Snoring , although not an independent disease, serves, however, as a signal that a person has some kind of pathology (most often ENT organs). By its nature, snoring is a sound phenomenon that occurs when breathing during sleep due to vibration of the soft structures of the nasopharynx or larynx. Snoring can occur at any age, but is more common in older people.
It should be remembered that snoring is not as harmless as many people think. In addition to causing inconvenience to others, snoring can pose a serious threat to the health and functioning of the snorer himself. If you are already thinking about how to get rid of snoring, then we invite you to the MedikCity Multidisciplinary Clinic in Moscow. We provide a full examination and treatment for snoring.
1 Consultation with an otolaryngologist in MedicCity
2 Consultation with an otolaryngologist in MedicCity
3 Consultation with an otolaryngologist in MedicCity
Causes of snoring
The reasons leading to the development of snoring are varied. Conventionally, they can be divided into anatomical disorders , which result in a narrowing of the airways, and functional disorders , leading to changes in the tone of the pharyngeal muscles.
Anatomical causes of snoring can be enlarged tonsils, a deviated nasal septum, nasal polyps, excess body weight, etc.
Functional disorders occur due to lack of sleep and fatigue, drinking alcohol, sleeping pills, smoking, decreased thyroid function and exposure to many other factors.
Therefore, patients with complaints of snoring often require consultation with specialists - a cardiologist, endocrinologist, or therapist.
The attitude of specialists towards selective interventions on the pharynx
Sometimes advertisements present laser treatment as the most effective treatment for snoring. And it seems that curing snoring is quite quick and simple. But in reality, the solution to the problem of snoring is not so obvious. We are often approached by patients who continue to snore, despite the fact that they previously treated snoring with laser and radiofrequency, which turned out to be ineffective.
Foreign experts are critical of selective interventions on the pharynx in patients with snoring and sleep apnea:
- There is low or no effectiveness of laser treatment for OSA [Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surgery, 1997]
- LUPP may be accompanied by pain. There are no significant differences in postoperative pain between LUPP and uvulopalatopharyngoplasty [J. Otolaryngol., 1997].
- LUPP can lead to various complications. Sometimes LUPP provokes the development of OSA in patients with uncomplicated snoring or aggravates existing OSA. [Am. J. Resp. Crit. Care Med., 1997].
Snoring in men
According to scientists, men snore on average 2 times more often than women. Men can snore for various reasons, but the main ones may be:
- unique structure of the respiratory organs (narrow upper respiratory tract, long uvula);
- deviated nasal septum;
- alcohol, smoking, which weaken the neck muscles, narrow the airways and provoke snoring;
- stress, general weakening of body tone;
- the appearance of adenoids;
- malocclusion;
- age-related changes that lead to weakening of the neck muscles, and, of course, to snoring;
- excess weight, fatty tissue around the neck that blocks the normal flow of air through the neck.
Responsibilities of doctors
The patient must be warned
that polysomnography or cardiorespiratory monitoring will clarify the diagnosis.
And the patient himself must decide whether he needs additional expenses for a diagnostic study or whether he agrees to surgery on the palate, but without a guarantee that this will help
.
But often no one informs patients about the additional and necessary research, and they take a certain risk without knowing it. Although useless and sometimes dangerous surgical interventions could have been avoided, with proper examination and if an accurate diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSA)
. With such a diagnosis, it is impossible to get rid of snoring immediately; this requires time and quite serious treatment methods (you need to lose weight or carry out assisted ventilation during night sleep - CPAP therapy).
Often after ineffective laser uvulopalatoplasty
(LUPP), which did not produce any results, patients are assured that nothing can be done and they are not told about the possibility of CPAP therapy, which is the most effective method for treating severe OSA.
Why snoring is dangerous
For some, one of the unpleasant consequences of chronic snoring is drowsiness, lethargy and fatigue during the day. Snoring can affect the very structure of sleep: sleep is interrupted, fragmented, the human brain and the body as a whole do not rest, and fatigue accumulates. And sleep disturbance, as is known, can lead to nervous disorders.
