In the treatment of asthmatic bronchitis it is necessary to take into account the phase of the disease. For example, during an exacerbation, bronchospasmolytics are prescribed, and in the case of infection, antibiotics may be prescribed. Most experts recommend taking vitamins. Therapeutic gymnastics and massage are used in the absence of acute inflammatory reactions, and during the period of remission, sanatorium-resort treatment gives good results.
The Medinef clinic has extensive experience in the treatment of asthmatic bronchitis . We have modern equipment, and our specialists have the necessary knowledge and experience. Highly qualified staff will help cope with the disease and return the patient to a full life.
About asthmatic bronchitis
Asthmatic bronchitis is a pathological disease that occurs in the bronchi of large and medium calibers. The disease occurs as a result of hypersecretion of the bronchial mucosa. Asthmatic bronchitis, to a greater extent, affects children of preschool and early age .
Asthmatic bronchitis is most often caused by various allergens, both of viral origin (fungal, viral, bacterial) and food (milk, strawberries, citrus fruits, etc.). The disease can also be initiated by other allergens that enter the body through the stomach or through breathing.
Asthmatic bronchitis can easily develop against the background of a protracted illness such as bronchopneumonia, or other viral infections. In cases where the nature of the disease is not viral, the attacks may stop. And if the disease is infectious, the disease will develop slowly and gradually.
Nutrition for asthma in adults
To prevent recurrence of asthma attacks and alleviate the course of the disease, the patient is recommended to follow a diet. The following are excluded from the diet:
- Seafood;
- Citrus fruits (except lemons);
- Beekeeping products;
- Nuts;
- Chocolate;
- Alcohol and cigarettes;
- Dairy products;
- Baking and white bread.
Meals should be divided into 4-5 small portions, and try to avoid overeating. With the right approach, avoiding contact with allergens and a favorable psycho-emotional environment, the patient can minimize the frequency of asthmatic attacks and improve their general condition.
Symptoms of asthmatic bronchitis
During the course of the disease, there are two periods: a period of exacerbations and periods of remission. The main sign of an exacerbation period is a cough at low-grade or normal temperatures, as well as noisy exhalations with a whistling and forced character.
The harbingers of coughing attacks in asthmatic bronchitis are: nasal congestion and sore throat, serous-mucous runny nose and mild malaise. The cough is paroxysmal and intrusive, bothering patients only at night. At the very beginning of the period, the cough is dry and can easily be provoked by laughter. From time to time, the cough with asthmatic bronchitis changes from dry to wet.
The general condition of the patient is not impaired; symptoms of asthmatic bronchitis can also be intoxication, pale skin and loss of appetite, there is no lethargy. Upon examination, it is clear that the chest is not enlarged, but characteristic wheezing in the bronchi is present in some patients. The level of immunoglobulins and histamine in the blood is increased.
A characteristic feature of asthmatic bronchitis is the recurrence of symptoms. Periods of exacerbation of asthmatic bronchitis last from a couple of hours to 30 days . Most children suffering from asthmatic bronchitis may also suffer from various allergic diseases. Children who are prone to asthmatic bronchitis have neurodermatitis, as well as frequent manifestations of allergic diathesis on the skin (especially in children in the first years of life).
Complications
The most serious complication of bronchial asthma is the development of status asthmaticus. This is a prolonged attack, characterized by severe obstruction, severe respiratory failure, and impaired bronchial drainage function. During such an attack, the patient’s usual inhaled medications do not help. Only inpatient treatment is required. One of the causes of status asthmaticus may be an overdose of inhaled sympathomimetics or rapid withdrawal of glucocorticoid drugs. There are three stages in the mechanism of formation of this complication of asthma:
- The first stage is similar to a protracted attack (can last more than 12 hours), which is not controlled by conventional inhaled drugs;
- The second stage - at this stage the patient develops tachycardia, lethargy is noted, the skin becomes bluish and becomes covered with sticky sweat. Shortness of breath is significantly pronounced;
- Third stage - at this stage the patient develops a sharp disturbance in the activity of the central nervous system up to coma, which causes death.
