Contusion is damage to the visual organ by a shock wave or a blunt object. It is characterized by a deterioration in the quality of vision, pain, the appearance of a film before the eyes, increased lacrimation and other symptoms. In critical cases, eye contusion leads to loss of vision and disability. Let's consider the causes of the pathology, symptoms, nature of manifestation, classification, complications, diagnostic method and treatment regimen for the pathology. We will also consider the issue of providing first aid for an eye injury and what should not be done after injury.
Description
Injury can be direct or indirect. In case of direct injury, the blow is directed to the eyeball, in the second case, surrounding tissues are injured. During an impact, intraocular pressure increases greatly, which provokes rupture of blood vessels and soft tissues. Because of this, swelling, hematoma, internal and external damage appears.
The danger of contusion is the risk of developing internal hemorrhage.
The causes of concussion are as follows:
- a fall;
- traumatic brain injury;
- blow with a blunt hard object;
- shock wave;
- directional flow of water.
At risk are military personnel who have direct contact with explosives and take part in hostilities. Those who work with mechanical devices are also at risk. However, almost half of the clinical cases relate to domestic injuries.
The consequence of injury is often a spasm of accommodation (false myopia), erosion of the corneal layer.
Ways to get injured:
- domestic - during a fight or family quarrel;
- sports - during sparring;
- military - during combat operations and exercises;
- industrial - injuries at work;
- agricultural - during harvesting and sowing crops.
If the injury was not severe, after therapeutic manipulations the functionality of the visual apparatus is completely restored.
Classification
Eye contusion is always an acquired form of pathology. In domestic ophthalmology, there are 4 degrees of damage to the visual organ:
| First degree - mild contusion | This is a mild contusion. Visually noticeable is slight swelling of the eye, hematomas, and blockage of the lens muscles. No ruptures or separation of the conjunctiva and eyelids are detected. The pain syndrome is slightly expressed. All pathological changes are restored, residual effects are not typical. |
| Second degree - moderate severity | This pathological condition is accompanied by a non-penetrating wound of the corneal layer. It is characterized by spasm of the intraocular muscles, severe tissue swelling, hematoma, iris ruptures, severe pain, lacrimation and photophobia. The pupil does not respond to the flow of light and is subject to deformation. There may be negative consequences for the health of the visual organ. |
| Third degree - severe | Rupture (sometimes separation) of the eyelids, iris, sclera. May be accompanied by (sub)luxation of the lens, retinal detachment, and deformation of the optic nerve. Severe pain, a sharp deterioration in the quality of vision until the light spot is distinguished, severe hemorrhage in the cornea. Severe pain is caused by an increase in intraocular pressure and a fracture of the bone wall of the orbit. |
| Fourth degree | This form of contusion is a complete deformation of the eyeball, deformation (rupture) of the optic nerve, complete loss of functionality of the visual apparatus. |
The degree of damage to the visual organs depends on the nature of the impact force. Not all lesions are dangerous to vision, but severe contusion can cause blindness.
Direct contusion of the eye - contact of the impact factor with the eye. This could be a blow with a hand, contact with a foreign body, a directed jet of water under high pressure, a blow with a heavy object, or a gas jet.
Indirect contusion - the impact force falls on the bones of the skull. This is a strong blow to the head, a fall from a height. In this case, internal structures are damaged; visual injury is not always noticeable.
Symptoms
With a mild degree of contusion, patients complain of:
- pain in the eyeball;
- lacrimation;
- photophobia;
- burning, stinging;
- It hurts to open your eyelids.
Within a few hours after the impact, the hemorrhage increases, and severe swelling of the tissues is observed. The bleeding then goes away within two or three weeks.
The second degree of damage is characterized by:
- severe pain when trying to open the eye or move the eyeball;
- a foggy veil appears before your eyes;
- vision is practically absent or poorly expressed.
