48719 06 August
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. We remind you that independent interpretation of the results is unacceptable, the information below is for reference only
T4 free, Free Thyroxine, FT4:
indications for use, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of the results and normal indicators.
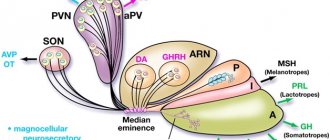
What is the hormone T4 (thyroxine)?
T4 – thyroid hormone
produced by cells of thyroid follicles. Thyrocytes synthesize thyroglobulin from amino acids and iodine, which is a precursor to thyroxine. Thyroglobulin accumulates in the follicles, and, if necessary, thyroxine is formed from it by dividing into fragments.
The main action of the hormone T4
is to accelerate catabolism - the process of obtaining energy from energetically significant metabolites (glycogen, fat). Excessive concentration of thyroxine in the blood leads to rapid heartbeat, irritability, and weight loss. But this does not mean that the hormone is harmful, these are only symptoms of its overdose. Normally, tetraiodothyronine maintains the tone of the nervous system, heart rate and adequate metabolism.
T4 hormone is not the most active thyroid hormone,
for comparison, its activity is almost ten times lower than triiodothyronine. The latter is also called the T3 hormone, since its formula contains 3 iodine atoms. T3 can be formed in the cells of the gland itself, as well as in the cells of the body from its predecessor, thyroxine. Essentially, it is a more active metabolite of T4.
Hormones T3, T4 are also called thyroid hormones
, since they are secreted by the thyroid gland, called “thyroid” in Latin. TSH is also sometimes referred to as thyroid hormone, but this is erroneous, because it is produced by the pituitary gland, located in the brain, and controls the hormone-forming function of the gland.
Often, together with a blood test for the hormones TSH, T3, T4, antibodies to TPO and thyroglobulin are simultaneously determined. Typically, endocrinologists use these indicators to diagnose thyroid pathologies. Sometimes thyroid hormones are studied during the treatment of the disease to determine its dynamics and the effectiveness of the prescribed therapy. This article will provide information about what the T4 hormone is, what functions it performs in the body, and how the analysis of its content is interpreted.
The T4 hormone belongs to the group of iodine-containing thyroid hormones. Its chemical formula contains two residues of the amino acid tyrosine and four halogen atoms of iodine. Synonyms for the T4 hormone are tetraiodothyronine and thyroxine. The substance received its name due to the number of iodine atoms contained in the molecule. Due to its simple structure, the concentration of tetraiodothyronine can be easily determined in the laboratory. For the same reason, the hormone can be synthesized artificially, which is used in hormonal therapy.
Normal values
Clear normal values are not available for determining T4. Reference ranges may vary between laboratories, as they depend on many factors: the age and gender of the patient, analytical methods and instruments used. It should also be remembered that the results must be assessed as a whole by a physician who knows the patient's medical history.
Possible reasons for deviation of T4 from normal values
Elevated thyroxine values indicate:
- hyperthyroidism;
- toxic goiter;
- inflammation of the thyroid gland (thyroiditis);
- Hashimoto's thyroiditis in the early stages.
In general, a high T4 level is a sign of an overactive thyroid gland, which produces excess amounts of hormones, forming the clinical picture of hyperthyroidism:
- tachycardia;
- anxiety;
- weight loss;
- feeling of warmth and intolerance to high temperatures;
- insomnia;
- diffuse tremors;
- feeling of weakness;
- hypersensitivity to light;
- nervousness;
- fragile nails and hair.
Low thyroxine values are mainly due to:
- hypothyroidism;
- endemic goiter;
- late stage of Hashimoto's thyroiditis.
A low level of T4 in the blood indicates that the gland is not producing enough hormones, and the classic symptoms of hypothyroidism appear in many ways the opposite of the previous ones:
- weight gain;
- dry skin;
- constipation;
- intolerance to low temperatures;
- fatigue;
- menstrual irregularity;
- hair loss;
- edema.
Effect of drugs on T4 values
Many drugs can lower or increase total T4 levels. The former include anabolic steroids, androgens, antithyroid drugs, alpha interferon, interleukin-2, lithium, propanolol and phenytoin. Drugs that increase total T4 levels: birth control pills, chlorofibrate, estrogens and methadone. For this reason, before performing a T4 blood test, it is important to inform your doctor about your current drug therapies. Typically, free T4 values are not affected by these drugs.
Hormone T4 in the blood
In the bloodstream, the T4 hormone is mainly in a protein-bound state. When thyroxine is formed in the thyroid follicles, it is captured by a special protein - thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG). This substance performs a transport function, delivering the hormone to the cells of the body. That small amount of thyroxine not bound by protein is called free T4. It is this fraction that is responsible for providing the biological effect. The part of the hormone that is bound to TSH is called T4 bound. If you separately determine free T4 and bound T4 in the blood, and then add these values, you get total T4.
