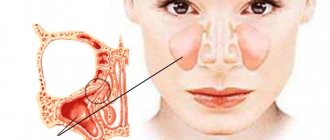
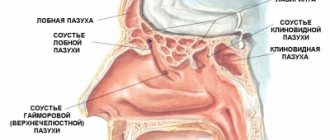
The ENT organs, being an outpost of the immune system on the path of infection into the body, are the first to encounter the effects of various pathogens. That is why inflammatory processes often begin in them. Inflammation of the paranasal sinuses is called sinusitis . In total, a person has 4 pairs of paranasal sinuses, these are cavities filled with air. As a result of inflammatory processes, pus is formed in the sinuses, and the person begins to feel weak and unwell.
1
Nasal endoscopy in MedicCity
2 Nasal endoscopy in MedicCity
3 Rhinoscopy in MedicCity
Symptoms of sinusitis
There are acute and chronic forms of sinusitis, which differ in their symptoms.
Acute sinusitis. Symptoms:
- Runny nose lasting more than 7-10 days, without signs of improvement;
- nasal congestion, mucous or purulent discharge from the nose;
- mucus running down the back of the throat, copious discharge of purulent sputum in the morning;
- headache, heaviness and pain in the inflamed sinus area. Sometimes pain in the teeth, eyes, cheekbones, cheeks;
- increased sensitivity of the facial skin in the projection of the affected sinus;
- increase in body temperature (up to 38°C and above). As a rule, this symptom is observed in an acute case. In a chronic process, body temperature rarely rises or remains at subfebrile levels (37-37.50°C);
- weakness, fatigue, irritability. Photophobia, lacrimation, loss of appetite, sleep disturbance;
- weakened or absent sense of smell;
- swelling of the cheeks and eyelids.
Chronic sinusitis. Symptoms:
Symptoms of chronic sinusitis depend on the form of the disease. Outside of an exacerbation, symptoms may be very mild or absent. The most common symptoms of concern are:
- nasal congestion, difficulty in nasal breathing;
- scant mucous or purulent discharge from the nose, may be in the form of drying crusts;
- constant leakage from the nose, causing cracks and abrasions at the entrance to the nose;
- mucus running down the back of the throat;
- dry throat;
- headache;
- bad breath.
As the disease worsens, symptoms characteristic of acute sinusitis may appear.
Physiotherapy
Drug treatment is usually accompanied by physiotherapy:
- Magnetotherapy. The procedure speeds up the healing process, quickly relieves swelling, improves the restoration of affected tissues, and accelerates the outflow of mucus from the sinuses.
- UHF heating. Ultra-high frequencies affect the source of inflammation, have an anti-inflammatory effect, and help improve the outflow of mucus.
- Balneotherapy. Hydrotherapy relaxes, reduces anxiety, strengthens the body's defenses, and helps speed up recovery.
Such procedures are effective in both acute and chronic forms. In the acute form of sinusitis, physiotherapy helps to quickly relieve inflammation; in the chronic form, it helps restore damaged tissue and suppress possible foci of inflammation.
Sinusitis in children
Sometimes sinusitis in children is more difficult to see than sinusitis in adults. The disease usually develops after an infection: influenza or sore throat, and is often accompanied by otitis media. The symptoms are somewhat blurred and appear weaker than in adults. Here are the main ones:
- purulent or mucous discharge from the nose;
- general weakness, malaise;
- pungent odor from the mouth.
With sinusitis in children, one side of the face is often inflamed. While sinusitis in adults is often accompanied by headaches, headaches in children are extremely rare.
Forecast
The prognosis is good in most cases. If the patient strictly follows all medical recommendations and begins treatment in a timely manner, then allergic sinusitis goes away completely. When complications have already begun to develop, the prognosis changes to serious or even poor in severe cases. A person’s condition is especially serious if complications affecting the brain arise or sepsis develops. In such a situation, it is not always possible to save the patient, even in modern medicine.