For severe eye damage:
- the patient sees practically nothing, only distinguishes light;
- the pain radiates to the temples, brow ridges, forehead;
- oscillatory movements of the iris are noticeable;
- the lens “trembles”.
Symptoms of the last degree of concussion:
- the functionality of the visual apparatus is impaired;
- complete blindness;
- mobility of the eyeball is limited;
- spots appear before the eyes, which indicates a detachment of the inner membranes.
In critical condition, the eyeball is completely crushed.
The nature of the manifestation of contusion in different parts of the visual apparatus
Conjunctiva
With a mild injury, the conjunctiva may not be affected; with more severe injuries, hemorrhage is observed. In mild clinical cases, treatment is not required; the hemorrhage will go away on its own.
Cornea
A damaged cornea manifests itself as photophobia, lacrimation, pain and burning, and spasm of the eyelids. Severe clinical cases are characterized by clouding of the corneal layer.
Sclera
Damage to the sclera causes vision loss. Its rupture is indicated by a sharp decrease in the quality of vision, a decrease in intraocular pressure, and hemorrhage into the vitreous body.
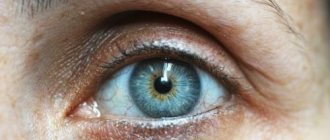
Iris
A minor injury leads to a narrowing of the pupil; in severe clinical cases, the iris ruptures.
Lens
This part of the visual apparatus may be damaged due to a sharp blow. Subluxation, dislocation or rupture of the lens body is observed. The impact often results in clouding of the lens - cataract.
Vitreous body
Hemorrhage into the vitreous body is characterized by the appearance of dark clots of various shapes before the eyes. This may affect the quality of vision.
Ocular fundus
Damage to the fundus manifests itself in:
- retinal detachment;
- retinal breaks;
- damage to the optic nerve;
- damage to the vascular network.
Bruises around the eye are a consequence of damage to the soft tissue of the periorbital structures.
Hyphema
This is the name for hemorrhage in the anterior chamber of the eye. Hyphema can appear as a result of injury to the vessels of the iris. In this case, blood descends to the bottom of the anterior chamber of the eye. A bloody stripe is directly visible in the lower parts of the anterior chamber. The appearance of the hyphema changes depending on the change in the position of the victim's head. Rapid resorption of the hyphema is possible within one to two days, but sometimes the healing process is delayed.
If the size of the hyphema is small, visual acuity may not be affected. But no matter the size, the victim should be examined by an ophthalmologist.
Treatment
The goal of treating hyphema is to prevent bleeding, which can lead to glaucoma with cloudy corneas. The patient is prescribed bed rest for three to four days. Aminocaproic acid and antifibrinolytics are prescribed. In general, the prognosis is favorable.
Complications of eye contusion
Damage to the visual apparatus does not always go away without leaving a trace; sometimes complications develop after the injury.
Purulent inflammation of the orbit . This happens when you fail to seek medical help in a timely manner. The inflammatory process can destroy the tissues of the visual apparatus up to the removal of the eyeball. Therefore, do not delay your visit to the ophthalmologist. A moderate injury without tissue ruptures can still lead to the onset of an inflammatory process in the internal tissues of the visual apparatus. Bacterial infections are especially dangerous.
Staphylococcus. This infection can destroy any organ in the body if left unchecked. Bacteria penetrate into organs when the integrity of the skin is damaged. Therefore, if the eye is injured, it is necessary to immediately treat the wound with antiseptic solutions. If there are no antiseptics in your home medicine cabinet, you need to seek help from an ophthalmologist or go to a traumatologist (on Sunday).
Keratitis . This is an inflammation of the eye socket that negatively affects the quality of vision. The danger is the penetration of infection into the internal structures of the corneal layer with subsequent disruption of visual perception.
Ophthalmia . This is a group of diseases of the visual apparatus with and without inflammatory processes. The pathology develops some time after damage to the eyeball. The nature of the development of the disease depends on the severity of damage to the ocular structures. In extreme cases, untreated pathology results in loss of vision.
