The danger of insufficient attention to the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes lies in the development of many extremely serious complications. In 8-10% of cases, diabetic foot becomes its manifestation at a late stage - the result of tissue death and dysfunction of blood vessels and nerves in the lower extremities. Ulcers form on the feet of patients, which in some cases can lead to gangrene and even amputation of part of the limb. Considering that up to 50% of patients with diabetes are at risk, it is necessary to take timely care of prevention and diagnosis. Our medical center in Moscow will help with this: at the CBCP clinic you will undergo examinations using the latest equipment and receive professional advice to avoid the development of diabetic foot.
What is diabetic foot?
Medical practice shows that many people with symptoms of diabetes ignore the problem of metabolic disorders in the body and seek treatment from a doctor only when serious complications occur. Only in 50% of cases are requests recorded at an early stage.
A number of patients really pay attention and begin treatment for this disease when they begin to show signs and symptoms of developing diabetic foot syndrome:
- tissues become overgrown with ulcers;
- necrosis develops under the influence of infections;
- the skin on the sole is cracking;
- in some vessels, blood flow is disrupted or stops altogether;
- the limb itself loses its functions.
A person cannot step on his foot due to pain, and then completely loses the ability to move independently. The tissues of the foot gradually die - this includes nerves, joints, bones and blood vessels. The patient inevitably becomes disabled.
Meanwhile, the symptoms of diabetic foot are a severe and advanced stage of diabetes mellitus (in 90% we are talking about type II diabetes), which requires immediate and qualified treatment. Ulcers will not “heal” on their own, and a gradual decrease in physical activity will lead to a worsening of the disease. Most often, signs and symptoms appear 10-15 years after the first manifestations of diabetes. However, in most cases this concerns patients who do not pay due attention to diabetic treatment and prevention.
Of course, not all patients with diabetes develop diabetic foot syndrome. However, about half of them are at risk, and statistics show that this complication occurs in 10% of diabetics.
Foot care for diabetes
Preventing the development of diabetic foot syndrome is much easier than curing it. Diabetes is a chronic disease, so careful foot care should become a daily habit. There are several simple rules, the observance of which significantly reduces the incidence of trophic ulcers.
The main problem for a diabetic patient is choosing shoes. Due to decreased tactile sensitivity, patients wear tight, uncomfortable shoes for years, causing irreversible skin damage. There are clear criteria by which a diabetic patient should select shoes.
- Consult a doctor if even minor inflammation occurs. Even minor inflammation can lead to serious consequences.
- Examine your feet every day to look for cuts, scrapes, blisters, cracks and other damage that could allow infection. The soles can be inspected using a mirror. In case of poor vision, it is better to ask a family member to do this.
- You need to wash your feet daily, dry them carefully, without rubbing. We must not forget about the spaces between the fingers - they also need to be thoroughly washed and dried.
- Inspect your shoes daily to prevent calluses and other damage that can be caused by foreign objects in the shoes, wrinkled insoles, torn lining, etc.
- Do not expose your feet to very low or very high temperatures. If your feet are cold, it is better to wear socks; you should not use heating pads. You must first test the water in the bathroom with your hand and make sure that it is not too hot.
- Shoes should be as comfortable as possible, fit well on the foot, you should not buy shoes that need to be worn in. If there is significant deformation of the feet, specially made orthopedic shoes will be required. Outdoor shoes should not be worn on bare feet; sandals or sandals with a strap that goes between the toes are contraindicated. You should not walk barefoot, especially on hot surfaces.
- Change socks or stockings every day, wear only those that fit, avoid tight elastic bands and mended socks.
- Do not injure the skin of your feet. Do not use drugs or chemicals that soften calluses, or remove calluses with a razor, scalpel or other cutting instruments. It is better to use pumice stones or foot files.
- In case of injuries, iodine, alcohol, potassium permanganate, and brilliant green are contraindicated - they have tanning properties. It is better to treat abrasions and cuts with special agents - miramistin, chlorhexidine, dioxidine, or, in extreme cases, a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide and apply a sterile bandage.
- If your skin is dry, your feet should be lubricated daily with a rich cream (containing sea buckthorn or peach oil), but the spaces between the toes should not be lubricated. You can also use creams containing urea (Balzamed, Calluzan, etc.)