Another rather rare complication of asthma is spontaneous pneumothorax. With a long and persistent course of asthma, pulmonary emphysema and cor pulmonale develop, which leads to pulmonary heart failure.
Asthmatic bronchitis in children
Asthmatic bronchitis in children is considered a manifestation of an allergic disease, although a specific allergen of this type is quite rare. Children whose parents have ever been exposed to allergic diseases often suffer from asthmatic bronchitis. Direct heredity is rare. The presence of such diseases in the mother during pregnancy is of particular importance.
Most often, asthmatic bronchitis affects children who exhibit symptoms of exudative diathesis . Such children at an early age suffer sensitization of the body with the help of food allergens, and then, when diseases of the upper respiratory tract and respiratory organs occur, attacks of bronchial asthma may occur.
As a result of certain structural and functional characteristics of the body in children, asthmatic bronchitis has some characteristics. The narrowing of the lumens in the bronchi in children is directly associated with an increase in the bronchial mucosa, as well as with increased mucus secretion.
Development mechanism
The general mechanism of development, which is inherent in different types of bronchial asthma, is a change in the sensitivity and reactivity of the bronchi, which is determined by the reaction of bronchial patency in response to the influence of pharmacological and physical factors.
In persons suffering from the atonic variant of bronchial asthma, the disease is of hereditary origin. Nonbacterial (plant pollen, house dust, animal hair, bird down and feathers) and bacterial (viruses, bacteria, fungi) allergens play a role in the occurrence of allergic forms of asthma. The mechanisms that underlie different types of inflammation are not well understood.
It is assumed that predominantly eosinophilic inflammation is associated with the activation of Th2 lymphocytes and their increased production of interleukins-5 and 13. Neutrophilic inflammation may be a consequence of the use of inhaled and systemic glucocorticosteroids. With an unexpressed inflammatory process, smooth muscles, fibroblasts and neurons of the respiratory tract play a leading role in the development and progression of the disease. The central role of immunoglobulins E in atopic asthma has been proven.
In bronchial asthma, remodeling of the airways occurs:
- Thickening of the basement membrane;
- Thickening and increase in the number of smooth muscles and goblet cells due to their excessive formation;
- Formation of new vessels.
This leads to irreversible changes in the ventilation function of the lungs and the appearance of ventilation defects. The central place in the mechanism of development of “aspirin” asthma is given to leukotrienes. In physical exertion asthma, heat transfer from the surface of the airways is disrupted.
Treatment of asthmatic bronchitis
Treatment of asthmatic bronchitis is individual, taking into account the current phase of the disease. During periods of exacerbations, bronchospasmolytic drugs are prescribed in combination with the organization of a treatment and nutritional regimen. For atonic forms of asthmatic bronchitis and concomitant dermatoallergoses, antihistamines are used. In special cases, if there are obvious symptoms of a bronchial infection, antibiotics are prescribed. When reducing acute inflammation, gymnastics and therapeutic massage are recommended.
In our ENT-Asthma clinic, leading medical specialists successfully achieve treatment of asthmatic bronchitis using finely dispersed sanitation of foci of chronic infection . If the allergen is identified using the skin test method, then during periods of remission, elimination therapy is carried out, as well as specific hyposensitization.
The prognosis for treatment in our clinic is favorable for most patients, as evidenced by the large number of positive reviews. Please note that if treatment for asthmatic bronchitis is not started in time, then in 30-40% of patients, asthmatic bronchitis changes into bronchial asthma.
Observation in the treatment of asthmatic bronchitis is carried out by two specialists - a pulmonologist and an allergist. For the purpose of rehabilitation, nonspecific and specific hyposensitization is carried out.
Video reviews about the treatment of bronchitis at the ENT-Asthma clinic
- Lanzman Lev Semenovich, 67 years old - asthmatic bronchitis
- Elena, 55 years old, bronchopulmonary disease
Basic therapy
Today, first-line medications for the preventive treatment of asthma in patients of any age include inhaled glucocorticoid drugs (ICS):
- Beclomethasone dipropionate;
- Flunisolide;
- Fluticasone propionate;
- Triamcinolone acetonide;
- Mometasone furoate.