Types of sinusitis
There are several types of sinusitis:
- sinusitis;
- frontal sinusitis;
- ethmoiditis;
- sphenoiditis, but the latter type of sinusitis is extremely rare and almost always together with ethmoiditis.
1 Examination of the nasal cavity in MedicCity
2 Examination of the nasal cavity in MedicCity
3 ENT unit Atmos S 31
Sinusitis
Sinusitis is one of the most common types of sinusitis. This disease is accompanied by inflammation in the maxillary and maxillary cavities. During inflammation, swelling of the mucous membrane occurs, which blocks the opening from the sinus to the nasal cavity. Mucus begins to accumulate in the sinus space, pathogenic bacteria multiply, and pus appears. Inside the cavity, pressure occurs on the vessels, and the person begins to feel pressing pain at the site of accumulation of pus.
Chronic sinusitis is the result of a long inflammatory process, when a person has had sinusitis for more than 2 months. The patient develops general weakness, nasal discharge has an unpleasant odor, the sense of smell is impaired, and a night cough appears. Chronic sinusitis is characterized by inflammation of only one sinus, right or left. Pressure in the sinus can cause a deviated nasal septum.
Symptoms of sinusitis
The following symptoms are characteristic of sinusitis:
- increased body temperature;
- copious discharge, nasal congestion;
- disturbances of smell;
- weakness;
- headache radiating to the forehead, bridge of the nose, teeth;
- pain that intensifies when tilting the head and pressing on the sinus;
- constant, intense pain;
- a feeling of fullness in the forehead and cheeks, aggravated by tilting the head, coughing and sneezing;
- photophobia and lacrimation.
Signs of sinusitis
If after a flu or cold the temperature rises again, your health worsens, severe pain appears when tilting your head and when pressing on the sinuses, then you need to urgently consult an otolaryngologist. These could be manifestations of sinusitis! Sinusitis in adults is often advanced, since adults are usually in no hurry to see a doctor.
Treatment of sinusitis
Antibiotics for sinusitis are used only after a complete examination of the patient, based on the characteristics of his body and possible allergic reactions.
Antibiotics are not advisable in case of sinusitis of allergic or fungal origin. For mild sinusitis, inhalations, rinses and immunotherapy are also sufficient.
1 Rhinoscopy in MedicCity
2 Video endoscopy of the nasopharynx in MedicCity
3 ENT office in MedicCity
Prevention
To prevent the development of sinusitis, it is necessary to treat the diseases that cause it and, if possible, eliminate predisposing factors. If inflammation develops, you cannot self-medicate - you must consult a doctor. Only he can prescribe the correct treatment for sinusitis. Strict implementation of these recommendations will help you recover quickly and prevent complications13.
Up to contents
“The information in this article is for reference only and does not replace professional advice from a doctor. To make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment, consult a qualified specialist."
Literature
- Ryazantsev S.V., Fanta I.V., Pavlova S.S. Pathogenetic therapy of rhinosinusitis in the practice of an otolaryngologist. Medical advice. 2019; 6: 68-73. DOI: https://doi.org/10.21518/2079-701X-2019-6-68-73
- Boykova N. E., Rybalkin S. V. Acute rhinosinusitis. The role of topical therapy // Medical Council / No. 06. – 2021. – pp. 18-21.
- Ryazantsev S.V., Karneeva O.V., Garashchenko T.I. Acute sinusitis // Clinical recommendations of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation - 2021.
- Shakhova E. G. Sinusitis: clinical picture, diagnosis, drug treatment // Bulletin of VolSMU / No. 4 (20). – 2006. – P. 78-84. — UDC 616.216–07–085.
- Derbeneva M. L., Guseva A. L. Acute rhinosinusitis: diagnosis and treatment. Consilium Medicum. 2018; 20 (3): 58–60. DOI: 10.26442/2075-1753_20.3.58-60
- Kryukov A. I., Turovsky A. B., Kolbanova I. G., Luchsheva Yu. V., Musaev K. M., Karasov A. B. The problem of treating sinusitis against the background of allergic rhinitis. Medical advice. 2019; 8: 110-114. DOI: https://doi.org/10.21518/2079-701X-2019-8-110-114.
