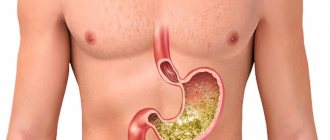
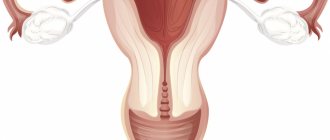
The urethra is a canal in both men and women that is used to remove urine and semen (in men). Discharge from the urethra is physiological in nature, since it involves the natural release of biological fluid. However, there are a number of pathological conditions in which discharge from the canal is not natural and warns of the presence of inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system.
It is quite easy to distinguish the former from the symptoms of the disease: they are not accompanied by unpleasant sensations, do not have bloody or purulent impurities and do not smell. In contrast, an atypical secretion may have various impurities, including blood, have a cheesy consistency, and have an unpleasant smell. They require immediate professional medical help. You can get it at the CELT multidisciplinary clinic: our specialists will make every effort to correctly diagnose and prescribe appropriate treatment. They have everything they need to make it successful: patients only need to contact us in a timely manner to avoid the development of serious complications.
At CELT you can get advice from a gynecologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,000
- Repeated consultation – 2,000
Make an appointment
Discharge from the urethra: types and causes
It is customary to distinguish physiological and pathological discharge from the urethra. Isolation of the former is a natural process and does not require treatment or medical supervision. They are presented in our table below:
| Physiological discharge from the urethra | What is it when it occurs? |
| Urine | It is a product of human activity in the form of liquid, which is excreted by the kidneys. Normally, it is yellowish in color, transparent, almost odorless and does not contain any inclusions or impurities; it consists of 99% water. |
| Transparent discharge from the urethra in women | The glands of the urethra produce a small amount of transparent secretion, which acts as a lubricant and prevents the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into it. |
| Smegma in men | The mixture of secretion from the sebaceous glands of the foreskin in the form of a white thick lubricant requires personal hygiene and regular removal with plain water. In large accumulations, it acquires a greenish tint and can lead to the development of inflammatory processes. |
| Ejaculate in men | The fluid that is released during ejaculation. It has a light gray color, is distinguished by viscosity and turbidity. |
| Prostate secretion in men | The liquid appears as a result of the activity of the prostate glands and is part of the sperm. It has a characteristic odor and ensures the fertilizing ability of sperm. |
Pathological discharge requires timely treatment and differs from natural:
- volume - too abundant or, on the contrary, scanty;
- appearance - cloudy, white, yellow-green;
- the presence of impurities - purulent inclusions, lumps of mucus, blood;
- smell - putrid, sour, fishy;
- thickness - too thick or liquid, sticky;
- systematic: constant or episodic.
The causes of such urethral discharge are presented in the table below:
| Kinds | Causes | |
| Infectious etiology | Specific | Diseases that are sexually transmitted |
| Nonspecific | Microorganisms that cause infectious urethritis | |
| Allergic reactions | Prolonged exposure to allergen | |
| Non-infectious etiology | Constrictions of the urethra | Injuries and advanced diseases |
| Violation of the integrity of the mucosa | Impacts of mechanical nature | |
| Irritation | Exposure to chemicals | |
The nature of pathological discharge often makes it possible to recognize the cause that caused it:
| Nature of the discharge | What disease resulted from |
| White discharge from the urethra | Pathological white urethral discharge can occur in both men and women. They are a symptom of the following diseases:
|
| Bloody discharge from the urethra | Such pathological discharge occurs when:
|
| Purulent discharge from the urethra | They have a strong smell of rot, have a greenish or yellowish tint and are a sign of sexually transmitted diseases. |
| Clear and yellow discharge from the urethra | Some forms of chronic urethritis are accompanied by the release of a clear secretion, which can become yellowish during exacerbation. They can also signal the presence of a disease such as trichomoniasis, which is accompanied by discomfort when emptying the bladder. |
It is important to understand that the nature of discharge from the urethra directly depends on a number of factors:
- pathogen;
- presence of other diseases;
- neglect of pathological processes;
- severity of inflammation.