Experts prescribe this group of medications to almost all patients with asthma, including those with mild severity of the disease.
ICS are the most powerful anti-inflammatory drugs. Having a wide spectrum of action, they exert their effect on both cellular and humoral mechanisms of the development of allergic (immune) inflammation. These drugs are the choice for patients with persistent asthma of any severity. In addition, ICS is prescribed to all patients with bronchial asthma who take short-acting β2-agonists more than once a day.
In second place in basic therapy are cromones (mast cell membrane stabilizers):
- Sodium cromoglycate;
- Undercut.
These drugs belong to the group of inhaled non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Used in the treatment of patients with mild persistent asthma. In addition, they can be prescribed for prophylactic purposes to prevent bronchospasm during physical activity, inhalation of cold air, and possible contact with an allergen. Antileukotriene drugs (leukotriene receptor antagonists): zafirlukast, montelukast. These drugs are recommended to be taken mainly by patients with aspirin-induced bronchial asthma, as well as to prevent bronchospasm provoked by allergens and physical activity.
Systemic glucocorticoid drugs:
- Prednisolone;
- Methylprednisolone.
If a patient is diagnosed with severe bronchial asthma, in which high doses of inhaled glucocorticoids in combination with regular use of bronchodilators are ineffective, systemic glucocorticoids are prescribed.
Cost of treatment
| Name | Cost, rub. | |
| 1 | Initial appointment with a doctor, doctor of medical sciences | 4500* |
| 2 | Procedures included as prescribed by a doctor: | |
| UZIS | 2700 | |
| Ozone ultraviolet sanitation | 450 | |
| Laser photoreactive therapy | 1800-2600 | |
| Application of a microcompress into the nasal cavity | 700 | |
| Application of gum-propolis suspension to mucous membranes | 600 | |
| 3 | Final examination by a doctor based on the results of treatment | 1000 |
* — When paying for the full course of treatment procedures, the cost of a doctor’s appointment is included in the amount of treatment. The course of treatment is prescribed by a doctor. The course duration is 7-12 sessions depending on the diagnosis.
Prevention
Prevention of an acute obstructive process in the bronchi is identical to the prevention of influenza and ARVI - these are annual, seasonal flu vaccinations. During the onset of cold weather in the off-season, it is necessary to avoid hypothermia and contact with already sick patients.
To prevent exacerbations of chronic obstructive bronchial disease, first of all, eliminate the external factors that cause it - tobacco smoking, dust in enterprises, work in a mine. Flu vaccination is carried out annually. For patients with chronic obstructive bronchitis, vaccination against pneumonia is carried out. It is carried out once every 5 years.
Treatment at special respiratory resorts is considered an important element of prevention. They exist in our country - Crimea. In Germany (Bad Reichenhall), southern coast of France, coast of Italy. The main task of a patient at a resort is active physical exercise in the fresh air.
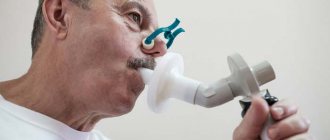
Diagnostics
To diagnose asthmatic manifestations, it is necessary to conduct a thorough examination of the body. The medical clinic in Mytishchi has equipment and reagents to perform allergy tests at any time of the year, regardless of the intensity of the disease.
Allergy tests are a diagnostic method for identifying the allergen to which the patient’s body reacts.
To determine the allergic status, it is necessary to conduct laboratory tests - tests for sensitivity to various allergens - fungal, pollen and household.
A study of respiratory function - spirography - allows you to estimate tidal volumes.
The doctor will prescribe a number of laboratory tests:
- General and biochemical blood test;
- Antibody test;
- Examination of stool for the presence of helminths;
- CT
Bronchial asthma: prevention and treatment
Bronchial asthma, the treatment and prevention of which requires only a serious and comprehensive approach, according to WHO, is diagnosed in 4-10% of the world's population. This respiratory disease is chronic, characterized by periodic attacks. The main signs of an asthma attack are a severe cough, shortness of breath, and difficulty breathing. The causes of bronchial asthma development consist of external and internal provoking factors.
