Types of psychoses and their significance in modern diagnostics
In modern psychiatry, psychosis is considered as a pathology that is accompanied by a mental disorder and mental disorder. The patient experiences deformation of the real environment, thinking is distorted, and mental activity is disrupted. If we compare diseases such as psychosis and neurosis, they are radically different from each other.
With psychosis, profound changes occur in a person’s mental activity and personality; this is a severe form of damage to the nervous system when compared with neurosis, which is considered a milder degree of the disease. Both a psychologist and a psychotherapist can help in the treatment of neuroses, but psychosis is usually treated by psychiatrists.
The reasons contributing to the emergence and development of psychosis can be both external and internal. External factors:
- stressful conditions;
- moral injuries;
- diseases of infectious nature;
- alcohol and drug abuse;
- uncontrolled use of medications;
- intoxication with industrial and other harmful substances.
Psychosis is a very complex condition; it can be triggered by an external factor, and then internal problems contribute to its aggravation. When the origin of a mental disorder is associated with an internal state, endogenous psychosis occurs. Usually its formation is associated with disorders in the nervous and endocrine systems.
Depending on the origin, the following classification of psychoses is accepted:
- situational - occurs as a result of a traumatic factor;
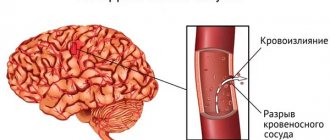
- organic - develops as a complication after tumors in the brain, infections, heart attack and other diseases. Traumatic psychosis is diagnosed when the head is injured, and epilepsy can sometimes be observed.
- reactive psychosis is the result of severe psychological trauma, is temporary and responds well to treatment;
- withdrawal symptoms (alcohol psychosis) are typical for alcoholics or patients after stopping their usual medications. Acute psychosis in alcoholism can be the result of prolonged binge drinking and be accompanied by hallucinations and various mental disorders;
- intoxication as a result of poisoning with chemical, narcotic or medicinal substances;
- Somatogenic psychosis manifests itself in pathologies in the functioning of internal organs and systems; it is a unique human reaction to illness in the form of fear and anxiety.
According to the clinical picture, psychotic disorders are divided into:
- hysterical psychosis, the symptoms of which are expressed in increased excitability of the patient;
- hypochondriacal psychosis - in such cases the patient has a fear of a non-existent fatal disease;
- paranoid psychosis, in which the sick person’s environment suffers, he develops delusional thoughts, feelings of hatred and aggression towards loved ones;
- depressive psychosis, when the patient experiences a feeling of depression and indifference;
- manic psychosis, in which the sick person has some kind of goal and is obsessed with it;
- manic-depressive psychosis, or circular, which is characterized by alternating manic and depressive phases;
- combined psychosis is a combination of several psychotic disorders at the same time.
Another type of psychosis - postpartum - is quite rare. Unlike postpartum depression, a woman develops severe mental disorders aimed at causing bodily and other harm to herself and the child.
Manifestations of psychosis are very diverse. Risk factors for the disease include:
- age;
- floor;
- living in large cities;
- social conditions;
- psychophysiological constitution.
Psychosis can occur at different periods of life. At a young age, manic-depressive psychosis is possible when life-changing changes occur; at a more mature age - senile psychosis. Alcoholic and traumatic psychosis are more common in men. People living in urban areas are more susceptible to stress and various types of psychoses and neuroses. Often mental disorders accompany people who have failed to express themselves in society. Temperament and psychophysiological constitution also influence the tendency to psychosis.
Each case of psychosis is very individual, so an experienced psychiatrist must diagnose the pathology, considering the clinical picture and dynamics of the disease. Diagnosis at the initial stages of the disease greatly facilitates treatment and improves the prognosis.
Signs of a depressive phase
Bipolar disorder begins in most patients without noticeable bright manifestations.
In a typical case of MDP, there are subtle fluctuations in the background mood with cycles of several days or weeks. Researchers of the problem emphasize that the unfavorable course of bipolar disorder is the onset of the disorder from the first depressive episode. During the depressive phase, 89% of suicides or suicide attempts occur. Depression occurs when high productivity of mental processes is abruptly replaced by its decline. Specific manifestations of the phase:
- severely depressed mood;
- slowing down the thought process;
- slower speech motor activity;
- decreased or complete absence of appetite, perverted taste sensitivity;
- weight loss;
- prostration;
- in women - problems with menstruation;
- mothers have problems with maternal instinct;
- lack of sexual desires;
- melancholy, which is felt physically as heaviness in the chest area;
- attacks of tachycardia, constipation, mydriasis (dilated pupils of the eyes);
- self-flagellation, guilt;
- increased anxiety;
- cognitive impairment.
