during childbirth, since excessive stimulation is life-threatening
The doctor selects the dosage individually, taking into account the reaction of the pregnant woman and the fetus to the administration of the medicine.
According to the instructions, the solution should be administered only intravenously or intramuscularly. You cannot use two injection methods at the same time. To stimulate labor, an intravenous drip is prescribed
When inserting, it is very important to monitor the infusion rate, constantly monitor uterine contractility and heart rate. If the contraction increases, stop administering the medication immediately.
The hormonal agent is administered according to the following scheme:
First, saline solution is administered, then Oxytocin. To prepare a standard solution for intravenous administration, under sterile conditions, mix 5 IU of a hormonal agent with 1 liter of a non-hydrophilic solvent, and then mix thoroughly. The initial injection rate of the solution should not be higher than 0.5-4 mU/min. Then every 20-40 minutes. it can be increased by 1-2 mU/min until the desired contraction frequency is achieved. For accurate dosing, use an infusion pump or similar device
In late pregnancy, the rate of solution administration must be increased very carefully. In rare cases, it can reach 8-9 mU/min
For premature birth, infusion rates above 20 mU/min are allowed.
To stop uterine bleeding after childbirth, both intravenous and intramuscular administration of the drug are used. According to the instructions for use, proceed as follows:
- Intravenous administration. Prepare a solution of 10-40 units of hormone and 1 liter of non-hydrophilic solvent. To prevent uterine atony (loss of tone and contractility), 20-49 mU/min is required.
- Intramuscular administration. After separation of the placenta, inject 5 IU of solution into the muscle.
In case of incomplete abortion, when the fertilized egg detaches from the uterus, the child dies, but remains in the mother’s body, the hormonal drug is used as follows. First, 10 IU of the drug is mixed with 500 ml of saline, then administered intravenously at a rate of 20-40 drops per minute.
The drug is used to diagnose uteroplacental insufficiency. The test involves intravenous administration of the hormone. According to the instructions, you need to act like this:
- start injecting the drug at a speed of 0.5 mU/min;
- every 20 min. double the speed until an effective dose is achieved, but not more than 20 mU/min;
- When three moderate uterine contractions appear within 10 minutes (40-60 seconds each), stop administering the solution, and then begin to monitor the fetus for the appearance of late or variable decelerations (decreases in heart rate).
Autism
Oxytocin may be associated with autism and may be an effective treatment for autism and autism-related behaviors. Oxytocin treatment increased emotional behavior abilities in autistic adults. Two relevant studies in adults, in 2003 and 2007, found that oxytocin reduced the repetition of autistic behaviors and improved the expression of emotions in autistic people. Recently, intranasal administration of oxytocin was found to improve emotional recognition in children aged 12 years diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder. Oxytocin has been linked to autism in the sense that autism is determined by deletion of the gene containing the oxytocin receptor gene (OXTR). Studies involving Caucasians and Chinese Mongoloids have provided evidence for the association of OXTR with autism. After inhalational oxytocin treatment, autistic patients exhibit more active social behavior. The benefits and side effects of oxytocin treatment for autism have not been thoroughly studied at this time - therefore, oxytocin treatment is recommended[ by whom?
], if possible, be carried out in conditions relevant to a clinical hospital.
Increased trust and decreased fear. In the experimental group, subjects who received nasal oxytocin showed “high levels of trust” twice as often as the control group, which did not receive oxytocin. Nasal administration of oxytocin demonstrated a reduction in fear, possibly due to suppression of the amygdala (which is thought to be responsible for fear of communication). Some researchers argue that oxytocin has a general effect on enhancing other social emotions: after intranasal administration of oxytocin, feelings of envy and schadenfreude increase.
Decreased trust in outsiders and increased cultural and racial prejudice.
- Showing generosity by increasing trust.
- Some learning and memory functions are impaired after oxytocin use.
Oxytocin also has weak vasopressin-like antidiuretic properties.
Oxytocin test
To determine the level of oxytocin in the body, you need to take a blood test. The procedure is unpleasant and partly ineffective. Modern methods make it possible to determine hormone levels non-invasively using functional screening.