How to distinguish a normal condition from a pathology?
| Sign | Norm | Deviation |
| Time of appearance, frequency | Before, during or after sexual intercourse, during arousal | Regardless of intimacy, after sleep, after urination, defecation, sometimes dripping constantly |
| Smell | Characteristic (egg white or chestnut) or odorless | Putrid, sour, fetid, fishy, etc. |
| Color, consistency | Transparent or whitish, the consistency often resembles raw protein, sometimes sticky, viscous. | Curdled, thick, white, greenish, brown, interspersed with blood clots and pus. Can be transparent in case of a viral disease |
| Additional symptoms | No | Itching, burning, redness, pain |
Discharges of a non-infectious nature
There are a number of diseases of non-infectious etiology, one of the symptoms of which is discharge from the urethra:
- Urolithiasis - the canal is injured when stones pass from the bladder, which leads to the appearance of blood in the discharge and urine. If an inflammatory process has begun in the damaged area, an odorless white mucous discharge appears from the urethra, which is accompanied by burning and itching during emptying of the bladder;
- Allergic reactions to the material from which underwear is made, hygiene products, as well as pharmacological drugs or food. As a result, clear, intense discharge occurs that does not smell and is accompanied by swelling, itching and discomfort when emptying the bladder;
- Neoplasms of a benign or malignant nature, localized in the bladder or urinary canal, lead to the appearance of bloody or brown discharge;
- Injuries sustained during medical procedures or sexual intercourse. Incorrect selection or violation of the catheter insertion technique can cause damage to the walls of the urethra, which leads to the appearance of pathological discharge.
Associated symptoms
In the presence of diseases that are characterized by white discharge, their symptoms may have a pronounced clinical picture.
Diseases may be accompanied by itching, burning during sexual intercourse or urination (candidiasis, ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, trichomoniasis), impaired urination (prostatitis), and decreased erectile function.
Sometimes symptoms do not always appear, which contributes to later detection of the disease (chlamydia).
In any case, it is necessary to conduct an examination if white discharge:
abundant;- quite scarce, but appear regularly;
- accompanied by pain, burning, itching or other symptoms;
- general weakness appears;
- an unpleasant or specific odor appears;
- the color of secretion changes;
- urinary problems occur;
- Erectile function decreases.
Signs of diseases may not always appear immediately, or may not have a pronounced manifestation at all, so preventive measures should be carried out regularly (at least once a year) to detect a possible disease.
Video: “White coating on the penis”
Discharge from the urethra: diagnosis
Diagnosis of discharge from the urinary canal involves the following:
- Medical examination of the perineum/penis to identify rashes, discharge or injuries to the penis;
- Conducting palpation and assessing the density, size and mobility of the lymph nodes in the groin;
- Conducting a digital examination of the prostate in men to obtain secretions and examine them;
- Collection of smears from the urethra for laboratory tests;
- Urethroscopy to assess the condition of the canal mucosa;
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs;
- General blood and urine analysis;
- CT scan.
Deviations from the norm
In addition to physiological discharge, which is considered normal, there are deviations. They can be easily identified by the structure of the secretion, color or smell:
- Bloody manifestations from the urethra indicate hemorrhea, a non-inflammatory disease that often develops due to trauma, for example, during a medical examination using an instrument.
- Spermatorea – the appearance of sperm without intercourse indicates a decrease in the tone of the vas deferens. The disease develops due to constant inflammation.
- White discharge in men on the head with a purulent-mucous structure is a sign of urethritis, which appears with chlamydia, mycoplasmosis and other infections. The problem is not accompanied by other symptoms such as pain, itching or stinging.
- A white foamy secretion appears during inflammation, which develops against the background of trichomoniasis. In addition, patients experience pain and burning, discomfort in the pelvic area.
- Yellow, green or brown manifestations of a thick consistency are a sign of gonorrhea. In addition, the patient has a number of other symptoms that cause discomfort.
- White or yellow mucus appears with prostatitis, inflammatory processes and other diseases occurring in the acute phase.
In addition to the described deviations, the shape of the urethral opening may change in patients, and the intensity of the transformation depends on the severity of the course and type of disease. Often the tissues swell and the color of the head changes.