One of the most serious consequences of snoring is obstructive sleep apnea ( short-term cessation of breathing ) during sleep. This disease is dangerous due to the cessation of pulmonary ventilation and a decrease in the level of oxygen in the blood, which often causes nocturnal strokes, heart attacks, sudden death during sleep, etc.
Snoring is also a risk factor for arterial hypertension, heart rhythm disturbances, heart failure and other serious diseases.
Snoring can occur not only in adults, but also in children. As a rule, this indicates that the child has adenoids, enlarged tonsils, chronic rhinitis, and a deviated nasal septum.
Lack of timely treatment for snoring (or rather, the underlying disease that caused it) in a child can lead to sleep apnea , nocturnal enuresis , decreased activity, decreased school performance, and emotional depression. In some cases, the child may even experience growth retardation .
The fact is that due to sleep disorders, the child’s body does not produce the somatotropic hormone in the required quantity (and its production occurs precisely at night), which is “responsible” for growth.
Can promises be trusted?
There are medical centers that encourage palate surgery to cure snoring. But at the same time they do not carry out preliminary diagnostics.
, for example, polysomnography or other studies that can diagnose sleep apnea.
Most operations for snoring on the palate are carried out without a preliminary full examination of the patient’s breathing during sleep. Sometimes you can hear that they treat sleep apnea, although this is absolutely contrary to international standards
. Surgery for snoring on the palate without research may at best be simply ineffective, but sometimes it can lead to tragic complications.
In Israel, for example, all ENT centers are required to first fully examine the patient’s nighttime sleep, and only after that decide on the possibility of surgery. Studies are also carried out after laser treatment for snoring. Unfortunately, in our country, standards of this kind have not yet been adopted at the state level, but every otorhinolaryngologist must responsibly
treat your patients. He needs to independently decide whether it is advisable to treat snoring and sleep apnea with laser or radiofrequency. Each specialist must be based on knowledge, clinical experience and remember the main thing - “Do no harm!”
Many centers that provide laser and radiofrequency treatment for snoring do not purchase diagnostic equipment for polysomnography because it is quite expensive. The studies themselves are quite labor-intensive, and therefore many centers take risks and do not conduct the study
, but rely only on the story of the patient, his relatives and on the clinical examination, which is carried out during the day. Therefore, diagnostic errors are often made. Sometimes patients themselves may refuse polysomnography in order to save money.
How to get rid of snoring
Preventative measures are very important when treating snoring. For example, experts recommend the following rules:
- sleep only on your side;
- use a special orthopedic pillow for sleeping;
- perform special exercises (for example, stick your tongue out to your chin and open and close your jaws);
- whistle tunes as often as possible;
- lose weight if you are overweight;
- correct problems with nasal breathing;
- get rid of bad habits;
- stop using sleeping pills;
- purchase special anti-snoring remedies in the form of tablets, sprays, drops and nasal patches.
Terminology
Selective surgical interventions on the palate include techniques such as surgery, laser plastic surgery, radiofrequency plastic surgery, injection methods and cryoplasty. The above methods are based on the principle of causing trauma to the palate of varying intensity
. During healing, the soft palate usually decreases in volume and thickens. The uvula is partially or completely removed. Thus, snoring can be eliminated or reduced, because the mobility of the structures of the soft palate is reduced.
Clip 2 in 1: “Anti-snoring” and magnetic therapy - you can’t feel it in your sleep
— How to use: insert into the nose before going to bed and remove after waking up. — How it works: slightly expands the nasal passages and acts on biologically active points inside the nose. This way, the clip enhances air flow and eliminates teeth grinding. — Suitable for: those who suffer not only from snoring, but also from bruxism. Fits even in a tiny nose.
Positional therapy
Indications: uncomplicated snoring and positional OSA (i.e., when snoring and apnea episodes occur exclusively during sleep on the back).
Positional therapy is perhaps the only method of treating snoring that can be used without first consulting a specialist. (But this does not exclude the need to visit a somnologist later). A high degree of collapse of the soft structures of the pharynx is most often observed while resting while lying on the back. And the essence of the method is to control the position of the body during sleep. For this purpose, auxiliary devices are used - from special belts to backpacks or ordinary tennis balls sewn into a pajama T-shirt in the back area.