Functional screening is carried out using the ATM Vega Test. Innovative equipment is aimed at assessing the general condition of the body, including determining hormone levels. Based on the results obtained, an individual scheme is developed.
Updated equipment allows screening to be carried out in a short time with accurate results. Based on the answers, the optimal treatment regimen is prescribed. Treatment is carried out non-medically, but with the use of special equipment. It affects the active points of the body, provoking the natural production of oxytocin.
Still have questions? You can make an appointment with specialists using the indicated phone numbers.
Cortisol
This is a steroid hormone that is released in the adrenal cortex under the influence of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH).
Like all steroids, cortisol has the ability to influence the expression of other genes - and this quality of it largely determines its importance. Cortisol is synthesized as a result of the body's response to stress, and the hormone's task is to accumulate the body's forces and direct them to solve the problem. Cortisol has a “little brother” - adrenaline, which is also secreted in the adrenal medulla. Adrenaline provides an immediate response to stress - blood pressure rises, heart rate increases, and pupils dilate. All this is needed to carry out a quick “fight or flight” reaction. Cortisol acts more slowly and over longer distances.
Under the influence of cortisol, blood sugar levels increase, the immune system is suppressed (so as not to waste energy), and gastric juice is released. Elevated cortisol over time slows wound healing and can stimulate inflammation in the body. Cortisol also reduces the activity of bone tissue building and collagen synthesis.
Under the influence of sunlight on the pituitary gland, cortisol levels begin to rise shortly before waking up and help a person wake up full of energy. During the day, cortisol helps us cope with normal stress (called eustress). This includes any tasks that require our reaction: answering a letter, holding a meeting, preparing statistics. Eustress does not harm our health - on the contrary, it is a necessary level of stress.
But when the level of stress begins to go off scale, eustress turns into distress - stress in its everyday understanding. Initially, these were life-threatening situations, but now they have been supplemented by any events to which a person attaches great importance. This could be overload at work, problems in relationships, failures, worries and losses, as well as a wedding, moving, receiving a Nobel Prize or just a million dollars - stress is not necessarily bad events, but any changes in circumstances that require changes from us. Evolutionarily, a person is prepared to react to stress, but not to be in it constantly. If a stressful situation stretches over time, a permanently elevated level of cortisol begins to negatively affect the body.
First of all, the hippocampus suffers, synaptic connections are destroyed, the volume of the brain decreases: these processes impair thinking and creative abilities. Under the influence of cortisol, especially at an early age, methylation occurs—some genes may be “turned off.” Children who were exposed to severe stress or poor maternal care as children experience changes in their ability to learn—and these changes last a lifetime. In this case, memory will be better able to retain negative impressions, so such children learn better under stress, while ordinary children need a safe environment.
Also, the prolonged effect of cortisol leads to weakened immunity and activation of inflammatory processes. That is why, after a nervous meeting or a sleepless night, a “cold” may appear on the lips - a manifestation of the herpes virus, which, according to statistics, is carried by approximately 67% of the population, but which does not show itself in “peacetime”. Chronic stress leads to early signs of aging - due to the fact that cortisol blocks collagen synthesis, thinning and dehydrating the skin.
Warm hugs, sex, favorite music, meditation, jokes and laughter will help reduce cortisol levels. It helps to get a good night's sleep - and it's not so much the quantity of sleep that matters, but its quality. If you offended someone or had a fight with loved ones, reconciliation will reduce cortisol levels to background levels.
Experts' opinion
Doctors leave positive reviews about Desaminooxytocin. Experts note that this drug acts more gently and has fewer contraindications than the cheaper Oxytocin. This medicine effectively increases uterine contractions and speeds up labor. However, before using it, it is necessary to carefully weigh and evaluate all indications and possible negative consequences. After all, the unreasonable prescription of a hormonal drug can cause dangerous complications and even fetal death due to asphyxia.
Experts also note the ease of use of the medicine. The injection of the drug "Oxytocin" is quite painful. Using the tablet form helps to avoid discomfort.