- Shilenkova V.V. Therapy of rhinosinusitis: present and future // Medical Council / No. 16. – 2021. – P. 96-100.
- Svistushkin V.M., Nikiforova G.N., Shevchik E.A. et al. Possibilities of pathogenetic therapy for patients with inflammatory diseases of the paranasal sinuses. Consilium Medicum. 2019; 21 (11): 57–62. DOI: 10.26442/20751753.2019.11.190648
- Turovsky A. B., Kolbanova I. G., Kudryavtseva Yu. S. Evidence-based approach to the treatment of acute sinusitis. Consilium Medicum. 2018; 20 (3): 85–89. DOI: 10.26442/2075-1753_20.3.85-89.
- Instructions for use of the drug TIZIN® Classic // Registration number P N014038/01 // GRLS of the Russian Federation. – URL: https://grls.rosminzdrav.ru/Grls_View_v2.aspx?routingGuid=93fbeb97-51eb-4e1b-bd2a-82dbeb93d3d7&t= (access date: 06/25/2008).
- Instructions for use of the drug TIZIN® Expert // Registration number LSR-009878/09 // GRLS of the Russian Federation. – URL: https://grls.rosminzdrav.ru/Grls_View_v2.aspx?routingGuid=08fa133c-a9ca-45d7-b5de-2cd76bf825c0&t= (access date: 12/04/2009).
- Instructions for use of the drug TIZIN® Alergy // Registration number P N014198/02 // GRLS of the Russian Federation. – URL: https://grls.rosminzdrav.ru/Grls_View_v2.aspx?routingGuid=aa7246a7-e710-413d-9155-6c7a9b4e9491&t= (date of access: 07/07/2010).
- Official website of the drug
- Topical decongestants in the complex therapy of acute respiratory infections in children, A. B. Malakhov et al. Medical Council No. 14, 2015
Up to contents
Frontit
Frontal sinusitis (frontal sinusitis) is an inflammatory disease of the frontal paranasal sinus. This type of sinusitis is the most severe. There are forms of acute and chronic frontal sinusitis.
Symptoms of sinusitis
Acute frontal sinusitis, symptoms:
- pain and swelling around the nose and eyes;
- increased pain when tapping in the projection area of the inflamed sinuses;
- heavy breathing due to inflammation of the nasal passages;
- runny nose with thick yellow or green mucus;
- increase in body temperature to 38-39 degrees;
- severe headache (minor relief occurs when lying down);
- pain radiating to the ears and teeth;
- fear of light;
- severe weakness;
- sometimes sore throat, difficulty identifying odors, decreased pungency of taste.
Chronic frontal sinusitis, symptoms:
- aching headache;
- purulent, unpleasant-smelling nasal discharge in the morning;
- slight increase in temperature;
- difficulty breathing through the nose;
- sputum discharge in the morning.
Causes of frontal sinusitis
The following reasons for the development of frontal sinusitis are distinguished:
- viral, bacterial or fungal infection;
- complication after influenza, ARVI, etc.;
- getting foreign objects into the nose;
- long-term infectious or allergic rhinitis (rhinitis);
- deviated nasal septum;
- adenoids;
- allergy;
- nasal polyps.
Treatment of frontal sinusitis
How to treat frontal sinusitis? Definitely under the supervision of an otolaryngologist! The disease is not only difficult for many patients to tolerate, but also has dangerous complications, including orbital abscess, meningitis, sepsis, etc.
Treatment of sinusitis is aimed at eliminating infection in the sinuses and stopping inflammation. Medicines will help relieve swelling, improve ventilation of the sinuses and lead to the discharge of contents from them. If the disease is viral in nature, then antibiotics for frontal sinusitis are mandatory!
