From this article you will learn:
- why does flux (abscess) occur?
- abscess on the gum: treatment, antibiotics,
- opening of a gum abscess: video.
Flux on the gum is a swelling of the gums associated with the development of purulent inflammation. Dentists do not use the term gumboil or abscess (only patients say so), but use terms such as “gingival abscess” or “periostitis”.
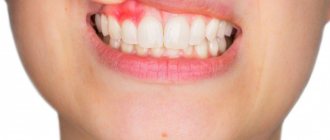
Flux on the gum: photo
What is flux and its types
Flux is an inflammatory process of the soft tissues of the periodontium and periosteum.
The scientific name of the disease is periostitis. It can occur on the gum under any tooth (or above it, if we are talking about the upper jaw). Caused by infection of dental tissues. The process of progression of periostitis goes through four stages (if you do not consult a dentist in a timely manner). The first is characterized by slight pain in the gums, “radiating” to the tooth. The second is the appearance of swelling and redness at the site of tissue infection (the tumor visually resembles a small sac). The third is an increase in body temperature, discharge of pus and swelling of the cheek due to inflammation. The fourth is manifested by severe throbbing pain and increased swelling. Types of flux:
- ordinary - the inflammatory process does not affect the periosteum;
- fibrous – inflammation spreads to the periosteum;
- orthodogenic – infection of bone tissue occurs (osteomyelitis);
- albuminous - a chronic form with a slight increase in temperature and periodic suppuration.
Frequently asked questions about flux
How many days does tooth flux last?
The serous form of periostitis turns into a purulent form after 2 days. After about 5 days after the soft tissue swelling appears, pus breaks through the periosteum under the mucous membrane.
Depending on the state of the body's defenses, the abscess can last up to a week. Then it spontaneously opens.
Chronic periostitis can exist for several years, periodically exacerbating with the formation of new subperiosteal abscesses.
Is a tooth removed during gumboil?
A tooth with periostitis is a source of constant infection. The question of its preservation is an important stage in drawing up a treatment plan.
If the tooth can be saved, then it is treated therapeutically.
How to treat flux at home?
Periostitis is subject to mandatory dental treatment. Without professional help, the infection will not go away. Self-medication will only complicate the situation.
Is it possible to cure gumboil in one day?
Periostitis is a complex infectious and inflammatory condition. Its treatment is aimed not only at eliminating the cause, but also at combating inflammation and intoxication of the body. Even with a timely visit to the dentist, it will take 3 to 5 days for a complete recovery.
What does gumboil look like on a tooth?
Flux is a reddish swelling in the area of several teeth. Sometimes pus may appear through the gums.
What to do if your cheek is swollen?
Swelling of the cheek is a sign of many dental diseases: periostitis, mumps, osteomyelitis. Therefore, if swelling of the cheek occurs, it is necessary to contact the dentist to establish a diagnosis and receive timely help.
What to do if there is a tooth flux under the crown?
A crown or other orthopedic structure is removed from the tooth for treatment. Sometimes a hole is created in it to access the channels. If the tooth cannot be treated, it is removed along with the crown.
How to reduce the temperature after removing the flux?
The use of drug therapy is prescribed by the dentist depending on the severity of the disease, the general condition of the patient, his age and concomitant diseases. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed to relieve pain and fever. The name and dosage of the drug will be determined by the doctor.
Causes and mechanism of flux occurrence
As already mentioned, the cause of periostitis is infection. It may be caused by the following factors:
- the presence of carious lesions on the teeth;
- injury;
- infection during treatment;
- poor oral hygiene.
And yet the most common cause of the disease is caries. If a person does not go to the dental clinic, pathogenic microflora destroys tooth enamel and then penetrates inside the tooth. Then pulpitis develops, accompanied by acute pain. If left untreated, the pain gradually stops as the nerve endings die. But the spread of infection does not stop, it reaches the tooth root, causes inflammation of the gum tissue, in which the pathological process begins with the formation of pus. Flux is formed.