If we are talking specifically about positional snoring and OSA, such therapy can significantly reduce symptoms. But by resorting to this method, a person will wake up every time he tries to turn on his back. This leads to a disruption in the structure of healthy sleep and can cause insomnia, fatigue during the day, and depressive disorders.
Snoring and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome
Otorhinolaryngologist, Scientific and Practical Center MSR named after. L.I. Shvetsova
Kuznetsova Elena Nikolaevna
What is snoring and why is it dangerous?
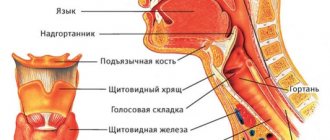
Snoring (ronchopathy, benign nocturnal snoring) is a sound phenomenon that occurs when the soft structures of the pharynx beat against each other against the backdrop of a stream of air passing through the narrowed airways. This is a specific process that accompanies a person’s breathing during sleep, expressed by a distinct low-frequency rattling sound.
*from 30 to 50% of the adult population snores in their sleep
*30% of snorers develop obstructive sleep apnea syndrome.
Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSA) is a disease characterized by snoring, periodic collapse of the upper airways at the level of the pharynx and cessation of pulmonary ventilation, decreased blood oxygen levels, severe sleep fragmentation and excessive daytime sleepiness (Guilleminault C., 1978).
Often witnesses to this disease are waking loved ones who watch with alarm as the snoring suddenly stops and a frightening cessation of breathing occurs, then the sleeper snores loudly and begins to breathe again. Sometimes there can be up to 500 respiratory arrests per night for a total duration of up to 4 hours, which leads to both acute and chronic lack of oxygen and significantly increases the risk of developing arterial hypertension, cardiac arrhythmias, myocardial infarction, stroke and sudden death in sleep.
Patients with breathing disorders during sleep experience restless, shallow, unrefreshing sleep, sweating and frequent urination at night, fatigue and headaches in the morning, severe daytime sleepiness, irritability, decreased memory and attention, and impotence.
The causes of OSA are the same as those of snoring. The difference lies only in the degree of their expression. If during snoring the walls of the respiratory tract only vibrate when a stream of air passes, then during illness they periodically collapse completely, stopping the access of air to the lungs.
The causes of snoring are:
1.Anatomical disorders leading to narrowing of the airways:
— Impaired nasal breathing
- Deviated nasal septum
- Chronic rhinitis
- Congenital narrowness of the nasal passages and/or pharynx
- Nasal polyps
— Pathology of the pharynx
- Elongated uvula
- Disturbance of the innervation of the muscles of the soft palate due to various degenerative neuromuscular processes or in connection with the use of substances with a muscle relaxant effect
(sleeping pills, tranquilizers, sedatives, alcohol) - Small, posteriorly displaced lower jaw (with malocclusion)
- Enlarged palatine tonsils
— Obesity
The risk of snoring in obese patients is 8-12 times higher than in patients with a normal body mass index. In patients with grade 3 obesity, a severe form of obstructive apnea syndrome (OSA) develops in 60% of cases. The risk of developing OSA increases significantly when the neck circumference in men is more than 42 cm and in women more than 40 cm.
Fat deposits in the area of the lateral walls of the pharynx lead to a narrowing of the lumen of the pharynx, increasing the likelihood of its collapse at the level from the uvula to the epiglottis.
2.Functional factors and diseases that reduce the tone of the pharyngeal muscles:
- Actually, sleep (decreased muscle tone)
- Sleep deficiency and fatigue
- Alcohol intake
- Taking sleeping pills
- Smoking
- Decreased thyroid function (hypothyroidism and acromegaly)
- Menopause in women
- Aging
Snoring, as a sound, is more of a social problem for others than for the person himself. However, snoring can be a harbinger and one of the main symptoms of a serious disease - obstructive sleep apnea syndrome.