Blood poisoning . This pathology occurs when an infection enters the bloodstream. Sepsis is a dangerous blood disease that can lead to death if medical care is not provided in a timely manner.
Ptosis . This pathology is a consequence of paralysis of the oculomotor nerve. The upper eyelid droops down and remains in a fixed position because the muscle does not receive a signal from the nerve. The cause of ptosis can be damage to the muscle itself, which controls the movement of the eyelid, as well as the consequences of bacterial infection and inflammation of the tissues surrounding the eye.
Brain abscess . This pathology is localized in the brain and is a consequence of inflammatory processes in the eyeball. Pyogenic bacteria and microorganisms enter the brain through the ethmoid bone of the nose and other routes. Dangerous Staphylococcus aureus, streptococcus, E. coli, candida and other protozoa can cause a serious pathological condition in humans - fever, dizziness, nausea and vomiting.
First aid
In case of a mild contusion, the victim can cope with first aid on his own. The main thing is not to harm yourself. Therefore, it is prohibited to do the following:
- rub the eye;
- press on the eyelids;
- touch the injured eye with unwashed hands;
- treat damaged tissues with iodine or brilliant green;
- wash the eye in case of penetrating wound or deep damage;
- apply a cotton swab to the eye in case of penetrating injury.
In case of minor damage, apply a compressive bandage to the eye and place an ice pack inside the bandage. This must be done immediately after the injury so that hematomas and swelling do not spread to healthy tissue. After this, you need to go to the emergency room so that the damage is examined by a doctor.
First aid includes the following procedures:
- applying a bandage to protect from light;
- the use of Albucid drops to prevent microbial infection;
- taking sedatives to relieve stress;
- taking analgesics to relieve pain;
- stopping bleeding (if necessary);
- exclusion of sudden movements, pushing, jumping, running.
A bandage is applied to the open wound to isolate the damaged tissue from contact with air and the environment.
If a chemical substance (fungicides, agrochemicals, etc.) gets on the eyeball, you need to rinse it with a large volume of water and go to the emergency room.
Diagnostics
First, the doctor asks the patient under what circumstances the injury occurred and how much time has passed since that moment. After examining the eyeball, sanitation is carried out - treating the tissues with a disinfectant solution.
In case of severe damage, hardware diagnostics are prescribed:
- biomicroscopy of the eye;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- gonioscopy;
- visometry;
- radiography of the facial part of the skull;
- MRI of the head;
- Ultrasound of the eye;
- non-contact tonometry.
Biomicroscopy is performed using a slit lamp. This is a quick, painless and effective method for diagnosing the eyeball. The ophthalmologist receives detailed information about the condition of the fundus, macula, retina, lens, corneal layer and other structures of the visual apparatus.
Ophthalmoscopy is an examination of the fundus of the eye using a beam of light that is directed onto the retina through the pupil. The ophthalmologist receives information about the condition of the retina, optic nerve and vascular system of the eyeball.
Gonioscopy - testing intraocular pressure, damage to the optic nerve, blockage of the tear ducts.
Visiometry is a test of visual acuity. Using the technique, you can determine the condition of the lens (presence of clouding), refractive error, pathology of the optic nerve and retina.
X-ray of the facial part of the skull is indicated for traumatic brain injuries that lead to eye contusion.
MRI of the brain shows the presence of internal hematomas and hemorrhages after receiving a strong blow to the head from a fall or other means. Sometimes, for a more accurate result, contrast is used - the introduction of a contrast liquid to highlight blood vessels and other structures.
Ultrasound of the eye is prescribed to clarify the condition of the visual apparatus after injury. The result gives an idea of the presence of hemorrhages, intraocular formations, the condition of the lens, and the nature of injury to the eyeball.
Non-contact tonometry gives an idea of the condition of the corneal layer. During the examination, a directed air flow is used.