In the body, the main effect is exerted by free thyroid hormones (free T4, free T3), therefore their content is of greatest importance for determining thyroid pathologies. In laboratories, blood tests are most often performed for thyrotropin and free T4. The TSH indicator is used to assess the regulation of the thyroid gland by the pituitary gland, and free T4, as the main hormone of the gland, directly reflects its function. The concentration of free T4 is increased in hyperthyroid conditions or as a result of an overdose of hormonal drugs used to treat hypothyroidism.
Preparation for the procedure
- Blood should be donated for testing at the same time (if it is necessary to track the dynamics of the indicator or the effectiveness of treatment), preferably between 8:00 and 12:00.
- Discuss with your doctor the use of medications that affect the level of thyroid hormones (hormone replacement therapy, thyreostatic drugs). To assess the function of the thyroid gland, it is necessary, in agreement with the doctor, to cancel them a month before the test.
- Two to three days before the test, avoid physical activity, sports training, and stress.
- On the eve of the analysis, it is not recommended to conduct studies using radiocontrast agents.
T4 hormone test
In the clinical practice of endocrinologists, analysis of the hormones TSH and T4 is the most commonly used diagnostic method. Hormonal tests are prescribed in various combinations, taking into account the symptoms and economic capabilities of the patient.
At the initial visit to the endocrinologist, if the patient does not have severe symptoms, it is often enough to take a test for the hormones TSH, T4, T3. As for the last two hormones, it is better to study their active, i.e., free fractions. In cases where the patient receives thyreostatics for the treatment of the early stage of Graves' disease (diffuse toxic goiter), it is better to determine only the free hormones T3 and T4. Under the influence of thyreostatic drugs, a rapid decrease in these indicators occurs, while the TSH level seems to be delayed and does not have time to decrease.
If a patient is being treated for a long time for insufficient gland function, then for periodic monitoring of the quality of therapy it is enough to determine only the concentration of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). Free T4 is tested only if there are specific indications. You should know that if you are taking thyroxine, you can take a blood test for the T4 hormone only before taking it
. If this rule is not followed, the result of the analysis will be uninformative, since the amount of thyroxine that came with the medication taken will be added to the T4 hormone secreted by the thyroid gland.
During pregnancy, the value of free T4 hormone increases especially
, because the level of thyrotropin may be reduced as a result of the action of hCG - human chorionic gonadotropin produced by the placenta. Therefore, when examining pregnant women, determining only TSH is insufficient for correct diagnosis. It is necessary to be tested simultaneously for TSH and T4.
In the direction or form with the research result you can find various abbreviations:
- FT4, FT3 – T4 and T3 free (English free, which means “free”);
- Hormone St. T4, hormone St. T3 is also a free form of hormone.
When should you take a general T4 test?
- Suspicion of hypo- or hyperthyroidism;
- Changes in the size of the thyroid gland;
- Uncontrolled weight loss;
- Prolonged depression or irritability;
- Increase or decrease in the concentration of thyroid-stimulating hormone;
- Routine examination during pregnancy;
- Examination in the absence of menstruation or suspected infertility;
- Deviations in the development of children;
- Control in the treatment of gland diseases;
- Examination of persons with a predisposition to thyroid diseases.
What is the normal level of the T4 hormone?
Free hormone T4.
To correctly evaluate the results of an analysis for free T4 hormone, it is not enough to know any specific standards. Normal thyroxine levels largely depend on the laboratory performing the analysis. These indicators are different for different analyzers; even the set of reagents used in each case matters. As a rule, the permissible concentration of T4 in the blood is indicated on the form after the test result. When using high-quality laboratory equipment of the 3rd generation in healthy people, the concentration of thyroxine ranges from about 9 to 20 pmol/l.
General hormone T4.
An indicator such as the total hormone T4 depends on the physiological state of the body. For example, it increases in pregnant women. Therefore, the normal limits for total thyroxine are more variable than for its free fraction.
Total T4 hormone (tetraiodothyronine)
| Patient age | nmol/l | mcg/dl |
| Men | 59 — 135 | 4.6 — 10.5 |
| Women | 71 — 142 | 5.5 — 11 |
| Pregnant | 75 — 230 | 5.8 — 17.9 |
| Children: 1-5 years | 90 — 194 | 7 — 15 |
| Children: 5-10 years | 83 — 172 | 6.5 — 13.4 |
T4 hormone (tetraiodothyronine) free
| Patient age | pmol/l | ng/dl |
| Adults | 9.0 — 22.0 | 0.93 — 1.71 |
| Pregnant | 7.6 — 18.6 | 0.6 — 1.45 |
| Children: 5-10 years | 10.7 — 22.2 | 0.83 — 1.73 |
| Children: 10-15 years old | 12.1 — 26.9 | 0.94 — 2.09 |
! Important:
How can thyroid disease be recognized by hormone analysis?
T4 hormone is increased
The following symptoms are characteristic of excess levels of the T4 hormone:
- Increased sweating
- Fatigue,
- Irritability,
- Increased heart rate and palpitations,
- Arrhythmia (extrasystoles, atrial fibrillation),
- Noticeable weight loss
- Trembling in the arms and legs (tremor).