Depression sometimes takes on an endogenous form - due to the biological nature of the disorder, not only mental, but also somatic and endocrine disorders occur.
Sometimes an “atypical” course of depression develops—increased appetite, hypersomnia. There is also a hypochondriacal type of disorder - in this case, obsessive hypochondriacal beliefs with an affective overtone are noted. With the delusional type of progression, “Cotard's syndrome” is present - in addition to anxiety, delusional beliefs of a fantastic nature are observed. With agitation depression there is noticeable nervous overexcitation. With the asthenic variant, the patient experiences a loss of the ability to feel anything.
Patients experience unmotivated sadness and a feeling of hopelessness especially acutely - from several hours to several days without the ability to be distracted by anything else. The person withdraws into himself and stops contacting family members and friends. Interest in those activities and things that previously had interests is completely lost. Low ability to learn new things. Appetite may be uncontrollable or absent.
Fatigue and lack of energy are felt around the clock. Sleep is interrupted, and episodes of awakening occur frequently, especially in the early morning. After sleep, a person does not feel rested. Memory problems arise and concentration is poor. Thoughts about suicide appear - a person experiences a clear conviction that life has no meaning and will never bring pleasure. With parasuicidal behavior, a syndrome of “tunnel thinking” is observed.
The depressive phase is very dangerous due to the high level of suicidal tendencies, parasuicides, and auto-aggressive acts. It is recommended to hospitalize the person for subsequent treatment in a hospital setting. 24-hour monitoring of the patient’s condition and indicators is important.
Find out if psychosis can be treated abroad
Doctors from leading clinics abroad successfully treat many diseases related to the human psyche. In addition to drug therapy and psychotherapeutic treatment of psychosis abroad, physiotherapeutic methods are also widely used: electrosleep, acupuncture, sports activities, etc. In the social rehabilitation of a patient diagnosed with psychosis, as well as in the treatment of addiction, one of the main directions is work in mutual support groups.
If drug resistance is observed, then in foreign specialized centers they practice transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and treatment with low-frequency currents.
Treatment of psychosis without antipsychotics in Israel: what is important to know?
The secret to effective treatment of psychosis in Israel is unique advanced techniques and a personal approach. Qualified assistance can be obtained in public medical institutions, as well as in private clinics. For example, the Renaissance rehabilitation center deals not only with the treatment of drug addiction in Israel, alcoholism, and various types of addictions, but also with the treatment of psychiatric pathologies that are treated comprehensively. This means that specialists from many areas take part in the elimination of psychosis, who collaborate with each other, and also use the latest generation of medications and effective psychotherapy programs.
In addition to basic treatment, patients receive recommendations from the attending doctor to attend classes in art therapy, hydrotherapy, and yoga.
Taking into account the course of the disease and the patient’s personality traits, therapy programs are developed individually for each person and allow one to achieve good results in a short time.
The importance of psychotherapeutic methods for treating psychosis in the Renaissance drug treatment clinic can hardly be overestimated, because they are an integral element of complex therapy and, when used correctly, successfully replace drug intervention.
Diagnosis of acute polymorphic psychotic disorder
When making a diagnosis of acute psychotic disorder, it is necessary to exclude other mental illnesses: schizophrenia, schizoaffective psychosis, or bipolar disorder. It is necessary to make sure that there are no organic lesions and the influence of various toxic substances on the body. To do this, it is necessary to conduct a thorough examination, which only a competent specialist can handle.
For differential diagnosis of acute psychotic disorder with schizophrenia, there are modern methods - Neurotest and Neurophysiological test system.
The following methods are used:
- functional and laboratory tests of the body - blood test, EEG; the influence of drugs, alcohol and organic lesions is excluded;
- psychiatric examination with analysis of anamnestic data and consultation with a clinical psychologist;
- Neurotest and Neurophysiological test system allow you to confirm a schizophrenia spectrum disease, assess the depth of the defect and the severity of the condition.
What anti-psychosis pills are used for treatment in Moscow
Treatment with medications, mainly antipsychotics, is considered one of the most effective ways to eliminate psychosis. In recent years, many medications have been developed that selectively act on the corresponding types of psychoses - they are successfully used in Moscow clinics. If psychosis is a consequence of intoxication, then, just as in the treatment of alcoholism, medications are used to cleanse the body.
Usually, in case of severe agitation, the doctor prescribes the neuroleptics triftazine and chlorpromazine. If the patient is in a delirious state, then stelazine and haloperidol help him. When drug treatment, the age, condition of the patient and the stage of the disease must be taken into account.