OPTIMAL DIAGNOSTIC TACTICS
The diagnosis of snoring itself, as a rule, does not cause any particular difficulties. It should be noted, however, that the person himself usually underestimates his snoring. People around you overestimate. For example, a person may snore softly 10 times during the night (total duration is 10-20 minutes), but this will wake up his roommate 10 times and he will have the impression that the whole night was ruined by loud snoring.
The situation with the diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome is much more complicated. For preliminary self-diagnosis, you can use a screening rule or a daytime sleepiness test, which allows you to suspect the disease.
An accurate diagnosis can only be established by a doctor based on consultation and polysomnogaphy.
Polysomnography and cardiorespiratory monitoring
Polysomnography is a method of long-term recording of various functions of the human body during night sleep.
The following parameters are registered:
- Snore.
- Breath.
- Blood oxygen saturation.
- Respiratory movements of the chest and abdominal wall.
- Body position.
- Electroencephalogram (brain activity).
- Electrooculogram (eye movements).
- Electromyogram (tonus of the mental muscles).
- Movements of the lower extremities.
Continuous video recording of sleep can also be carried out. Polysomnography is performed in sleep laboratories that have appropriate diagnostic equipment.
Cardiorespiratory monitoring
The same parameters are recorded as with polysomnography, with the exception of paragraphs. 6,7,8. The main difference between cardiorespiratory monitoring (CRM) and polysomnography is that the sleep structure itself is not analyzed. To a certain extent, this reduces the diagnostic accuracy of the method, however, for the diagnosis of breathing disorders during sleep (snoring and sleep apnea), CRM is often sufficient.
If it is necessary to diagnose sleep disorders themselves (insomnia, narcolepsy, etc.) or movement disorders during sleep (periodic limb movement syndrome during sleep), polysomnography is necessary. Polysomnography should also be performed in cases of suspected combination of sleep-disordered breathing with sleep disorders or movement disorders during sleep.
OPTIMAL TREATMENT TACTICS
There is no single and 100% effective treatment for snoring and obstructive sleep apnea. Accordingly, one should be treated with a dose of healthy skepticism towards announcements of miraculous interventions that eliminate snoring in all patients in one session.
The diversity of snoring and the varying severity of the condition require an individualized treatment approach. Sometimes it is enough to reduce your weight by 5-7 kg to stop snoring. An accurate assessment of difficulty in nasal breathing during the occurrence of snoring is of great importance. In some cases, eliminating a deviated nasal septum eliminates snoring. Laser plastic surgery and cryoplasty of the palate are effective only for uncomplicated snoring or mild forms of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. With severe hypertrophy of the tonsils, it is necessary to raise the question of tonsillectomy, especially in the case of severe breathing disorders during sleep. The use of intraoral snoring devices is most effective in patients with retro- and micrognathia.
In severe cases of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and the absence of obvious anatomical defects that could be corrected surgically, the only effective treatment is the creation of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP therapy)
CPAP (English CPAP ) - therapy (an abbreviation for the English words C ontinuous P ositive A irway Pressure , which reflect the meaning of the method). The mechanism of action of CPAP therapy is quite simple. If excessive positive pressure is created in the airways during sleep, this will prevent them from collapsing and eliminate the main mechanism for the development of the disease, which is the cyclic closure of the airways at the level of the pharynx.
Thus, specific treatment approaches should be determined by a qualified professional depending on the cause and severity of the condition. Below is a brief description of all the possible treatments for snoring and obstructive sleep apnea.
GENERAL PREVENTIVE MEASURES AND SELF-MEDICATION
Do not increase or decrease body weight
If you have certain problems with breathing disorders during sleep, an increase in body weight by 10% of the initial one can worsen breathing parameters by 50%. This is usually accompanied by a transition to the next most severe stage of OSA. Patients were observed who gained 15-20% of their body weight over a period of one and a half to two years. These patients with a mild form of OSA, after gaining weight, received a severe form with all the ensuing consequences. This includes a significant deterioration in the quality of sleep, increased frequency of urination at night, crisis morning hypertension, morning headache, severe daytime sleepiness, irritability and a number of other symptoms. A significant reduction in body weight can, accordingly, significantly improve the situation.
