Author:
- Strigunov Andrey Alekseevich doctor – urologist
4.64 (Votes: 14)
- What should be used for differential diagnosis?
- Drug treatment
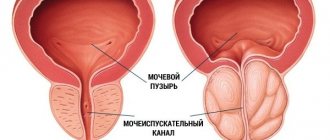
Prostate adenoma (currently the term “prostatic hyperplasia” is used) is an enlargement of the prostate due to the proliferation of predominantly cells from its transition zone.
This disease is most common in older men. Men over 50 years of age are at risk. And with age, the number of patients with this problem only increases. By the age of 80, almost 90% of men have symptoms of this disease.
What causes prostate hyperplasia?
Until now, the exact causes of this disease are not known. There is no clear relationship between the occurrence of prostate adenoma and excessively high or low sexual activity, alcohol abuse and smoking. The main role is played by imbalance in the levels of androgens and estrogens.
With age, against the background of hormonal imbalance, paraurethral glands grow in the central zone of the prostate. Histologically (under a microscope), the number of not only the glands themselves, but also the connective tissue may increase, so histologists distinguish glandular, stromal and glandular-stromal forms of prostate adenoma. Macroscopically, a nodule (or many nodules) forms in the prostate gland, which grows and gradually deforms not only the prostate gland itself, but also compresses the urethra. At the same time, the middle and lateral lobes are formed in the prostate depending on the number of nodes and their direction of growth. Therefore, the main symptom of the disease is primarily a deterioration in the quality of urination. Prostate hyperplasia itself is a benign process. It does not metastasize or grow into other organs, like prostate cancer. However, one way or another, the risk of the cells inside it degenerating into malignant ones exists. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor PSA levels and be sure to undergo regular examinations with a urologist.
Ceftriaxone
The antibiotic "Ceftriaxone" is prescribed for bacterial and chronic prostatitis. The drug quickly relieves inflammation and pain, reduces swelling of the gland, and normalizes urination. Ceftriaxone has the shortest course of treatment among all the antibiotics presented above (5-10 days). To improve the therapeutic effect of the drug, urologists recommend administering Ceftriaxone every day at the same time. The drug is affordable and begins to act quickly. Ceftriaxone is also prescribed to patients after operations to reduce the risk of infections.
Ceftriaxone
What is the clinical picture?
All symptoms of this disease are usually called lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and are divided into storage symptoms and emptying symptoms.
Symptoms of accumulation:
- Urgent (urgent) urge to urinate;
- Frequent urination at night (nocturia);
- Frequent urination during the day (polyuria);
Symptoms of bowel movement:
- Sluggish stream of urine;
- Delay in starting urination;
- The need to tense the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall to begin urination;
- Intermittent urination (“urination in several passes”);
- Feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
Obstruction of the normal flow of urine leads to overstrain of the bladder muscle, which is involved in the expulsion of urine (detrusor). This leads first to its hypertrophy (thickening of the muscle layer), then, when its capabilities “exhaust,” the bladder ceases to adequately expel urine and over time its wall can become thin, like “papyrus paper.”
According to the type of growth, they are distinguished:
- Intravesical form (the tumor grows towards the bladder).
- Retrotrigonal form in which the tumor is located under the triangle of the bladder.
- Subvesical form (the tumor grows towards the rectum).
The type of growth of the adenoma, and not its size, has a major role in the severity of this or that symptomatology. Also, in the presence of an adenoma and its practically asymptomatic course, errors in diet (abuse of spicy foods and alcohol), hypothermia or excessive overheating can provoke a sharp deterioration in symptoms, up to acute urinary retention.
What stages of the disease are distinguished for prostate adenoma?
First stage
Unfortunately, only a small percentage of men consult a urologist at the initial stage of the disease. A sluggish stream during urination, especially in the morning, frequent trips to the toilet at night - men perceive this as a natural process of aging and try to “live with it.” Thanks to the great compensatory capabilities of the detrusor (the muscle that is involved in expelling urine from the bladder), the bladder is almost completely emptied. Kidney function is usually not affected.
Second stage
When compensatory capabilities are exhausted, the bladder stops emptying fully. Its wall becomes hypertrophied (thickened), and the formation of diverticula (“bladder hernia”) is possible.
In this case, men experience incomplete emptying of the bladder. The frequency of trips to the toilet increases during the daytime. Often in the morning, patients have to urinate in 2-3 doses. The stream of urine becomes vertical, interrupted by drops, the patient is forced to push, which can lead to the formation of a hernia or prolapse of the rectum. With hypertrophy of the bladder wall, rough folding is formed, which prevents the flow of urine from the upper urinary tract, causing it to stagnate in the ureters and kidneys. Gradually, thinning and atony of the detrusor muscle fibers occurs. The part of the bladder wall free from muscle fibers stretches, forming bags - false diverticula of the bladder. Residual urine is 100-200 ml, and sometimes up to a liter or more. Signs of renal dysfunction develop: dry mouth, increased thirst, etc.