Positive results from taking medications are reinforced by a psychotherapeutic course of treatment. In addition, great importance is given to the social adaptation of patients with psychosis, as well as the rehabilitation of drug addicts after undergoing therapy sessions.
It is imperative to take into account that treating psychosis at home or with the help of alternative medicine is unacceptable and very dangerous. The patient should receive qualified medical care only in specialized medical institutions that effectively treat this disease and prevent its transition to a chronic condition.
Acute polymorphic psychotic disorder without symptoms of schizophrenia
This variant of the development of the disease is also called acute delusional disorder and is characterized by rapid and repeated changes in the content of hallucinations, delusions and affective disorders.
A person experiences suddenly alternating outbreaks of delusions of persecution, ideas of his own greatness, or confidence in his guilt and the presence of a serious illness. The content and type of accompanying hallucinations varies from day to day or more frequently. In the emotional sphere, constant changes are also observed: hypertrophied elation after a few hours is replaced by a strong decline and vice versa.
Symptoms in acute polymorphic disorder change constantly, sometimes every few hours.
There may be acceleration or deceleration of thinking, physical retardation or motor agitation. The person is confused, anxious, inattentive.
Thus, the main distinguishing features of acute polymorphic psychotic disorder without symptoms of schizophrenia are:
- Constant changes in the nature and intensity of psychotic (delusions and hallucinations) and affective manifestations (mood).
- Sudden onset and rapid development of symptoms.
- Failure to meet diagnostic criteria for other psychotic disorders.
Where to get effective treatment for psychosis in St. Petersburg
There are a number of medical centers in St. Petersburg that treat drug addiction, alcoholism, various addictions and mental disorders. Many clinics effectively treat pathologies such as psychosis.
Among them:
- medical;
- AndroMeda clinic.
But, unfortunately, based on the specifics of a psychotic disorder, even despite confidentiality, it is not always easy for many patients to contact a psychiatrist, so many of them prefer treatment abroad and very often choose Israel.
Consequences
Possible consequences of psychotic complications:
- more severe, rapidly progressing dependence syndrome;
- periods of remission become shorter;
- increased organic damage to the brain, which is manifested by chronic encephalopathy;
- reduction of professional and labor qualifications;
- committing antisocial acts;
- aggression and violent actions towards loved ones and others;
- persistent memory impairment;
- the patient receives injuries, often incompatible with life;
- loss of family;
- personality degradation with a decrease in cognitive and thinking abilities;
- isolation from society;
- inability to self-service;
- causing road traffic accidents and industrial emergencies;
- exacerbation of other chronic diseases;
- death.
Metal-alcohol psychoses can be isolated, repeated, or not occur at all, even with continued abuse. The course of each clinical case is individual, so the prognosis depends on the individual patient.
Read reviews about psychosis treatment
“My father was treated for psychosis in one of the clinics in St. Petersburg. He had symptoms such as hallucinations and persecutory delusions. After a two-month course of treatment, he was discharged. His condition, of course, improved, but he was under constant medical supervision, and he became somewhat indifferent to everything. We were very worried about him, we were afraid of a relapse, because no one gave us guarantees. I heard that in Israel they treat such pathologies in a new way, so we decided to try treatment in Israel, we are happy with the choice, now everything is fine with it.”
Grigory Kurchenko, Kronstadt
“We treated our grandmother for senile psychosis at the Renaissance Center in Moscow. We went there because we know that excellent specialists work there. My grandmother was in the acute phase of her illness; she did not recognize any of us: neither our children nor our grandchildren; she became very suspicious and demanded constant attention from everyone. The clinic diagnosed her with senile psychosis. Thanks to the fact that we sought psychiatric help in time, we were able to help her.”
Tatyana Vedeneeva, Balashikha
Questions and answers
What should you do if a loved one has signs of a disorder, but does not want to undergo treatment?
You need to talk to him about this, try to understand and support him. The main thing is to identify how much the violation affects his work, personal relationships and life in society. If these parties suffer greatly as a result of the disease, then consultation with a psychiatrist and subsequent implementation of his recommendations are required.
Can the disorder be cured with medications alone?
Treatment must be prescribed by a doctor, and he takes into account many aspects and characteristics of each patient’s body. In some cases, for mild forms of disorders, only psychotherapy can be used. For moderate disorders, combined treatment with the use of medications. Severe types of illness require the use of drugs to normalize the condition, and psychotherapy acts as an additional method for the rehabilitation and resocialization of the patient.