Quit or limit smoking
Smoking often causes chronic inflammation of the pharynx and trachea, accompanied by swelling of their walls and decreased tone of the pharyngeal muscles. This, in turn, causes narrowing of the airways and increases snoring and OSA. However, one should be extremely careful when approaching the issue of smoking cessation in patients with OSA and obesity. This can lead to further weight gain and disease progression (see above), negating the benefits of quitting smoking. In this situation, you must first attempt significant weight loss, and only then resolve the issue of smoking. If you continue to smoke, it is advisable to at least abstain from it two hours before bedtime.
Avoid taking tranquilizers and sleeping pills
Tranquilizers and sleeping pills tend to reduce muscle tone and promote relaxation of the pharyngeal muscles, which in turn can worsen snoring and OSA.
Don't drink alcohol before bed
Alcohol also relaxes the pharyngeal muscles, causing snoring and OSA. The human liver processes about 10-15 ml of pure alcohol per hour. For example, 100 ml of vodka contains 40 ml of pure alcohol, respectively, the negative effect of this dose will last about 2.5-4 hours. You should especially refrain from taking alcohol and sleeping pills at the same time.
Treatments that do not require medical intervention
Positional treatment
- Mild forms of snoring and OSA are often position-dependent and occur only on the back. This is due to the retraction of the tongue. There is a simple and effective way to wean a person from sleeping on their back. On night pajamas or a special vest, a pocket is sewn between the shoulder blades in which a tennis ball is placed. In this case, every attempt to lie on your back will end in waking up and turning on your side. At the beginning of using this method, the quality of sleep may deteriorate, especially in people who are accustomed to sleeping on their backs, but within 3-4 weeks a strong conditioned reflex is developed not to sleep on their backs.
- It is necessary to ensure an elevated position of the headboard. An elevated position of the torso reduces tongue retraction even in a supine position. Moreover, the fluid in the body shifts downward, which leads to a decrease in swelling of the mucous membrane at the level of the nose and pharynx, an increase in their lumen, and, accordingly, a weakening of snoring.
- You should not use tightly stuffed large pillows to ensure an elevated position of the head, since this tends to cause the torso to slide off the pillow and the head to be tilted too much, which can even increase snoring.
- The head should be positioned as parallel to the body as possible. To achieve this, it is advisable to use small flat pillows, orthopedic or special contour pillows. The listed positional treatment methods help not only with snoring, but also with belching of gastric contents, which is often observed in overweight people who snore. Our pharmacies offer a number of drugs for the treatment of snoring. Drops for gargling “Good night” These drops are a mixture of 10 different essential oils, used diluted for gargling. According to manufacturers, drops have the following effects:
- They have a tonic effect on the pharyngeal muscles, which reduces snoring.
- Reduce or eliminate dry mouth during sleep, sore throat and other unpleasant sensations in the throat in the morning.
They lubricate the tissues of the pharynx, which reduces their injury and swelling during snoring.
Unfortunately, the initial enthusiasm for these drops gave way to moderate skepticism. Based on the results of controlled studies reported at the V World Congress on Sleep Apnea (Marburg, Germany, 1996), it was concluded that there was no clear clinical effect of the drops on OSA.
Despite this, it is quite possible to recommend this drug, since, firstly, it clearly reduces the subjective discomfort in the throat associated with snoring (dryness, soreness, pain), and secondly, it may have a preventive effect regarding the progression of the disease by reducing chronic trauma to muscle tissue at the level of the pharynx (works as a lubricant). The latter position has not yet been confirmed, but has not been refuted either, although from a pathophysiological point of view it has a right to exist.
Drug SnorStop (SnoreStop)
Snorstop is a complex homeopathic medicine
Dosage form: Tablets for sublingual administration (under the tongue).
Indications for use: Snorstop is used as a symptomatic remedy to reduce the intensity of snoring during sleep.
Contraindications: There are no absolute contraindications. The drug should be used with caution in cases of obstructive sleep apnea (sleep apnea) and pregnancy.
Take Snorstop once immediately before bed (put the tablet under the tongue until the drug is completely dissolved in the oral cavity). Weight up to 72 kg – 1 tablet before bedtime. If you weigh more than 72 kg – 2 tablets before bedtime. If the severity of snoring decreases, take Snorstop every other day; if the dynamics are positive, gradually reduce the frequency of use until you stop taking it.