- Trim your nails straight, without rounding the corners. Thickened nails should not be cut, but filed. If your vision is poor, it is better to take help from family members.
- Stop smoking; smoking can increase the risk of amputation by 2.5 times.
Causes
Often, diabetic foot syndrome is a consequence of diabetes mellitus, which is accompanied by atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, arterial hypertension, smoking, and alcohol abuse.
However, a diabetic leg ulcer can also be caused by a seemingly harmless cause. People suffering from diabetes may not pay attention to calluses, corns, cracked heels, or ingrown toenails that appear due to tight shoes. Meanwhile, these small injuries provoke the disease.
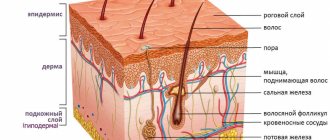
Diabetes mellitus negatively affects the functioning of the entire body, but the lower extremities suffer the most (especially since they bear a serious daily load). Saturation of the blood with excess sugar and glucose destroys blood vessels - large and small (a distinction is made between macro- and microangiopathy in diabetes), bones and muscles. Due to anatomical features, blood circulates in the legs of any person worse than in other parts of the body, so it is the feet that are the first to suffer from total circulatory problems in diabetes.
Angiopathy
In diabetes, damage to blood vessels often occurs - angiopathy. They become covered with atherosclerotic plaques, which leads to circulatory failure in the foot. It looks a bit like rusty pipes. Very little water comes out of the tap due to rust blocking the inside of the pipes. The same thing happens when blood vessels are clogged. If the vessels in the legs become clogged or completely blocked, the skin and tissues will suffer first from poor circulation. The process of delivering oxygen and nutrients to the limb will be disrupted, which means cell death in the affected area.
- Decreased ability to fight infection
- The ability to heal wounds will decrease.
- Signs of blood vessel damage
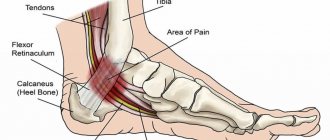
- Pain in the lower leg when walking,
- A change in the normal color or temperature of the feet,
- Leg pain at night or while resting.
If nerve damage is combined with poor circulation, the risk doubles. You are more likely to get injured (because you don't feel pain) and the injury will lead to infection or ulceration. Healing will not occur due to poor circulation, which will inevitably lead to gangrene.
Risk factors for developing diabetes include poor diet and glucose control, poor circulation, smoking, and diabetes mellitus of more than 10 years.
Mechanism of diabetic foot
Nerves are affected, tissue sensitivity is dulled, so a person may faintly feel pain from cracks on the soles, small ulcers on the skin of the foot. This phenomenon is called diabetic neuropathy, and it is extremely insidious.
Minor injuries take a long time to heal, but the patient does not take them seriously, as the level of pain decreases. By the way, this prevents many diabetics from feeling that they are wearing the wrong shoes, which injure their feet. Only over time do the growing ulcers and cracks begin to interfere with walking.
Due to deterioration of tissue nutrition:
- the skin of the foot becomes darker;
- ulcers form on it;
- the shape of the nails changes;
- bones are deformed;
- joints work poorly.
As a result, any bruise threatens to form a wound into which infection and bacteria can easily penetrate. In turn, they soften the tissues - the wounds grow into trophic ulcers, the cells begin to die, forming black necrotic areas. The process affects the subcutaneous fat, muscles, and then penetrates the ligaments and bones. Eventually, gangrene, abscesses, and phlegmon develop from the ulcers.
Classification of diabetic foot forms
Diabetic foot syndrome is classified according to the severity of the disease. There are 6 stages, starting from zero (the foot is deformed, hyperkeratosis occurs, and calluses form) and ending with stage five (extensive spread of gangrene).
The traditional classification includes 3 forms of the disease.
1. The most common neuropathic form (about 70% of all cases). Diabetes mellitus primarily affects the nervous system of the legs, which significantly reduces the sensitivity of tissues to heat, pain, and touch. The skin becomes dry, hyperkeratosis occurs (the skin is excessively flaky), anhidrosis (sweating is impaired), and flat feet develop. The bones of the foot can become deformed (a common symptom is the formation of a Charcot joint) and become excessively fragile, which increases the risk of unexpected fractures.