Third stage
The amount of residual urine will increase significantly. The bladder expands greatly. The patient complains of intermittent urination, often in extremely small portions. Severe thickening of the bladder wall deforms the orifices of the ureters, thereby disrupting the adequate outflow of urine from the kidneys. Also, a large volume of residual urine contributes to the development of a focus of chronic infection.
At this stage, there is an extremely high risk of developing acute urinary retention, which requires immediate qualified medical care. After all, the impaired outflow of urine from the body poisons it and can lead to the death of the patient.
Cefotaxime
Cefotaxime is an inexpensive broad-spectrum antibiotic that is prescribed for different stages of prostatitis. The drug is injected intramuscularly or intravenously. The concentration of the drug remains in the body for about 12 hours. Among the contraindications is the simultaneous use of Cefotaxime with vitamin K, because bleeding is possible. Usually the drug is administered twice a day with an interval of 12 hours (no more than 12 g of the drug per day).
Cefotaxime
CJSC FF "Lekko", Russia; MJ Biopharm, India; Sintez OJSC, Russia; Belmedpreparaty, Belarus; Deco, Russia; OJSC Borisov Plant of Medical Preparations (Borimed), Belarus; Kraspharma, Russia; PJSC "Biokhimik", Russia; Protek-SVM, Russia
Antibiotic, third generation cephalosporin.
Used for: Severe infectious and inflammatory diseases caused by microorganisms sensitive to cefotaxime, incl. peritonitis, sepsis, abdominal and pelvic infections, infections of the lower respiratory tract, urinary tract, infections of bones and joints, skin and soft tissues, infected wounds and burns, gonorrhea, meningitis, Lyme disease. Prevention of infections after surgery. from 19
5.0 1 review
621
- Like
- Write a review
Possible complications
Self-medication, ignoring early symptoms of the disease, and neglecting doctor’s recommendations lead not only to a deterioration in the quality of life, but can also significantly affect the functions of many body systems.
- Acute urinary retention is possible in stages I and II of the disease. Most often, it is provoked by “overaccumulation” of urine in the bladder (when it is no longer able to contract adequately), excessive hypothermia or overheating, and errors in diet (alcohol, spicy foods).
- Bladder diverticula, hydronephrosis (expansion of the renal pyelocaliceal system, which leads to the progression of renal failure).
- Hematuria (blood in the urine) is caused by damage to varicose veins in the bladder neck (occurs in 20-30% of patients).
- Bladder stones are formed as a result of a constant large amount of residual urine.
Treatment of prostatitis
Treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. In rare cases, patients may be required to be hospitalized if a purulent process is suspected.
Treatment of prostatitis in men is usually carried out using drug therapy, which includes the use of:
- Antibacterial drugs to eliminate infection;
- Anti-inflammatory drugs to eliminate symptoms of the disease;
- Painkillers to relieve pain symptoms;
- Drugs to improve blood supply to the pelvic organs.
Additionally, the urologist can refer the patient to other specialists. This will completely restore men's health.
How to diagnose?
Conversation with the patient, including filling out special questionnaires:
- IPSS (International Prostatic SymptomScore - International Prostatic Symptom Score);
- QoL – assessment of quality of life;
- IIEF 5 – International Index of Erectile Function;
- Digital rectal examination: in patients with prostatic hyperplasia, it is usually enlarged, with a smoothed longitudinal groove, elastic or dense elastic consistency, painless;
- PSA blood test for early diagnosis of prostate cancer;
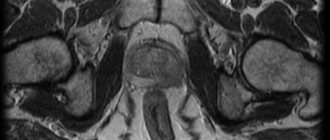
- Transrectal ultrasound examination (TRUS) of the prostate allows one to assess the size, volume of the gland, and the presence of “suspicious” foci;
- Ultrasound of the bladder allows you to assess the thickness of the walls, the presence of bladder stones, tumors, and measure the volume of residual urine after urination;
- A general urinalysis and urine culture are necessary to determine the presence of pathogenic microflora in case of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- Uroflowmetry evaluates the rate of urination.
What should be used for differential diagnosis?
First of all, when diagnosing prostate adenoma, it is necessary to exclude prostate cancer. To do this, it is necessary to perform a digital rectal examination, a PSA blood test, and TRUS of the prostate. It is also necessary to exclude prostatitis, urethral stricture, sclerosis of the bladder neck, and overactive bladder. To exclude these diseases, it is sometimes necessary to perform a series of examinations (urethrogram, complex urodynamic study).