The following antibiotics are used to treat sinusitis:
- penicillin antibiotics (semi-synthetic or synthetic amoxicillin preparations);
- cephalosporin antibiotics;
- macrolide antibiotics (they do not affect the intestinal microflora);
- local antibiotics in the form of nasal drops, nasal spray, aerosol;
- homeopathic medicines;
- symptomatic remedies for frontal sinusitis in the form of vasoconstrictor nasal drops, antipyretics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
In case of severe frontal sinusitis and insufficient effectiveness of conservative treatment, sinus lavage using the method of displacement and puncture is prescribed.
1 Rhinoscopy in MedicCity
2 Consultation with an ENT specialist in MedicCity
3 ENT consultation in MedicCity
Prevention of frontal sinusitis
To prevent frontal sinusitis, you need to monitor the state of your immune system, promptly eliminate foci of inflammation in the ENT organs, harden your body, and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Causes of damage to the mucous membrane
It is not so difficult to damage the mucous membrane. The most common cause of damage is the uncontrolled use of nasal drops, which dry out the surface due to their vasoconstrictor effect. Dry and thinned mucous membranes cannot restore healthy microflora, thereby becoming defenseless against attack by viruses and bacteria.
Other factors also influence the condition of the mucous membrane:
- inhalation of polluted air;
- foreign bodies entering the nasal cavity;
- taking drugs;
- inhalation of hot steam;
- chronic diseases of internal organs;
- deformation of the nasal septum;
- temporary damage after surgery.
In the winter and autumn seasons, when there are outbreaks of acute respiratory diseases, the likelihood of getting something more serious than a runny nose is quite high. The same can be said about the swimming season: the water of natural reservoirs is not always safe and can cause inflammation.
Ethmoiditis
Ethmoiditis is an acute or chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane of the cells of the ethmoid labyrinth (anatomical labyrinth in the bridge of the nose). Ethmoiditis is bacterial or viral in nature.
There are acute and chronic ethmoiditis. Acute ethmoiditis accompanies influenza, rhinitis and is complemented by inflammation of the paranasal sinuses.
Ethmoiditis in adults affects both the frontal and maxillary cavities. With weak immunity, the acute form of ethmoiditis turns into long-term chronic ethmoiditis with periods of exacerbation and remission.
Polypous ethmoiditis is characterized by the appearance of polyps in the mucous membrane of the ethmoid labyrinth of the forehead. Polypous ethmoiditis may appear after chronic, allergic rhinitis.
Catarrhal ethmoiditis occurs due to the activity of viruses. It is characterized by increased lacrimation, weakness, nausea, dizziness, swelling in the bridge of the nose, and fever.
Ethmoiditis in children is a very serious disease. The infection spreads very quickly due to the anatomical structure of the ethmoid labyrinth. The development of ethmoiditis in children requires urgent hospitalization.
Symptoms of ethmoiditis
Acute catarrhal ethmoiditis. Symptoms
- pain in the bridge of the nose and at the wings of the nose;
- heavy breathing through the nose;
- loss of smell;
- headache, weakness;
- profuse nasal discharge, which gradually becomes purulent;
- temperature rises to 38 degrees;
- In children, the inner corner of the eye socket also swells and turns red.
In the acute form, primary and secondary ethmoiditis are distinguished.
With primary ethmoiditis, anxiety, vomiting, dyspepsia and toxicosis appear, the temperature is 39-40 degrees.
Secondary ethmoiditis is more severe and develops faster. The patient is in extremely serious condition with pronounced septic symptoms. The eyelids become swollen and cyanotic, swelling of the conjunctiva and noticeable protrusion of the eyeball are observed, and nasal breathing becomes difficult.
Chronic ethmoiditis. Symptoms
- headaches that are difficult to register by localization;
- weakness, rapid fatigue of the patient;
- soreness in the bridge of the nose when pressed and painful points at the wings of the nose;
- purulent discharge with a nauseating odor;
- extensive mucus in the nasopharynx, which is difficult to spit out;
- emerging polyps.