The drug Snorstop has been used in Russia since 2000. Snorstop is intended for situational relief of uncomplicated snoring. It does not have a healing effect. After stopping the course of treatment, snoring appears or intensifies again after some time. In addition, Snorstop is practically useless for obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, when, in addition to snoring, there are pauses in breathing followed by loud snoring. It is usually recommended to use Snorstop for situational elimination or relief of snoring, for example, when traveling on a business trip, being in a hospital, etc. The effect of treatment is usually noticeable on the first night, but usually increases and reaches a maximum within 3-4 days. Thus, it is advisable to start taking the drug early. Snorstop is also recommended for situational use in patients whose snoring appears or worsens after drinking alcohol. The drug is also indicated for the treatment of snoring that occurs after a sore throat or pharyngitis.
It is not recommended to take Snorstop for more than 40 days. After this, it is necessary to take a break for approximately the same period during which the drug was used, since any long-term use of pharmacological agents carries the risk of potential complications
In the case of chronic snoring and, especially, obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, it is better to contact a specialized sleep center to clarify the causes and severity of the disease and choose the most effective treatment.
It is also worth mentioning various sprays to relieve snoring, “Hrapex”, “Slipex”. The mechanism of action of these drugs also lies in toning the muscles of the pharynx.
Ensuring maximum free nasal breathing
Difficulty in nasal breathing can significantly increase snoring and OSA. Let us dwell on therapeutic methods for improving nasal breathing, especially at night. The best effect is achieved by using special stickers on the nose (see picture). These stickers are a springy strip that sticks to the wings of the nose and pushes them apart, which makes nasal breathing much easier. You can predict the effectiveness of the strips quite simply by asking the patient to grab the wings of the nose with his fingertips, spread them apart and take a few breaths through the nose. These stickers are installed throughout the night. They can be used constantly or situationally, when you need to alleviate snoring as much as possible or there are factors that provoke snoring (alcohol consumption, ARVI).
For transient nighttime nasal congestion, it is necessary to consider the possibility of an allergic reaction to bedroom objects (dust, feathers, house mites), as well as a reaction of the nasal mucosa to dry air. In the latter case, humidification of the air during the night has a good effect. Constant use of drugs such as glazolin or sanorin is not advisable due to the rapid decrease in their effect and the development of dependence. In case of chronic nasal obstruction, consultation with an otolaryngologist is necessary.
Exercises to reduce snoring
There is a set of exercises for training the muscles of the tongue, lower jaw and pharynx, aimed at reducing snoring:
USING INTRAORAL DEVICES FOR SNORING
There is a domestic intraoral device for the treatment of snoring prevention and treatment “EXTRA-ENT”. In appearance, it vaguely resembles a regular baby pacifier and consists of a cup-shaped petal that touches the tongue, and fixing rims that protect it from swallowing or falling out of the mouth. The mechanism of action is to fix the tongue in a certain position, which prevents snoring. However, this mechanism does not give 100% results. The cup-shaped petal cannot permanently fix the tongue.
The therapeutic effect of the device is more logically explained by its reflex action on the muscles of the tongue and pharynx. If there is a foreign body in the oral cavity, the tongue constantly tries to touch it, sometimes even against our desire. The presence of a cup-shaped lobe in the anterior cavity of the mouth reflexively causes the tongue to move forward and tension its muscles, as well as the muscles of the pharynx, which prevent vibration and collapse of its walls.
This device has the greatest effect in individuals without severe obesity, with uncomplicated snoring and normal nasal breathing. The main obstacle to using the device is the possibility of deterioration in sleep quality due to the presence of a foreign body in the mouth.
There are also intraoral devices that push the lower jaw forward, which increases the anteroposterior size of the airway and, accordingly, reduces snoring and the severity of OSA. These can be blanks made of thermolabile material, which, when heated, are installed on the upper jaw (like a boxer’s mouthpiece), after which the patient closes his mouth with the lower jaw extended forward. The blank hardens and, when used again, allows the lower jaw to move forward (picture on the right). Intraoral devices provide the best effect for uncomplicated snoring, mild and moderate forms of OSA in patients with micro- and retrognathia. The main disadvantages of simulated devices are their high cost and the need for the participation of a doctor in their installation.