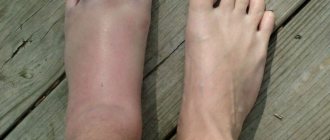
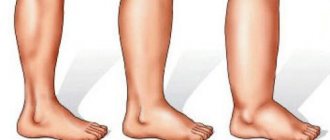
2. The ischemic form accounts for up to 10% of cases. It is characterized by atherosclerotic disruption of the blood supply to the foot due to the destruction of large and small vessels under the influence of excess sugar and glucose. As a result, the leg swells noticeably, and the swelling practically does not subside. Walking causes discomfort or pain in the patient, he limps, gets tired quickly and is unable to walk long distances. Visually you can notice how the pigmentation of the skin changes.
3. Approximately 20% of cases of diabetic foot syndrome occur in the mixed form , which is also called neuroischemic. This is the most complex disease, since the symptoms and signs of previous forms are clearly expressed.
Most often, individual forms (neuropathic or ischemic) are diagnosed in the early stages. Their occurrence depends on what problems the patient faces - whether he is worried about neuropathy or ischemia. Over time, the manifestations of the disease become more complex, and both forms flow into one another.
The most severe form is considered diabetic gangrene . In this case, the blood supply is disrupted over a large area of the leg - right up to the top of the lower leg. This provokes the development of an anaerobic infection, since the cells on the affected limb do not resist its penetration. This is the most advanced form of the disease, when only amputation can help. That is why treatment for diabetic foot symptoms should be started as early as possible.
Folk remedies
In the early stages of diabetic foot, the following folk recipes can be used in treatment:
- To make lotions for ulcers and rinses, it is worth pouring 1-2 tbsp. l. yarrow herbs with a glass of boiling water and leave on low heat for 5 minutes. Strain using gauze.
- Make ulcer washes and compresses using a decoction of bird cherry fruits. For this preparation, pour 4 tbsp. l. fruits 500 ml of boiling water and keep for 15 minutes in a water bath. Strain and cool.
- A water infusion of meadow clover is useful for lotions. To prepare it, 2 tbsp. l. Place the flower in a thermos and pour boiling water over it. After 2 hours, strain.
- For especially difficult-to-heal ulcers, a tincture of centaury is suitable, for the preparation of which the herb should be poured with boiling water in a ratio of 1 to 10 and left to steep for several hours.
- Horsetail is used as a disinfectant when preparing a decoction: 1 tbsp. l. pour a glass of boiling water over the herbs and place on low heat for 10 minutes.
- To treat a wound, calamus root is suitable, from which an infusion is prepared: 3 tbsp. l. herbs are poured into 700 ml of boiling water and kept in a water bath for 10 minutes. Leave for about an hour and a half and filter.
- Wounds can be treated with nettle or aloe juice, first applying it to a tampon or napkin.
Baths will also help in the treatment of diabetic foot, and honey baths are especially effective. To prepare them, 2 tbsp. l. honey is dissolved in 1 liter of warm boiled water. These baths can be taken every day, soaking your feet for 15 minutes.
Signs of diabetic foot
- An ingrown toenail occurs if the corners are not trimmed correctly. They can grow into tissues, and in these places inflammation occurs and pus forms, which is fraught with more serious consequences.
- A darkened nail indicates hemorrhage underneath it. Most often the reason is uncomfortable shoes. The consequences are the same - inflammation, pus, ulcer.
- A thickened nail can be the result of a fungal infection. Due to the irregular shape of the nail, the tissue under it is injured, and it can put pressure on neighboring fingers. In general, diabetics need to be careful about preventing fungal diseases.
- Calluses and corns are a common sign of the onset of diabetic foot. It is in them that invisible hemorrhages occur and pus is formed. Most patients “treat” these formations with patches and ointments, only worsening the problem.
- Cuts occur due to various factors, but in any case they should be carefully treated, since the wounds can be attacked by infection.
- Cracked heels are directly related to dry skin in neuropathic diabetic foot. Cracking leads to the formation of ulcers and bleeding.
- Deformation of the joints and bones of the foot provokes the formation of calluses and wounds on the skin.
Complications
Diabetic foot can be complicated by:
- Necrosis (death) of tissues - the cause of necrosis is usually the spread of a pyogenic infection, but a violation of the blood supply and innervation of tissues can contribute to the development of this complication.
- The formation of ulcers - their depth and severity of soft tissue damage can vary within significant limits.