Bright side
Oxytocin
You spent the evening with an old friend. They laughed a lot, touched his hand during a conversation, remembered their common past, and hugged goodbye. The whole next day you are in high spirits and are impenetrably happy and calm.
The most important hormone of attachment and communal behavior, oxytocin is produced during all social interactions. First of all, it is associated with love for children and spouses, but its level also increases greatly from communication with friends. This is true not only for humans. For example, in chimpanzees, oxytocin levels increase when they pick each other's fur, and the concentration of the hormone will directly depend on how closely the two individuals know each other.
In 2003, scientists from the University of Zurich experimentally proved that oxytocin has a powerful anti-stress effect. They forced people to speak in front of a hostile audience and then measured the levels of stress hormones in their blood. It turned out that stress was minimal in those who had oxytocin dripped into their noses before the experiment, or in those who were encouraged by a friend before the experiment, which also led to an increase in the level of the hormone.
Prolactin
You met your husband after several days of forced separation. The kids are at grandma's, it's a day off, no one is in a hurry and you have great sex. After orgasm, you turned into raspberry syrup, lying with him in an embrace, filled with great tenderness.
We are accustomed to thinking that prolactin is a breastfeeding hormone. But it seems that it is responsible not only for the secretion of milk, but also for tenderness, and not necessarily towards the child, but also towards the sexual partner too. It is known that orgasm sharply increases prolactin levels - and in men too, although in women it is twice as strong.
Endorphins
You started going to the gym regularly and noticed an interesting effect: after training, your mood improves! A husband who is simply jealous scares you with his mysterious addiction to sports. You are fearless: if sports could truly be truly addictive, the world would be full of beefy, handsome men.
For millions of years of evolution, we did not have fitness clubs. There was wild nature in which our ancestors sought to save energy. From the point of view of the brain, if you are running somewhere and are already at the limit of exhaustion, then you probably really really need to run - for example, a crowd of enemies from a neighboring tribe is chasing you. This means dulling any pain you might experience while running so you don't have any distractions - and if your enemies catch up, pain relief can be helpful.
For approximately the same reasons, the brain synthesizes endorphins - a natural pain reliever, a safe analogue of opiate drugs. If you really were in pain, they would all be spent on objective problems. But since you're actually doing well, those extra endorphins give you a feeling of euphoria, including the joy of physical activity.
Prolactin
It is a peptide hormone known to be essential for lactation.
The pituitary gland is mainly responsible for its synthesis, but in addition to the brain, prolactin is also synthesized by the placenta, mammary glands and even the immune system. Prolactin levels increase many times during pregnancy, childbirth and, most importantly, during breastfeeding. Putting the baby to the breast and biting the nipple stimulates the production of colostrum (a natural protein shake with a high content of immunoglobulins that is secreted by the mammary glands in the first few days after birth) and the transformation of colostrum into milk. Despite the high level of prolactin during pregnancy, lactation begins only after childbirth, when the level of progesterone, which previously prevented the start of the “dairy plant,” drops. Also, high levels of prolactin block the synthesis of follicle-stimulating hormone, which is necessary for ovulation. So regular feedings become a natural hormonal “contraceptive”. But the effect of prolactin does not end with lactation: it is also a stress hormone. Its level increases in response to anxiety, severe pain, and physical activity. Prolactin has an analgesic effect in inflammatory diseases and, unlike cortisol, activates the immune system - stimulates stem cells to form hematopoiesis and participates in the development of blood vessels.
Prolactin levels increase during crying and orgasm. High levels of prolactin block dopamine D2 receptors, and dopamine, in turn, blocks the secretion of prolactin: from an evolutionary point of view, nursing mothers do not need insatiable curiosity and a desire to learn new things.
Who is responsible for happiness
Scientists believe that happiness is the result of the integration of two factors, external and internal.
- External factors are physically tangible things: the place where we live; the food we eat; the people we interact with; the amount that “falls” into the account every month.
- The internal factor - biological - is the result of hormones, health status and genes. It is generally accepted that at the chemical level, hormones from neurotransmitters are responsible for our best emotions and impulses. We are talking about dopamine, serotonin, oxytocin and endorphins.