Discharge from the urethra: treatment
The treatment method in this case directly depends on the cause that caused such a phenomenon as pathological discharge from the urethra. It is important to understand that self-treatment can cause complications and is therefore unacceptable. Discharge can occur due to the penetration of various types of pathogens, which must be combated using different methods. Most often, drug therapy involves the use of antibiotics, but their selection should be carried out on an individual basis. As a rule, the following means are used:
| Group | When to use | Name |
| Antibacterial | STD | "Azithromycin", "Amoxiclav" |
| Uroseptics | Urethritis | A solution of chlorhexidine and collargol |
| Sulfanilamide | When bacteria that cause inflammation are detected | "Doxycycline" |
| Antimicrobial | Trichomoniasis | "Metronidazole" |
In addition, patients are recommended to wash their genitals with decoctions of knotweed, chamomile, calendula or special antiseptic solutions. Warming applications and electrophoresis give good results.
Additional therapies
Problems of the genitourinary system should be treated comprehensively. In addition to medications, doctors choose:
- Rectal prostate massage;
- Therapeutic massages of the lumbar region;
- exercise therapy;
- Physiotherapy;
- Reflexology.
Such procedures restore natural metabolism and prevent stagnation. The urologist prescribes a special diet that helps strengthen men's health. It is necessary to take vitamin complexes: vitamin C, E, A, group B.
Prevention
A healthy lifestyle is a prevention against many diseases, and those that cause pathological discharge from the urethra are no exception. That is why preventive measures in this case are as follows:
- A balanced diet, minimizing the consumption of fatty and spicy foods, preservatives and carcinogens, which create a serious burden on the kidneys and bladder;
- Eliminating the risk of body hypothermia by wearing warm, comfortable clothing that reliably protects the lower body during the cold season;
- Elimination of stressful situations and excessive physical activity;
- Quitting consumption of alcoholic beverages and smoking;
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- Refusal to wear underwear made of synthetic materials that can cause an allergic reaction.
Contact the specialists of the CELT clinic when the first symptoms of the disease appear: your treatment will be even faster and more successful if it is started in a timely manner. Save yourself the discomfort: contact CELT!
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Diagnosis and treatment
A diagnosis can be made only after laboratory and instrumental examination. Initially, doctors recognize the patients’ complaints, conduct an examination and determine the nature of the discharge. Possible diagnostic methods include:
- Examination of the head, perineum and foreskin to determine changes, the presence of mechanical damage, inflammation and the nature of plaque.
- Palpation of lymph nodes to assess their condition.
- Massage the prostate to examine it, and the resulting secretions are sent to the laboratory for examination under a microscope. Before the procedure begins, the patient must not urinate for 2-3 hours.
- A smear must be submitted for analysis to determine pathogens. It must be taken no earlier than 3 days after using local preparations against fungi and bacteria. Before the test, you should not urinate for 3 hours or wash your penis.
- Blood donation for general clinical picture and sugar.
- Submission of urine for a detailed examination.
- Ultrasound of the prostate and kidneys.
- CT and urography.
If the inflammatory process is severe and accompanied by severe symptoms, then the patient is prescribed antibiotics until the results are obtained. In case of heavy discharge with blood, the man is hospitalized to stop the bleeding. If cancer is suspected, doctors do a biopsy.
Treatment depends on the specific type of pathogen and is determined individually for each patient. Most diseases are treated by using broad-spectrum antibiotics. Specific drugs are prescribed after determining the pathogen and its susceptibility to the active substances.
In case of infection with intracellular bacteria, the patient is prescribed an antibacterial drug, which can enter the DNA of the infection and destroy it from the inside. For fungal infections, therapy is carried out with external antifungal agents; tablets can also be used. The course of treatment is selected individually, sometimes supplemented with painkillers or anti-inflammatory drugs.
If a man has an accumulation of smegma, he will need to perform a number of simple procedures:
- In the morning and evening, perform penile hygiene using soap or other means.
- Apply Tetracycline ointment to the head to prevent inflammation.
- Wash the foreskin with a light solution of potassium permanganate or Miramistin.
There is no need to take tablets orally if there is no severe inflammation. Local antibacterial agents are suitable to remove bacterial infections:
- Cream Baneocin.
- Levomekol.
- Tetracycline ointment.