External provoking factors
External causes of bronchial asthma include:
- house dust;
- pollen;
- animal hair;
- tobacco smoke;
- household chemicals,
- cosmetics and personal care products;
- diseases of the respiratory system;
- professional activities (chemical production workers, construction materials workers, hairdressers and other beauty salon workers, office and warehouse workers are susceptible to asthma);
- some medications;
- frequent stress, prolonged fatigue;
- poor nutrition;
- unfavorable environmental conditions.
Most often, the development of attacks is facilitated by direct contact of the patient with the allergen. Exacerbations often occur in the warm season, especially in windy weather.
Internal causes of the disease
Due to internal causes, bronchial asthma also develops. Prevention and treatment, by the way, should be carried out taking into account the factors that provoked the disease. Internal causes of the disease include primarily hereditary predisposition (in this case, a diagnosis of “atopic bronchial asthma” is made). Internal causes also include concomitant diseases of the respiratory system.
Classification of bronchial asthma
There are several types of diseases such as bronchial asthma. Various medications and therapy methods are used to treat and prevent bronchial asthma (depending on the type and severity of the disease). So, according to etiology we can distinguish:
- endogenous asthma, attacks of which are triggered by internal factors (physical exercise, concomitant infections);
- exogenous form of the disease, when exacerbations are caused by allergens (pollen, dust mites, animal hair, tobacco smoke, and so on);
- bronchial asthma of mixed type, in which attacks can be caused by exposure to both internal and external factors.
Depending on the severity of the disease, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- intermittent asthma, relatively mild and short attacks of which occur no more than once a week;
- mild persistent asthma is characterized by exacerbations at least once a week, but not more than once a day;
- persistent moderate asthma makes itself felt with attacks every day;
- Severe persistent asthma is the most complex form of the disease and is characterized by very frequent complications, limitation of physical activity and insomnia.
The first signs and symptoms of the disease
Asthmatic attacks are accompanied by the following symptoms:
- dry cough (if the condition improves, it produces sputum with dense white inclusions);
- increased breathing and heart rate;
- suffocation, severe shortness of breath;
- the chest swells with deep breaths;
- the veins in the neck become puffy;
- difficulty breathing, which can appear either gradually or suddenly;
- heavy sweating, cold sweat;
- weakness, drowsiness;
- fainting state;
- bluishness of the facial skin;
- body temperature rises to 37-37.5 degrees;
- feeling of tightness in the chest;
- anxiety, panic;
- Some patients have increased blood pressure;
- When exhaling, whistling and wheezing are heard.
The typical position that a patient with an asthma attack strives to take is a sitting position with a slight bend forward, while the person breathes heavily and rests his elbows on his knees. Small children do not always take this position; a baby, for example, can lie calmly on his back, behave actively and play even during an asthmatic attack.
First aid for asthmatic conditions
The global strategy for the treatment and prevention of bronchial asthma also involves taking measures to alleviate the patient’s condition during attacks. So, it is necessary to calm the person down, give medications prescribed by the doctor (usually in an inhaler) and warm water, which should be drunk in small sips. It is necessary to convince the patient to wait calmly for the medications to take effect; panic will complicate the situation. You should not force a person to lie down - asthma attacks are tolerated easier and faster in a sitting position. If the measures taken do not alleviate the patient’s condition, you must immediately call an ambulance. Before doctors arrive, you should try to calm the patient down; special attention should be paid to a child with an asthmatic attack. You should immediately call an ambulance if a person’s condition is critical: there is bluishness of the skin and puffiness of the veins in the neck, signs of confusion appear, the patient is choking, instinctively tries to expand his chest and take in air, he lifts his shoulders and chin. If the attack continues and the condition becomes life-threatening, emergency hospitalization may be necessary. The asthmatic condition is controlled by intensive medication; some patients may need oxygen masks and special medical equipment to make breathing easier.