Diagnosis of the disease
If you are almost sure that you have flux, then you need to perform the following diagnostic procedures:
- It is necessary to carefully and efficiently examine the oral cavity for the presence and detection of inflammation;
- At the dentist's appointment, palpation and percussion (tapping) of the tooth, which is the source of inflammation, is performed;
- It is necessary to take an x-ray of the mouth to determine the current condition of the tooth causing the gumboil, surrounding teeth, and jaw.
Symptoms
- The formation of a small lump on the gum under (above) the tooth
- Throbbing pain radiating to the back of the head, chin, temple
- Redness of the gums
- Swelling of the cheek due to inflammation
- Increased pain when touching a tooth next to a lump
- Deterioration of general condition caused by intoxication
- Temperature increase (low to high)
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck
Note: sometimes swelling on the cheek occurs without any apparent reason or pain. But nevertheless, if this symptom appears, you need to consult a dentist as soon as possible. The doctors in our network of clinics have extensive experience in treating flux, regardless of its type and complexity of the clinical case.
Flux - treatment in children
If a child has flux, you should never give him medications on your own, and especially antibiotics. Only a dentist can prescribe a medicinal course of treatment. Antibiotics destroy both pathogenic and beneficial bacteria that help fight infection, so the unauthorized use of such serious drugs can lead to negative consequences for the child’s entire body.
Treatment of gumboil largely depends on the causes of its occurrence. So, this process is not much different from the treatment of periostitis in adult patients. As a rule, to begin with, the specialist makes a small incision in the area of the inflammation and ensures the outflow of pus using a special drainage system. The treatment then continues at home under the supervision of parents. Most often, a complex of medications is prescribed, but in some cases, a specialist may allow you to limit yourself to rinsing with special decoctions and solutions.
What happens if flux is not treated?
Many patients, when symptoms of periostitis appear, hope that everything will “resolve” on its own, as people say. This is an erroneous and dangerous opinion, following which can have dire consequences. This situation can have a particularly serious impact on the child’s health, because the protective immunity at an early age is not well developed. If left untreated, the infection remains in the body, causing the emergence of new diseases, some of which can result in sepsis and death. What is most likely to happen? We list them according to the severity of the problem.
How a fistula forms on the gum: photos and other details
The formation of a fistula occurs as a result of granulation (proliferation) of connective tissue, as a response of the body to an external irritant - this complicates the process of natural healing of the inflamed nerve and tooth root, which leads to subsequent infection, rapid proliferation of pathogenic bacteria and the appearance of suppuration.
In the absence of timely treatment, the structure of the mucous and bone tissue of the gums is disrupted - a fistula opens, through which pus flows out.
The main reasons for the development of gumboil on the gums include:
- Absence or untimely treatment of carious lesions/pulpitis;
- Unskilled filling of dental canals, allowing infection to penetrate through the installed filling and affect the root;
- Presence of perforation on the root of the tooth;
- The appearance of inflamed neoplasms near the root of the tooth (granuloma, cyst);
- Pathological development of wisdom teeth, accompanied by improper eruption of gum tissue;
- A number of less common dental causes.
In addition to the main reasons, there are a number of factors contributing to the development of flux: weakened immunity, concomitant or past diseases, chronic fatigue, as well as severe overheating or hypothermia.
Consequences of untreated flux:
- abscess (abscess) - the formation of a purulent sac;
- phlegmon - an extensive inflammatory process after the rupture of an abscess;
- osteomyelitis of the jaw - inflammation of the tissues of the jaw bone;
- inflammation of the sinuses of the skull - the sphenoid, maxillary and frontal sinuses are involved in the pathological process. Sometimes the infection penetrates into the brain tissue.
Important: specialists from the “Smile” clinic network recommend starting treatment as early as possible. The faster the inflammation is stopped, the less effort will be required to eliminate the problem and restore the patient’s health.
Classification of periostitis
Like any inflammatory dental disease, periostitis can manifest itself in various forms. So, based on the cause of the development of pathology, it is customary to distinguish the following types:
- odontogenic: develops against the background of untreated diseases of the teeth and gums,
- hematogenous: occurs as a result of infection through the circulatory system,
- lymphogenous: becomes a consequence of the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the lymphatic system,
- traumatic: develops as a result of mechanical trauma to the periosteum, damage to the integrity of the jaw bone, or surgical intervention.