Augmentin
Augmentin is suitable for the treatment of the earliest stages of prostatitis, and Augmentin can be purchased in tablets, powder and injections. Moreover, you need to start treatment for prostatitis with injections, and then continue with pills. The active ingredients of Augmentin are amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. This antibiotic is well suited for fighting chronic infections, which is why it is the most popular drug in its category for the treatment of prostate diseases. When treated with Augmentin, urination returns to normal, discomfort in the groin goes away, and pain disappears. If prostatitis is mild, Augmentin is prescribed for two weeks, but taken every 8 hours. If the disease is chronic and severe, there should be more injections every 4-6 hours (the doctor determines the treatment regimen).
Augmentin powder
GlaxoSmithKline, GSK, UK
Augmentin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic.
Has a bactericidal (bacteria-destroying) effect. Active against a wide range of aerobic (developing only in the presence of oxygen) and anaerobic (capable of existing in the absence of oxygen) gram-positive and aerobic gram-negative microorganisms, including strains that produce beta-lactamase (an enzyme that destroys penicillins). Clavulanic acid, which is part of the drug, ensures the resistance of amoxicillin to the effects of beta-lactamases, expanding its spectrum of action. from 29
5.0 1 review
81
- Like
- Write a review
How to treat this disease?
Treatment of prostate adenoma is divided into two large groups - surgical and conservative (with medications).
Regardless of the size of the adenoma, if there are good results (small volume of residual urine, high rate of urination, absence of complaints about urination), long-term drug therapy is possible.
Drug treatment
The main medications prescribed for the treatment of prostate adenoma include:
- Alpha-blockers - by relaxing the muscle component of the prostate and urethra, they reduce symptoms, but do not affect the volume of the prostate. However, these drugs can lower blood pressure and cause retrograde ejaculation (“dry orgasm”).
- 5 alpha-reductase inhibitors - by blocking this enzyme, they prevent the transition of testosterone to its more active form (dehydrotestosterone), which affects the growth of adenoma. This drug is used for prostate volume from 40 to 80 cm3. However, this group of drugs reduces libido (sex drive).
- The most commonly prescribed combination therapy is alpha-blockers + 5 alpha-reductase inhibitors.
- Herbal preparations, most often derivatives of plants from the Palm family. The mechanism of these drugs is similar to the group of 5 alpha-reductase inhibitors.
Surgery
It is carried out when conservative therapy is ineffective or intolerant.
Indications for surgical treatment are:
- Acute or chronic urinary retention;
- Hematuria (blood in the urine);
- Bladder stones;
- Hydronephrotic transformation of the kidneys (with a large amount of residual urine and impaired outflow of urine from the kidneys);
- Large bladder diverticulum;
- Progressive renal failure.
Currently, the gold standard for the treatment of prostate adenoma is endoscopic treatment methods:
- Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) . Unlike endoscopic enucleation, this operation is indicated for prostate volumes up to 80 cm3.
- Transurethral endoscopic enucleation of prostatic hyperplasia . This operation can be performed using thulium, holmium lasers (laser vaporization of prostate adenoma), bipolar electricity. Endoscopic enucleation is possible for any size of the prostate. Simultaneous cystolithotripsy (crushing stones in the bladder) is also possible. The entire period of hospitalization takes on average 3 days.
- For large prostate adenomas, open/laparoscopic adenomectomy . However, these operations, although they have good postoperative results, are inferior to endoscopic methods in the speed of postoperative rehabilitation.
Vilprafen
This antibiotic acts directly on the source of inflammation, is characterized by high bioavailability and a rapid therapeutic effect. The course of treatment is determined by the doctor, but it should not exceed three weeks. In addition to Vilprafen, there are also Vilprafen Solutab tablets, which should be taken orally without drinking water. They are absorbed into the blood through the oral mucosa. This antibiotic is most effective for chlamydial prostatitis - according to patient reviews, after the second dose of the tablet, symptoms decrease. "Vilprafen" helps restore potency, relieves inflammation and pain. The drug is prescribed with caution to patients with chronic renal failure.
Vilprafen
Yamanouchi Europe, Netherlands
Treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases caused by microorganisms sensitive to josamycin: infections of the upper respiratory tract and ENT organs (including pharyngitis, tonsillitis, paratonsillitis, otitis media, sinusitis, laryngitis);
diphtheria (in addition to treatment with diphtheria antitoxin); scarlet fever (with hypersensitivity to penicillin); lower respiratory tract infections (including acute bronchitis, bronchopneumonia, pneumonia, including atypical form, whooping cough, psittacosis); oral infections (including gingivitis and periodontal disease); infections of the skin and soft tissues (including pyoderma, boils, anthrax, erysipelas / with hypersensitivity to penicillin /, acne, lymphangitis, lymphadenitis); infections of the urinary tract and genital organs (including urethritis, prostatitis, gonorrhea; with increased sensitivity to penicillin - syphilis, lymphogranuloma venereum); chlamydial, mycoplasma (including ureaplasma) and mixed infections of the urinary tract and genital organs. from 44
930
- Like
- Write a review