In the case when an asthma attack overtakes a patient when he is alone and there is no one to help, you should remember the rules for relieving a dangerous condition on your own:
- If symptoms warning of an asthma attack appear (changes in breathing, wheezing, chest tightness), you must use an inhaler or take a medication prescribed by your doctor.
- Next, you should try to calm down, sit down and take a comfortable position, close your eyes and breathe slowly.
- It is necessary to relax the muscles of the body one by one without holding your breath. You need to start with your face, then move on to your arms and legs, then try to relax your whole body. You must try to stabilize your breathing: do not swallow air through your mouth, inhale through closed lips so that a whistle is heard when you exhale.
- To relieve an attack, you should lean forward, resting your feet on the floor and your elbows on your knees, then take a deep breath and hold your breath for a couple of seconds, then cough into a tissue to get rid of phlegm.
- If after the measures taken the condition does not improve, you must call an ambulance.
Drug therapy for asthma
Therapy of bronchial asthma with drugs involves taking basic and symptomatic complexes of drugs. The basic course is aimed at the mechanism of the disease, controls the course of the disease itself, while symptomatic therapy is the treatment and prevention of exacerbation of bronchial asthma.
Basic course drugs include:
- Cromons.
- Monochannel antibodies.
- ASIT (allergen-specific immunotherapy).
- Leukotriene receptor antagonists.
- Glucocorticosteroids
To prevent attacks of bronchial asthma, medications used for symptomatic therapy are used:
- Short-acting beta-adrenergic agonists effectively relieve asthmatic attacks with fewer side effects.
- Long-acting beta-agonists are medications that, in addition to relieving symptoms, also reduce the frequency of attacks.
- Xanthines are used for emergency relief of the patient’s condition, as well as to enhance the effect of the above remedies.
Inhalers help minimize acute asthmatic attacks, with the help of which the medicine enters the body faster and begins to act.
Also, prevention of asthma attacks includes the use of additional medications, such as antibacterial agents and expectorants.
Non-drug therapy for the disease
Non-drug treatment involves eliminating the provoking factors of the disease, following a special diet, speleotherapy and halotherapy. Speleotherapy is a treatment method that involves the presence of the patient in a room where the microclimate of karst caves is provided. Halotherapy is an analogue of speleotherapy, which involves treatment with “salty” air. Sessions in salt caves can significantly extend the period of remission and generally have a positive effect on the respiratory system. The diet for bronchial asthma recommends avoiding seafood, citrus fruits, smoked meats, fatty foods, raspberries, eggs, legumes, nuts, chocolate, fatty meats, caviar, yeast-based foods, currants, peaches, melons, strawberries, alcohol, honey, and sauces. tomato based. It is necessary to limit the consumption of baked goods, dairy products, sugar and salt. It is advisable to steam cook food. The diet should include 4-5 warm meals per day. It is recommended to fill the menu with cereals, non-rich soups, vegetable and fruit salads. You can eat doctor's sausages, lean meats, rye and bran bread, oatmeal or biscuits. To prevent bronchial asthma, sanatorium-resort treatment is also used. It is better for patients with respiratory diseases to relax in Crimea.
Treatment with folk remedies
There are also a sufficient number of traditional methods for treating bronchial asthma, but before using any of them you should definitely consult with a specialist - bronchial asthma is not such an easy disease to experiment with. Prevention and treatment using traditional methods may include the following:
- Treatment according to the method of Dr. Batmanghelidj (with water). The essence of the method is to drink two glasses of water thirty minutes before meals and one glass 2.5 hours after the next meal. Water should be used melted or salted (half a teaspoon of sea salt per two liters of clean water) alternately.
- Consuming ginger according to a specific pattern. Grate 4-5 cm of ginger root, add cold water and heat in a water bath. After boiling, you need to boil the product under a closed lid for 20 minutes. Take 100 ml of heated decoction before meals.
- Inhaling salt air. For regular procedures, it is enough to purchase a salt lamp at a home improvement store and install it in the patient’s room.