- Pathological bone fracture - a pathological fracture occurs as a result of a violation of the normal strength of the bone, when exposed to loads that usually do not lead to any damage.
- Foot deformation - flexion contractures of the fingers (fingers are fixed in a bent, crooked position), muscle atrophy (reduction in muscle size and strength), deformation of the arch of the foot with a violation of its shock-absorbing function.
- Osteomyelitis is a purulent-necrotic lesion of bone tissue that develops as a result of the spread of infection from existing ulcers.
- Sepsis is a life-threatening condition that develops when pyogenic microorganisms and their toxins enter the bloodstream.
Diabetic foot symptoms
A common symptom for all forms of diabetic foot is discomfort or pain when walking, associated with tissue damage, wounds, suppuration, and ulcers.
- In the ischemic form, the patient quickly feels tired in the legs when walking and limps. After minor exertion, the limbs swell, the skin is cold to the touch, has a pale tint, against which pigmented spots stand out. When palpating the veins of the foot, a noticeably weakened pulsation is observed. Calluses, cracks, and wounds form on the skin, which do not heal for a long time. They are replaced by festering or scabby ulcers. The skin itself becomes dry, sweat production is extremely scarce.
- In the neuropathic form of diabetic foot, the areas of the foot that receive the greatest pressure when walking are usually affected: the big toes, the interphalangeal space. Also characteristic are signs such as cracks, abrasions, and edematous ulcers. Very often, joints and bones change shape (protruding bones, hook-shaped, hammer-shaped fingers), they are affected by osteoporosis, joints swell, bones undergo fractures. Fluid accumulation in the tissues is often observed, the pulse in the arteries remains, and the sensitivity of the tissues decreases.
Which doctor treats diabetic feet?
In order to undergo high-quality diagnostics and receive qualified treatment, you must contact one of the following doctors:
- diabetologist - most often he is an endocrinologist who deals with problems of metabolic disorders and, in particular, diabetes;
- general and vascular surgeons treat dysfunction of the vessels of the lower extremities and the consequences of atherosclerosis;
- a neurologist will determine the degree of dysfunction of the nervous system in the legs;
- an orthopedist will select the right shoes to unload the foot;
- A podiatrist specializes in foot care and treats patients with diabetic foot syndrome.
Medical examination
Patients with diabetes mellitus and signs of DFS can be examined by an endocrinologist in Sergiev Posad at the Paracelsus clinic.
The center is equipped with expert-class ultrasound equipment. Our own laboratory quickly produces accurate results on the day of testing.
Reception is conducted by highly qualified endocrinologists with 11 years of experience in the specialty. In the department of endocrinology, appointments are conducted by a doctor of medical sciences with 37 years of experience in the specialty.
Patients at high risk of developing diabetic foot should be observed not only by an endocrinologist, but also by a vascular surgeon and orthopedic traumatologist. It is important to conduct self-examination for diagnosis, the purpose of which is to early detect signs of diabetic foot: changes in skin color, dryness, swelling and pain, crooked toes, fungal infections.
At the Paracelsus clinic, a comprehensive diagnosis is carried out, based on the results of which the doctor will select treatment. In the clinic, you can examine arteries and veins, identify vascular damage at an early stage and determine the state of blood flow.
Competent treatment from our doctors will prevent the development of complications. The doctor will help you adjust your lifestyle and diet.
Diagnosis of diabetic foot syndrome
When heading to the diabetic foot office of an endocrinologist-diabetologist, be prepared for the fact that it may be necessary to visit an orthopedist, vascular surgeon, etc. Accordingly, the range of diagnostic procedures in each individual case may vary.
An important role in diagnosis and identifying signs of the disease is given to... the patient himself. If you are at risk, periodically conduct a self-examination of your feet for the signs of the disease described above. If you have the slightest suspicion, visit a diabetic foot clinic.
- The doctor determines the degree of sensitivity of the foot tissues, reflexes and other indicators.
- Laboratory tests that demonstrate characteristic changes in the composition of the blood are extremely important.
- Most often, the presence of ulcers requires bacterial culture of their contents for microflora.
- In the ischemic form, ultrasound examinations of blood vessels are prescribed. The method of duplex scanning of the veins of the lower extremities is extremely informative.
- Depending on the specific case, angiography and CT arteriography may be used.