LASER PLASTY AND CRYOPLASTY OF THE PALATE
The therapeutic effect of these methods is based on causing a thermal or cold burn of the mucous membrane of the soft palate. A laser or cryoapplicator causes linear or pinpoint burns in the area of the soft palate and uvula, which causes inflammation. As the tissue heals, there is a decrease in volume and thickening of the palate, which reduces its vibration and the sound phenomenon of snoring. Technically, the procedure is quite simple and is performed on an outpatient basis. However, the patient experiences significant pain, reminiscent of a severe sore throat. The procedure can be repeated 1-3 times at intervals of 2-3 weeks until the desired effect is achieved.
Plastics are effective for uncomplicated snoring and mild OSA in patients with a low-lying soft palate and an elongated uvula. In moderate and severe forms of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, especially in obese patients, the effectiveness of these techniques is low.
SURGICAL REMOVAL OF ANATOMICAL DEFECTS AT THE LEVEL OF THE NOSE AND PHYNAX
Difficulty in nasal breathing is one of the causes of snoring and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSA). Moderate and severe forms of OSA should be considered an absolute indication for the elimination of chronic nasal obstruction caused by a deviated nasal septum, polyps or thickening of the nasal mucosa. For mild forms and uncomplicated snoring, especially in older age groups, it is necessary to carefully weigh the possible benefits and risks. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the social significance of snoring for the patient and his desire to eliminate this sound phenomenon.
The main surgical intervention at the pharynx level is uvulopalatopharyngoplasty. This operation involves excision of the uvula, part of the soft palate and palatine arches, as well as removal of the tonsils. This operation is very traumatic and must be used according to strict indications, since a number of complications may develop (postoperative respiratory arrest or bleeding; in the long term - a nasal voice and food getting into the respiratory tract). It should also be noted that in severe forms of OSA in obese patients, the positive effect of this surgical intervention is achieved only in 20-30% of those operated on. This is due to the persistence of narrowing of the underlying parts of the pharynx at the level of the root of the tongue and the epiglottis.
In any case, the decision on surgical treatment should be made by an ENT surgeon, taking into account clinical examination data, polysomnography results and other additional examination methods.
TREATMENT WITH CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE
CPAP (CPAP therapy)
This type of treatment has already been mentioned above. This method is non-invasive and easy to use, but requires special, expensive equipment.
Treatment is carried out using a small compressor that delivers a constant stream of air at a certain pressure into the airways through a flexible tube and a sealed nasal mask. If in a healthy person the presence of a tube and a mask on the face can cause a deterioration in the quality of sleep, then in a patient with a severe form of OSA, accompanied by hundreds of pauses in breathing per night, and, accordingly, hundreds of micro-awakenings of the brain, sleep with the device is perceived as a much lesser evil. Moreover, daytime sleepiness is eliminated almost immediately and the overall quality of life improves.
The procedure for selecting therapeutic pressure is carried out in sleep clinics. Subsequently, the patient independently uses the device at home.
In severe cases, the device must be used every night. With a milder course of the disease, periodic use of the device is possible (4-5 times a week). The treatment has virtually no side effects. Cancellation of hardware treatment (even if it has been carried out for several years) does not entail any complications, except for the gradual return of the original symptoms. The use of the device does not cure a person, but provides normal sleep, improves the quality of life and prevents serious complications. Even very seriously ill patients can feel a significant improvement in their well-being within a few days.
CONCLUSION
In today's lecture we tried to find out what snoring is and what are the reasons for its occurrence.
-Treatment of snoring is not an easy task, requiring increased attention to the diagnosis of not only ENT organs, but also the general somatic condition of the patient.
-In most clinical cases, snoring treatment is a step-by-step process.
-None of the existing methods can give a 100% guarantee of getting rid of snoring. The average effectiveness of modern methods is 70%.