Increased T4 hormone accelerates the breakdown of fats in the body, therefore body weight decreases. Excessive amounts of released energy have a negative impact on organ function. This manifests itself in acceleration and strengthening of the heart, and increased sweating. Excessive stimulation of the nervous system causes irritability and frequent mood swings, and acceleration of neuromuscular transmission leads to tremors of the limbs. Losing weight in this condition is not physiological, because it occurs against the background of dysfunction of internal organs. If an elevated concentration of thyroxine is maintained for a long time, calcium is washed out of the bones, which is fraught with an increased risk of fractures and osteoporosis.
Reasons for increased T4 hormone (total and free):
- Multiple myeloma with high levels of immunoglobulin G;
- Excess body weight (obesity);
- Glomerulonephritis with nephrotic syndrome;
- HIV infection;
- Postpartum thyroid dysfunction;
- Acute and subacute thyroiditis;
- Choriocarcinoma;
- Diffuse toxic goiter;
- Chronic liver diseases;
- Taking synthetic analogues of thyroid hormones, cordarone, methadone, oral contraceptives, radiopaque iodine-containing substances, prostaglandins, tamoxifen, insulin, levodopa;
- Porphyria
Treatment of abnormalities
Most often, deviations from the norm in free T4 levels occur due to poor nutrition or taking any medications.
If the amount of T4 is below normal for other reasons, then the patient is prescribed long-term complex therapy for hormone replacement. If its level exceeds the norm, then treatment is carried out with drugs that suppress the function of the thyroid gland.
Reference! The most commonly prescribed drug for this pathology is levothyroxine, which is a synthetic form of free T4.
The thyroid gland is a producer of endocrine hormones, one of which is the important hormone T4.
In addition to promoting the body’s most important metabolic processes, it also promotes the absorption of all proteins, carbohydrates and fats consumed by a person.
Violation of the free T4 content in the body can lead to malfunctions of the endocrine system and other pathologies of internal organs.
T4 hormone is low
Low T4 hormone is usually characteristic of insufficient hormonal function of the thyroid gland. This pathology is called hypothyroidism.
The causes of low T4 hormone levels include the following conditions:
- Treatment of thyrotoxicosis with thyreostatics or radioactive iodine;
- Autoimmune thyroiditis (the body produces antibodies against the cells of the thyroid follicles, which leads to insufficient production of thyroxine);
- Removal of the gland or part of it through surgery.
There are cases when apparently healthy people have low free T4 hormone.
Most often this is due to errors when performing research in the laboratory.
When rechecked in better laboratory centers, it turns out that the thyroxine concentration is normal. To avoid errors in diagnosis, it is necessary to take into account the clinical picture and the value of the TSH level. In all cases when the T4 hormone is low in the analysis, and the TSH hormone is within the normal range,
the result should be interpreted with caution and, if possible, a repeat test should be performed.
If a recheck in a good laboratory again shows a reduced level of thyroxine, you need to contact an endocrinologist. Insufficiency of thyroid function is usually lifelong. Therefore, continuous therapy with the administration of the synthetic hormone T4 is necessary. Artificially obtained thyroxine is identical in structure to the natural hormone and does not cause any side effects if the dosage is correctly selected.
Reasons for decreased T4 hormone (total and free):
- Sheehan syndrome;
- Congenital and acquired endemic goiter;
- Autoimmune thyroiditis;
- Traumatic brain injuries;
- Inflammatory processes in the pituitary gland and hypothalamus;
- Hypothyroidism
- Treatment with tamoxifen, antithyroid drugs (mercazolyl, propylthiouracil), steroids and anabolics, beta-blockers (metoprolol, propranolol), NSAIDs (diclofenac, ibuprofen), statins (atorvastatin, simvastatin), antituberculosis and anticonvulsants, diuretics, lithium salts, taking X-ray contrast substances.
T4 hormone during pregnancy
Thyroxine levels play a very important role in fetal development. The free hormone T4 in the first 3 months of pregnancy ensures the development and growth of the embryo's nervous system, so its deficiency can lead to various congenital pathologies. The thyroxine content in women and men is approximately the same, but during pregnancy it is not recommended to determine the level of total T4. In a pregnant woman, there is a physiological increase in the synthesis of thyroxine-binding globulin, and it binds most of the T4 in the bloodstream. Determination of total T4 during this period is not very informative, since its value will invariably be elevated, despite the fact that the free fraction of the hormone is normal.
During pregnancy, it is necessary to test free T4 hormone
, this indicator will help to objectively assess the functioning of the gland. It happens that healthy pregnant women experience a slight increase in free thyroxine that does not require treatment. But if this indicator significantly exceeds the upper limit, it is necessary to reduce the indicator through drug therapy. Treatment is carried out very carefully, under constant monitoring of thyroxine, to ensure normal development of the fetus.
Author of the article:
Kuzmina Vera Valerievna |
Endocrinologist, nutritionist Education: Diploma of the Russian State Medical University named after. N.I. Pirogov, specialty “General Medicine” (2004). Residency at the Moscow State Medical and Dental University, diploma in Endocrinology (2006). Our authors