- Metrogil.
It is permissible to make lotions based on a solution of Chlorhexidine or Miramistin. For severe swelling and redness of the foreskin, the antibiotic Azithromycin or Tsiprolet is prescribed. To eliminate fungi, antimycotic drugs are recommended:
- Pimafucin.
- Clotrimazole.
- Candide.
The head is treated with medications 2-3 times a day. To strengthen the immune system, take immunomodulators and vitamin complexes. If antibiotics are prescribed, you should immediately buy probiotics and prebiotics to complement them, which will restore the microflora. The diet must be adjusted, excluding:
- Sour.
- Spicy.
- Salty.
- Smoked.
- Roast.
If a fungus is diagnosed, then you need to give up baked goods, sugar and carbohydrates. The menu is balanced and high in calories so that the body can fight the disease.
At the initial stage of development of diseases with white discharge on the head of the penis, you can use traditional medicine. They will help speed up the healing process and remove characteristic symptoms. It is recommended to use herbal infusions and decoctions, and for white plaque it is best to use:
- Oak bark.
- Calendula.
- Bird cherry.
- Alternately.
- Chamomile.
Ready-made liquids are consumed internally or applied externally. In addition, the immune system is strengthened, but use all recipes only after prior consultation with a doctor. Self-treatment can lead to negative consequences and a general deterioration of the condition.
Physiological discharge that is normal
Content:
- Physiological discharge that is normal
- When does discharge indicate the onset of the disease?
- Discharge without infection
- Standard classification of discharge
- Features of discharge during pregnancy and in babies
- How is diagnosis carried out and treatment prescribed?
- Relapse Prevention
Despite the fact that doctors recommend that if you discover suspicious discharge, you should immediately go to the clinic to get tested, not all of them pose a threat to health. We are talking about a transparent secretion, which is considered the norm in urological practice. If you find such traces on your underwear, there is no need to sound the alarm, because this just shows that everything is fine with the body.
Particular attention should be paid to the consideration of mucus, which begins to bother women of reproductive age. Clear, thick vaginal discharge indicates that they will be ovulating in a few days. They last for approximately three days, usually without causing significant discomfort. This phenomenon is considered quite normal for the female body, provided that the stretching clots are not white, but transparent, do not have a fetid, putrid odor and disappear in a couple of days.
The reason for this reaction of the body to ovulation is changes in hormonal levels. The separation of mucus from the vagina is within the normal range if the process is completed in a day or two.
Separately, options for the natural discharge of secretions from the urinary tract in men and from the urethra and vagina in women are considered. This is possible in case of strong sexual arousal after completion of sexual intercourse.
A common scenario for the normal discharge of mucus from the urethra for both sexes and from the vagina in women is a sudden release of a large amount of hormones. The reasons for such an outcome can be either an extreme degree of sexual arousal before sexual intercourse, or some specific stressful situations.
Tactics of behavior of men when discharge appears
In this case, you need to start abstaining from sexual intercourse and contact a specialist to determine the cause of the discharge. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate. The first stage of the examination is a laboratory examination for the presence of a possible infectious agent that led to the onset of inflammation in the urethra. For laboratory diagnostics, a whole range of diagnostic tests are used: from light microscopy to molecular biological methods. If pathogens are detected, specific antibacterial and/or antiviral therapy is prescribed.
The second stage is a comprehensive instrumental examination. It includes ultrasound - examination of the genital appendages (prostate) and kidneys. This is necessary to exclude their involvement in the pathological process. To exclude the salt nature of inflammation of the urethra (oxalate, phosphaturia, etc.), as well as possible inflammation of the bladder and kidneys, it is necessary to conduct a urine test. Complex therapy of discharge is carried out only after a complete examination and clarification of its nature. If the genital appendages and/or other organs of the urinary system are involved in the inflammatory process, the complex therapy includes appropriate medications and physiotherapeutic procedures. After treatment, you should make sure that the pathological process is stopped. This is especially important when identifying sexually transmitted infections during the initial examination.
Reference and information material
Author of the article
Khaldin Alexey Anatolievich
Dermatovenerologist, clinical immunologist, MD, professor
Loading...
Take other surveys