Forecast
The prognosis depends entirely on the degree of damage and the location of the injury to the eye structures. The first and second stages have a favorable prognosis in most cases. Difficult stages end disappointingly. The patient must be under the supervision of a doctor for at least 1 year.
During the examination, the doctor makes a diagnosis using ophthalmoscopy and tonometry to monitor intraocular pressure. If antihypertensive drugs do not have the desired effect, the patient undergoes surgery to eliminate glaucoma.
Drug treatment
Restoring the functionality of the damaged organ is carried out taking into account the nature of the injury. When treating contusion, it is important to prevent dangerous complications. Therapy is aimed at:
- restoration of the integrity of damaged tissues;
- stopping hydrodynamic processes;
- elimination of foci of inflammation.
Minor damage may not be treated, but the doctor will prescribe Albucid drops to prevent bacterial infection. If you experience any discomfort, you can always make an appointment with an ophthalmologist.
If there are extensive bruises, anti-swelling ointments and antibacterial drops are prescribed.
For any mechanical damage to soft tissue, prophylaxis against the development of a purulent bacterial infection is necessary. Drops and gels for treating damaged eyes
| Albucid | Inexpensive, time-tested drops to prevent the development of bacterial infections. They have an anti-inflammatory effect. |
| Hyphenation | Drops moisturize the mucous membrane of the eye. The lacrimal membrane prevents the development of microbial infection in the mucous membrane of the eye. Relieves irritation, burning and stinging in the eyes, accelerates the healing of injured tissue. |
| Balarpan | The drops contain substances present in the corneal layer. They moisturize the cornea, create a protective layer, and accelerate regenerative processes in the corneal layer. |
| Vitasik | The drops accelerate the regeneration processes of damaged tissues and restore the damaged membrane of the corneal layer. |
| Kornegel | The delicate texture of the gel moisturizes the cornea and mucous membranes, protects against adverse external factors, and fights microbial and bacterial infections. |
| Solcoseryl gel | Moisturizes, protects and nourishes the eye shell with useful substances. Helps cope with the consequences of injury, even treats the consequences of burns. |
Prevention
There are no specific rules for preventing eye contusion. Herbs can arise at any time. This is due to external factors and mechanical stress. You can protect yourself from this by following safety rules. In general, safety glasses should be used.
Sometimes blunt force trauma can be caused by another person. For example, an attacker. In this case, it is difficult to protect yourself from such a situation. Therefore, the only advice is to follow general safety rules. If any degree of contusion occurs, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Traditional therapy
Before using decoctions and lotions, you should consult an ophthalmologist: in treatment it is important not to harm or aggravate the condition.
Iodine mesh
This method is widely used for many diseases. Iodine eliminates swelling and relieves pain from bruises. The mesh is applied to the hematoma under the eyes with severe swelling and bruising. The substance stops inflammatory processes in tissues and destroys pyogenic bacteria. The mucous membrane of the eyes cannot be treated with iodine, otherwise there will be a burn.
Salt compresses
A 10% salt compress, which is applied to the swollen tissues under the eyes or under the eyebrows, helps relieve swelling. Salt applications are not applied to the eyes. The compress should be kept for 10 minutes, then the skin should be gently washed.
Burdock leaves
An ancient folk remedy for bruises and swelling, eliminates pain. The sheet should be washed well in running water and dried. This sheet is applied to the bruised area, a plastic bag for insulation and a warm cloth are fixed on top. This method should not be used on a fresh bruise, as heat will cause swelling to spread. Immediately after the blow, ice or a cold compress is applied to stop the spread of the hematoma. Warming is done the next day if the bruise hurts a lot.
Cabbage leaves
This remedy is used to eliminate the effects of a bruise and relieve a hematoma. The fresh leaf is slightly beaten with a rolling pin until the juice appears and applied to the eye. To keep the sheet in place, it is fixed with a bandage or towel. As the cabbage leaf dries out, replace it with a new one.