Complications after ethmoiditis:
- meningitis;
- encephalitis,
- intraocular and intracranial pressure;
- destruction of the ethmoid bone.
Treatment of ethmoiditis
Treatment of ethmoiditis in acute form is predominantly conservative. It is necessary to ensure the outflow of mucus with the help of vasoconstrictors and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Treatment of ethmoiditis in chronic form is predominantly surgical.
1 MRI in MedicCity
2 Laboratory diagnostics in MedicCity
3 Ultrasound examination of the paranasal sinuses in MedicCity
Diagnosis of sinusitis using modern techniques
To confirm the diagnosis of sinusitis, the following types of examination are used:
- Video endoscopy of the nasal cavity and nasopharynx to identify features of the anatomical structure and determine predisposing factors for the development of sinusitis;
- radiography of the paranasal sinuses;
- Ultrasound examination of the paranasal sinuses is a safe method with no contraindications, used to diagnose sinusitis and monitor the treatment process;
- CT, MRI - according to indications;
- laboratory diagnostics according to indications in full.
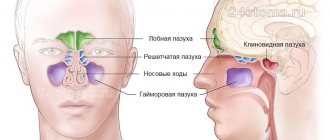
Anatomy of the nose
The outer part of the nose consists of a pair of bones. The lower part - the tip and wings - is formed by cartilage. Each half (what we call the nostrils) consists of three parts: the lower, middle and upper passage. The passages are responsible for the circulation of inhaled and exhaled air. The sinuses, also known as the paranasal sinuses, are located in the cranial bones, behind the nose.
The inside of the nose cleans and warms the incoming air. This is a mucous membrane covered with a huge number of cilia. Cilia retain contaminants drawn in from the external environment, and mucosal glands purify the air from pathogens. Therefore, when talking about nasal health, we first of all talk about the integrity and health of the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity.
Treatment of sinusitis at MedicCity
Conservative methods of treating sinusitis
If you are concerned about how to treat sinusitis in Moscow, be sure to contact the MedicCity specialists! Our clinic provides treatment for sinusitis without puncture and without pain. However, non-surgical treatment of sinusitis is possible only at the initial stage. Don't waste time!
In the vast majority of cases, treatment of sinusitis in our clinic is carried out without a puncture.
- Using YAMIK (sinus catheter). The YAMIK method is the use of a device called the “YAMIK sinus catheter.” Using the YAMIK sinus catheter, controlled pressure is created in the nasal cavity and the purulent contents of the sinus are pumped out through the natural anastomosis (openings), and then a medicinal substance (antibiotics, mucolytics) is administered.
- Rinsing the nose and paranasal sinuses using the moving method (“cuckoo”). It is carried out using a special suction - an aspirator; in the process, pathological contents are removed from the nasal cavity and sinuses and the drug is injected into the sinuses.
- Inhalation therapy using a special inhaler PARI SINUS. This method is based on the introduction of microparticles of the drug into the affected paranasal sinuses through a pulsating supply of an aerosol. In this case, the aerosol of the medicinal substance is deposited in the sinuses and has an effect directly at the site of inflammation.
All proposed methods for treating sinusitis are painless and effective.
When using combined treatment, complete recovery in case of acute sinusitis is achieved within 7-10 days.
If puncture treatment is necessary, it is possible to install special catheters in the sinus, which eliminate the need for repeated punctures.
Possibility of complications
If you self-medicate, do not follow the doctor’s recommendations, or start treatment late, complications cannot be avoided.4 These include:
● Attachment of a bacterial infection.
● Otitis media is a purulent inflammation of the middle ear that connects to the back of the nose.
● Meningitis is a purulent inflammation of the meninges.
● Worsening of asthma symptoms. Sepsis is a systemic inflammatory reaction in response to the generalization of a local infectious process.