- Taking medicine based on oats. Half a kilo of oats needs to be poured with 2 liters of milk and 0.5 liters of water, and cooked for 2 hours over low heat. Then you need to add one teaspoon of honey and butter to the product. The decoction should be consumed hot, in the morning before breakfast. The product must be stored in the refrigerator. The course of therapy is one year.
Primary prevention of disease
Primary prevention of bronchial asthma involves the implementation of a set of measures aimed at preventing the disease. Everyone should be familiar with the principles of prevention, regardless of age, gender and social status. In addition, it is important not only to know, but also to observe measures to prevent the disease. The principles of primary prevention are slightly different for adults and children. Thus, young patients more often suffer from atopic bronchial asthma, the main cause of which is unfavorable heredity. The main provoking factor in this case is allergens that enter the body with food. Prevention of bronchial asthma in children with a genetic predisposition to the disease involves preventing the occurrence of allergic reactions. It is recommended to continue breastfeeding such children for as long as possible, which will strengthen the baby’s immune system and maintain normal intestinal microflora. Prevention of bronchial asthma in adult patients is aimed at preventing the negative influence of provoking factors of the disease: tobacco smoke, pollen, house dust, chemicals. So, firstly, it is necessary to eliminate possible causes of the disease from among the sources of infection, and only then begin treatment for existing pathologies of the respiratory system.
Bronchial asthma, the prevention of which should be comprehensive, most often affects the following groups of patients:
- people with a hereditary predisposition (those whose close relatives suffered directly from asthma, chronic diseases of the respiratory system, allergic reactions);
- heavy smokers;
- persons suffering from atopic dermatitis (inflammatory skin lesions of an allergic nature and genetically transmitted);
- persons with broncho-obstructive syndrome due to acute respiratory viral infections;
- people who work in special conditions (stuffy and dusty rooms) or with perfumes and chemicals. It is these groups of people that are especially important to take care of.
Prevention of bronchial asthma involves the following main measures:
- use of hypoallergenic cosmetics;
- quitting smoking (including passive smoking);
- creating a favorable environmental environment around you (if possible);
- keeping the house clean;
- eliminating contact with possible allergens;
- timely treatment of respiratory diseases, during epidemics - compliance with preventive measures, vaccination.
Secondary prevention of asthma
Special prevention rules also apply to those patients who already have asthma. Secondary prevention of bronchial asthma is aimed at preventing the development of complications and acute attacks of the disease. It is recommended to follow the rules of secondary prevention for those whose relatives suffer or have suffered from bronchial asthma, atopic dermatitis, allergies, or eczema.
The following measures involve secondary prevention of bronchial asthma:
- medications (antiallergic), especially those prescribed by a doctor, must be taken without fail in order to reduce or completely eliminate the body’s increased sensitivity;
- exclusion of highly allergenic foods from the daily diet;
- complete cessation of smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages;
- use of synthetic (anti-allergenic) pillows and blankets;
- limiting communication with pets, it is better to even give up keeping fish, because dry food often causes allergies;
- regular cleaning of the living space, ventilation;
- timely treatment of acute respiratory viral infections during the cold season;
- performing breathing exercises and other methods of therapy (acupuncture, herbal medicine);
- taking vitamin complexes prescribed by your doctor.
Patients with bronchial asthma need to take special care in the warm season, when it is more difficult to avoid contact with possible allergens. Prevention of bronchial asthma in children involves the same measures. Tertiary disease prevention
Tertiary prevention of asthma
aims to generally alleviate the course of the disease and prevent death during the period of exacerbation of the disease. Prevention of bronchial asthma attacks at this stage involves adherence to an elimination regimen - this is the complete exclusion of the possibility of patient contact with an irritating factor that causes suffocation. Fortunately, death from this disease is rather rare, so knowledge about tertiary prevention methods is necessary primarily for resuscitators. Bronchial asthma, the prevention and treatment of which requires serious attention, is characterized by a positive prognosis, but much depends on the stage of the disease at which the patient sought qualified medical help.