Marigold
Calendula is one of the popular folk methods for treating many diseases. It is used as a local remedy - in applications, lotions, rinses, compresses. For half a cup of boiling water, take a tablespoon of dried flowers and infuse. This compress can be used to treat a damaged eye and the skin around the eye. The application is applied in a warm state and kept until it cools.
Bottom line
An eye contusion is a serious injury that can lead to critical vision loss. Therefore, immediately after providing first aid, the victim must be checked by a doctor (traumatologist, ophthalmologist), undergo the required tests and complete the course of therapy to the end. An untreated disease is dangerous for the development of complications that are worse than the disease itself.
Sources used:
- Stratton GM Vision without inversion of the retinal image (English) // Psychological Review (English) Russian. : journal. — 1897.
- Eye diseases. Fundamentals of ophthalmology / Edited by Professor V. G. Kopaeva. — M.: OJSC “Publishing House “Medicine”, 2012.
- D. Hubel. Structure of the eye, brain, vision. — ed. A. L. Byzova. - M.: Mir, 1990.
- Department of Ophthalmology - University of Colorado
Sources
- Wu S., Bian C., Li X., Chen M., Yang J., Jin Y., Shen Y., Cheng L. Controlled release of triamcinolone from an episcleral micro film delivery system for open-globe eye injuries and proliferative vitreoretinopathy. // J Control Release - 2021 - Vol333 - NNULL - p.76-90; PMID:33771623
- Formica MK. An Eye on Disparities, Health Equity, and Racism—The Case of Firearm Injuries in Urban Youth in the United States and Globally. // Pediatr Clin North Am - 2021 - Vol68 - N2 - p.389-399; PMID:33678293
- Wang B., Zuo X., Peng L., Wang X., Zeng H., Zhong J., Li S., Xiao Y., Wang L., Ouyang H., Yuan J. Melatonin ameliorates oxidative stress-mediated injuries through induction of HO-1 and restores autophatic flux in dry eye. // Exp Eye Res - 2021 - Vol205 - NNULL - p.108491; PMID:33587908
- Dhoot AS., Koziarz A., Lee Y., Chopra C., Micieli JA. Eye Injuries and Visor Use in the National Football League. // Ophthalmology - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33545169
- AlMahmoud T., Elhanan M., Abu-Zidan F.M. Eye injuries caused by date palm thorns and leaves. // Saudi J Ophthalmol - 2021 - Vol34 - N1 - p.13-17; PMID:33542981
- Jovanovic N., Peek-Asa C., Zhang L., Cavanaugh J.E., Pidro A., Alajbegovic-Halimic J. The Risk and Protective Factors for Pediatric Eye Injuries: A Case-Crossover Study. // Ophthalmic Epidemiol - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.1-9; PMID:33502942
- Martin G.C., Le Roux G., Guindolet D., Boulanger E., Hasle D., Morin E., Vodovar D., Vignal C., Gabison E., Descatha A. Pediatric Eye Injuries by Hydroalcoholic Gel in the Context of the Coronavirus Disease 2021 Pandemic. // JAMA Ophthalmol - 2021 - Vol139 - N3 - p.348-351; PMID:33475712
- Ratanapakorn T., Kongmalai P., Sinawat S., Sanguansak T., Bhoomibunchoo C., Laovirojjanakul W., Yospaiboon Y. Predictors for Visual Outcomes in Eye Injuries with Intraocular Foreign Body. // Clin Ophthalmol - 2021 - Vol14 - NNULL - p.4587-4593; PMID:33456307
- Sun F., Zhou Y., Dong L., Qin H. Relationship between the use and type of eye protection and work-related corneal and conjunctival foreign body injuries. // Inj Prev - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33443032
- Kuhn F., Morris R. Early vitrectomy for severe eye injuries. // Eye (Lond) - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33235339