According to the degree of spread, limited and diffuse forms of the disease are distinguished. If in the first case the infection spreads to one or several teeth, then in the second it spreads to a large segment or the entire jaw (although this is less common).
It is also customary to distinguish between acute and chronic periostitis. In this case, the acute form of the pathology can be serous or purulent. With serous periostitis, almost clear liquid accumulates in the periosteal tissues, which easily resolves with timely treatment. The purulent form is accompanied by the formation of a characteristic lump - the flux itself, which gradually increases in size.
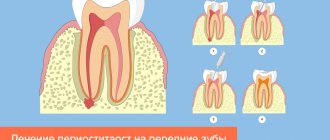
Treatment algorithm
The treatment protocol for periostitis involves a combination of surgical, medicinal and physiotherapeutic methods:
- taking (or a course of injections) antibiotics to destroy pathogenic microflora;
- opening the purulent sac (using local anesthesia), and in difficult cases, installing temporary drainage to drain the pus;
- eliminating the cause that caused the formation of flux: treating a tooth or extracting it if therapeutic measures are inappropriate, cleaning periodontal pockets;
- treating the wound with an antiseptic (gel, rinsing) until it is completely healed;
- course of physiotherapeutic procedures.
Expert advice: after opening a purulent sac, you should not apply warm compresses or take antibiotics that have not been approved by the doctor. If pain continues more than 8 hours after surgery, you should contact the clinic immediately.
How to remove flux
To avoid purulent damage to the pulp zone and periosteum, you need to receive qualified dental care in a timely manner. In the early stages of the disease, in order to prevent further progression of the inflammatory process, the patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics. It is mandatory to open the abscess. The wound is then cleaned and washed with an antiseptic.
In some cases, to prevent re-accumulation of pus, drainage is installed for several days. All surgical procedures are always performed under general anesthesia so that the patient does not experience pain.
To support the patient’s body, he is additionally prescribed a vitamin and mineral complex. If necessary, physiotherapy is included in the treatment course. Good results can be obtained using UHF and electrophoresis.
It is important to strictly follow all medical recommendations and under no circumstances interrupt antibiotic therapy. Treatment is considered successfully completed if pus is no longer released, pain does not occur, and the entire wound has healed. In some cases, after healing, a small bluish scar remains on the gum. You shouldn't worry about it. This means that the defeat was very deep. Over time, the gums will return to their normal appearance.
Recommendations from prevention experts
- Timely treatment of caries
- Thorough hygienic care of teeth and gums at least 2 times a day
- Rinsing your mouth after every meal and sugary drinks
- Visiting the dentist for a preventive examination twice a year
- Have it professionally cleaned at least once a year
- Eating firm, raw fruits and vegetables daily
The network of dental clinics “Smile” offers services for the treatment of dental flux in adults and children. Contacting our centers has a number of important advantages:
- highly qualified specialists;
- compliance with examination and treatment protocols in accordance with international standards;
- system of family and cumulative discounts;
- stable price of treatment, depending on the severity of the clinical case.
You can contact any of the branches of our clinic in Moscow, located within walking distance from metro stations:
- Art. Alekseevskaya (VDNKh district, etc. Mira), address: st. 3rd Mytishchiskaya house 3, building 2;
- Art. Shelepikha, address: Shelepikhinskaya embankment, address: building 34, building 1.
Do not delay your visit to the doctor, make an appointment when the first symptoms of periostitis appear. This will significantly shorten the treatment time and save costs. Our specialists will provide effective medical care regardless of the severity of the disease. We will take care of your health!
How many days does tooth flux last?
Waiting for the flux to disappear on its own is, to say the least, naive. Some patients believe that if the flux bursts and pus comes out of the wound, then further treatment may not be carried out at all. This is a big mistake, since complete removal of pus requires special drainage, as well as complex therapy and subsequent treatment in the dentist’s chair. With timely and correct treatment, the flux disappears on average in 12-14 days; rehabilitation after severe periostitis can take more than a month.