- To diagnose changes in bones and joints, radiography is performed.
At the CBCP Clinic, we offer the latest methods for studying vascular dysfunction in diabetic feet. Ultrasound of the vessels of the lower extremities, performed on modern expert-class equipment, allows the doctor to obtain maximum information about the pathology.
Exercise therapy
For diabetic feet you can do:
- Exercise 1. Starting position - sitting on a chair, legs lowered down and brought together. Alternately bend and straighten your toes 5 to 10 times, first on one leg and then on the other.
- Exercise 2. The starting position is the same. First, you should raise your toes up for 5 to 10 seconds, keeping your heel pressed to the floor. Then the toes should be lowered and the heel raised up (also for 5 - 10 seconds). Repeat the exercise 3 – 5 times.
- Exercise 3. The starting position is the same. Raise one leg 5 - 10 cm above the floor and begin to perform circular movements with your foot, first in one direction (3 - 5 times), and then in the other. Repeat the exercise with the other leg.
- Exercise 4. The starting position is the same. First, you should straighten one leg at the knee, and then bend it at the ankle joint, trying to pull the toes as low as possible. Hold your leg in this position for 5 - 10 seconds, then lower it and repeat the exercise with the second leg.
- Exercise 5. The starting position is the same. Straighten your leg at the knee, then straighten it at the ankle joint, trying to reach your toes with your fingers. Repeat the exercise with the second leg.
Physical therapy (physical therapy) and special gymnastics can have a certain positive effect on diabetic feet. The purpose of physical exercise in this case is to improve blood supply to ischemic tissues of the lower limb. However, it is worth remembering that in the ischemic form of the disease, the mechanism of damage is the blockage of the blood vessels through which blood flows to the tissues, so excessive loads can lead to increased pain and the development of complications. That is why you should immediately exclude any exercises and activities associated with increasing the load on the feet (walking, running, cycling, lifting weights, staying in a “standing” position for a long time, and so on).
How to treat diabetic foot?
- If the patient’s condition does not require hospitalization and the disease is not advanced, the doctor makes nutritional adjustments in order to achieve the correct balance of carbohydrates and the release of the required amount of hormones in the body.
- If diagnostics reveals problems with blood pressure, systemic drug therapy with beta blockers, inhibitors, diuretics, etc. is prescribed.
- Treatment of diabetic foot is inextricably linked with therapy for diabetes mellitus. Therefore, the patient takes insulin and medications in strictly adjusted doses to stabilize blood sugar and glucose levels.
- To combat the expansion of ulcers due to the proliferation of microbes, antibiotic therapy is carried out. The patient takes antispasmodics, Actovegin, and a-lipoic acid preparations.
- If there are suppurations or ulcers on the foot, treatment by an orthopedist is necessary. Special orthopedic devices, bandages, insoles, motion restraints, etc. are used.
- Wounds and ulcers are treated with antiseptics and antibacterial agents. If necessary, the surgeon excises necrotic tissue and removes potentially dangerous calluses and corns.
- Severe vascular lesions are treated by a vascular surgeon. Modern medicine offers a wide range of low-traumatic methods: stenting, bypass surgery, angioplasty, thromboembolectomy, etc.
- If the foot is gangrene and cannot be treated, amputation is performed.
Preventing diabetic foot symptoms
- Particular attention to prevention should be paid to people with extensive diabetic experience. In addition to preventive measures for diabetes (monitoring nutrition, blood glucose levels, etc.), there are specific recommendations:
- wearing special shoes without seams, with orthopedic insoles;
- performing foot exercises and self-massage;
- careful foot hygiene, careful pedicure;
- treating the skin with creams recommended by a doctor.
The following recommendations should be followed every evening
- carefully examine your feet, using a mirror to examine hard-to-reach areas (if your eyesight is poor, you should use the help of your family);
- wash your feet with warm (never hot) water with baby soap or a slightly pink solution of potassium permanganate;
- thoroughly dry the skin with a personal towel, especially the spaces between the fingers (blot, do not rub);
- lubricate the skin with a thin layer of softening (vitaminized, bactericidal) cream;
- treat the interdigital spaces with vodka;
- if necessary, cut your nails very carefully, leaving them not very short, cutting the nail straight (if you have poor eyesight, cutting your nails yourself is prohibited).