-For uncomplicated snoring, you can try conservative treatment methods yourself (gymnastics, sprays, positional treatment). But with obstructive apnea, this is a waste of precious time.
Thank you for your attention. Be healthy!
Symptoms of the disease
Knowing the signs of the disease will help determine whether snoring is affecting a person’s health. Warning symptoms include:
- loud and sharp sound that occurs during sleep;
- constant daytime sleepiness;
- headaches in the morning;
- chronic fatigue;
- stopping breathing.
The last symptom is a sign of a serious disease - apnea syndrome. For proper treatment, it is recommended to consult a doctor. Our clinic provides professional assistance and identifies the causes of snoring.
Anti-snoring finger ring Anti-snoring - for aesthetics in sleep
— How to use: before going to bed, put it on your little finger with the hole on the back side. — How it works: based on the principle of Chinese acupuncture — it affects active points. - Suitable for: those who feel uncomfortable when there are foreign objects in the mouth or nose - mouthguards, inserts or clips. Can be worn as a stylish accessory.
Anti-snoring helmet bandage - will not fall off if you toss and turn in your sleep
— How to use: before going to bed, fix the headband on your head. — How it works: it presses the lower jaw and prevents air from penetrating through the mouth. — Who is it suitable for: people who snore due to their mouth being open during sleep. Can only be worn with good nasal breathing.
Diagnostics
Only a qualified ENT specialist can correctly identify snoring, the causes of its occurrence, and also correctly relieve the patient from the potential danger associated with the development of obstructive apnea syndrome. Doctors at our clinic conduct a comprehensive examination, including:
- detailed medical history;
- examination using video endoscopic equipment (to accurately determine possible internal pathologies of the nasopharynx);
- instrumental examination through respiratory monitoring with pulse oximetry using SOMNOcheckmicro (this small device is attached to the wrist before bed, it records the frequency of snoring, pulse and the percentage of oxygen saturation of the blood).
Kappa Anti-Snoring - you can regulate breathing: nose - mouth
— How to use: before use, “brew” it in boiling water to soften it, and then insert it into your mouth. — How it works: it slightly holds the tongue, preventing it from sinking, and tones the soft palate. — Who is it suitable for: those with narrow respiratory passages and those who snore due to tongue sinking. Cannot be used by children and people who suffer from apnea.
Hypoglossal nerve stimulation
Indications: OSA caused by weak soft tissue tone in the posterior parts of the pharynx.
Another way to reduce the risk of obstruction at the pharyngeal level is to subcutaneously implant a pulse generator in the subclavian region. The device increases muscle tone through weak electrical stimulation of the hypoglossal nerve. Implantation takes 1-1.5 hours. The battery life is 15 years. The generator is replaced under local anesthesia.
However, many patients perceive implantation of a foreign body even more critically than traditional surgery. However, such manipulation helps only a small proportion of patients with OSA. And due to the lack of long-term studies, the pathophysiology of the therapeutic effect itself requires further detailed analysis.
Drug therapy
Indications: snoring and OSA caused by obesity, as well as narrowing of the airways as a result of allergic or cold-induced swelling.
The existence of effective anti-snoring pills could minimize the need for other treatments. But, unfortunately, the possibilities of drug therapy are limited. Firstly, it is worth understanding that the action of pills and sprays is aimed at snoring, and not at eliminating the causes that cause it.
Therefore, to identify the problem and get a prescription, you cannot do without consulting an ENT specialist or somnologist. Secondly, there are not many problems that provoke snoring that can be solved with the help of medications. We are talking about pills for weight loss, “softening” the throat or relieving swelling of the larynx during colds or allergies. But even in carefully selected groups of patients, the therapeutic effect does not always live up to expectations. And thirdly, most medications have side effects. And often the harm from these drugs exceeds the potential benefits of their use.
IMPORTANT TO UNDERSTAND! Most drugs that are positioned as a cure for snoring are not pharmacological agents, but biologically active additives based on herbal components. In view of this, the requirements for evidence regarding their effectiveness are significantly reduced. In addition, for many of them, OSA is a strict contraindication.